APUSH: Period 2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Maryland Act of Toleration (1649)
First colonial statue granting religious freedom to all Christians
It called for death of all non-Christians
Roger Williams
Dissenter
1636, he founded the settlement of Providence (Rhode Island)
Believed that the individual's conscience was beyond the control of any civil or church authority

Quakers
Members of the religious group: Society of Friends
Believed in inner light (divine guidance within each person), equality for all people, religious tolerance, and pacifism

William Penn
English Quaker leader who founded the colony of Pennsylvania as a haven for Quakers and other persecuted religious groups, establishing democratic principles and promoting religious freedom and diversity

Captain John Smith
Because of his forceful leadership, Jamestown barely survived its first five years.

Jamestown
1607, the first permanent English colony in America was founded at this location.
The Virginia Company, was a a joint-stock company chartered by England's King James I.

John Rolfe
Helped Jamestown develop a new variety of tobacco which became popular in Europe and became a profitable crop. (married Pocahontas)

Separatists
Radical dissenters to the Church of England, they were known by this name because they wanted to organized a completely separate church that was independent of royal control. They became known as Pilgrims, because of the travels.

Puritans
In 1630, founded the Massachusetts Bay Colony at Boston
They believed in predestination, valued hard work and community governance, and used their religious beliefs to shape New England's social structure, including advocating for public education and creating strict social norms that often led to intolerance of other beliefs.

Plymouth Colony
This colony was started by the Pilgrims at Plymouth (Massachusetts). In the first winter nearly half of them perished. They were helped by friendly American Indians and celebrated the first Thanksgiving in 1621.
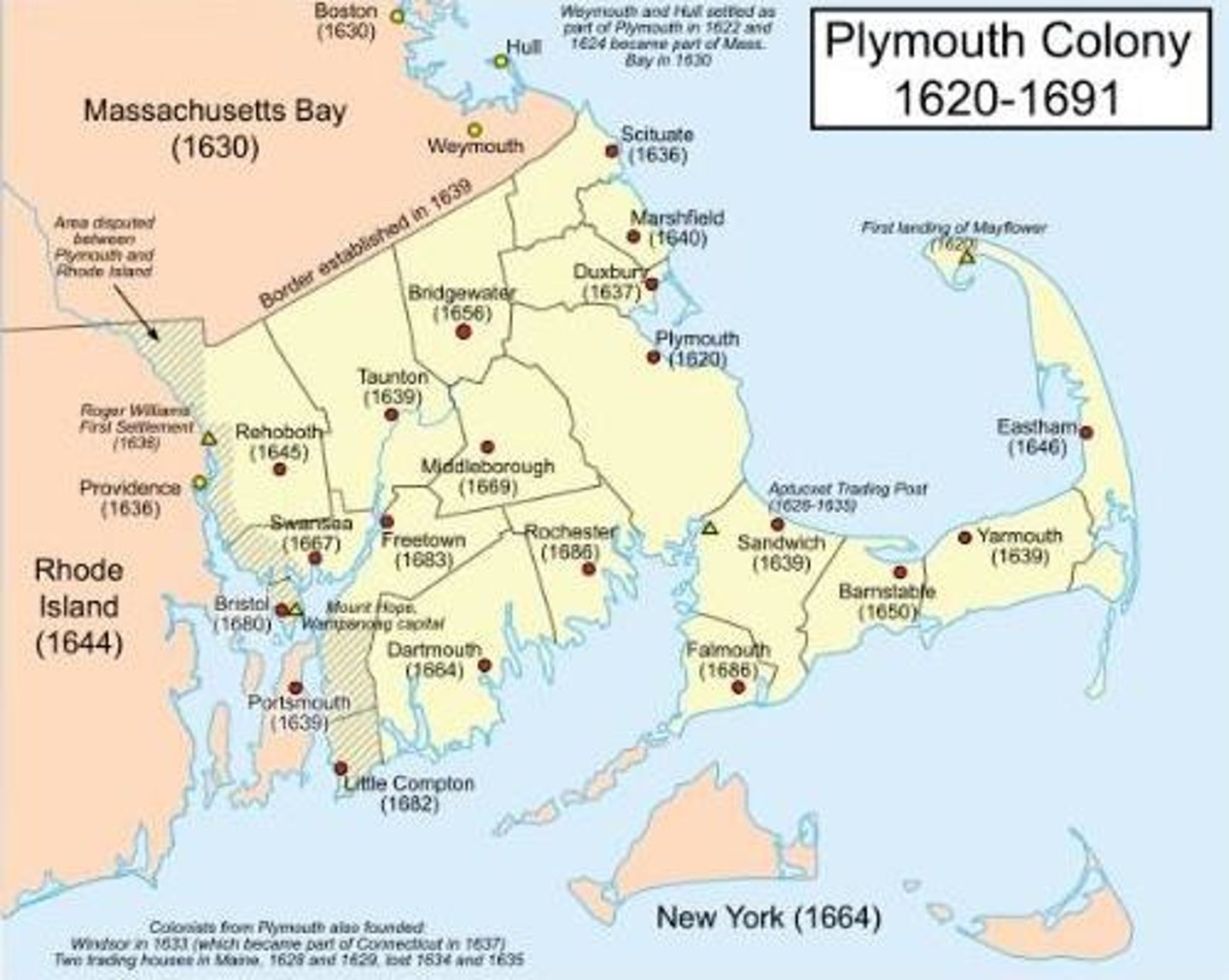
Anne Hutchinson
This Puritan believed in antinomianism and was banished from the Bay colony because of her beliefs. In 1638, she founded the colony of Portsmouth.

