EKG Rhythms
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
atrial depolarization
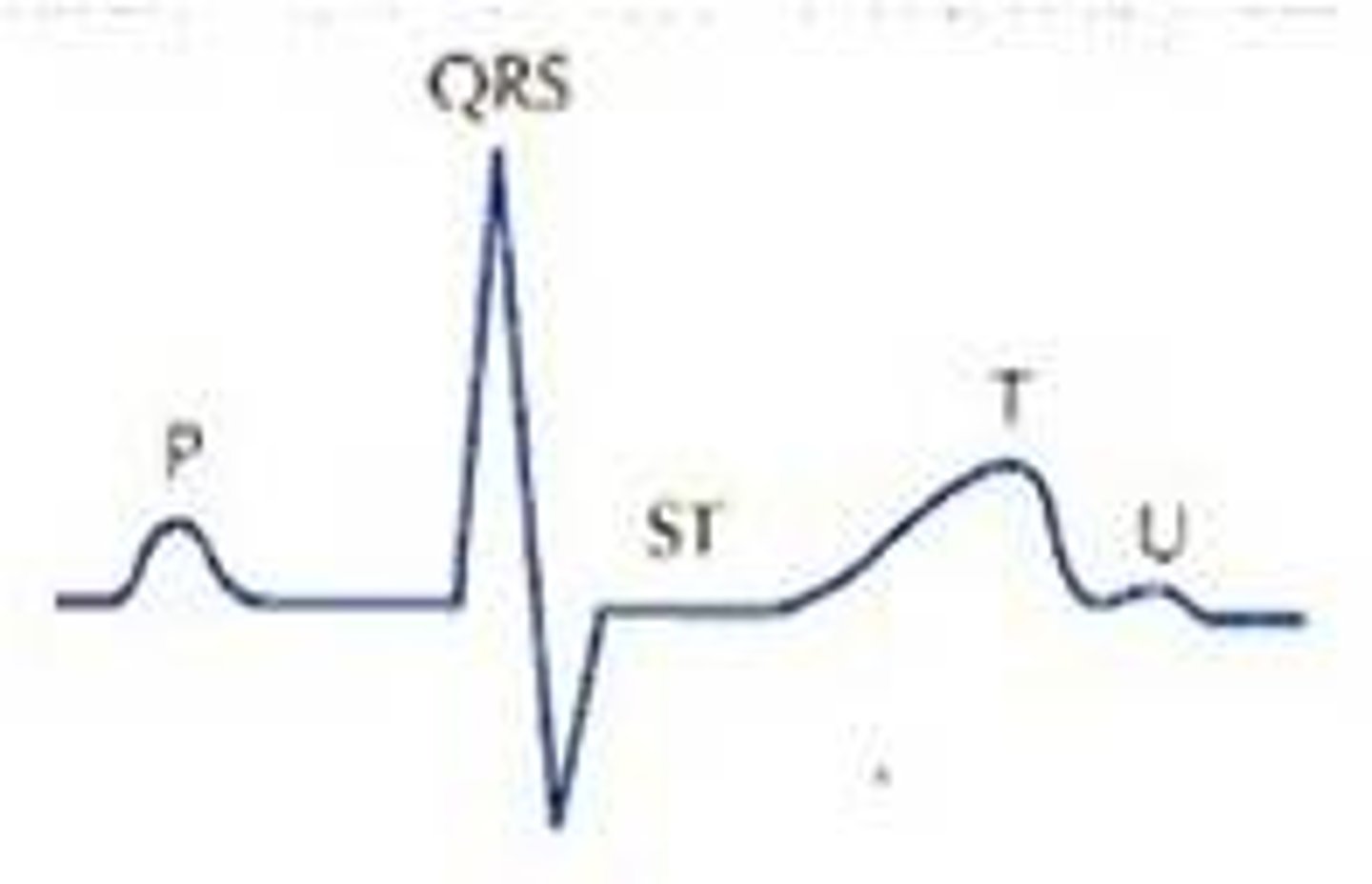
What does the PR interval represent?

