OMIS CH 17 Week 8
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Big Data, BI, Analytics, ML
Benefits from Data Mastery

What did Disney do with Broadway?
Introduced dynamic pricing
Set ticket prices for Broadway production of the musical The Lion King
It was the only show to see revenue grow exponentially
What is dynamic pricing? What are the pros vs cons?
When a firm sets prices in real or near-real time in order to maximize sales and profits
Pros is that is works where supply is constrained and subject to demand spikes
Cons is that i can leaving consumers feeling taken advantage of:
Consumers make repeated purchases are away of past prices
Consumers have alternative choices, like grocery or department store shopping
What companies use Dynamic Pricing?
Uber
Lyft
Professional Sports Teams
Airbnb Smart Pricing
Feature that uses machine learning to tweak accuracy of models that suggest the perfect rate and all sorts of data that can influence price
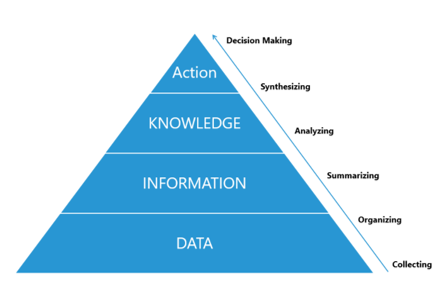
Information Hierarchy
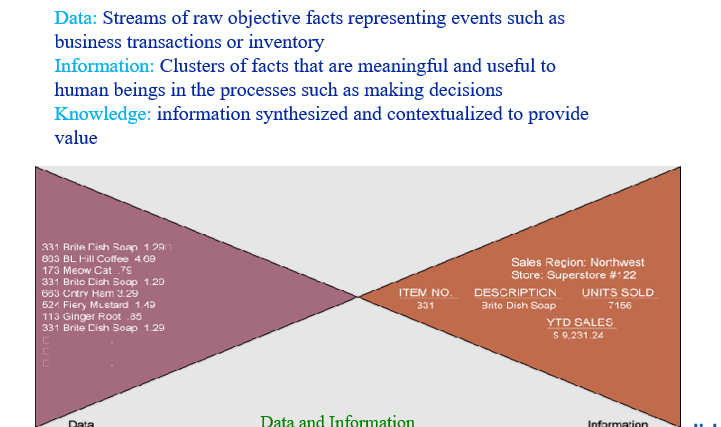
Core drivers of the information age
Data, Information, Business Intelligence, Knowledge
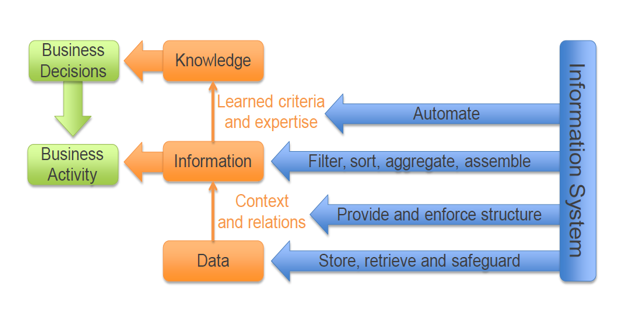
Role of Information Systems
Types of Data
Human generated: Data that is generated through human interaction with computers
Machine-generated: Create by machine without human intervention
Structured: Stored in a traditional system such as a relational database or spreadsheet
Unstructured: Not defined and does not follow a specified format eg. images, videos, audio
Big Data: Data high in volume, variety, and velocity but low in veracity
requires advanced storage and analytics for processing
Data Hierarchy
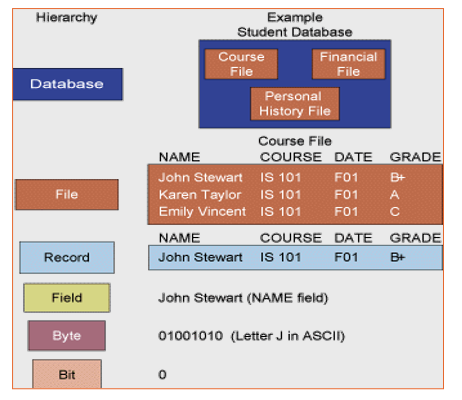
Database, DBMS, SQL, DBA

Uses of Multiple Database Application (rewrite this)
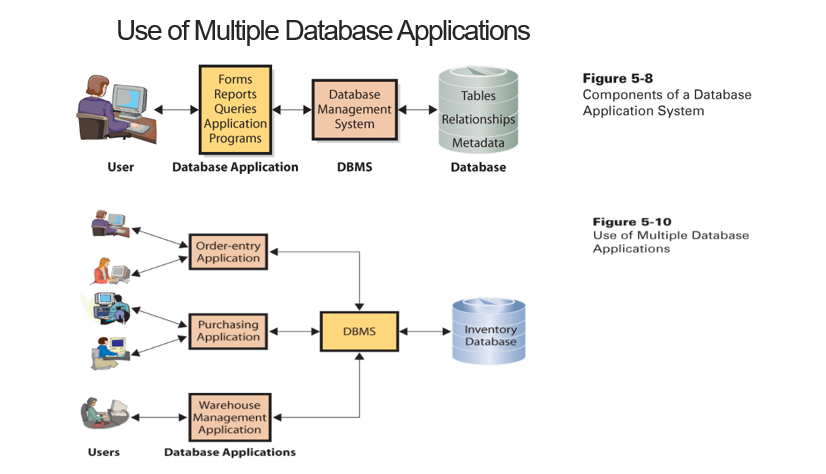
Key terms associated with database systems are:

Entity, Attribute, Primary Key VS Foreign Key, Simple vs Composite Key
Entity: A table that stores information about a person, place, thing, transaction, or event
Attribute: Data elements associated with an entity
Primary Key: Unique Identifiers
Foreign Key: Identifiers that enable a dependent relation to refer to its parent relation
Simple Key: Single Field
Composite Key: More than one field
Transaction processing systems, transaction, loyalty program

How do companies gather data on its consumers?
CRM: Empower employees to track and record data at nearly every point of customer contact
Surveys: Firms supplement operational data with additional input from surveys….direct survey can give better info than a cash register
External Sources: Organizations can have their products sold by partners and can rely on heavily on data collected by others
Data Aggregators

