Coelom & Viscera
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
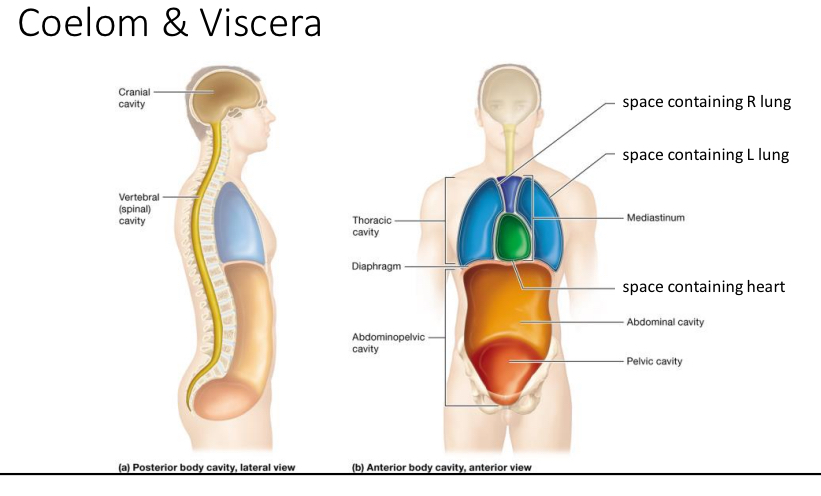
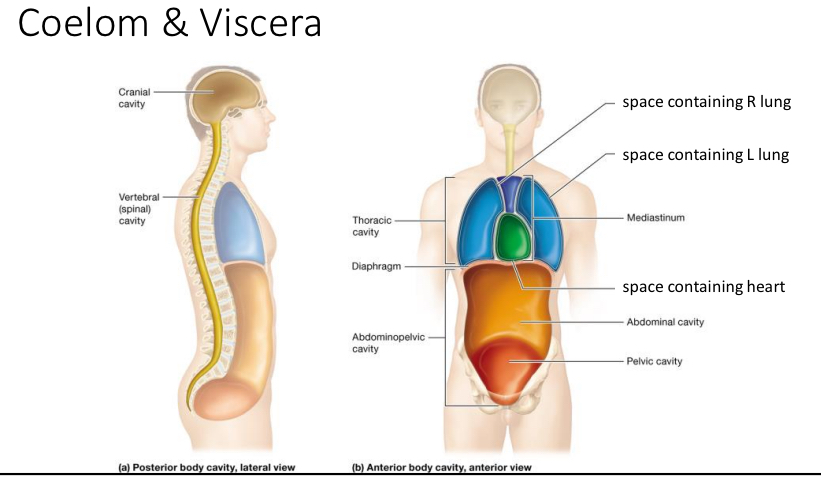
Coelom
Anterior body cavity aka ventral body cavity
Thoracic cavity and abdomniopelvic
Posterior body cavities
Cranial cavity
Vertebral cavity
Diaphragm
Structure: Dome shaped sheet of skeletal muscle tissue with openings
Function: divides the thoracic and abdominal cavities
3 openings
Viscera
Organs within coelom
Names of all organs found in the coelom
Hiatus
Opening
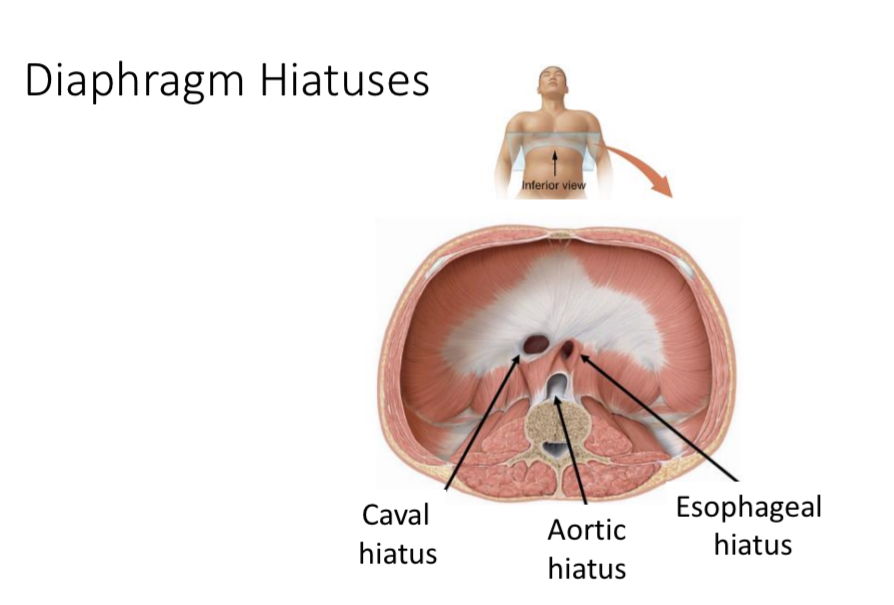
Aortic hiatus
Opening for the aorta through the diaphragm
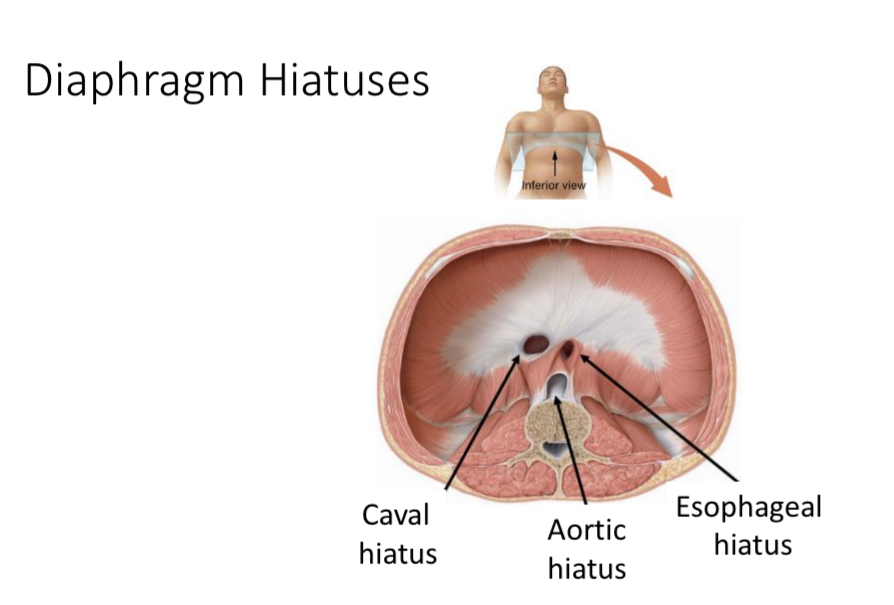
Caval hiatus
Opening for the inferior vena cava
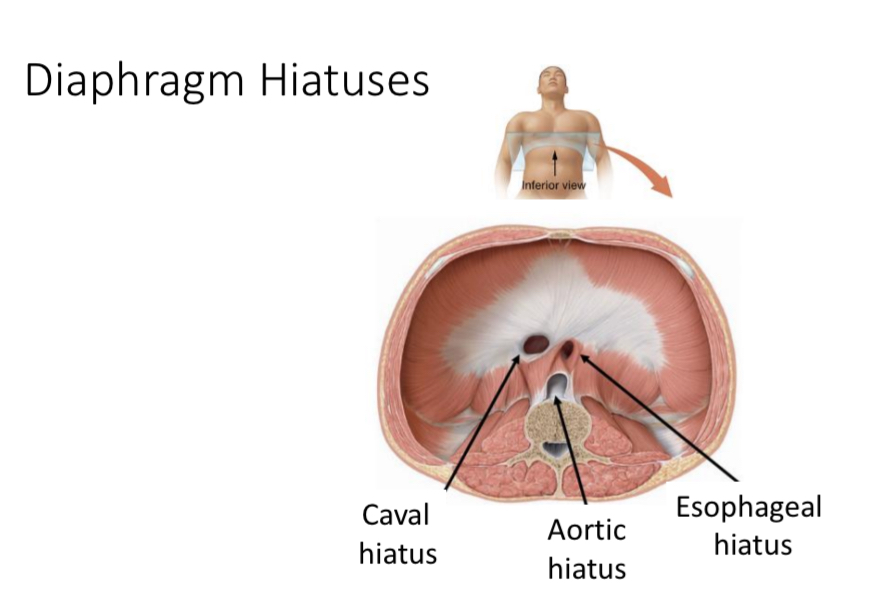