ventricular depolarization
What does the QRS wave represent?
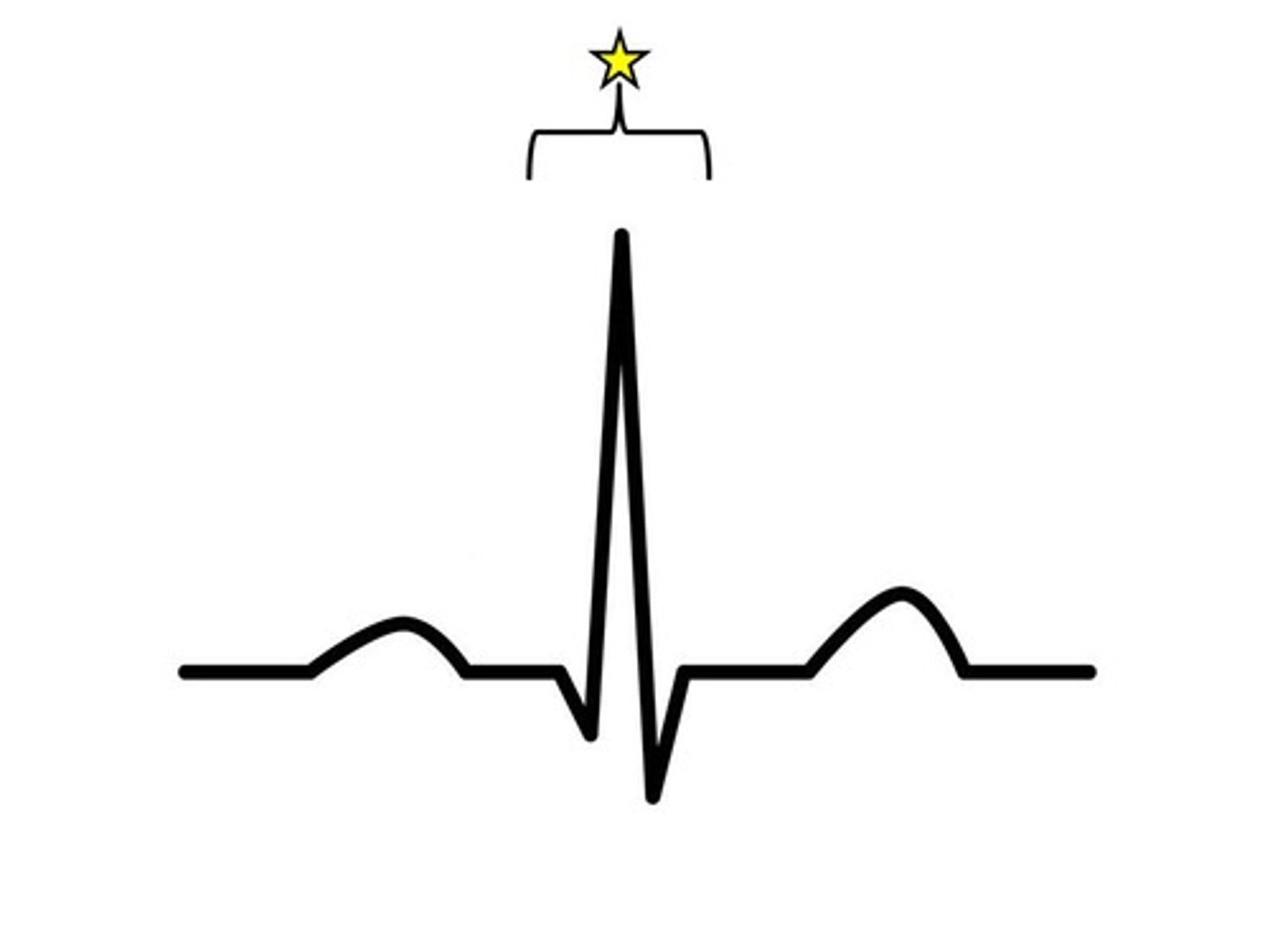
early ventricular repolarization/ atrial hidden in u wave
What does the ST segment represent?

ventricular repolarization
What the U wave represent?
cardiac cells generate cardiac muscle contraction; an increase in electrical charge
What is depolarization of the heart?
Ventricles are Resting and are filling up w bld
Repol = Resting "R = R"
What is repolarization of the heart?
should always occur prior to QRS complex.
Duration: 0.06-0.12 seconds.
rounded
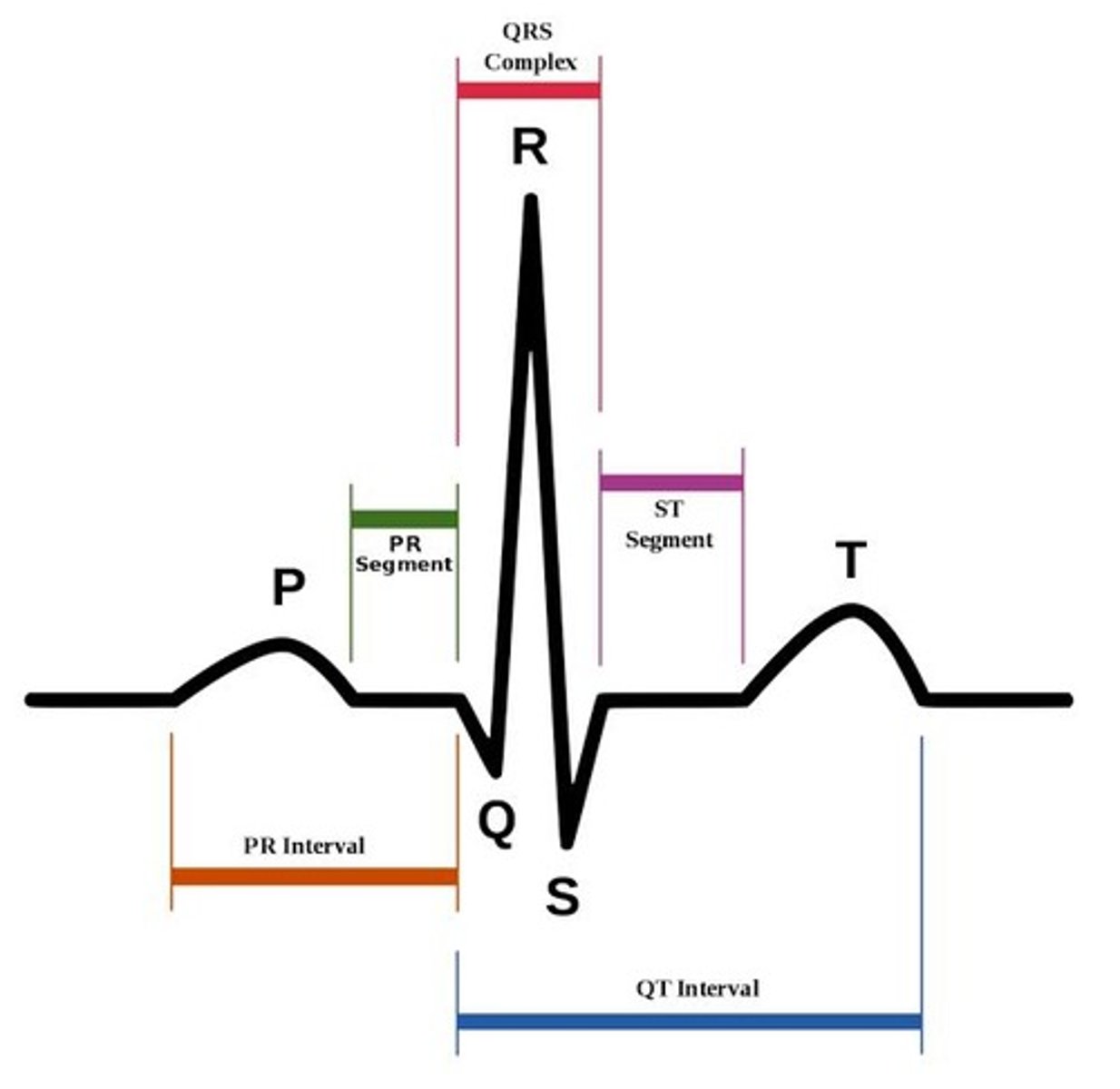
P wave measurements
beginning of P wave to beginning of QRS complex.
Duration: 0.12-0.20 seconds
PR interval measurements

