Welfare, Consumer and Producer Surplus
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is welfare?
Welfare is the overall wellbeing and happiness of people. Economics primarily investigates how it can be achived through material goods and services.
What is:
Marginal Benefit?
Marginal Social Benefit?
Marginal Social Benefit Curve?
Marginal Benefit - The utility one gains from the additional consumption of a good. (the value of one more unit of good or service)
Marginal Social Benefit - The utility society gains from the adittional consumption of a good.
Marginal Social Benefit Curve = Demand curve
What is consumer surplus?
The value that consumers gain from consuming good and service over and above the price paid.
The difference between the price consumers are willing and able to pay and the price they actually paid for the good or service.
Consumer surplus is the welfare gained by the society by consuming the product, over and above the price they paid.
Where on a graph can we read the consumer surplus?
The area underneath the demand curve and over the price, bounded by the quantity demanded.
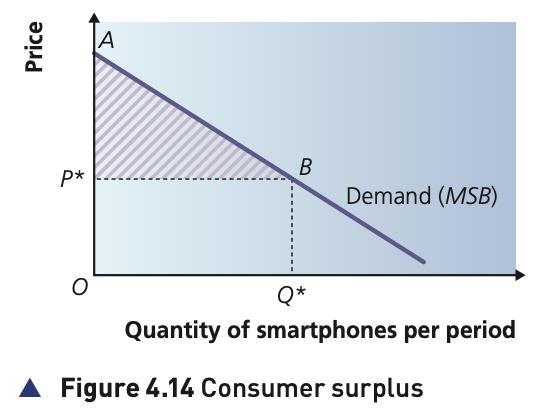
What happens to consumer surplus when price:
Increases?
Decreases?
Price Increases - CS decreases, less people will be able to buy the good with extra welfare
Price Decreases - CS increases, more people will be able to buy with extra welfare
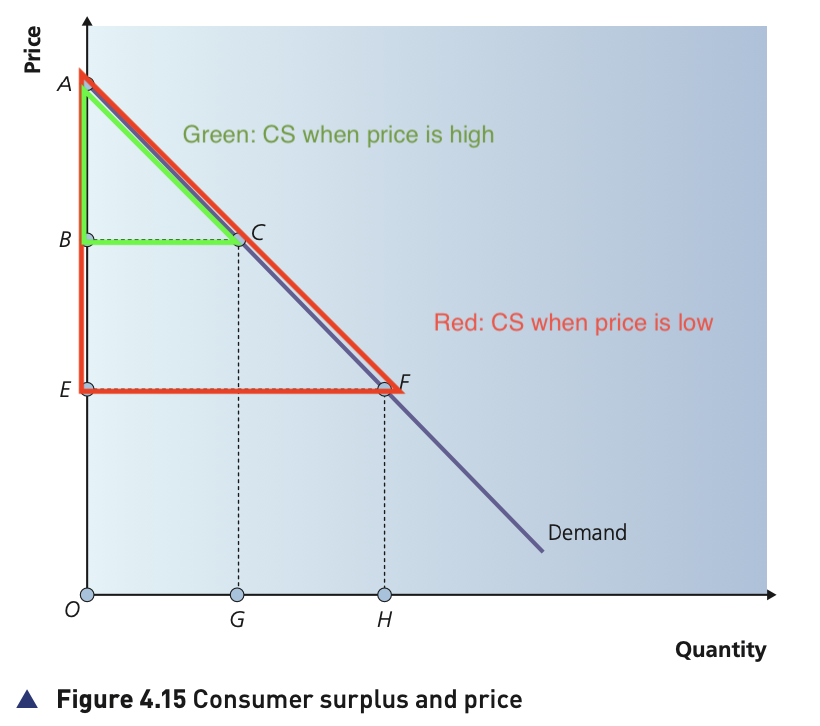
What is producer surplus?
The difference between the price producers actually recieve and the price they were originally willing and able to sell of a good or service.
PS represents the benefit gained by firms over and above the price at which they would have been prepared to supply a product.
What is:
Marginal cost?
Marginal Social Cost?
Marginal Social Cost Curve?
Marginal cost it the additional cost required to make one more of a good or service. It is the minimum price producers must recive to be willing and able to recieve one more of the good. A profitability threshold.
Aggregate of all the MC of producers is MSC
Marginal Social Cost Curve = supply curve
What is society surplus?