Great Migration
migration of English colonists from Europe to North America, particularly the establishment of the Puritans in New England
From the 1630s, around 20,000 Puritans migrated to this region, seeking religious freedom and the opportunity to build a model Christian society, a movement that profoundly influenced American culture and identity
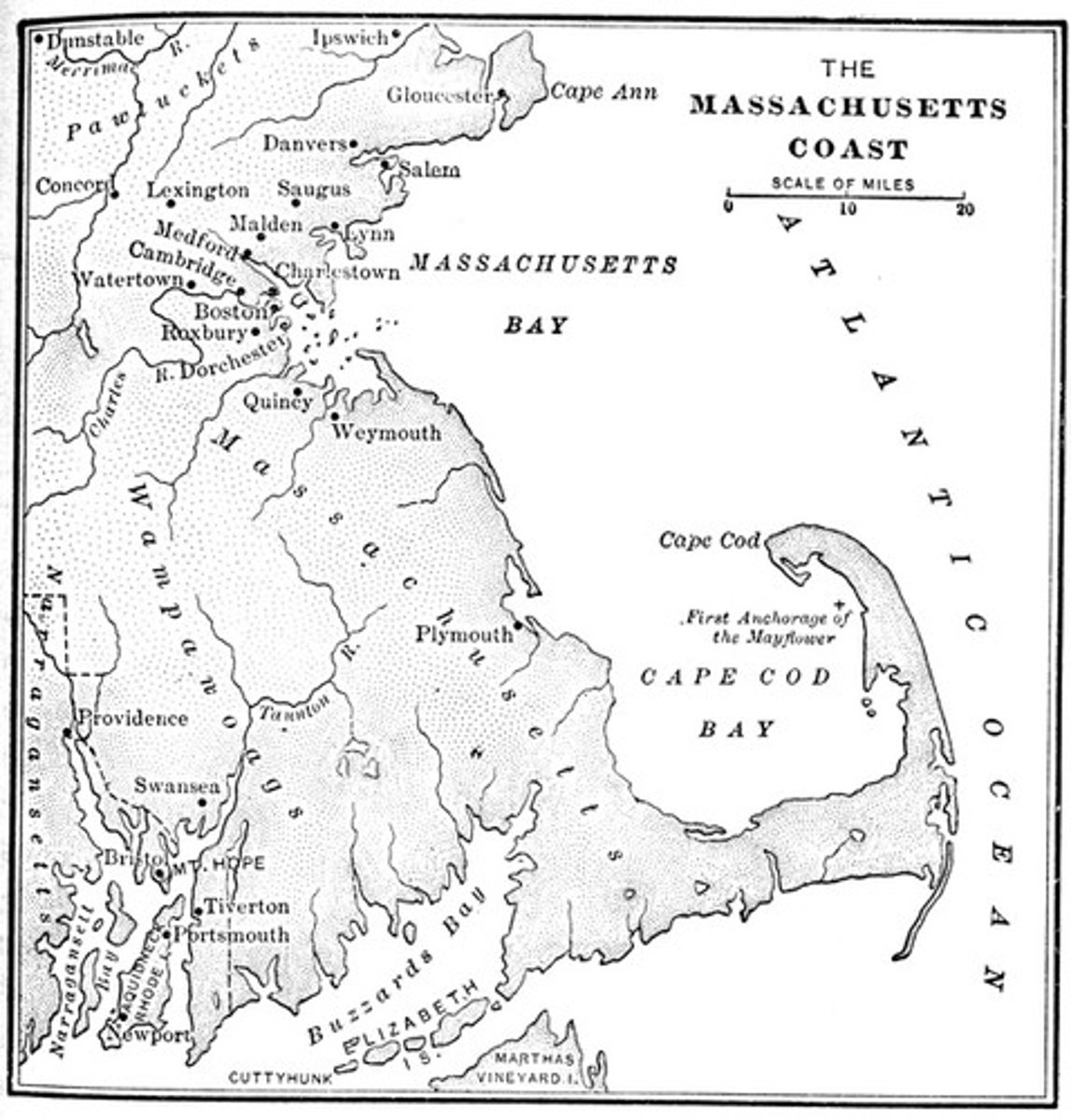
