Chemistry Midterm Vocab
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Acid Base reaction
(also called neutralization reactions) generally form water and an ionic compound—called a salt—that usually remains dissolved in the solution.
Aqueous Solution
a substance is dissolved in water. When a substance dissolves in water, the mixture is called a solution.
Balanced Equation
represents a chemical reaction.
Combustion Reaction
Combustion reactions are a subcategory of oxidation–reduction reactions, in which electrons are transferred from one substance to another.
Complete ionic equation
show aqueous ionic compounds that normally dissociate in solution as they are actually present in solution.
Decomposition reaction
a complex substance decomposes to form simpler substances.
Double displacement reaction
two elements or groups of
elements in two different compounds exchange places to form two new compounds. can be precipitation reactions, acid–base reactions, and gas evolution reactions.
gas-evolution reaction
Reactions that occur in liquids and form a gas
insoluble
Does not dissolve in the liquid
molecular equation
a chemical equation showing the complete, neutral formulas for every compound in a reaction.
net ionic equation
whihc show only the species that actually participate in the reaction
neutralization reaction
Form water adn an ionic compound
oxidization-reduction (redox) reaction
Reactions involving the transfer of electrons
precipiate
The solid which forms after the two aqueous solutions are mixed.
precipiation reaction
when two aqueous solutions react and a solid is formed.
salt
ionic compound form in acid based reactions.
Single displacement reaction
one element displaces another in a compound.
solubility rules
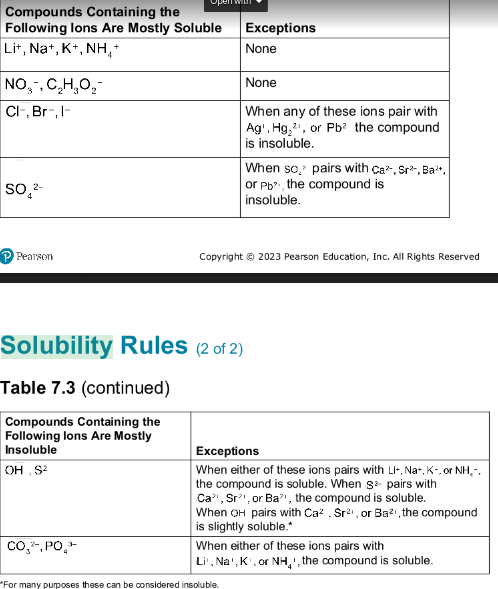
soluble
dissolves in that specific liquid
spectator ions
some of the ions in solution appear unchanged on both sides of the equation. These ions are called spectator ions because they do not participate in the reaction.
strong electrolyte solution
Substances (such as NaCl) that completely dissociate into ions in solution are called strong electrolytes.
synthesis (combination) Reaction
two simple substances combine to make a more complex substance.
Matter
Anything that occupies space and has mass and is made up of atoms. Ex. Water, Wood, Steel
atoms
submicroscopic particles that are fundamental building blocks of matter
molecules
2 or more atoms joined together in specific geometrical arrangements
Crystalline
Atoms or molecules arrange in geometric patterns with long range repeating order Ex. Salt and Diamond
amorphous
atoms or molecules do not have a long range order.
Liquid Matter
Free to move relative to one another
Molecules: Close together
Shape: Indefinite
Volume: Definite
Compressablity: Incompressible
Gaseous Matter
Free to move relative to one another
Molecules: Far apart
Shape: Indefinite
Volume: Indefinite
Compressablity: Compressible
Solid Matter
Oscillation/ vibration about fixed point
Molecules: Close together
Shape: Definite
Volume: Definite
Compressablity: Incompressible
Pure Substance
composed of only one kind of atoms or molecules
Mixtures
Composed of two or more kinds of atoms or molecules combined in variable proportions.
Element
A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substaces
Compound
A pure substance Composed of two or more elements in fixed definite proportions
Heterogenous Mixture
A mixture in which the composition is not uniform throughout
Homogenous Mixture
A mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout
Physical Property
Is one that a substance displays wtithout changing its composition
Chemical Property
Is one that a substance displays only through changing its composition
Physical Change
Matter changes its appearance but not its composition
Chemical Change
Matter does not change its composition
Reactants
the substances present before the chemical change
Products
The substances present after the chemical change
Law of Conservation of Mass
matter is neither created nor destroyed in an ordinary chemical reaction.
Chemical Reaction
the sum of the masses of the reactants will be equal to the sum of the masses of the products
Energy
Capacity to do work
The Law of Conservation of Energy
The law of conservation of energy states that energy is neither created nor destroyed, the total amount of energy is constant, and energy can be changed from one form to another.
Work
defined as the result of a force acting through a distance
Electrical Energy
Associated with the flow of electrical charge
Thermal Energy
associated with the random motions of atoms and molecules in matter
Chemical Energy
form of potential energy associated with the positions of the particles that compose the chemical system.