▪ Measured from the beginning to the end of the QRS
▪The interval normally measures between 0.04 and 0.12 seconds
▪> than 0.12 is considered to be abnormal
▪ Reflects the period of time required to depolarize the ventricles
▪ Can occur without Q or without S
QRS complex measurements

Normal interval 0.36-0.44
QT interval measurements

- Normal sinus rhythm
- Sinus bradycardia
- Sinus tachycardia
- Sinus arrhythmia
- Sinus arrest/pause
What are the main5 sinus rhythms?
Normal sinus rhythm
What rhythm is this?

Sinus bradycardia
rate: below 60 bpm
What rhythm is this?
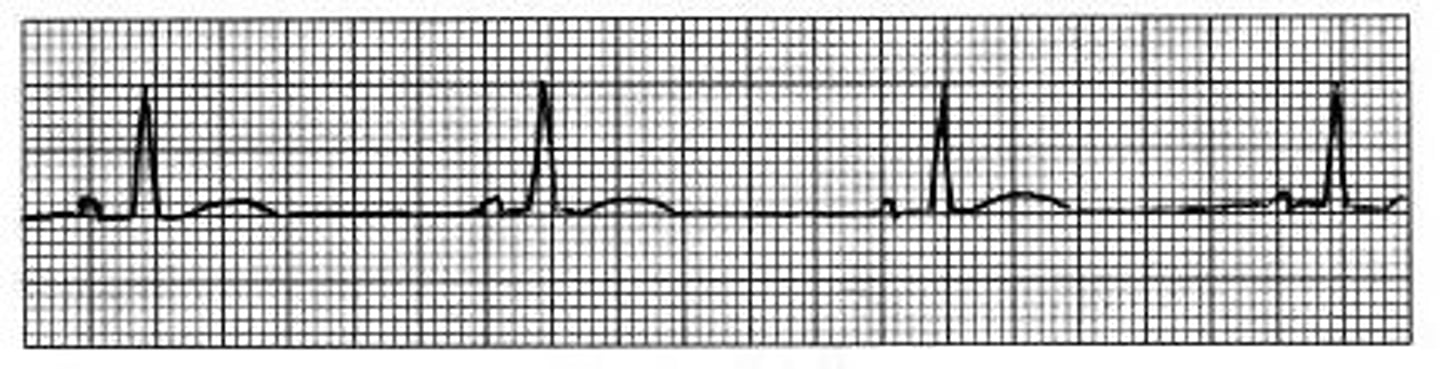
sinus tachycardia
Rate: 100-160
What rhythm is this?

Causes
- Rest/sleep, good athletic conditioning, MI, Hypothermia, medications (digoxin, verapamil)
Symptoms
- Chest pain, SOB, CHF, HTN, altered LOC
Treatment
- O2, IV, Atropine IV, transcutaneous pacing
What are the causes and treatment for sinus bradycardia?
Causes
- Fever, Pain, Anxiety, Infection, Dehydration, Activity, Caffeine, Atropine, Epinephrine
Symptoms
- usually asymptomatic but can be angina
Treatments
- Correct underlying cause
What are the causes and treatment for sinus tachycardia?
sinus arrhythmia
What rhythm is this?

