Ch 1.1 - Ecology + Biosphere
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Ecology
Study of Earth
- The relationship between the living and nonliving
Biosphere
Is the Earth
- All areas that are inhabited and support organisms
- Composed of Atmosphere, Geosphere and Hydrosphere
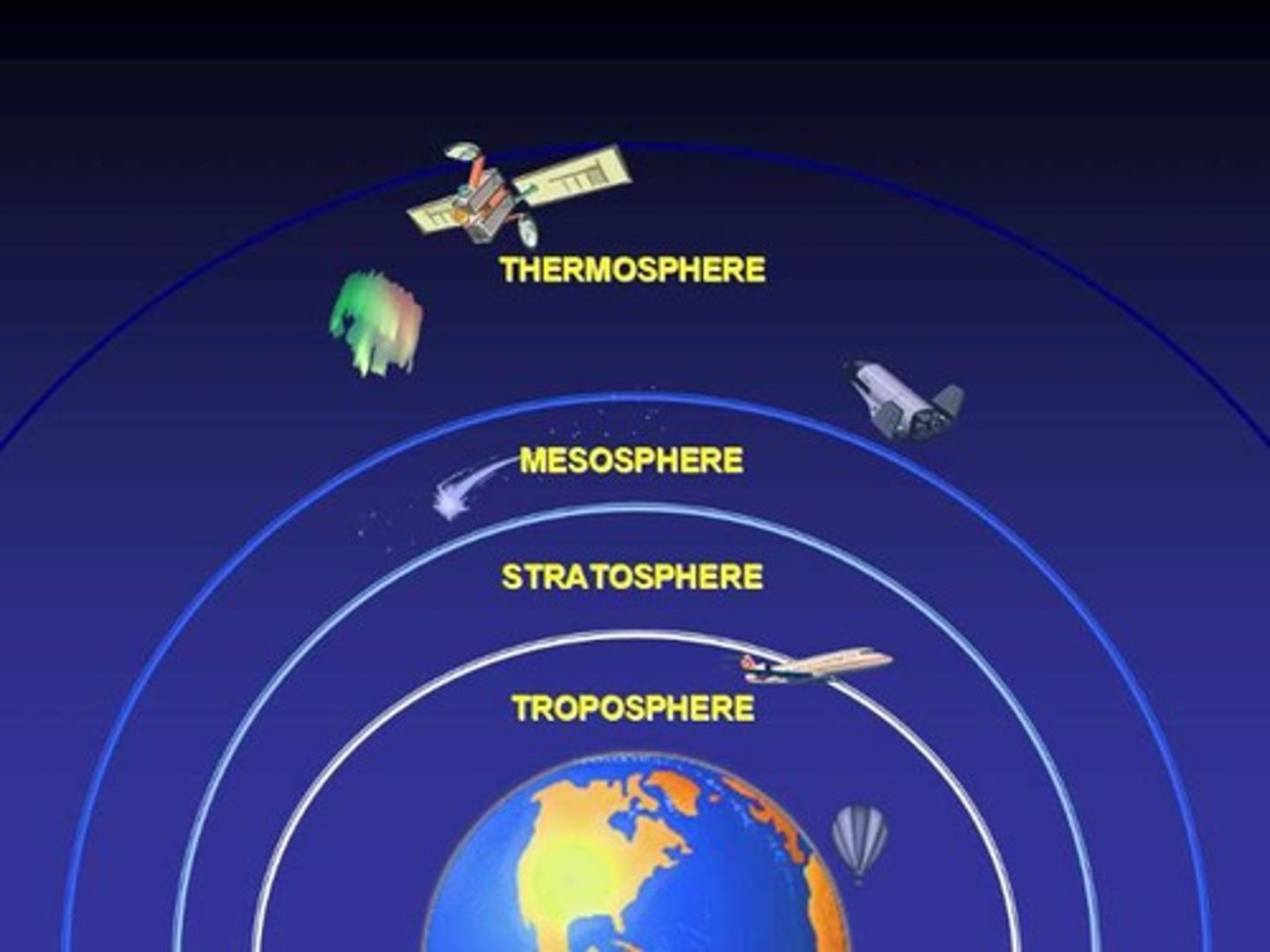