Legacy Systems
Older information systems that are incompatible with other systems, technologies, and way of conducting business
Operational Data cannot always be queried to:
Most transactional databases are not set up to be simultaneously accessed for reporting and analysis
Database analysis requires significant processing
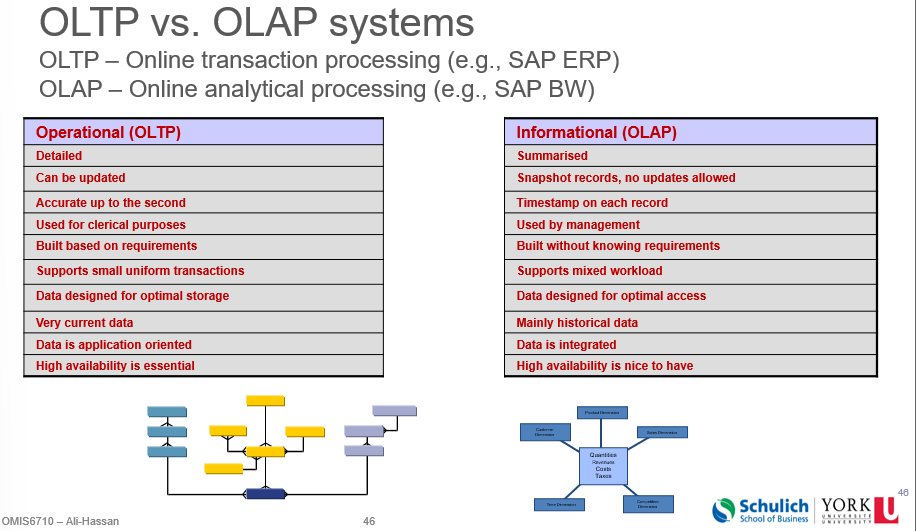
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) vs. Online Analytical Processing (OLAP)
OLTP Data Models
Built to enhance transaction speed
Highly normalized - low redundancy
OLAP data models built to enhance dimensional analysis speed
Not normalized — high redundancy (start schema)
Organized based on analysis business logic
Star schema is the basic design
OLTP vs OLAP systems
Data Warehouse, Data Mart, OLAP
Big Data
A collection of large, complex data sets, including structured and unstructured data, which cannot be analyzed using traditional database methods and tools
The Four V’s of Big Data
Volume
Scale of Data
Velocity
Analysis of Streaming Data
Veracity
Uncertainty of Data
Variety
Different Forms of Data
Big Data: From Data to Decisions
Data Creation
Data Acquisition
Info Processing
Business Process
Data Lake
A catch-all term for storage and access technologies used in big data
Data Warehouse, Data Mart, OLAP
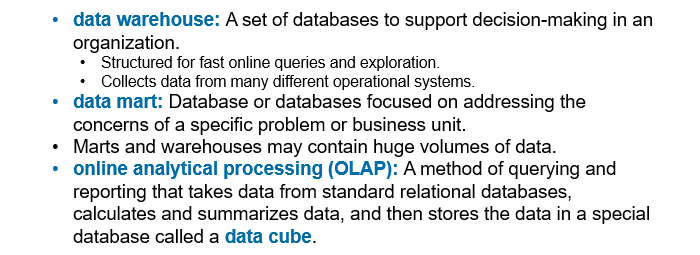
Flow of Operational Systems to Data Analysis
Hadoop and Data Cloud

Four primary advantages when using Big Data

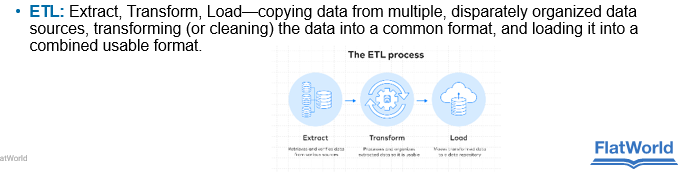
ETL
What is Analytics?
•Analytics is any mathematical or scientific method that augments data with the intent of providing new insight.
•Insight creates competitive advantage when used to inform actions and decisions
•Data is becoming the world’s new natural resource, and learning how to use that resource is a game changer.
•Through the use of analytics, insights from data can be created to augment the gut feelings and intuition that many decisions are based on today.
Query tools, Python, R. Graphical Query Tools

Canned & Ad hoc reporting tools, dashboards, data visualization

Data Mining & Machine Learning

Data Mining: Key Areas of Leverage

Over-engineer
Build a model with so many variables that the solution arrived at might only work on the subset of data used to create it.
Machine Learning: Supervised vs Unsupervised learning vs Reinforcement Learning
•In reinforcement learning, the system is trained to maximize a reward based on input data, going through a trial-and-error process until it arrives at the best possible outcome.
•Example learn how to play games or research (e.g., autonomous robots navigating new environments)
•More advanced ML that can be considered AI

Narrow, General, Super
•Artificial narrow intelligence (ANI) refers to intelligent systems designed or trained to carry out specific tasks or solve particular problems.
•Artificial general intelligence (AGI), is still a hypothetical concept as it involves a machine understanding and autonomously performing vastly different tasks based on accumulated experience. This type of intelligence is more on the level of human intellect, as AGI systems would be able to reason and think more like people do.
•Artificial superintelligence (ASI) would be a machine intelligence that surpasses all forms of human intelligence and outperforms humans in every function
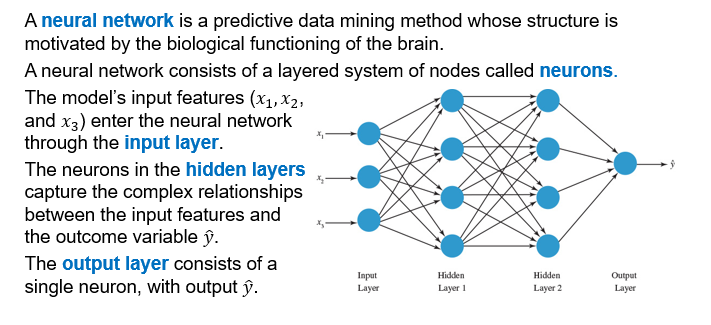
Neural network, input layer, hidden layers, output layer
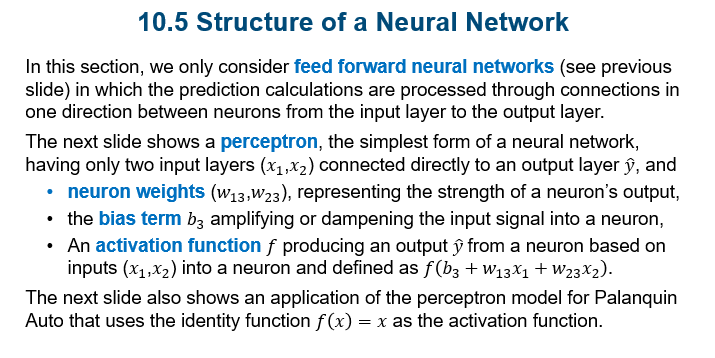
Feed forward neural networks, perceptron, neuron weights, bias term, activations function
AI Winter, Generative AI