Causes
-Breathing
Symptoms
- None
Treatment
- None
- No emergency intervention needed
What are the causes and treatments for sinus arrhythmia?
Sinus arrest/pause
- PQRST is absent for 1 or more cycles
- No conduction from sinus node (fails to initiate impulse)
What rhythm is this?

- Premature atrial contractions PAC's
- Supraventricular tachycardia SVT
- Atrial fibrillation A-FIB
- Atrial flutter A-flutter
What are the 4 Atrial rhythms?
Premature atrial contractions PAC
What is this rhythm?

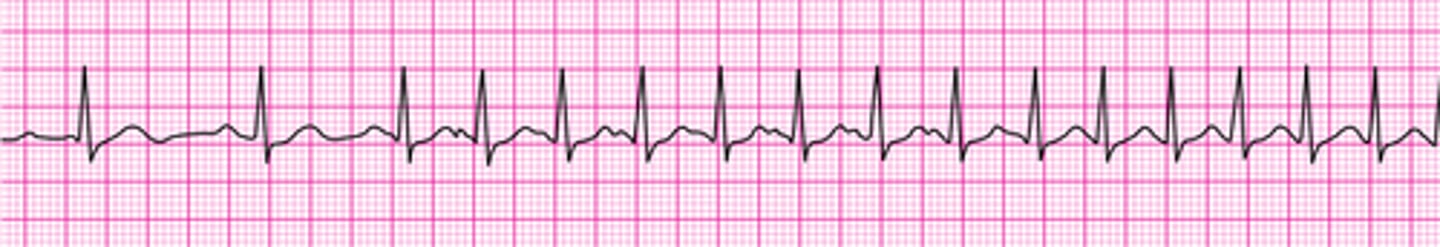
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Rate: 150-250
What is this rhythm?
Causes
- Hypoxia, CAD after MI, Respiratory failure, Digitals toxicity,
Symptoms
- Sudden racing of heart, anxiety
Treatments
- (Stable): O2, IV, Vagal maneuver
- (Unstable): O2, IV, Meds " Adenosine, verapamil", synchronized countershock
What are the causes and treatment for Supraventricular tachycardia?
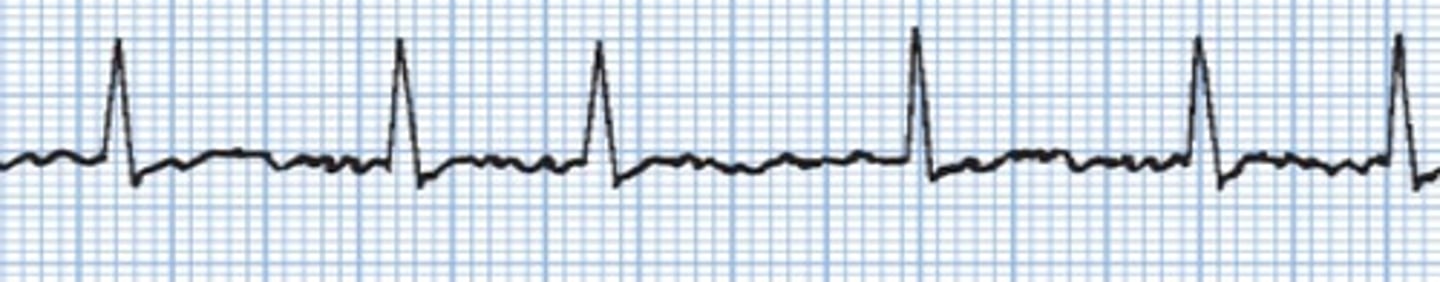
Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib)
What rhythm is this?
Symptoms
- Palpations, weakness, dizziness, chest pain, and skipped beats
Treatment
- (stable): Calcium channel blockers, Beta-blockers
- (unstable): synchronized cardioversion
What are the causes and treatment for Atrial Fibrillation?
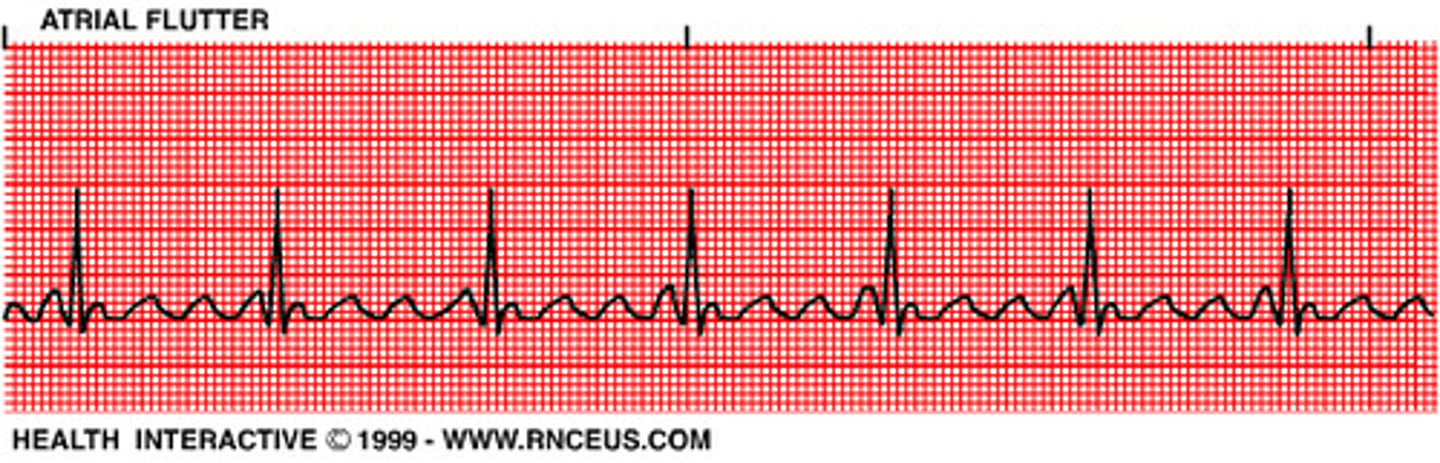
Atrial Flutter
- Sawtooth look
What is this rhythm?
Symptoms
- Palpation, weakness, dizziness
Treatment
- (stable): calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers
- (Unstable): Synchronized cardioversion
What are the causes and treatments for Atrial flutter?
third-degree heart block
- atria and ventriculus beat independently
What rhythm is this?