Esophageal hiatus
Opening for the esophagus and the vagus nerves through the diaphragm
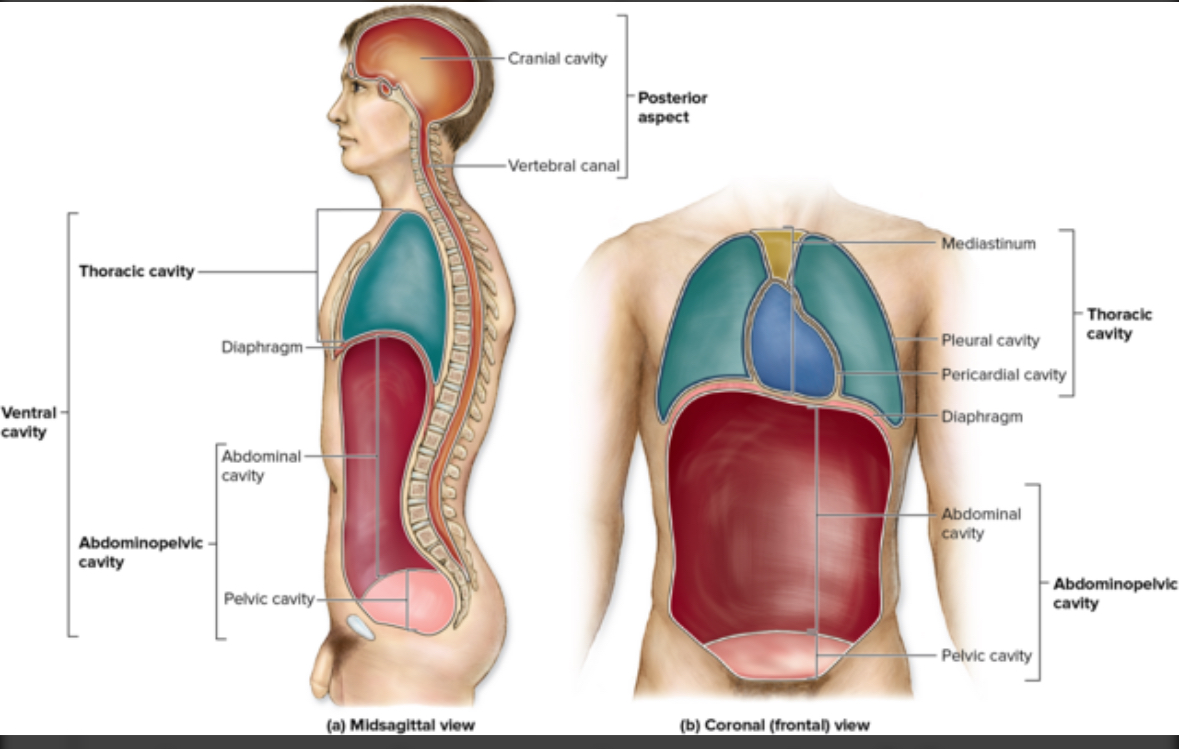
Thoracic cavity
Includes the pleural cavities, pericardial cavity, and mediastinum
Serous fluid
Fluid in the serous sacs
Structure: slippery
Function: reduce friction as organs move
Serous sac
Structure: 2 layer membrane, serous membrane separated by serous fluid
Fluid sac that surrounds all visceral organs
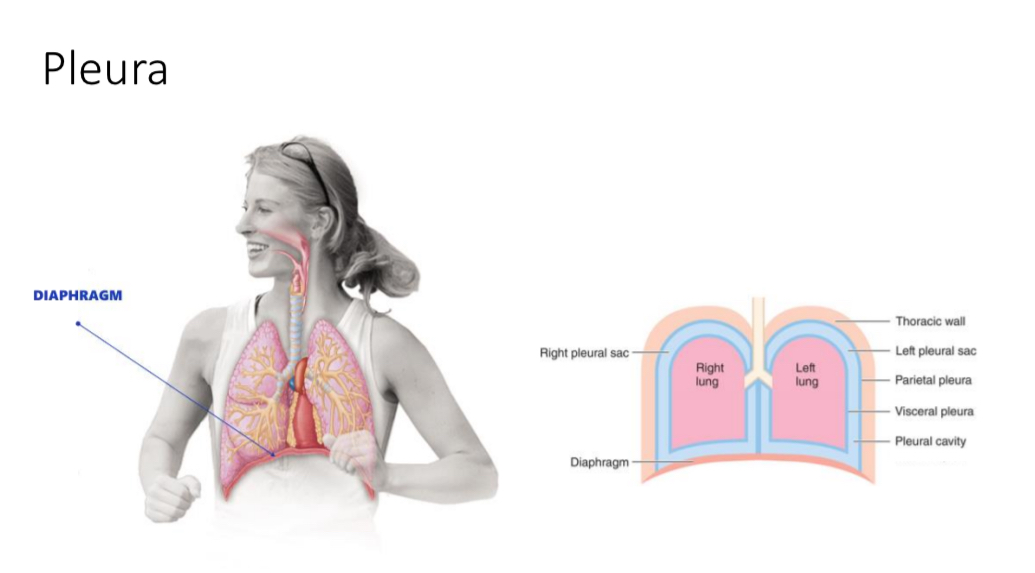
Serous membrane AKA serosa
Wall
Named after associated organ
Structure: inner and out layers. Serous cavity, 2 parts
Serous membrane/serosa inner layer
Structure: simple squamous ET
Function: Make serous fluid
Serous membrane/serosa outer layer