How LLMs Used in Generative AI Are Created
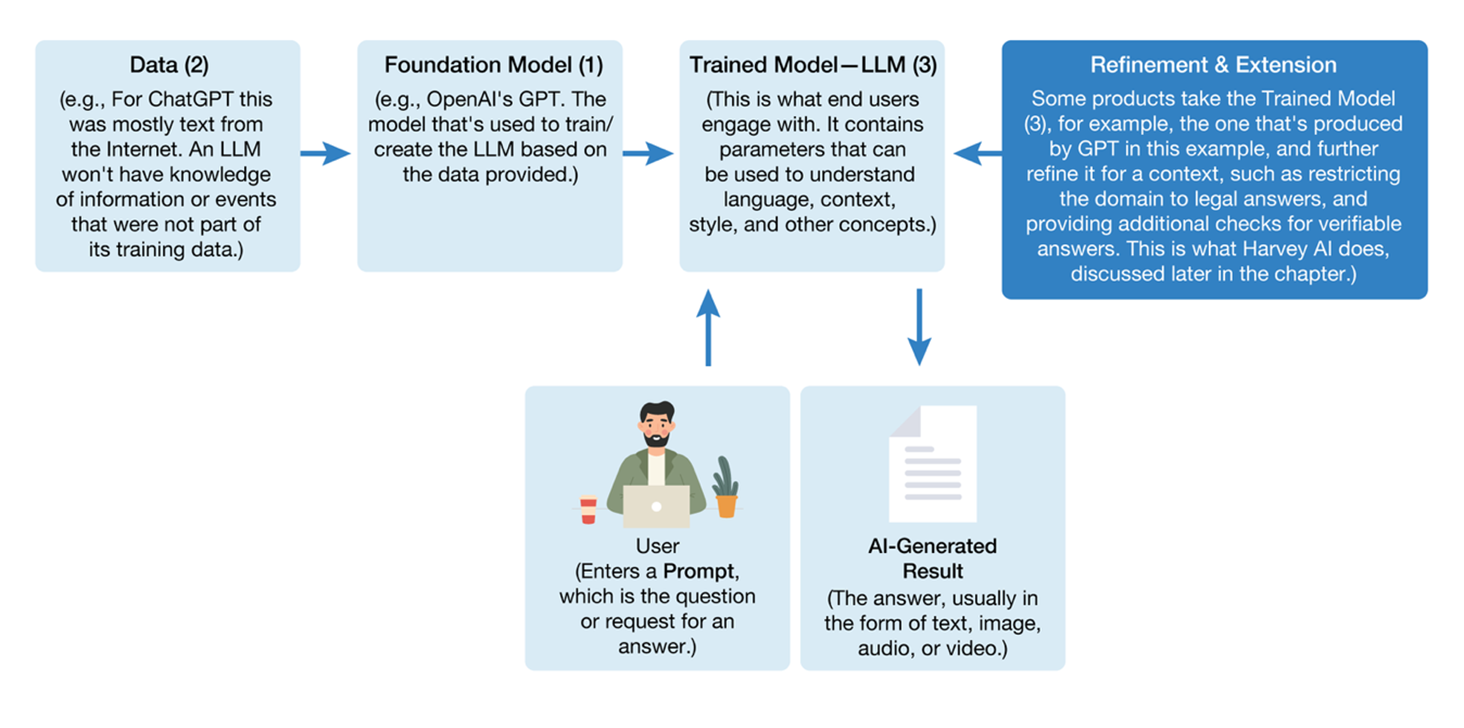
Parameters & Corpus

Prompt, Prompt Engineering, Hallucination, AGI

Turing Test, Expert Systems, Genetic Algorithms

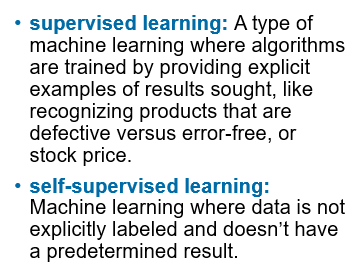
Supervised Learning, Self-Supervised Learning
Semi-supervised learning, Reinforcement learning from human feedback & Constitutional AI

Pair Programming
•where two coders work side-by-side on the same product at the same time, looking at the same screen and sharing their combined insight.
Canva vs Adobe genai work
•Canva
•Baked generative AI image tools into its cloud-based graphic design platform.
•Built these by leveraging tools from various providers:
•OpenAI
•Stable Diffusion
•Provides options for text-to-image and text-to-video generation.
•Provides tools to help generate ad copy, brainstorm ideas and suggest designs, translate documents to different languages, and change a product from one format to another.
Adobe
•Includes Photoshop and Illustrator
•Developed its own underlying generative AI technology—products introduced under the name Adobe Firefly
•GenAI tools in Photoshop can be used to create new images or add and enhance an existing image.
•Also allow AI to add all sorts of graphic effects to manipulate text
•In Illustrator, AI will create line-based vector images that scale without jagged edges.
•Will incorporate these and additional tools into other products, including video-focused GenAI for Adobe’s Premiere Pro video editing tool.
CAPTCHA & OCR

Understanding AI Risks: Prompt injection, Data Poisoning

Deepfakes
•Sophisticated media (audio, image, video) created by AI that attempts to look or sound like a real person or event.
•Presenting generative AI outputs as your own work.
Benefits of AI in education

Seed Round
The initial round of capital provided to a startup.
What if we cant understand how i thinks?
•The “black box” nature of AI based on deep learning, with multilayered statistical weights, makes it especially difficult to break apart and demonstrate how these systems make their decisions.
•Heighten the possibility of unintended consequences like software that crosses ethical boundaries
•Obscure impact and risk
•Eventually contributed to a global recession-causing crisis
•Just because it can be done using AI doesn’t mean it will be legal
•Even firms that believe their technology is “behaving ethically” may be asked to provide extraordinarily difficult-to-prove evidence that laws are not being broken.
Change management
Refers to techniques to facilitate organization change, including preparing individuals for change and offering training and support during and after implementation.
Issues of ai that concerned citizens and managers should know about

Steps in developing and deploying more ethical, less risk-prone systems (hiring)

Steps in developing and deploying more ethical, less risk-prone systems (Auditing)
•Gather and act on input regarding flaws. If a user encounters a troubling flaw while using the system, there should be a clear, extremely easy way to submit feedback so that it can be addressed.
•Provide a means for remediation. A study led by technology and audit firms found that only 43 percent of organizations have clear procedures for overriding AI results that are suspicious or questionable.
•Test and audit. Firms deploying risky technology, or technology that might endanger others should be sure that these technologies are thoroughly tested.
•“Red Teaming”: Where a group unaffiliated with developers deliberately tries to undermine safety procedures in a system, hack the technology, and raise any additional concerns that should be addressed before deployment.
•Continually evaluate best practices and incorporate proven techniques. Firms should incorporate new tools as they are developed.
•ITIL: IT Infrastructure Library, which covers best practices for delivering IT services.
•COBIT: (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) A continually-evolving best-practices framework for IT governance that includes guidance on implementation, monitoring, and improving IT systems and organizations.
•Roll out technology gradually. Many firms choose to roll out technologies gradually to see how their post-test offerings work on smaller populations before releasing them more widely.

