final supply chain
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Customer Relationship Management
Transforms the people, processes, and technology required to become a customer-centric organization
Philosophy of putting the customer first
Partnering with SELECTIVE CUSTOMERS to create superior value
Why do Companies need CRM
Acquire New Customers
Retain their Existing Customers
Meet the Changing Expectation of Customers
Loyal customers are the source of most profits, and a relatively small percentage of those customers may generate most of the profits for the company.
Strategically Significant Customers
Customers with high lifetime value, i.e., customers that will constantly buy the product(s) or use the service(s) in the long term.
Customers who serve as role models or benchmarks for other customers.
Customers who inspire change in the supplier or the supply chain.
CRM does not work for everyone, only with those who have Brand Loyalty
True
Key Tools and Components of CRM
Predicting Customer Behaviour
Personalizing Customer Communications
Segmenting Customers
Target Marketing
Event-Based Marketing
Cross-Selling
Up-Selling
Relationship / Permission Marketing
Customer Defection Analysis
Churn Reduction
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Predicting Customer Behaviour
Collecting customers’ buying history, preferences, and trend information, which could be used to forecast buying behaviors
Also determine if marketing or advertising and their budget is effective or needs change
Personalizing Customer Communications
Language aimed at specific groups of customers is likely to result in greater sales and shows that they care
Clickstream: tracking how customers navigate a website
Segmenting Customers
Dividing a customer base into groups of similar individuals or grouping customers based on demographics, etc.
Allows them to sell a specific product or define it for the group more efficiently
Target Marketing
A segment or group of customers the company has decided to AIM its marketing efforts towards
More effective than mass marketing, more efficient, less labor and costs
Event-Based Marketing
Identifies key events in the customer and business lifecycle
When an event occurs, a specific marketing activity is undertaken
Holiday seasons, birthdays, marriage, or graduations
Cross-Selling
Complimentary
Sells an additional related product or service to an existing customer after the initial purchase
ex: would you like fries with your burger
Up-Selling
Upgrade or add-on to increase price
Ex: super-size order / make the order a meal
Relationship / Permission Marketing
Customers SELF-SELECT or agree to receive the type of marketing communication they want
ex: “opt-in” emails, permits the company to send them emails
Customer Defection Analysis
Analyzing the customers who have stopped buying to determine why
Churn Reduction
Efforts to stop losing customers to competition
Goes in hand with customer defection analysis
5% improvement in customer retention can result in 75% increase in profits
Customer Lifetime Value
A prediction of the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a particular customer
CLV is an essential metric for determining how much money a company is willing to spend on acquiring new customers and how much repeat business a company can expect from particular customers.
Order Management
Receiving and accepting orders, then shipping, invoicing, and updating the customer about order status
Order Management Steps
1. Receive and validate the order to confirm accuracy.
2. Check inventory to see when the order can be shipped.
3. Acknowledgement to the customer with a target ship date.
4. Schedule the warehouse picking of the order (also called Waving).
5. Pick and pack the order.
6. Prepare all the paperwork needed for the shipment.
7. Arrange for transportation.
8. Confirm shipment to the customer.
9. Produce and send an invoice to the customer.
Omnichannel
Multichannel approach to sales that provides seamless shopping experience
Successful omnichannel = dynamic inventory system and consistent pricing
ordering method: online, in store
delivery method: pickup, deliver
payment method: card or cash
Customer Service
Philosophy: commitment to providing customer satisfaction
Activity: order processing, billing, returns handling
Performance Measure: percentage of orders deleivered on time, number of orders etc.
Customer Service Elements
PRE-transaction elements
Transaction elements
POST-transaction elements
Seven R’s
right product
right quantity
right quality
right place
right time
right customer
right costs
+ right documentation = PERFECT ORDER
Call Centers
Links an organization and its customers together to provide technical support
They can:
categorize calls
increase customer satisfaction
provide input to forecast future demand
increase productivity
can be outsourced
Reverse Logistics or Returns Management
Backwards flow of goods from customers in the supply chain
Five R’s of Reverse Logistics
Returns
Recalls
Repairs
Repackaging
Recycling
Problems w/ Reverse Logistics
4-5x more expensive
Unwanted supply chain activity
Quality or compliance issue
Green RL Programs
Recycling, reusing materials or products, or refurbishing unused products
Measuring Customer Satisfaction
Surveys, phone calls, etc, asking customers opinions
Very little value until it is acted upon
Website Portals
Customers can access their account information, ask questions, get shipping info, etc.