New York
Originally settled by the Dutch in 1624, became a diverse economic trade center, would later taken by English in 1664
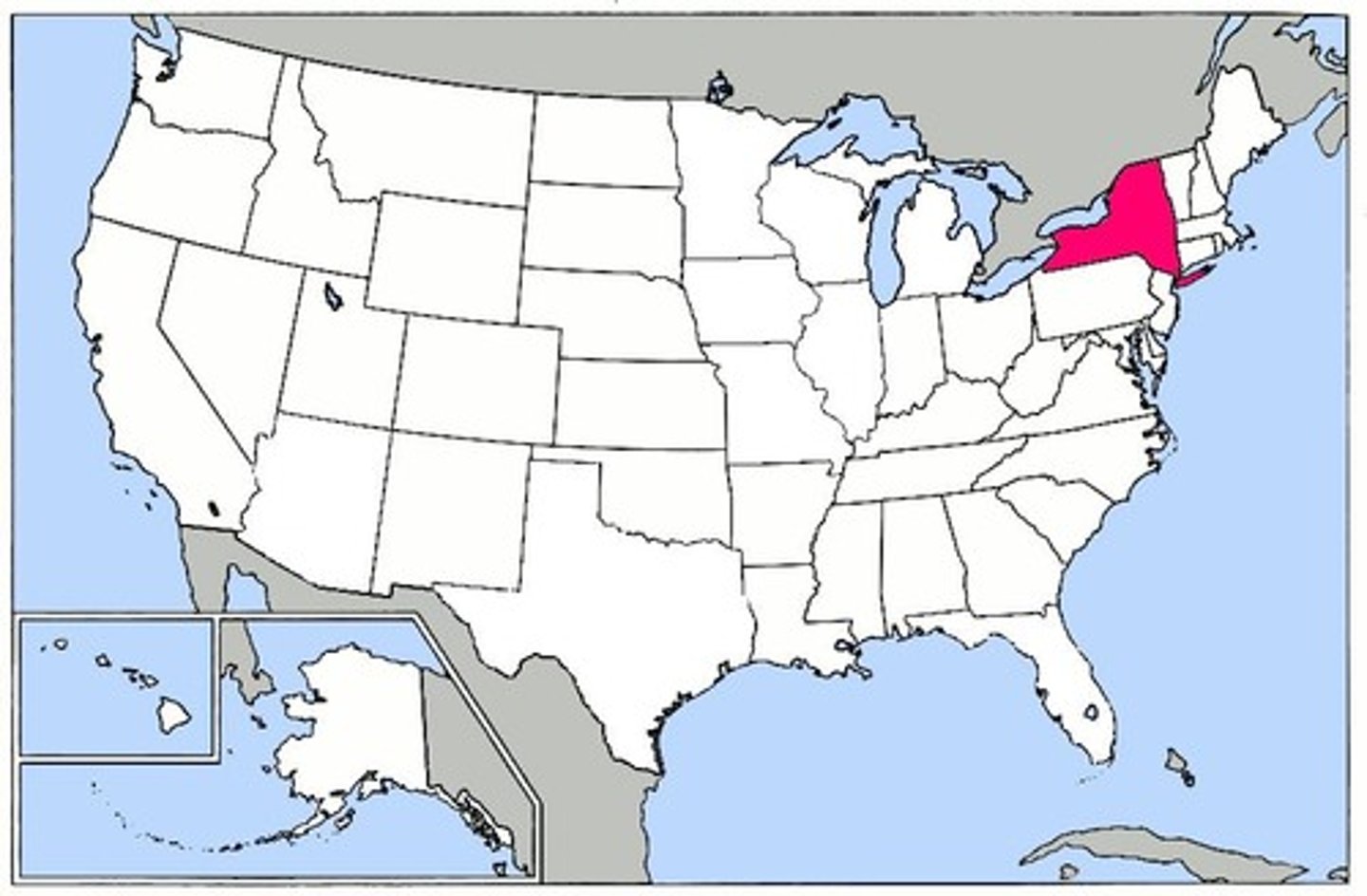
Pennsylvania Colony
Colony formed from the "Holy Experiment"; settled by Quakers. Founded by William Penn, who bought land from the Native Americans. Allowed religious freedom