Atmosphere
Layers of gas that surround Earth
- Found at different altitudes, within 10km of the surface and higher
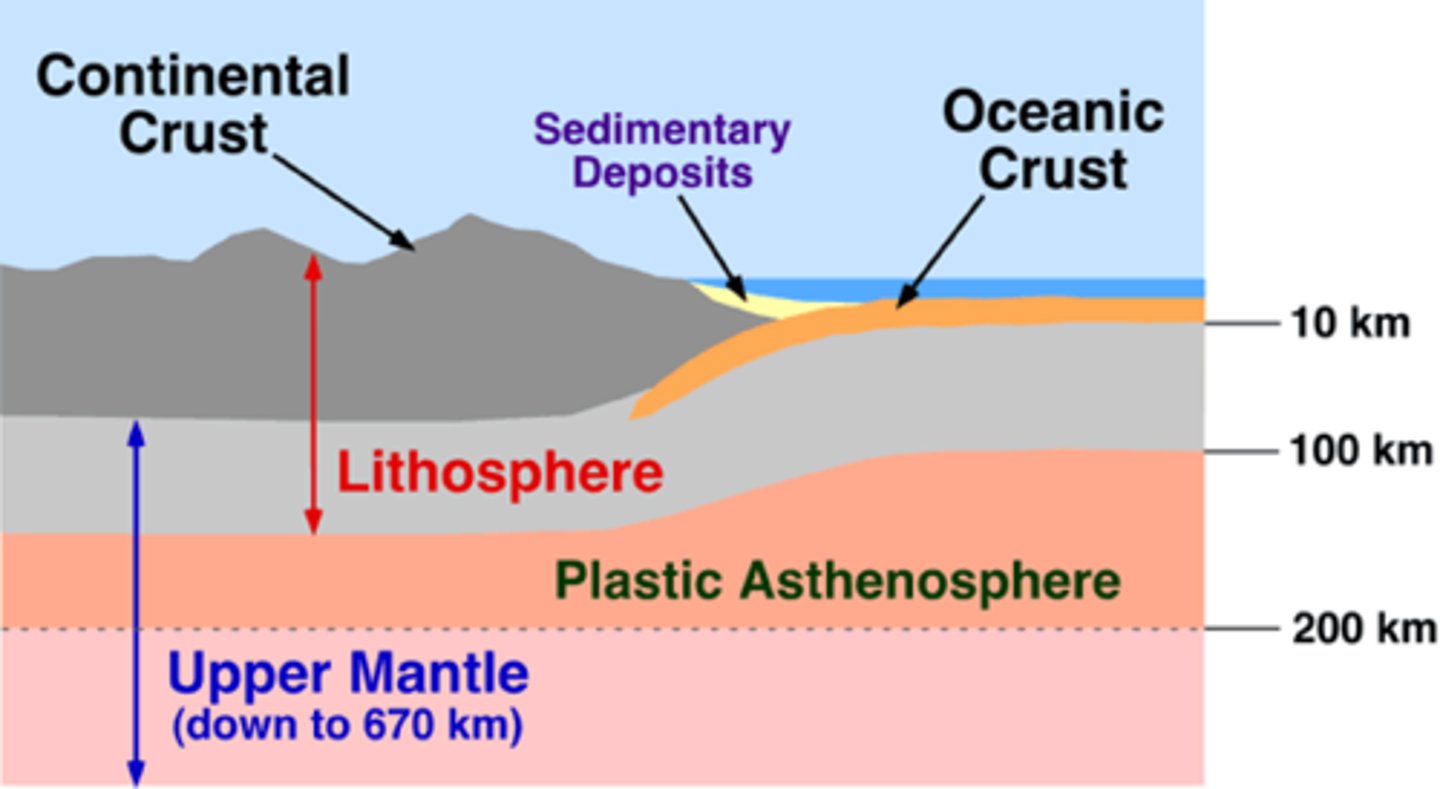
Geosphere
Solid, mainly rocky part of Earth
- Lithosphere
Hydrosphere
All of Earth's water, both liquid and solid that moves through the geosphere