6 Steps of a Successful CRM Program
Create the CRM plan
Involve CRM users from outset: involve employees since it will affect them
Select the Right Application and Provider
Integrate Existing CRM applications: centralized database or data warehouse
Establish Performance Measures
Provide CRM Training for All Users
Trends in CRM
Customer Data Privacy
Social Media
Cloud Computing
Pure Services
Offers very few or no tangible products to customers
ex: education, consulting, storage space, etc.
End Product Services
Offer tangible components along with the service component
ex: restaurants, food with sevice
State Utility Services
Directly involve things the customer owns
ex: car repair, dry cleaning, haircuts, healthcare
Difference between Goods and Services
Services cannot be inventoried
Services are produced and consumed simultaneously
Services have high customer interaction
Services are decentralized, must be near customer base
Service Productivity
Improving service productivity is challenging because of:
High labor content
Customized services
Difficulty of automating services
Problem of assessing service quality
Cost Leadership (Service Strategies)
Lowest cost service provides
Requires a lot of investment in equipment and efforts to control
Ex: route planning, UPS optimization
Differentiation (Service Strategies)
Unique service created based on customer input and feedback
ex: sunday car servicing made for those who are working on weekdays
Focus (Service Strategies)
Serve a narrow niche better than other firms
ex: person doing grocery shopping for you
Service Delivery System
Low Customer Contact Systems
Mass prodouced
ex: ticket kiosks, vending machine, ATM
High Customer Contact Systems
Highly customized
ex: personal shopper, hair stylist, manager
Blended Delivery
Customer centric and no contact
ex: restaurant
Explicit Services
Availability and access to the service
Consistency of service performance
Training of service personnel
ex: vault, safe deposit boxes, loans
Implicit Services
Attitude of servers
Atmosphere
Waiting time
Privacy and security
Facilities and Equipment
Location
Layout
Equipment
ex: ATMS, drive up ATMS
Facilitating Goods
Tangible elements consumed or used by the customer along with the service
ex: spoons, forks, or napkins at a restaurant
Service Location Strategy
Make it easy for customers to find store
And once they are there, make it easy for them to find or do what they want like pick up or drop off
Layout Strategy
Maximize closeness and reduce distance traveled
Service Response Logistics is managing:
Service Capacity
Waiting Times
Distribution Channels
Service Quality
Long Range Service Capacity
Market is too small for 2 competitors, so you are the first to capture all the business possible
Short Range Service Capacity
Lack of short range planning capacity will lead customers to go to competitors
Capacity Utilization Formula
CU = Actual customers served per period / Capacity
Level Demand Strategy [SRL]
Capacity remains constant regardless of demand
if demand exceeds, queue management tactics help
Chase Demand Strategy [SRL]
Capacity varies with demand
if demand exceeds capacity, having more lines or calling workers for help is helpful
if Demand Exceeds Capacity [SRL]
Turn customers away aka lose business
Make them wait until help is available
Increase service capacity aka more workers and more infrastructure
hiring, training people is 75% of operating costs so we can:
use cross trained employees to help
have part time employees
use tech
if Capacity Exceeds Demand [SRL]
do other jobs
do cross-training
shift demand from peak times to non peak times with discounts or incentives
Queueing Systems [SRL]
Helps control the flow and prioritize people expecting to receive a service
Structured Queues
Set in a fixed position such as an airport or bank
take a ticket number allows person to walk around
Unstructured Queues
when people form queues informally in different directions and locations
ex: people waiting for a taxi, ATM, or retail stores
Mobile Queues
formed virtually with technology
ex: real time electronic queue
Queue System Assumptions
Balking: when customer refuses to join the queue
Reneging: when customers decide to leave the queue
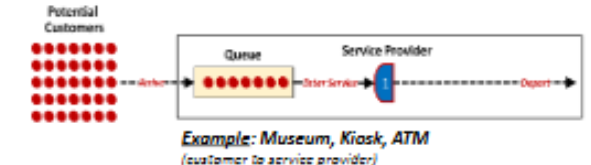
Single Channel, Single Phase
Customer at the head of the line proceeds to single service provider who completes the service
ex: ATM
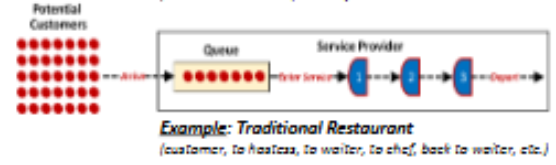