Structure: areolar CT
Function: metabolic support
Serous cavity
Contains serous fluid
Location: between parietal and visceral
Named after serosa
Example: pleural cavity
2 parts of serosa
Visceral serosa
Parietal serosa
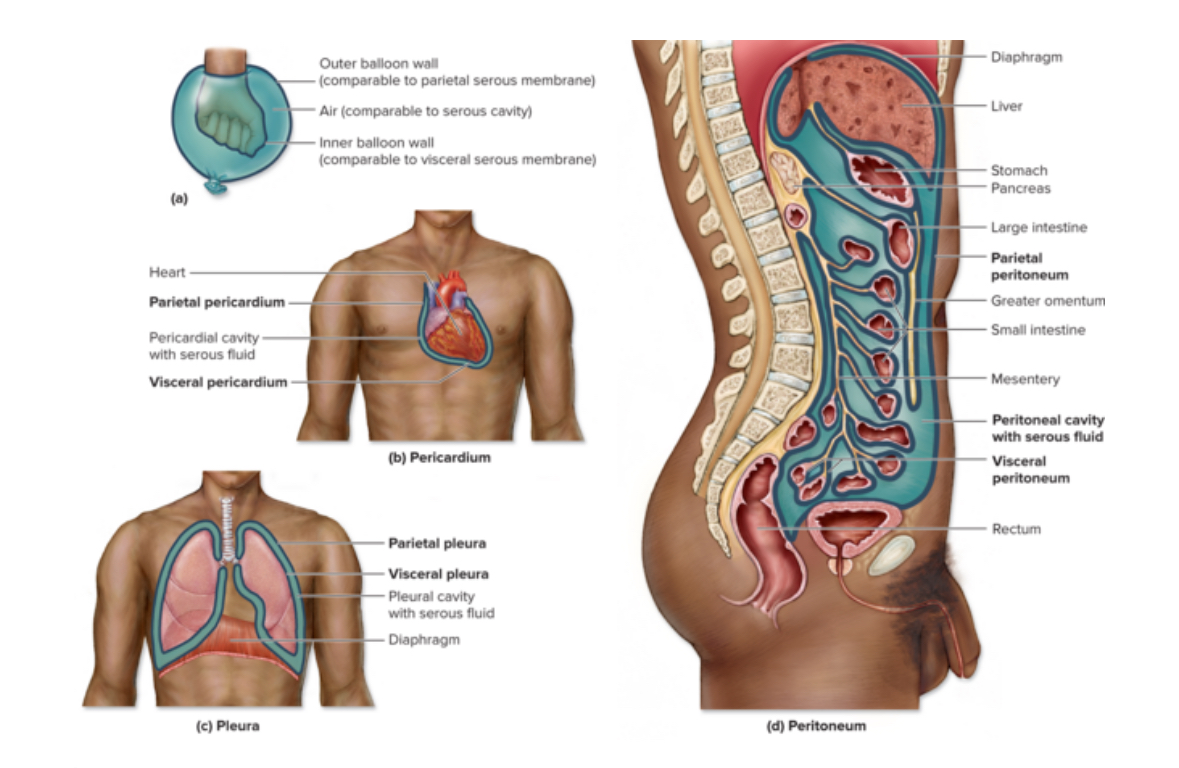
Visceral serosa
Sticks to organ surface
Example: visceral pleura
Parietal serosa
Sticks to body wall and surrounding organs
Example: parietal pleura
Peritoneal cavity
Subset of the abdomenopelvic cavity and pelvic cavity
Filled with serous fluid and surrounds all the abdominalopelvic viscera that are Intraperitoneal
Peritoneum
Serious membrane that surrounds abdominal organs
Parietal peritoneum
Location: body walls
Lines anterior and posterior body walls
Visceral peritoneum