Causes
- (Above Bundle of HIS): Damage to AV node, Increased parasympathetic tone associated with inferior MI
- (Below Bundle of HIS): Anterior MI, extensive conduction system disease
Treatment
- (narrow QRS): O2, IV, Atropine, Pacing, Dopamine, Epinephrine
- (wide QRS): O2, IV, transcutaneous paving
What are the causes and treatments for third-degree heart block?
- Premature ventricular contraction PVC
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation V-Fib
- Asystole
- Pulseless electrical activity
What are the 5 ventricular rhythms?
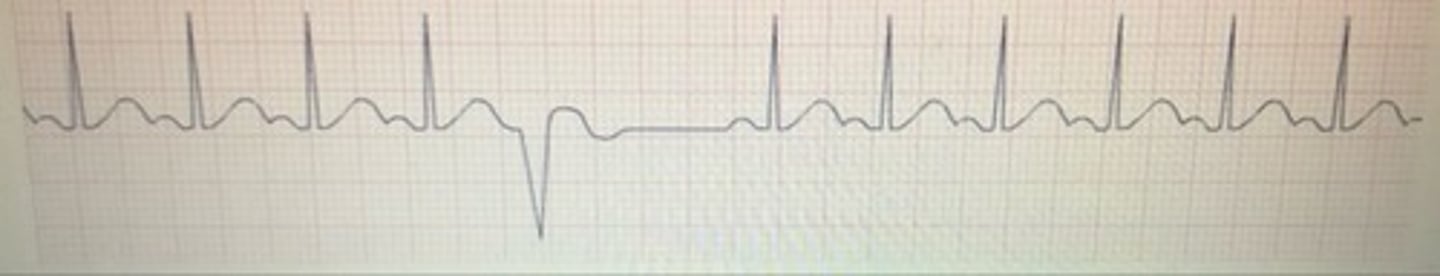
premature ventricular contraction (PVC)
What rhythm is this?
Cause
- Normal variant, Anxiety, exercise, MI, acid-base imbalance, Hypokalemia, caffeine, drugs
Symptoms
- Skipped beats, palpations, angina
Treatment
- (nonacute area): Oral antiarrhythmics, beta, and calcium channel blocker
- (in acute area): IV Amiodarone & procainamide
What are the causes and treatment for PVC's?
Bigeminy
- Every other one
What kind of PVC is this?

Trigeminy
- Every third one
What kind of PVC is this?

Quadrigeminy
- Every other 4
What kind of PVC is this?

Unifocal
- Same place in ventricle
What kind of PVC is this?

Multifocal PVC because the 2 PVC look different from each other. They are coming from 2 (multi) different irritated areas of the ventricle
What kind of PVC is this?