Single Channel, Multiple Phase
Customer proceeds to initial provider and then is passed of to next service provider and it keeps happening until entire service is completed
ex: to hostess to waiter to chef to waiter
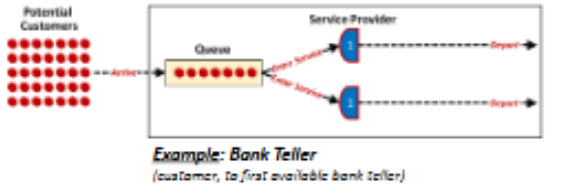
Multiple Channel, Single Phase
Customer proceeds to the first available service provider from a group of service provider which completes the service
ex: bank teller
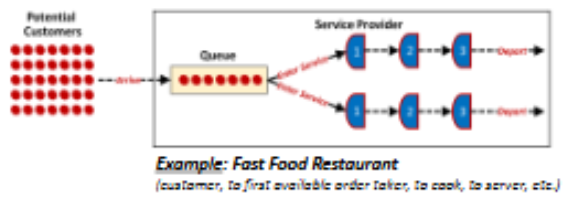
Multiple Channel, Multiple Phase
Customer proceeds to first available service provider and then is passed off to next provider until service is completed
ex: first available to take order to cook to server
First and Second Rules of Service
Satisfaction = customer perception >= customer expectation
It’s hard to play catch-up
Waiting Time Management Techniques
Keep customers occupied
Start the service quickly
Relieve customer anxiety
Keep customers informed
Group customers together
Design a fair waiting system
Managing Distribution Channels [SRL]
Eatertainment: combines restaurant and entertainment ex: rainforest cafe
Entertailing: combines retail with entertainment ex: malls
Edutainment: combines learning with entertainment ex: science center
Franchising
Allows businesses to expand quickly
ex: fast food restaurants
International Expansion
Operate or partner with firms that are familiar with the locations market
Can help address language and culture barriers
5 Dimensions of Service Quality [SRL]
Reliability
Responsiveness
Assurance
Empathy
Tangibles
Offshore Factory
Manufacturing in a country where raw materials or labor is less expensive
Low labor costs
Minimal technical or managerial resources
ex: Clothing in India or Bangladesh
Source Factory
Manufactures products at low cost with skilled workers
More managerial resources like supplier selection and product planning
ex: HP producing calculators and keyboards in Singapore
Server Factory
Takes advantage of government incentives like tariffs by making minor improvements
Reduces taxes and logistics cost
Set up to serve local market
ex: Coca Cola bottling; mix final ingredients to take advantage of taxes
Contributor Factory
Focuses on product development for products they already make
ex: 973 Sony built a Server factory in Wales and
then 15 years later got involved in development
planning, etc. and now is a Contributor factory
Outpost Factory
Factory set up in area with abundant and advanced suppliers, competitors, research facilities, etc.
ex: Silicon Valley, California
Lead Factory
Source of innovation and competitive advantage for the whole company
World-Class
ex: Intel factory in Penang, Malaysia opened in mid
1970’s, now is a lead factory.
“This is your “Go-To” factory
12 Pillars of Competitiveness
Institutions
Infrastructure
Macroeconomic stability
Health and primary education
Higher education and training
Goods market efficiency
Labor market efficiency
Financial market sophistication
Technological readiness
Market size
Business sophistication
Innovation
Taxes and Incentives [GLF]
Designed to protect local businesses
Countries with high tariffs discourage importing and encourage to produce locally
Currency Stability [GLF]
Impacts business costs and location decisions
Access and Proximity to Markets [GLF]
Trend —> being in delivery proximity of your customers
Even more important in the service industry
Labor Issues [GLF]
Labor availability, productivity, and skill.
Unemployment/underemployment rates
Wage rates; turnover rates; labor force
competitors.
Right to Work Laws [GLF]
28 states have laws protecting
employees’ right to join or
support a union.
Access to Suppliers and Cost [GLF]
Supplier proximity influences the delivery of materials and the
effectiveness of the supply chain.
Utility Availability and Cost [GLF]
Environmental Issues [GLF]
Land Availability and Costs [GLF]
As land and construction costs in big
cities continue to escalate, the trend is
to locate in the suburbs and rural areas.
Quality-of-Life Issues
Business Clusters
World Trade Organization
Weighted-Factor Rating Model
Break-Even Model
When was the Department of Homeland Security established
2003
Global Supply Chain Oppurtunities
Global Supply Chain Challenges
Global Logistics
US Customs Border Protection
Trade Compliance
Import Process
Export Process
Foreign Trade Zones
Deemed Exports
Custom Brokers
Move global shipments through customs and handle documentation