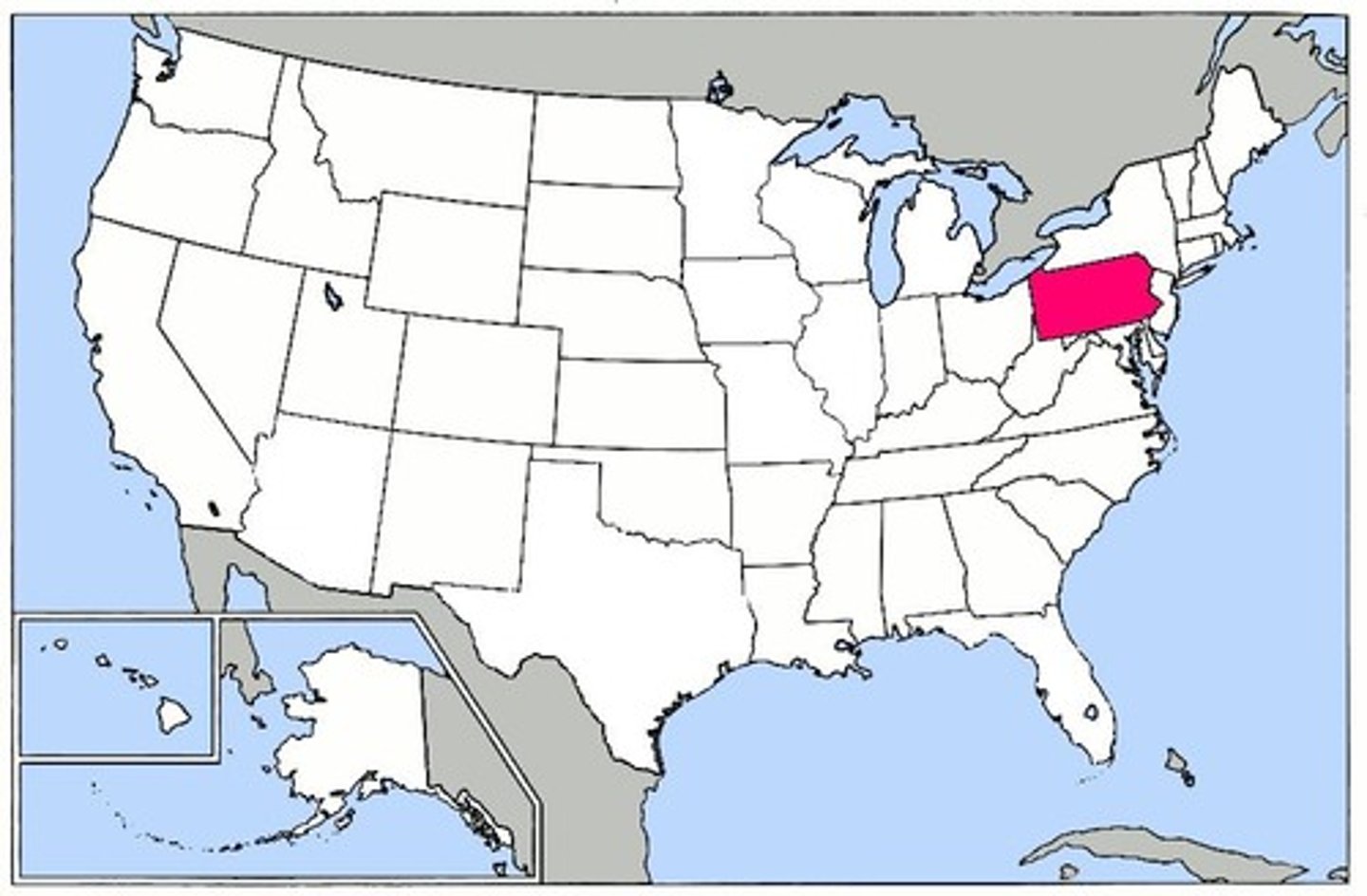
Georgia
In 1732, Georgia was formed to provide a buffer between wealthy Georgia and Spanish controlled Florida, and to provide a place for the many debtors of England to begin again.
James Oglethorpe
Founder of Georgia's first settlement, Savannah, in 1733. He acted as governor of Georgia and had strict laws which included a ban on rum and slavery.