1 cal
4.184 joules
1 Cal
1000 calories
1 kWh
3.60 × 10 ^ 6 Joules
TNT Molecules
tend to go through rapid chemical changes that lower their potential energy making them explosive.
Exothermic
Energy is Released
Temperature of a substance
is a measure of the thermal energy of matter
Heat
which has units of energy, is the transfer or exchange of thermal energy caused by a temperature difference.
On the Farenheit Scale
Water freezes at 32 ºF.
Water boils at 212 ºF.
Room temperature is approximately 72 ºF.
On the Celcius Scale
Water freezes at 0 ºC.
Water boils at 100 ºC.
Room Temperature isapproximately 22 ºC.
Kelvin Scale
avoids negative temperatures
by assigning 0 K to the coldest temperature possible,
absolute zero.
Absolute zero is the temperature at which molecular
motion virtually stops.
Water freezes at 273 K.
Water boils at 373 K.
Room temperature is approximately 295 K.
K
C + 273.15
C
F - 32 / 1.8
Specific Heat Capacity
is the quantity of heat (usually in joules) required to change the temperature of 1 g of the substance by 1 C.
J / g C
C
specific Heat Capacity
ΔT
Temerature change =
Tf-Ti
Kinetic Energy
the energy associated with its
motion
Potential Energy
the energy
associated with its position or composition.
States of Matter
Liquid, Gas, Solid
Can energy be transferred between objects?
Yes
Can energy be created out of nothing or vanish into nothing
NO
Endothermic Reaction
Energy is Absorbed
Q
Heat
M
mass in grams
Leucippus and Democritus
theorized that matter was ultimately composed of small, indivisible particles. Democritus suggested that if you divided matter into smaller and smaller pieces, you would eventually end up with tiny, indestructible particles called atoms.
John Dalton
Each element is composed of tiny indestructible particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from the atoms of other elements. Atoms combine in simpler, whole number ratios to form compounds.
J. J Thompson
Discovered the electron and that they are negatively charged, that they are much smaller and lighter than atoms. His experiments proved that the indestructible atom can be chipped. Raised the question of balancing positive charge. At that time atoms were known as having neutral charge. Plum Pudding Model suggested negatively charged electron are held in a sphere of positive charge.
Ernest Rutherford
Tried to prove J.J Thompson model right but proved it wrong. Directed tiny, positively charged particles called alpha particles at an ultrathin sheet of gold foil. Alpha particles are about 7000 times more massive than electrons and carry a positive charge. These particles act like probes of the gold atoms structure. The results showed that most particles passed through but some deflected and some bounced back.
Nuclear Theory of the atom
Most of the atom’s mass and all of its positive charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus. Most of the volume of the atom is empty space through which the tiny negatively charged electrons are dispersed. There are many charged electrons outside the nucleus as there are positively charged particles indie the nucleus, so that the atoms is electrically neutral.
Electrical charge
fundamental property of protons and electrons just as mass is a fundamental property of matter. Positive and negative electrical charges attract each other. Positive and positive and negative and negative charges repel each other. Positive and negative charges cancel each other when paired the charge is neutral.
Atomic Number
the number of protons in the nucleus
Periodic law
When the elements are arranged in order of increasing relative mass, certain sets of properties recur periodically. Mendeleev organised all the known elements in a table in which relative mass increased from left to right and elements with similar properties were aligned in the same vertical columns. Mendeleev left gaps for elements that weren’t discovered yet.
Periodic Table
elements are listed in increasing atomic number and mass
German chemist Clemens Winkler
discovered element called eka-silicon
Metals
occupy the left side of the periodic table and have similar properties: they are good conductord of electricity and heat. Malleable, ductile, often chiny and they tend to lose electrons when they go through chemical changes.
Non metals
occupy the right side of the periodic table and poor conductors of heat and electricity and they gain electrons when they go through chemical changes.
metalloids
semi conductos because of their intermediate electrical conductivity can be changed or controlled.
Noble Gases
chemically inert gases
Alkali metals
very reactive metals
Alkaliine Metlas
fairly reactive
halogens
very reactive non-metals
ions
atoms often lose or gain electrons that create charged particales.
ion charge formula
ion charge = # protons - # electrons
cations
postively charged ions
anions
negatively charged ions
valence electrons
outermost electrons in an atom
Isotopes
atoms with thename number of protons ut different numbers of neutrons. Writing: A / z X or X - A
atomic number (z) mass number (A) chemical symbol (X) and #n = Z - A
Percent natural abudance
percents in isotopes
mass number (A)
number of protons + number of neutrons
Atomic Mass
Percent tunred into decimal times number + percent turned into decimal times number = # amu
chemical formula
indicates the elements present in the compound and the relative number of atoms of each element.