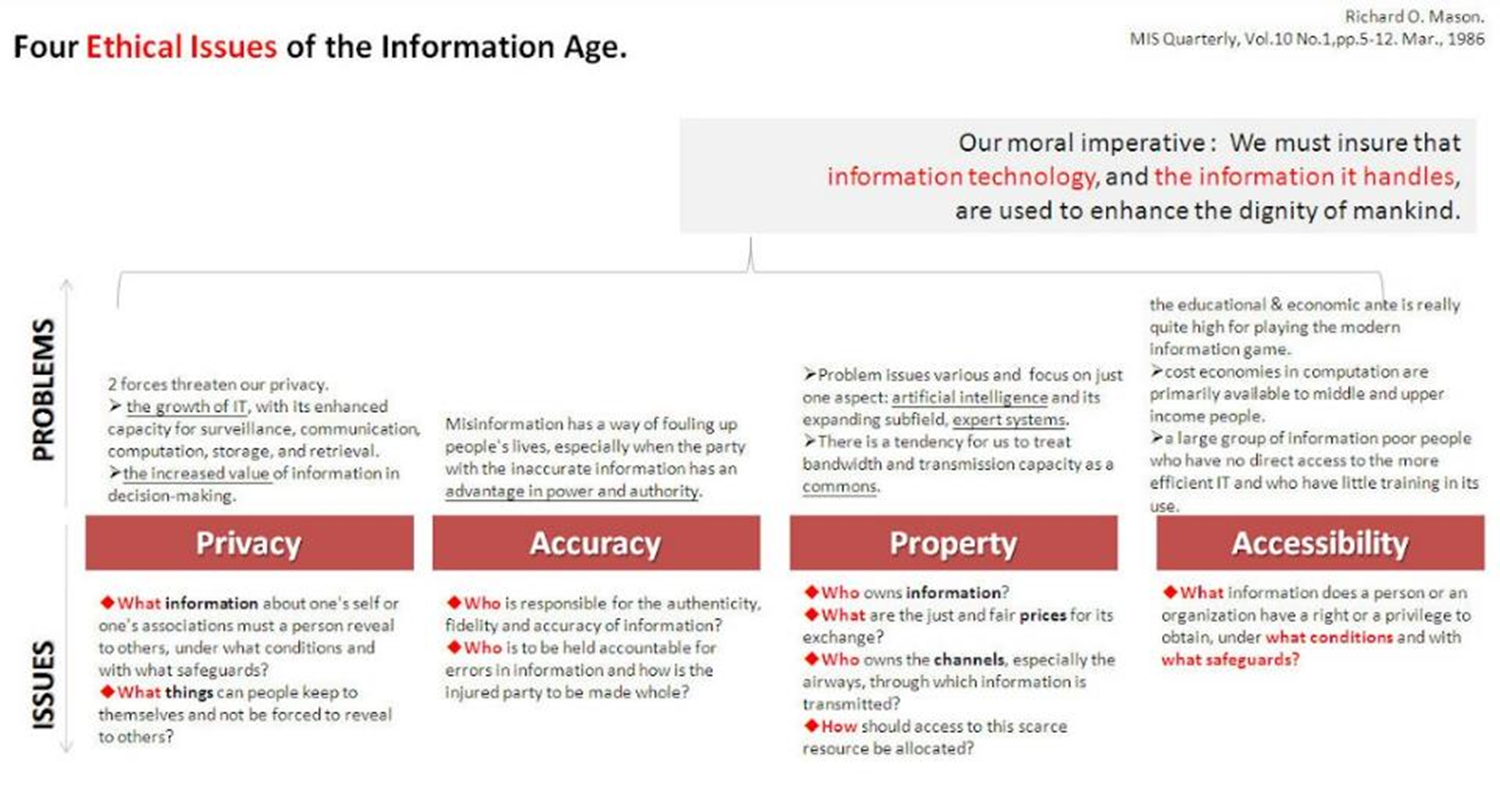
Four Ethical Issues of the Information Age
5 things the tech giant does with your data

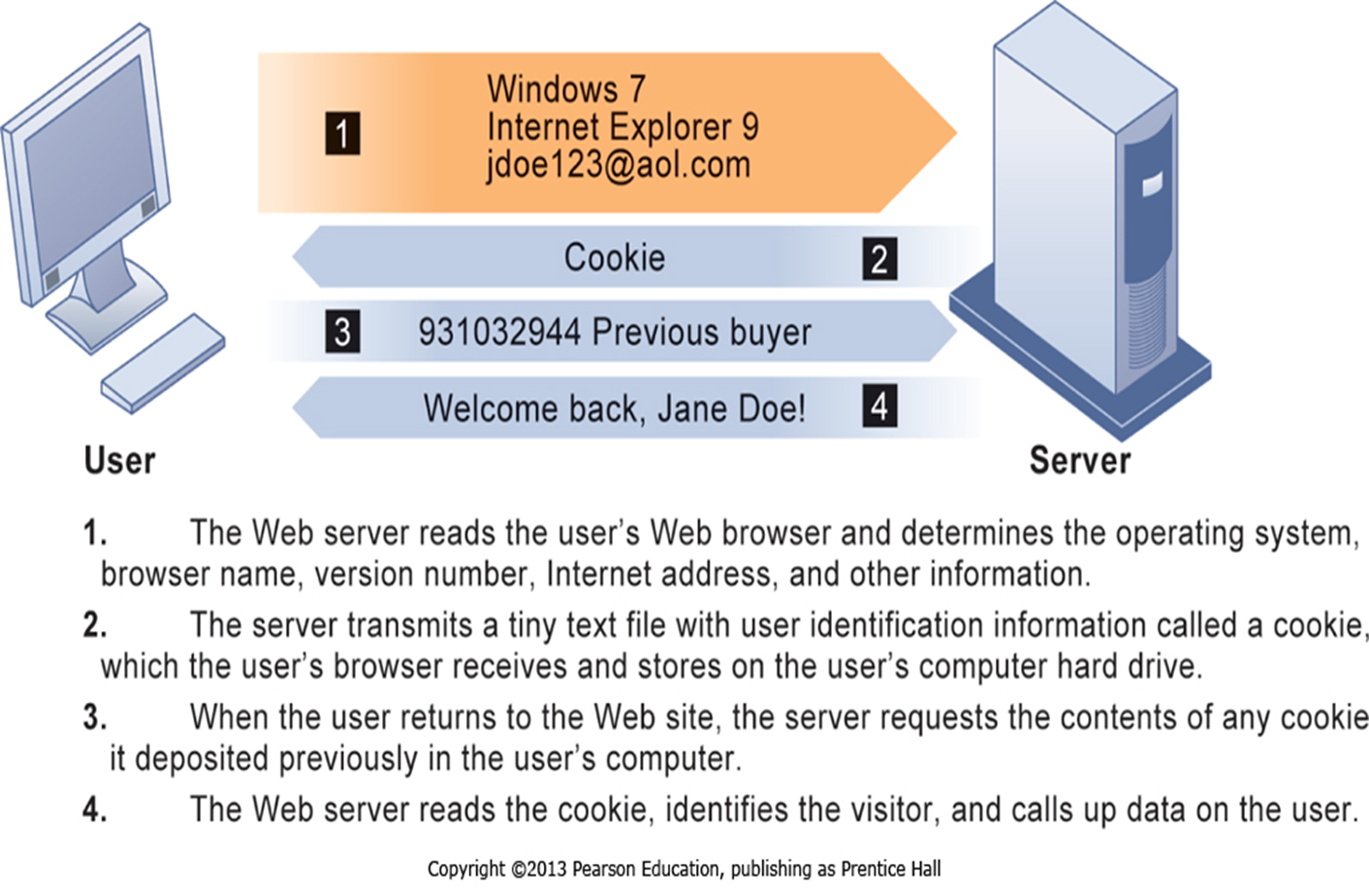