Wampanoags
An American Indian tribe led by Metacom.

Mayflower Compact
In 1620, while they were sailing to America on the Mayflower, the Pilgrims created this document that pledged them to make decisions by the will of the majority
early form of self-government and a social contract for the Plymouth Colony

joint-stock company
Corporate colonies, such as Jamestown, were operated by groups, at least during the colony's early years.

Bacon's Rebellion
1676
Armed uprising in colonial Virginia led by Nathaniel Bacon against Governor William Berkeley, fueled by frustrated frontier farmers (including former indentured servants and poor whites) who felt neglected by the wealthy elite

Virginia Company
Joint-Stock Company in London that received a charter for land in the new world. Charter guarantees new colonists same rights as people back in England.
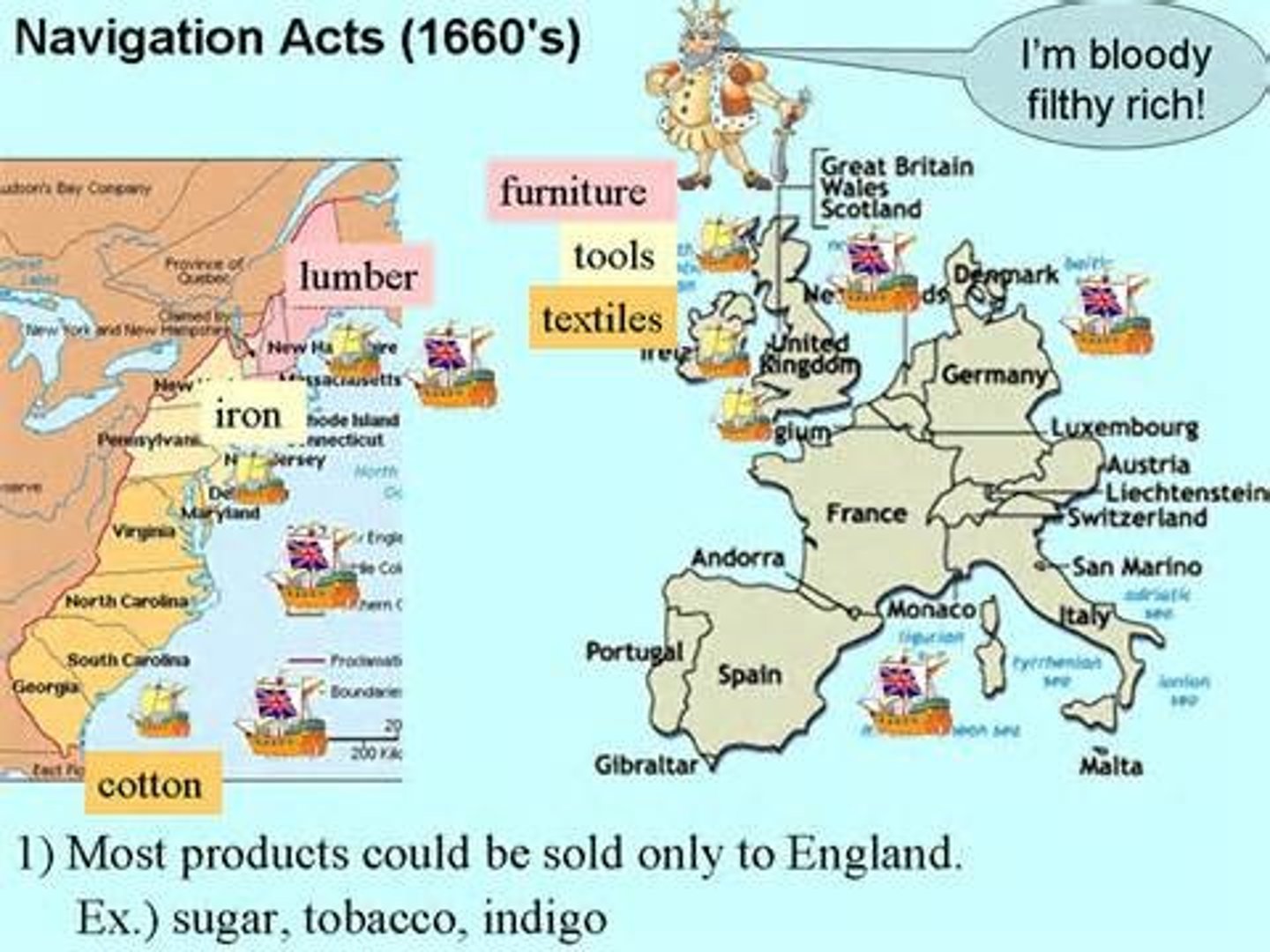
mercantilism
An economic policy in which the colonies were to provide raw materials to the parent country of growth and profit of the parent country.