Unifocal couplet
- 2 in a row
What kind of PVC is this?
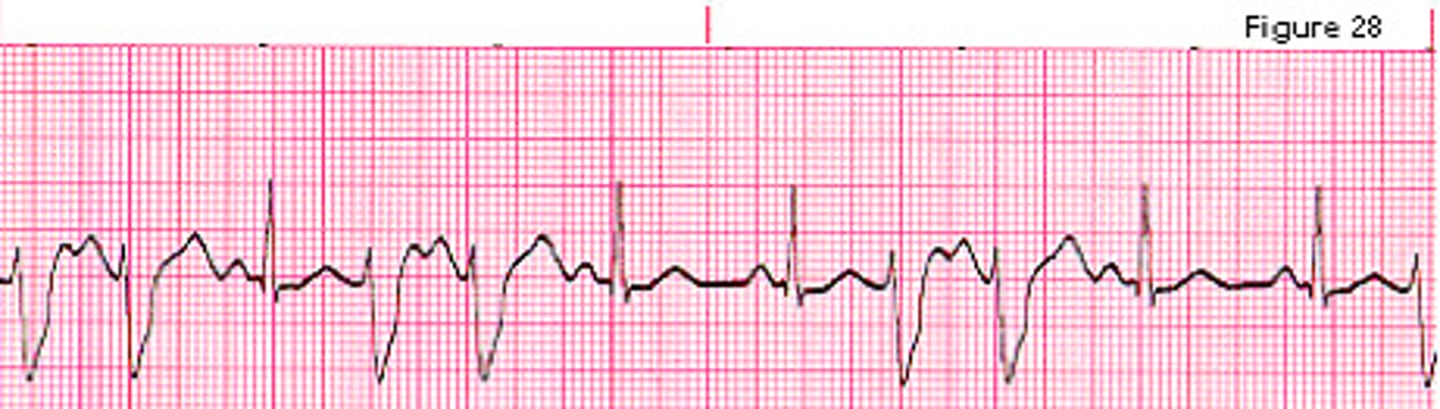
Ventricular tachycardia
- 3 or more PVC's in a row
- Rate: 110-250
- Grave stone look (will take u to the grave lol)
What is this rhythm?
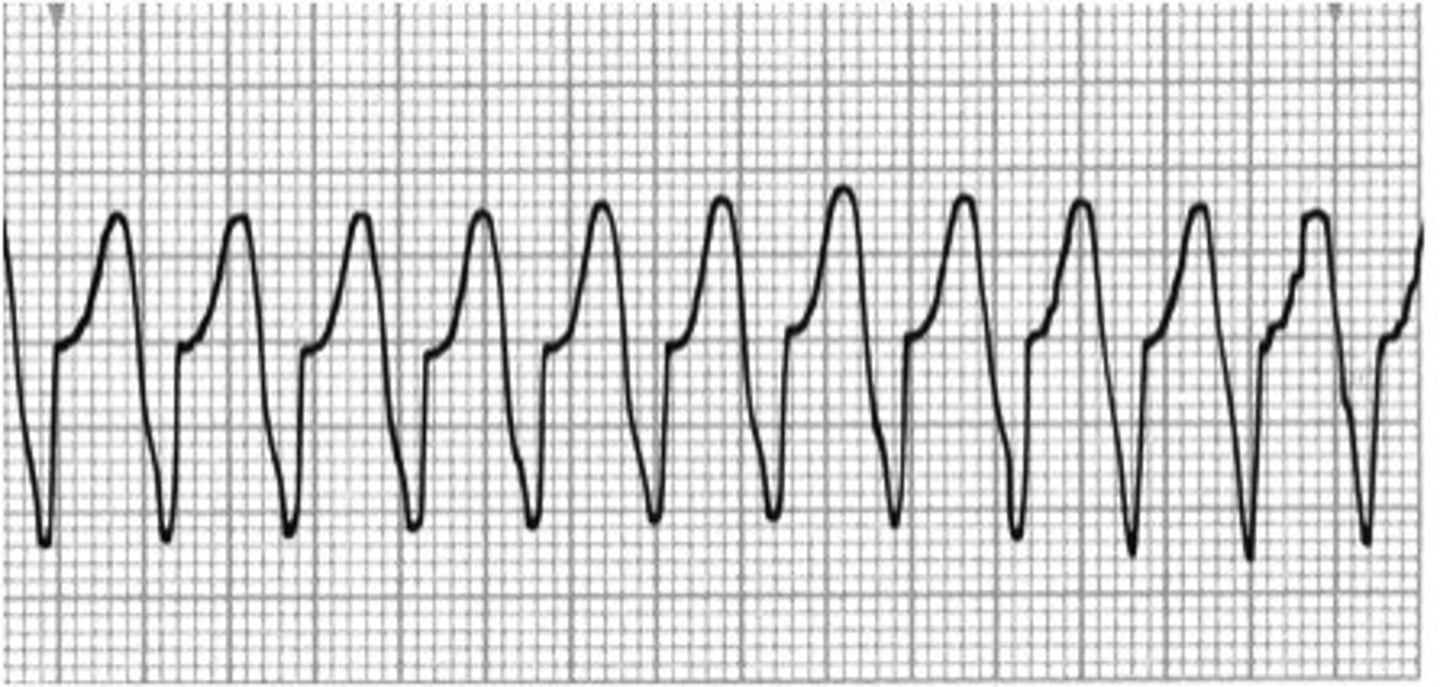
Causes
- Hypoxia, exercise, acid-base imbalance, ventricular aneurysm
Symptoms
- Pulmonary congestion, Acute MI, CHF, Decrease LOC
- (pulseless): LOC change, no palpable pulses
Treatments
-( Stable): O2, IV Amiodarone
- (unstable w/pulse): O2, Synchronized cardioversion, Amiodarone
- (unstable/ Pulseless): CPR and defib
What are the causes and treatment for Ventricular tachycardia V-Tach
ventricular fibrillation V-Fib
What rhythm is this?