How Cookies identify web visitors
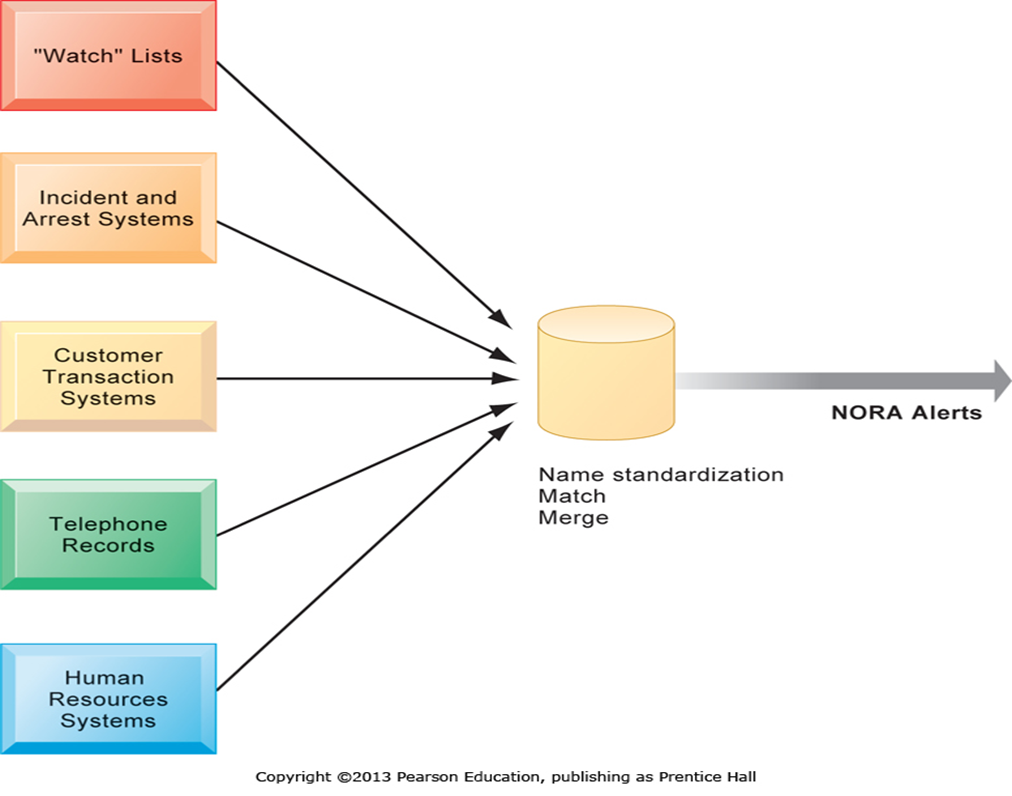
Nonobvious Relationship Awareness
Display ads, rich media ads, interstitials