Location: surface of internal organs only
Mesenteries
Extensions of visceral peritoneum to the posterior body wall
Contains NAVL
Function: anchor organs to body walls, stores belly fat
Visceral organs
Intraperitoneal
Retroperitoneal
Intraperitoneal
Organs fully covered by peritoneum
Includes:
Super sexy singles jump in to get laid
sigmoid colon,
stomach,
spleen,
Jejunum,
ileum,
transverse colon,
gallbladder,
liver
Retroperitoneal
Organs partially covered by peritoneum
SAD PUCKER =
Suprarenal (adrenal) gland
Aorta (and inferior vena cava)
Duodenum
Pancreas
Ureters
Colon
Kidneys
Esophagus (distal)
Rectum (proximal)
Urinary bladder (below peritoneum)
Peritoneal cavity
Serous cavity in abdominal cavity
Location: Between visceral and parietal layers
Mesentery proper
Extension of the visceral peritoneum. Function: Anchors jejunum and ileum to posterior wall
Mesocolon
Function: anchors transverse and sigmoid colon to posterior body wall
Sigmoid colon
Last segment of the large intestine
S shaped
Greater omentum
Extension of visceral peritoneum. Drape in front of small intestines. Function: Attach stomach to transverse colon
Lesser omentum
Function: Attach stomach to liver
Coronary ligament
Attaches liver to diaphragm
Falciform ligament
Attaches liver to anterior wall
Ligamentum teres hepatis
Structure: liver to umbilicus vein. Dense irregular CT
Function: Remnant of umbilical vein = carried oxygen blood to fetus before 1st breath. No longer functional.