Navigation Acts
Between 1650 and 1673 England passed a series of laws which establish rules for colonial trade.
* Trade to and from the colonies could be carried only by English or colonial-built ships, which could be operated only by English or colonial crews.
* All goods imported in the colonies, except some perishables, had to pass through the ports in England.
* Specified goods from the colonies could be exported only to England.
Dominion of New England
James II wanted to increase royal control in the colonies, so he combined them into larger units and abolished their representative assemblies.
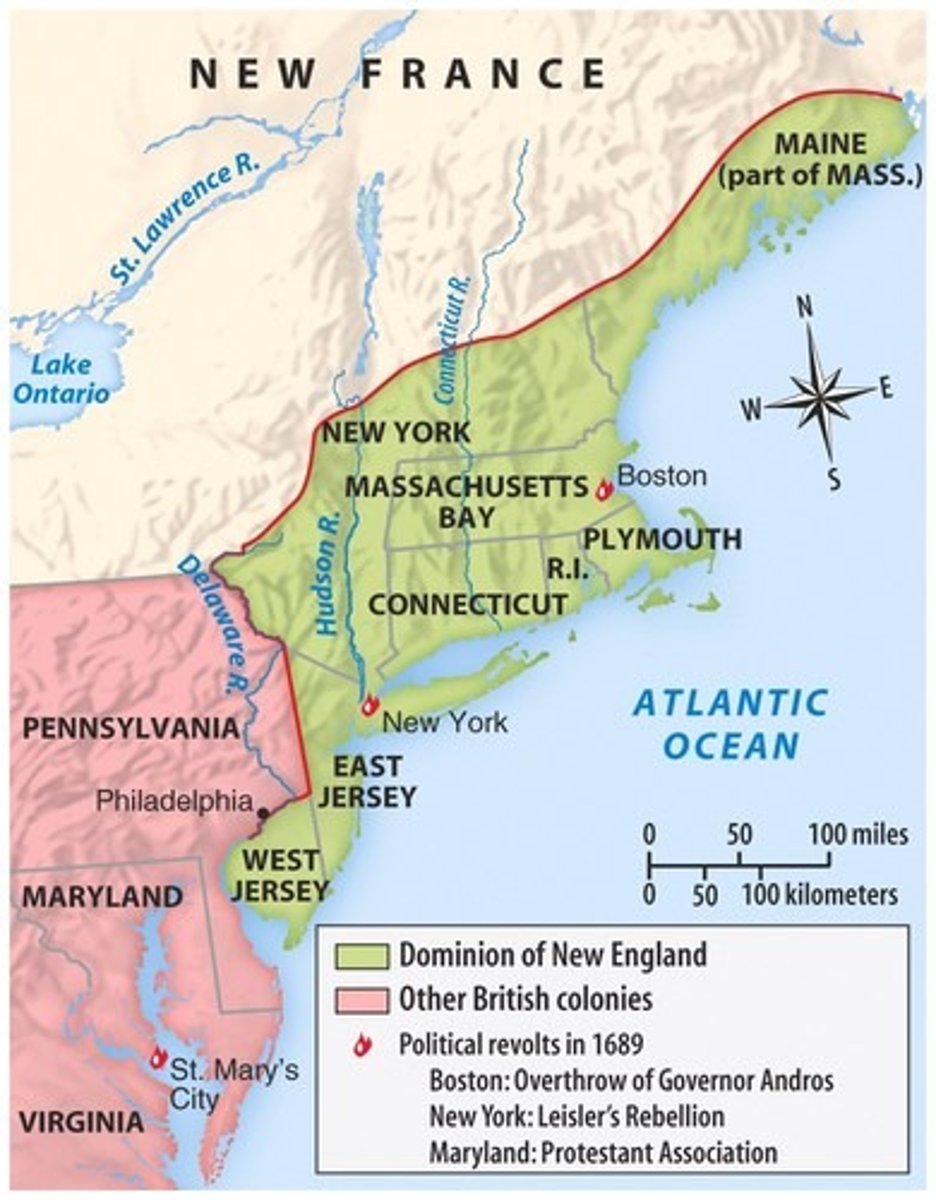
Glorious Revolution
In 1688, King James II was deposed and replaced with William and Mary. This brought the end to the Dominion of New England, and the colonies operated under their previous structure.