Interactive Advertising Bureau, Cost-per-click, CPM, Cost-per-action, affiliate program

Zero-party data, first-party data, second-party data, third-party data
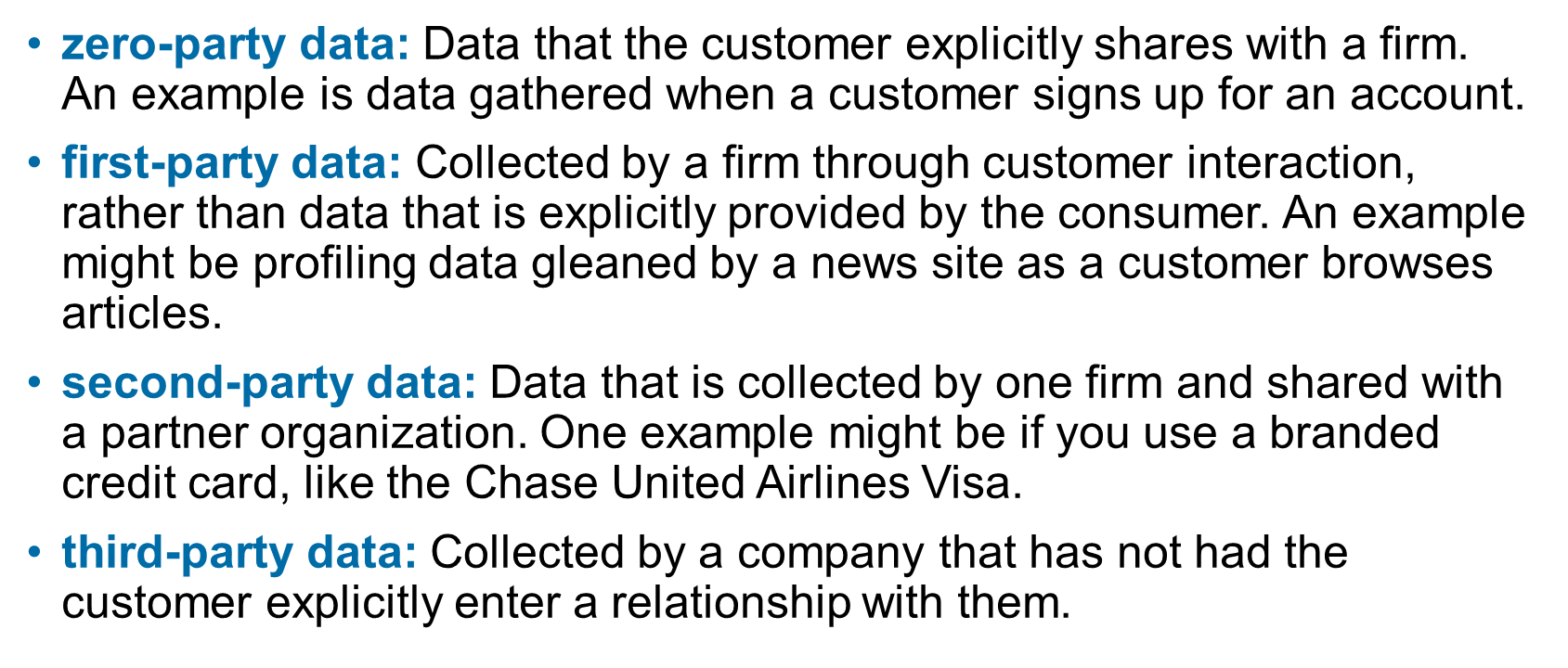
Cookie
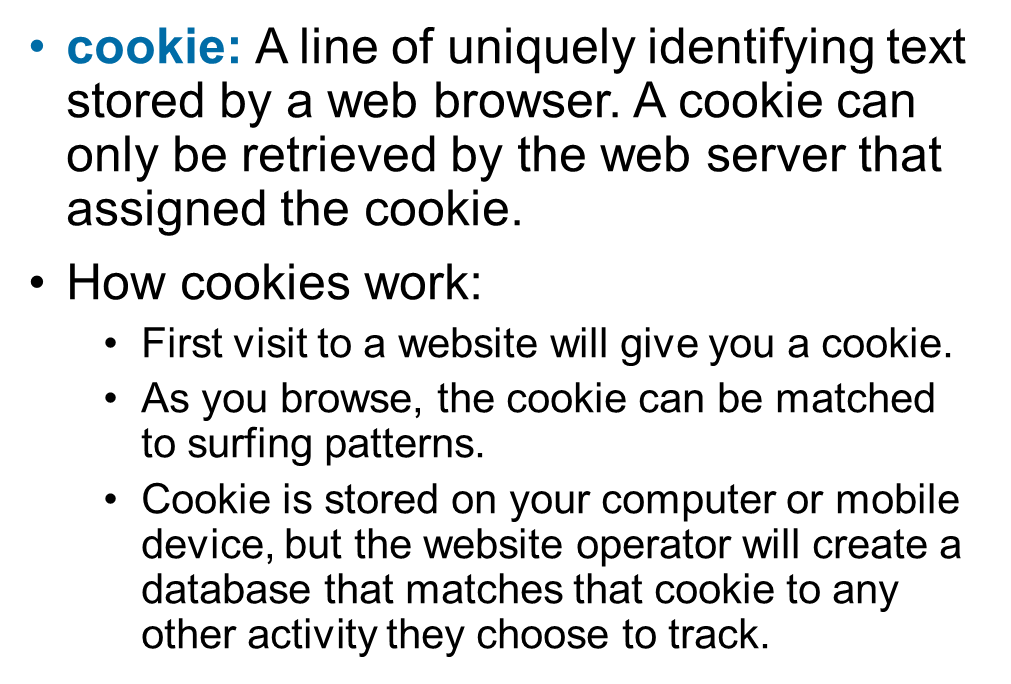
First party cookies vs third party cookies
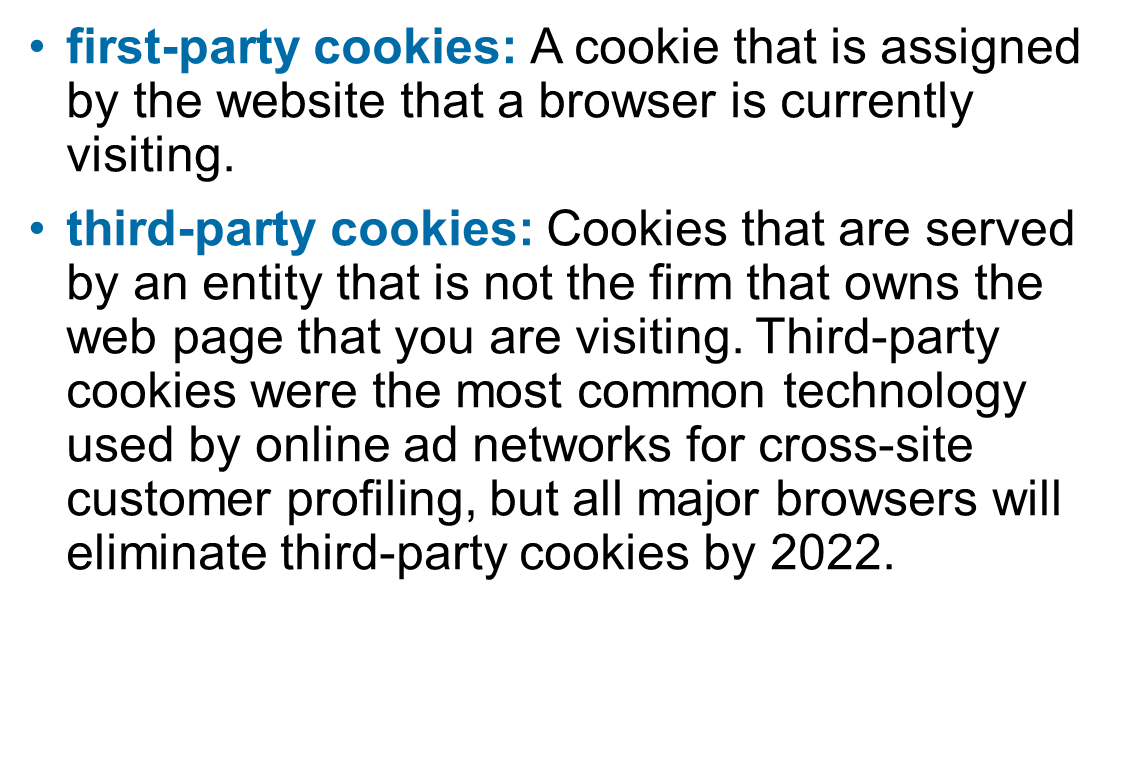
Tracking pixels and & retargeting

