Chemistry- Periodicity 🟢
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
How are elements classified
In s, p, or d block, according to which orbitals the highest energy electrons are in
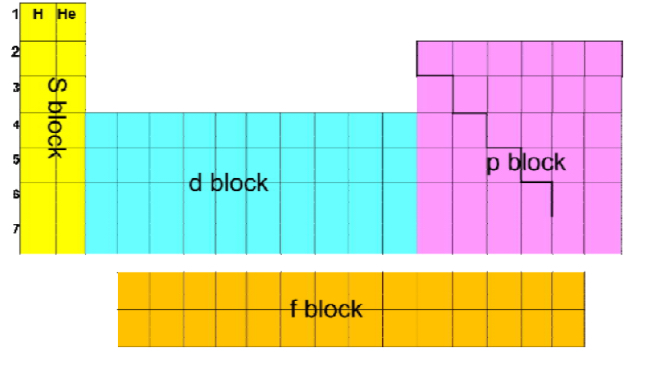
Which is period 2 and 3
Period 2- row beginning with Li
Period 3- row beginning with Na
Describe and explain the trend in atomic radius across a period
Decreases
Nuclear charge increases across the period
Shielding is similar as the no of energy levels is the same
The attraction between the nucleus and outer shell is increasing therefore attracting it closer
Describe and explain the trend in first ionisation energy
general increase across the period
Nuclear charge is increasing
Shielding remains similar
Atomic radius is decreasing
Therefore the electron is more strongly atttracted to the nucleus
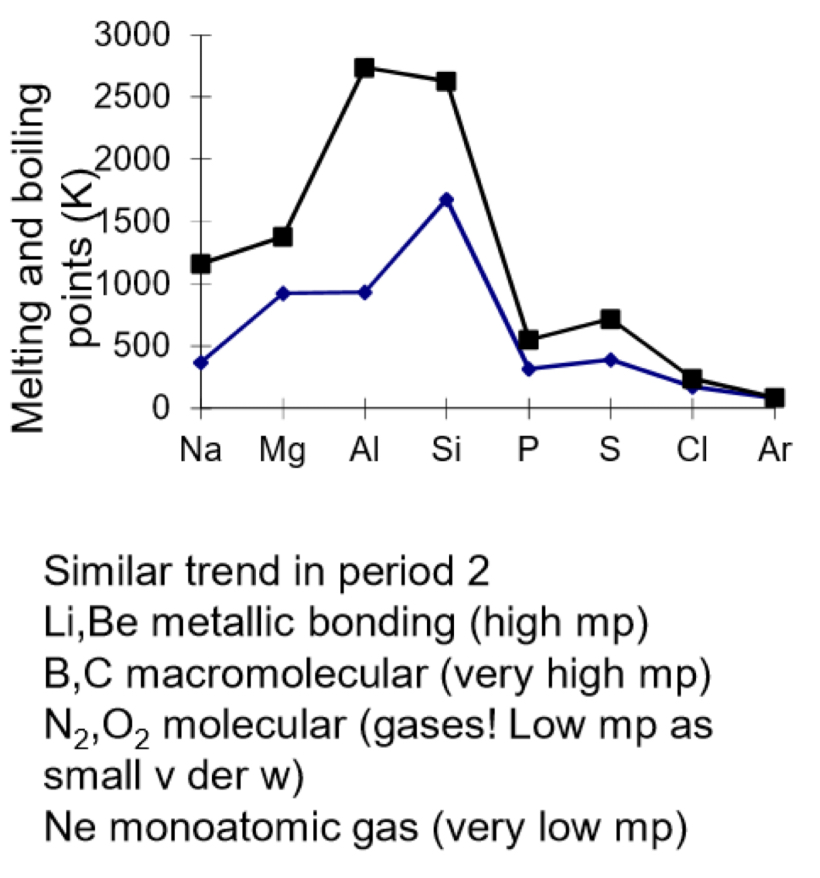
Trend in melting and boiling points across period 3 and period 2
Na to Al- metallic bonding- number of delocalised electrons increases per atom increases & ionic radius decreases increasing nuclear charge and increasing charge density
Sillicon- macromolecular- strong covalent bonds between atoms which require a lot of energy to overcome
P to Cl- simple molecular: weak vdw forces between molecules so little energy is needed to break them- low mp and bp
Sulfur (S8) has a higher melting pointt than phosphorus (P4) as it has more electrons so has stronger vdw forces between molecules
Ar is monoatomic- weak vdw forces between atoms