headright system
A method for attracting immigrants, Virginia offered 50 acres of land to each immigrant who paid for passage to America and to any plantation owner who paid for an immigrants passage.

Triangular Trade
A three way system of trade during 1600-1800s Africa sent slaves to America, America sent Raw Materials to Europe, and Europe sent Guns and Rum to Africa
Middle Passage
A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies
Indentured Servitude
A worker bound by a voluntary agreement to work for a specified period of years often in return for free passage to an overseas destination. Before 1800 most were Europeans; after 1800 most indentured laborers were Asians.
cash-crop agriculture
Agricultural production, often on a large scale, of crops for sale in the market, rather than for consumption by the farmers themselves.
House of Burgesses, 1619
The first elected lawmaking body in North America, established by the Virginia Company to allow representative government in Virginia.
Great Awakening (1739-1744)
Puritanism had declined by the 1730s, and people were upset about the decline in religious piety. The Great Awakening was a sudden outbreak of religious fervor that swept through the colonies. One of the first events to unify the colonies.
George Whitefield (1714-1770)
Popular preacher during the First Great Awakening. Emphasizing common beliefs rather than theological differences. His revivals attracted diverse congregations, including Anglicans, Baptists, and Presbyterians, who participated in joint meetings. This emphasis on unity helped to diminish sectarian divides and fostered a spirit of collaboration among different faith communities, which had lasting impacts on American religious life
Jonathan Edwards
Preacher during the First Great Awakening; "Sinners in the hands of angry god"
William Bradford
A Pilgrim, the second governor of the Plymouth colony, 1621-1657. He developed private land ownership and helped colonists get out of debt. He helped the colony survive droughts, crop failures, and Indian attacks.
Dissenters
individuals who disagree with the established religious or political views of the majority
Enslaved Labor
Forced labor of enslaved individuals for economic gain.
plantation agriculture
raising a large amount of a "cash crop" for local sale or export
cash crop
a readily salable crop that is grown and gathered for the market (sugar, rice, indigo, cotton or tobacco)
John Winthrop
In 1630, he led about a thousand Puritans to America and and founded Boston and several other towns.

King Philip's War (Metacom's War)
1675-1678: Series of assaults by Metacom, King Philip, on English settlements in New England. The attacks slowed the westward migration of New England setters for several decades and virtually ended Native American resistance in this region.
Pequot War
1637- conflict between the Pequot tribe and an alliance of English colonists and other Native American tribes, resulting in the near destruction of the Pequot Nation.