Total surplus enjoyed by producers and consumers (Also consider the Government. Tax revenue is added to the surplus and subsidies and deducted.
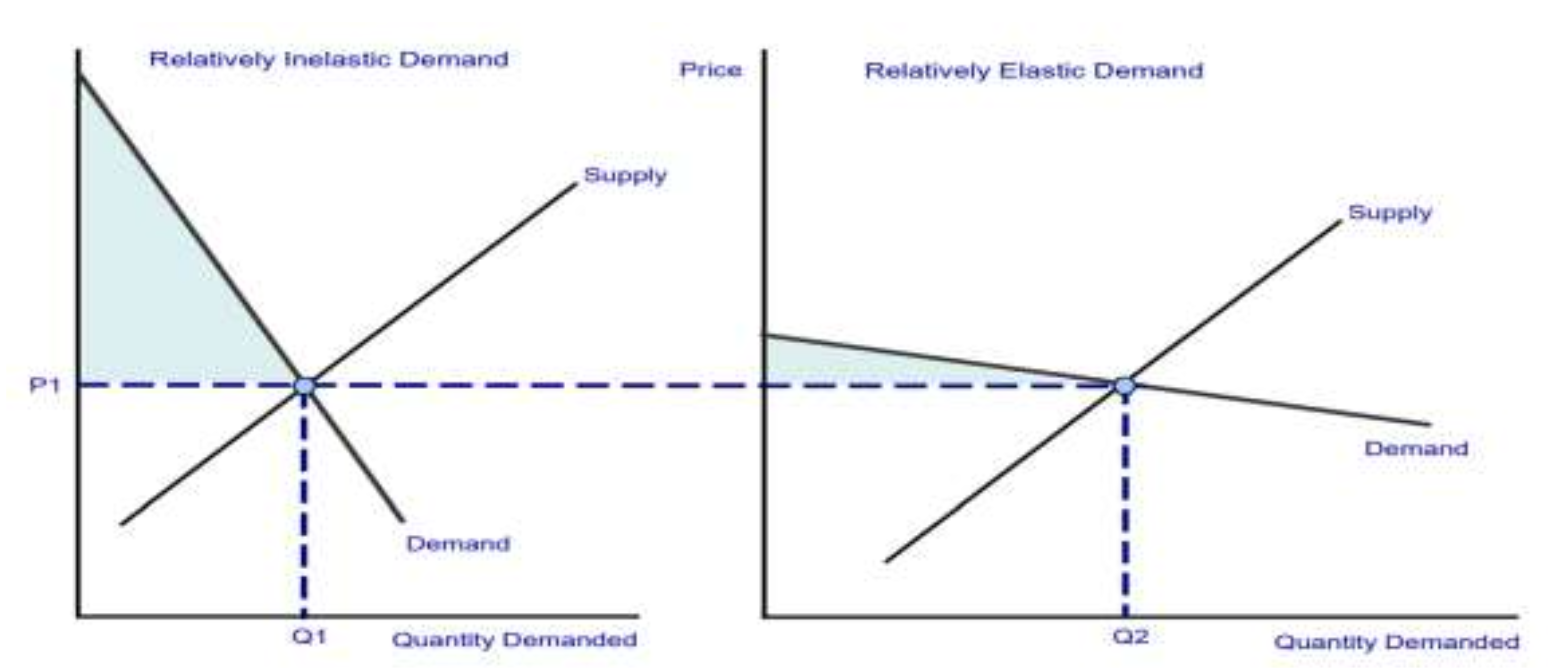
What is the relationship between PED and consumer surplus?
If the PED is generally inelastic, CS is larger.
If PED is generally elastic, CS is smaller
What is the relationship between PES and producer surplus?
If PES is generally inelastic, the producer surplus is larger
If PES is generally elastic, the PS is smaller
How do changes in demand affect the entry and exit of firms into a market?
If demand increases, equilibrium price increases, and PS increases. Firms will be attracted to enter this market, which increase supply. Equilibrium price will fall back down.
If demand decreases, equilibrium price decreases, and PS decreases. Firms will be attracted to exit this market and look for profits elsewhere , which decrease supply. Equilibrium price will climb back up.
What is a deadweight loss?
A fall in total surplus due to market distortions. Also known as allocative inefficiency or excess burden.