IDFA ATT

Tracking URL

Geotargeting, geofencing, IP Address, MAC address

Proxy servers, virtual private network (VPN)

GPS & Line-of-sight

ACR & DAI

Three normative theories of business ethics
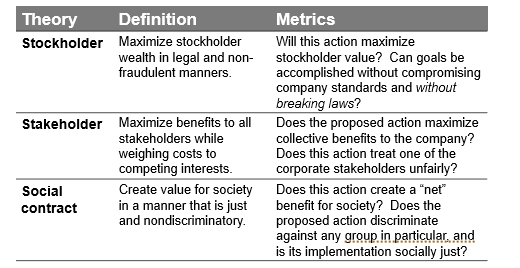
Factors that can amplify a firm vulnerability of a security beach
•Personnel issues
•Technology problems
•Procedural factors
•Operational issues
Constant vigilance regarding security needs to be
•Part of one’s individual skill set.
•A key component in an organization’s culture.
Data harvesters, cash-out fraudsters, botnets, distributed denial of service DDos attack

Ransomware Attacks

Cyberwarfare
•has also become an increasingly used tool among both spy agencies and military organizations, and the fallout can spread far beyond the borders of the nations in conflict.
Hacktivists
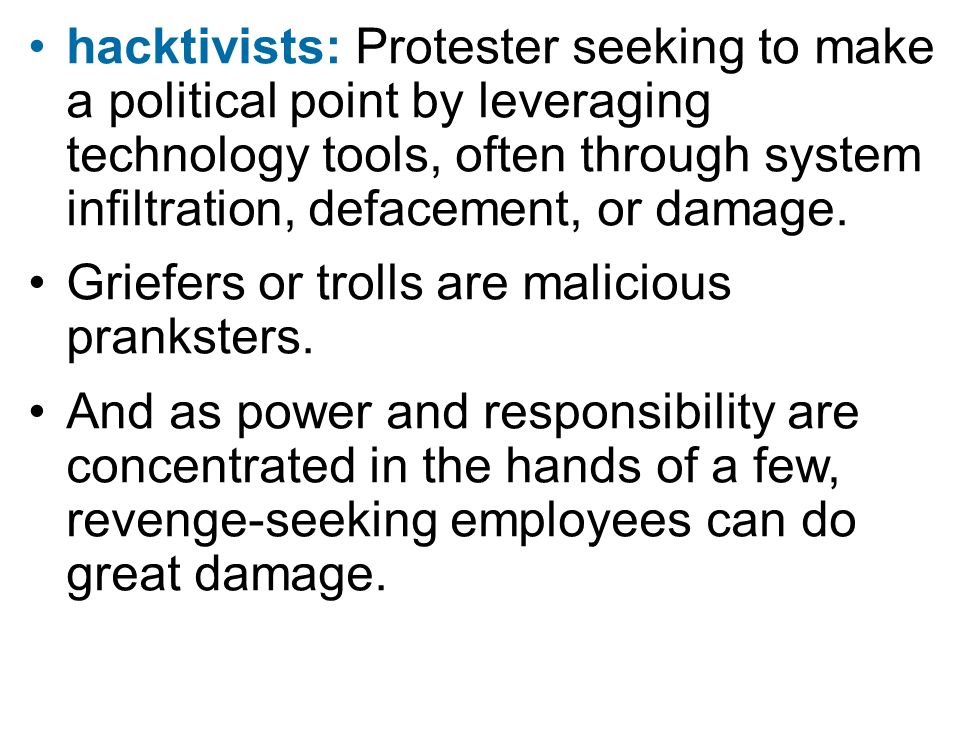
hacker, hack, white hat hackers, black hat hackers, red team, blue team
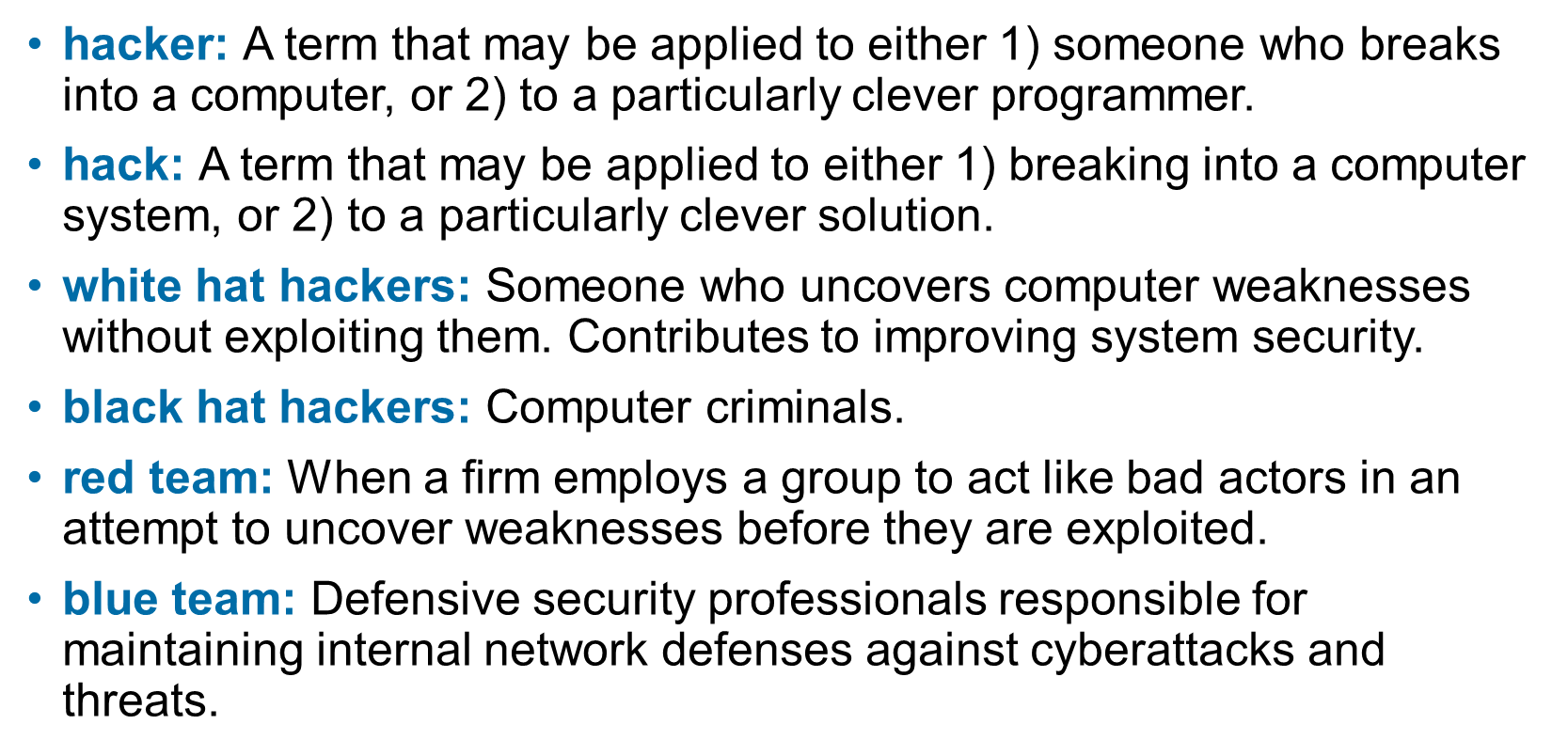
Bad apples, social engineering, phishing

Spoofed

Deepfakes, Script kiddies

How to build a better password:

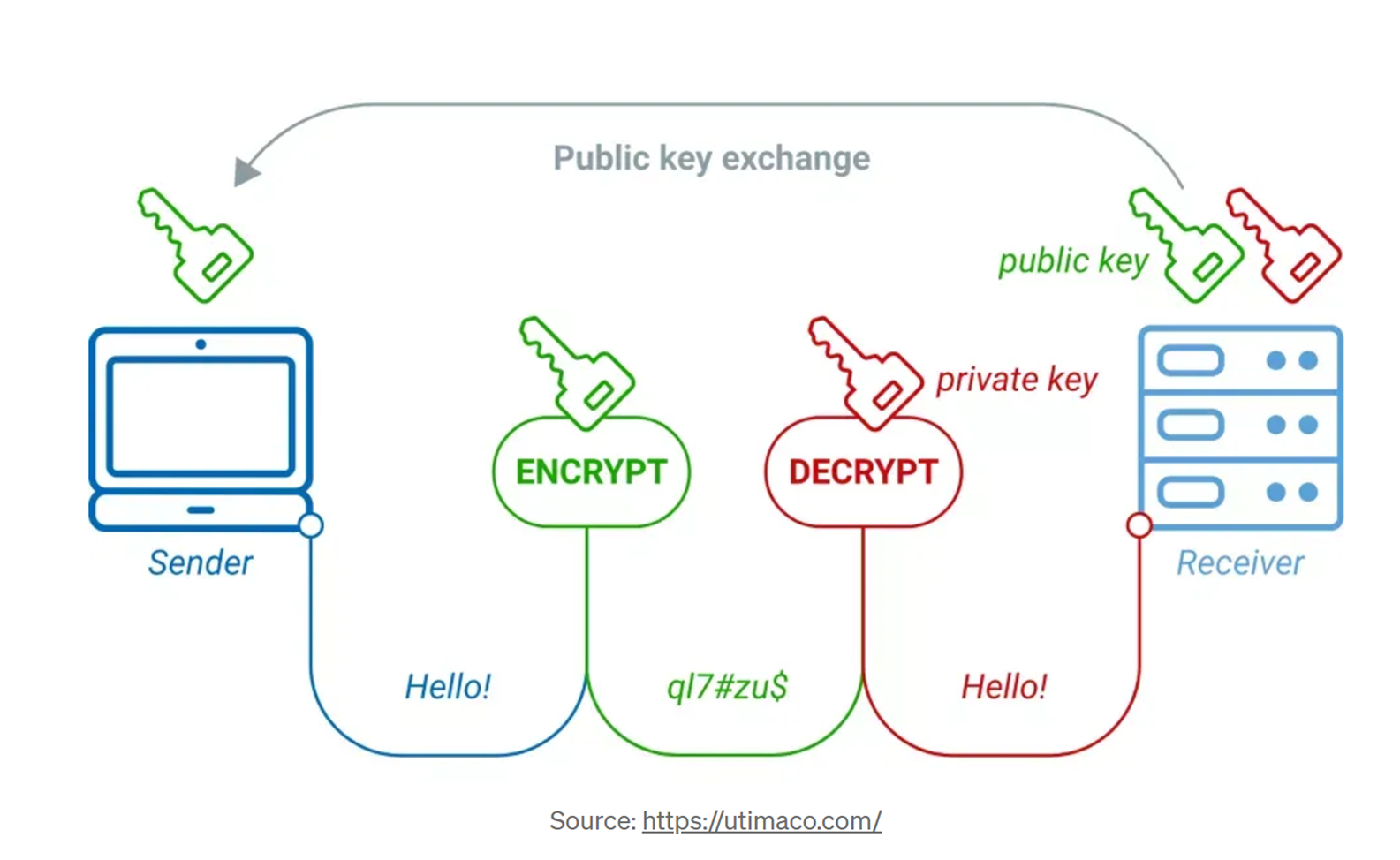
Public-key cryptography and drawbacks to passkey system
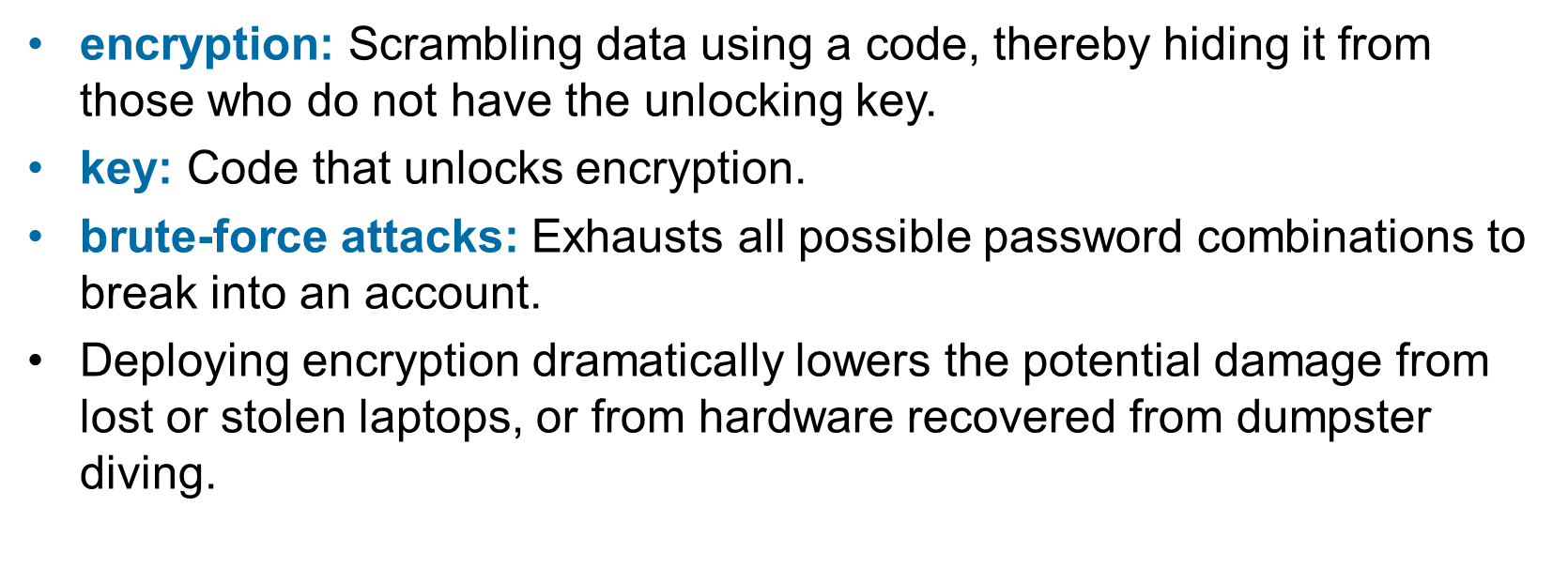
Malware and its goals
•Goals of malware (continued)
•Spyware: Monitors user actions, network traffic, or scans for files.
•Keylogger: Records user keystrokes.
•Screen capture: Records pixels that appear on a user’s screen to identify proprietary information.
•Card skimmer: Captures data from a card’s magnetic strip.
•RAM scraping or storage scanning software: Malicious code that scans for sensitive data.
•Ransomware: Malware that encrypts user’s files with demands that a user pay to regain control of their data and/or device.
•Blended threats: Attacks combining multiple malware or hacking exploits.

Physical hacking threats

Encryption, key, brute-force attacks
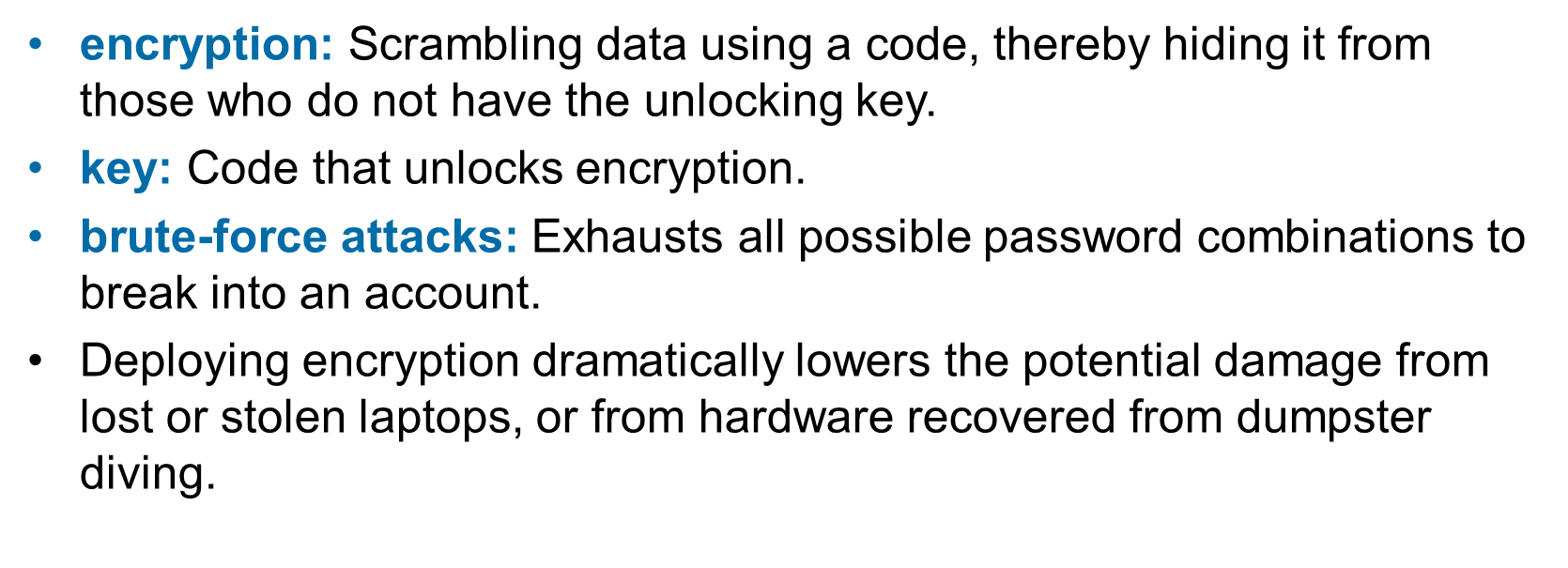
What needs to be protected and how much is enough?

Patches, Lockdown hardware, Lockdown networks

•blacklists: Deny the entry of specific IP addresses and other entities.
•whitelists: Permit communication only with approved entities or in an approved manner.