Open System
Energy and matter is allowed to cross
- ex. Earth is an open system for energy, sun (energy) enters the atmosphere and some is reflected or absorbed (leaves) through the atmosphere

Closed System
Allows energy, but not matter to cross
- Some matter does move between Earth and space, but not in large amounts
- Matter on Earth is recycled but the overall amount does not change over time
- ex. Earth is a closed system for matter, matter already on Earth stays here permanently
Need for Energy
- All organisms need energy to live
- The major source for energy is the Sun
- All living things require energy to do things associated with life (such as moving)
- A lot of energy is lost through the body as heat and cannot be used in the biosphere
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only change forms
First and Second Law of Thermodynamics
First Law: Energy is conserved and can be converted
Second Law: Energy can flow
Producers/Autotrophs
Convert light energy into stored energy in carbs, self feeders
- Done via photosynthesis or chemosynthesis (w/o sunlight and instead energy from chemicals)

Photosynthetic Producers
Convert CO2, H2O and light energy into biological energy through photosynthesis
- ex. Bacteria in the ocean's deep sea vents use hydrogen sulfide
Chemosynthetic Producers
Convert energy from chemical bonds into stored biological energy
- Produces much less energy but allows life to exist in extreme environments on Earth
- ex. Bacteria in the soil (limited access to oxygen) use ammonia

Consumers/Heterotrophs
Convert stored energy into carbs to power their cells
- Consumes or eats organic matter made by producers or other organisms
- Done via cellular respiration

Primary Consumers (Herbivores)
First eaters of plants or other producers
- Only eats plants, bacteria, algae and any other organisms that are producers
- ex. Some insects, snails, birds, mammals, clams

Secondary Consumers (Carnivores)
Animals that eat herbivores
- ex. Spiders, frogs, owls

Tertiary Consumers (Also Carnivores)
Animals that eat other carnivores or secondary consumers
- ex. Wild cats, giant crabs, tuna, humans

Decomposers
Obtain energy by consuming dead organisms, shedded part of organisms, or waste materials (ex. feces)
- They fit in all levels of consumers
- Important in life cycles because their waste is inorganic and can return to the soil to be reused by producers
- ex. Bacteria, fungi, earthworms, some insects