Causes
- Sudden cardiac death, untreated VT, Accidental electrocution, Lightening strike, Mitral valve prolapse
Symptoms
- No cardiac output, No pulse/Bp, Apnea. cyanosis
Treatment
- CPR, Defib, Intubation
What are the causes and treatments for ventricular fibrillation V-Fib
Torsade's de pointes
- may or may not have a pulse
- follow ventricular tachycardia protocalls
What is this rhythm?
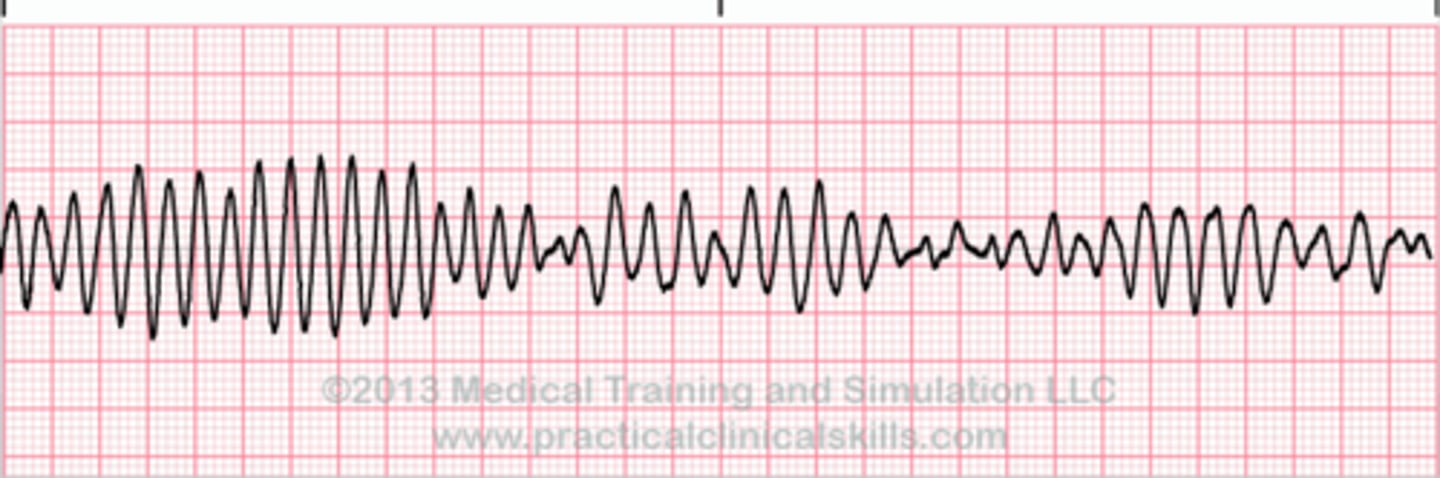
Asystole
What is this rhythm?
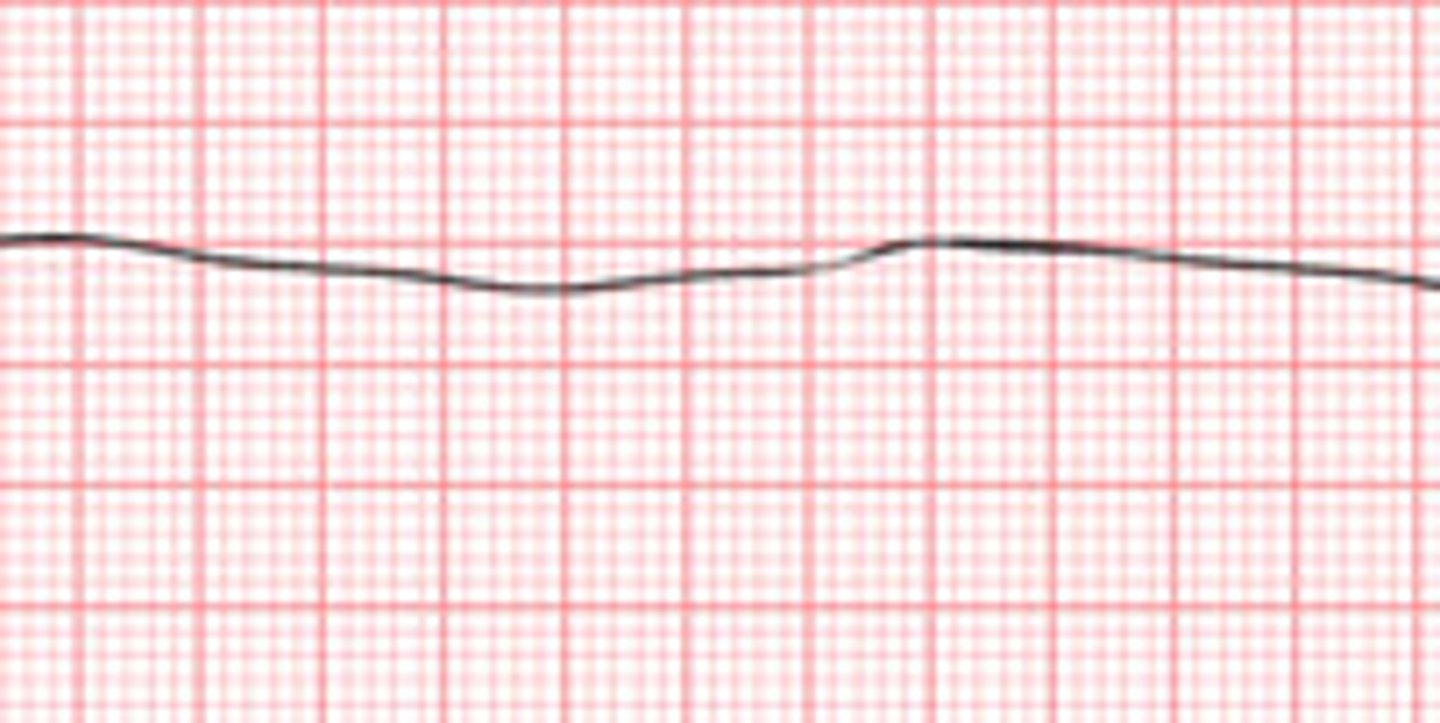
causes
- Traumatic cardiac event, result of countershock
Symptoms
- No pulse/bp, unconsciousness, cyanosis, seizures
Treatment
- CPR, endotracheal intubation, IV access, medications, find cause of rhythm
What are the causes and treatments for asystole?
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
- Organized electrical activity observed without a palpable pulse
What rhythm is this?

