Biology- Circulatory and Respiratory
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Arteries
Oxygen rich blood, or oxygenated blood is carried away from the heart is large blood vessels called arteries.
Capillaries
These are microscopic blood vessels where the exchange of important substances or waste occurs.
Veins
Carry oxygen poor blood, or deoxygenated blood, back to the heart.
Valves
Structures in veins that prevent backflow of blood, ensuring it flows toward the heart.
Heart
The muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients while removing carbon dioxide and waste.
Pacemaker/ SA Node Sino Atrial
A group of cells located in the right atrium that regulate the heartbeat by sending electrical signals to stimulate contractions.
Plasma
The clear yellowish liquid component of blood that makes up about 55% of its volume, transporting cells, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
Red blood cells
These cells are responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs.
Platelets
Cell fragments involved in blood clotting.
White blood cells
These are the body’s disease fighters, and are produced in the bone marrow.
Breathing
This is the mechanical movement of air into and out of your lungs.
External respiration
This is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the blood, which occurs in the lungs.
Internal respiration
This is the exchange of gases between the blood and the body’s cells.
Trachea
This is the tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi, serving as the main airway for air to enter and exit the lungs.
Bronchi
The two main branches of the trachea that lead into each lung, allowing air to pass to and from the lungs.
Lungs
The organs that facilitate gas exchange in the respiratory system, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled.
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs, allowing oxygen to diffuse into the blood and carbon dioxide to be removed.
Cilia
Microscopic hair-like structures that line the respiratory tract, helping to trap and transport particles and debris out of the airways.
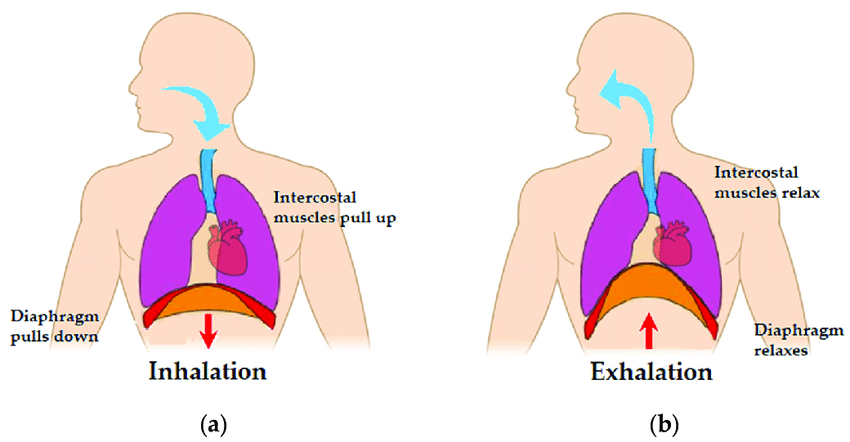
Diaphraphm
A dome-shaped muscle located at the base of the thoracic cavity, playing a crucial role in respiration by contracting and relaxing to facilitate inhalation and exhalation.
Exhale
Relax and become smaller to expel air from the lungs.
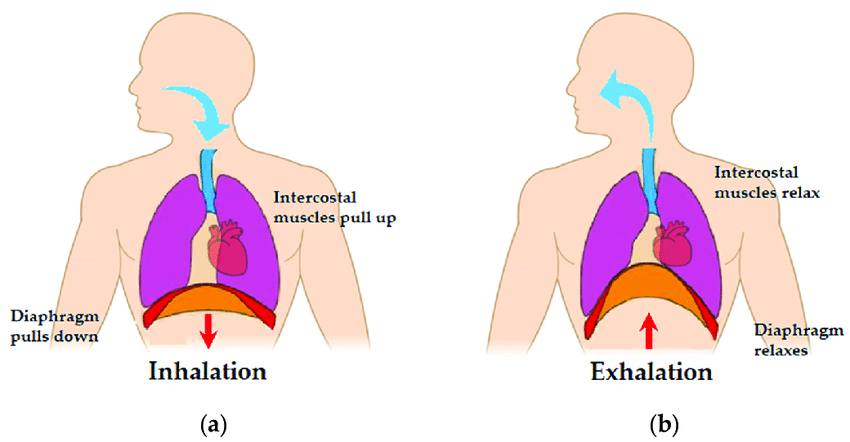
Inhale
The process by which air is taken in in which the diaphragm contracts and expands.