Sunlight and Earth
When sun hits/collides with matter, heat may be produced
The main outcomes are:
- Reflection
- Absorption
- Transmission
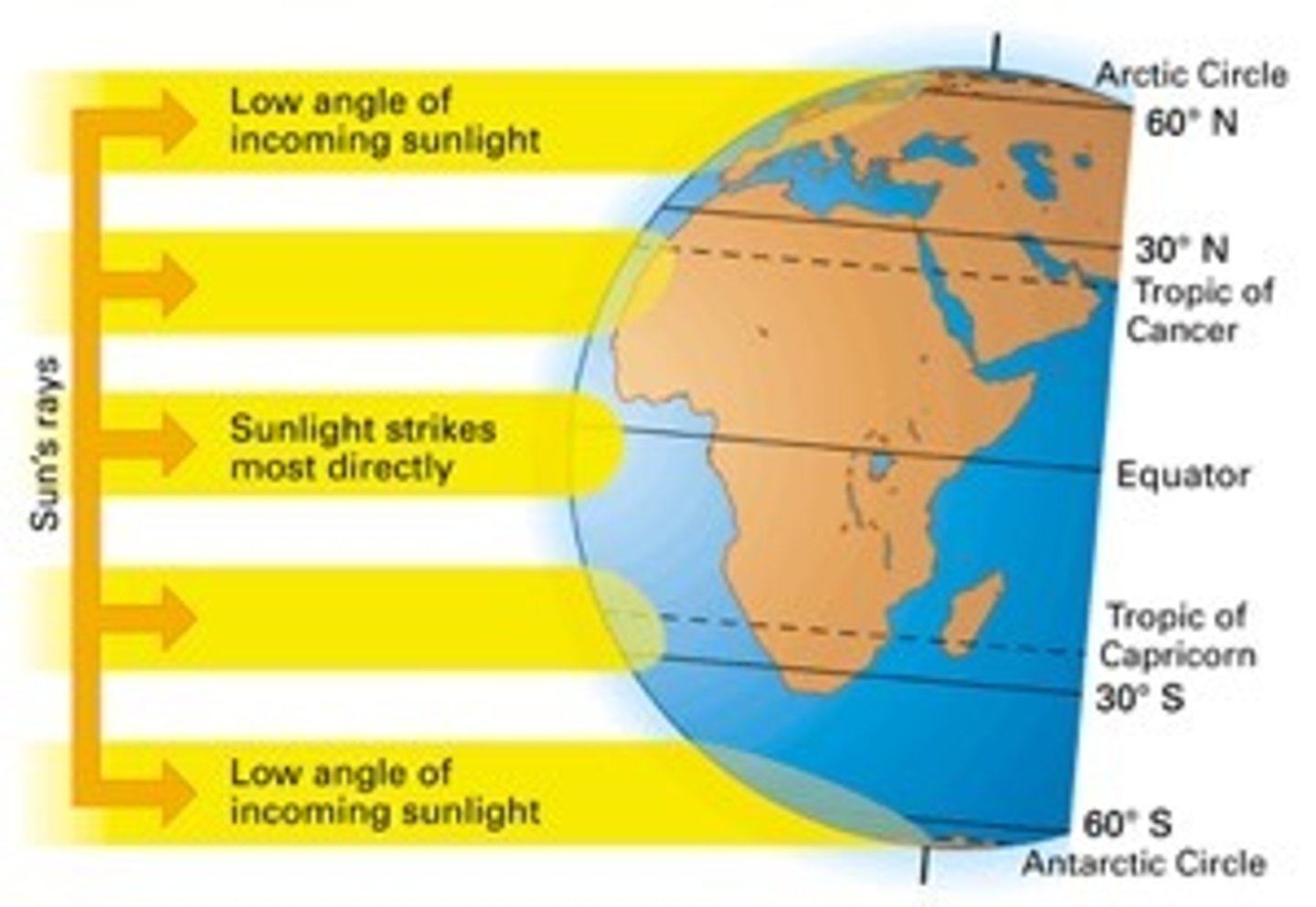
Sunlight and Earth Percentiles
30% is reflected back toward space
- Lower energy wavelengths
Around 20% is absorbed by the air
- Some heats the atmosphere and some radiates back into space
Around 50% is absorbed by the Earth's surface and only 1-2% reaches consumers
Things That Can Affect How Much Sunlight Hits earth
- Changes in the atmosphere (dust, pollution, greenhouse gasses)
- Changes in the hydrologic cycle (clouds, fog, snow)
- Changes in Earth's surface, affecting albedo
Albedo
Amount of light an object reflects
- Expressed as a percentage, higher percentage means the more reflection
- White objects have the highest albedo, vice versa for black
What Happens to Light/Energy
- Light hits Earth's surface
- Lower energy wavelengths are reflected back to space (infrared radiation)
- Light now goes straight to space or can be absorbed/reflected back by what is in the atmosphere
Composition of the Atmosphere
Full of matter: dust, debris and gases
- Gases interact with incoming energy and light reflected from Earth's surface
Gaseous composition:
~80% Nitrogen
~20% Oxygen
~1% other gases (ex. Carbon dioxide, water vapour, methane, other gases)
Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases are good at absorbing the infrared energy from the sun and keep the earth warm
- Gases include: CO2, H20 (water vapour), CH4 (methane), nitrogen oxides, ozone and chlorofluorocarbons (CFC's)
Greenhouse Effect
1. Sunlight hits Earth and warms the surface
2. Earth reflects some of this energy back as heat (infrared radiation)
3. Greenhouse gases absorb this heat and re-radiate it, some goes out, but much comes back to Earth.
4. Keeps the Earth warm enough for life = global warming.