Causes
- Obstructive shock (Tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, massive pulmonary emboli, drug overdose
Symptoms
- No pulse/bp, unconsciousness, or electrical activity on a monitor
Treatment
- CPR, endotracheal intubation
What are the causes and treatments for PEA?
Atrial, ventricular and Dual chamber
What are the 3 types of pacemakers?
Atrial Pacemaker
What kind of pace maker is this?

Ventricular Pacemaker
What kind of pacemaker is this?
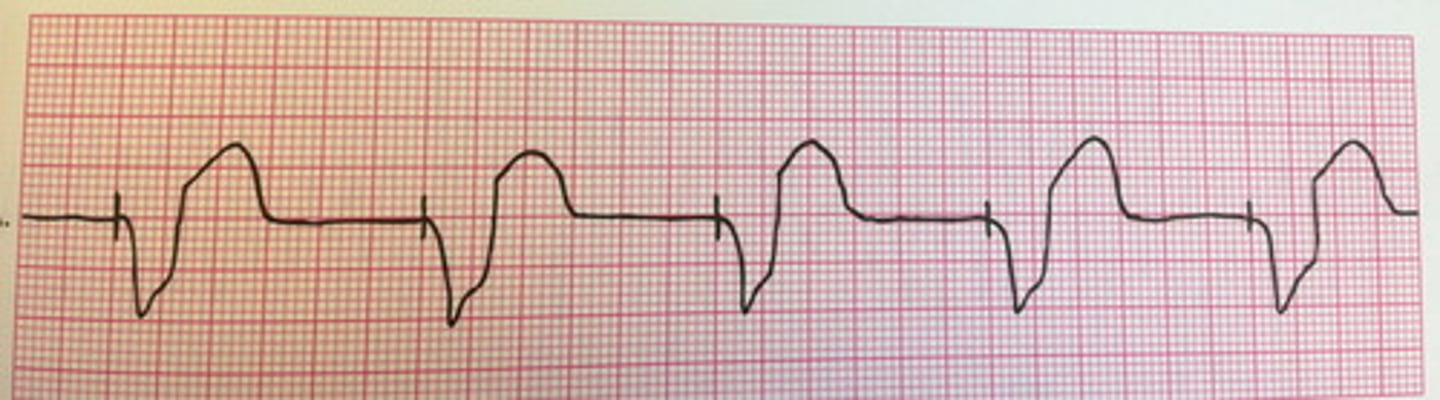
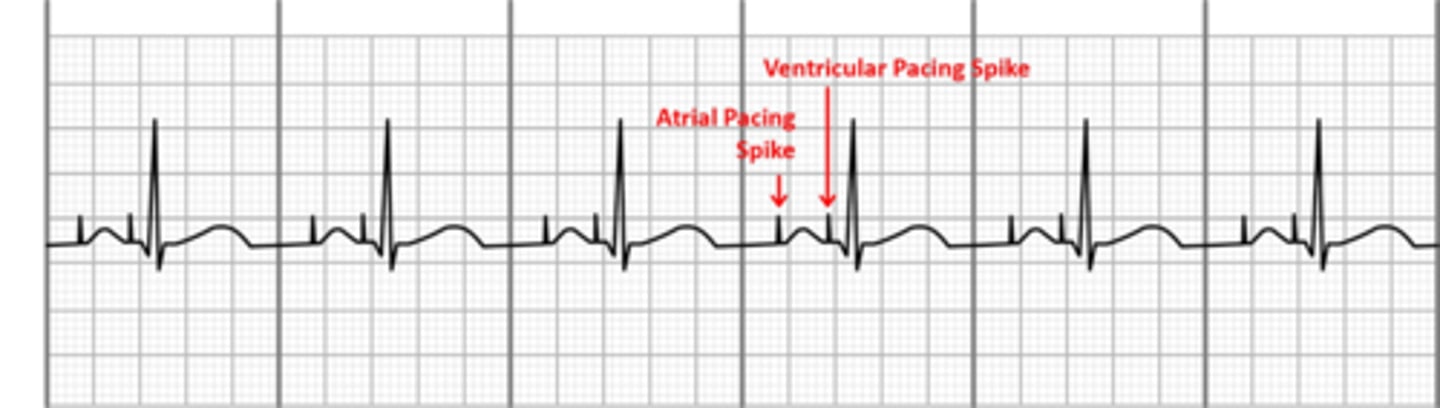
Atrial and ventricular (Dual)
Whay kind of pacemaker is this?
"Atropine to Speed, Adenosine to Slow, Amiodarone for Rhythm to Flow!"
Atropine: Deals mainly with SA (sinus rhythm issues)
Adenosine: Deals mainly in the middle between AV (atrial rhythm issues)
Amiodarone: Deals mainly with Ventricular issues
A fun rhythm to Remember the 3 A meds :)
