Set 1: Cells, Cell Division, Cancer, Stem Cells
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are the 3 main purposes of cell division?
Growth, repair/replacement of damaged cells, and reproduction.
What is the cell cycle?
The sequence of events that a cell goes through to grow, prepare for division, and divide into two daughter cells.
What are the 3 main parts of interphase and their functions?
G1: Cell grows and carries out normal functions.
S: DNA is copied (synthesis).
G2: Cell prepares for division (organelles duplicated).
What does IPMAT stand for in mitosis?
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase.
What happens in Prophase?
Chromosomes condense, spindle fibers form, nuclear membrane begins to break down.
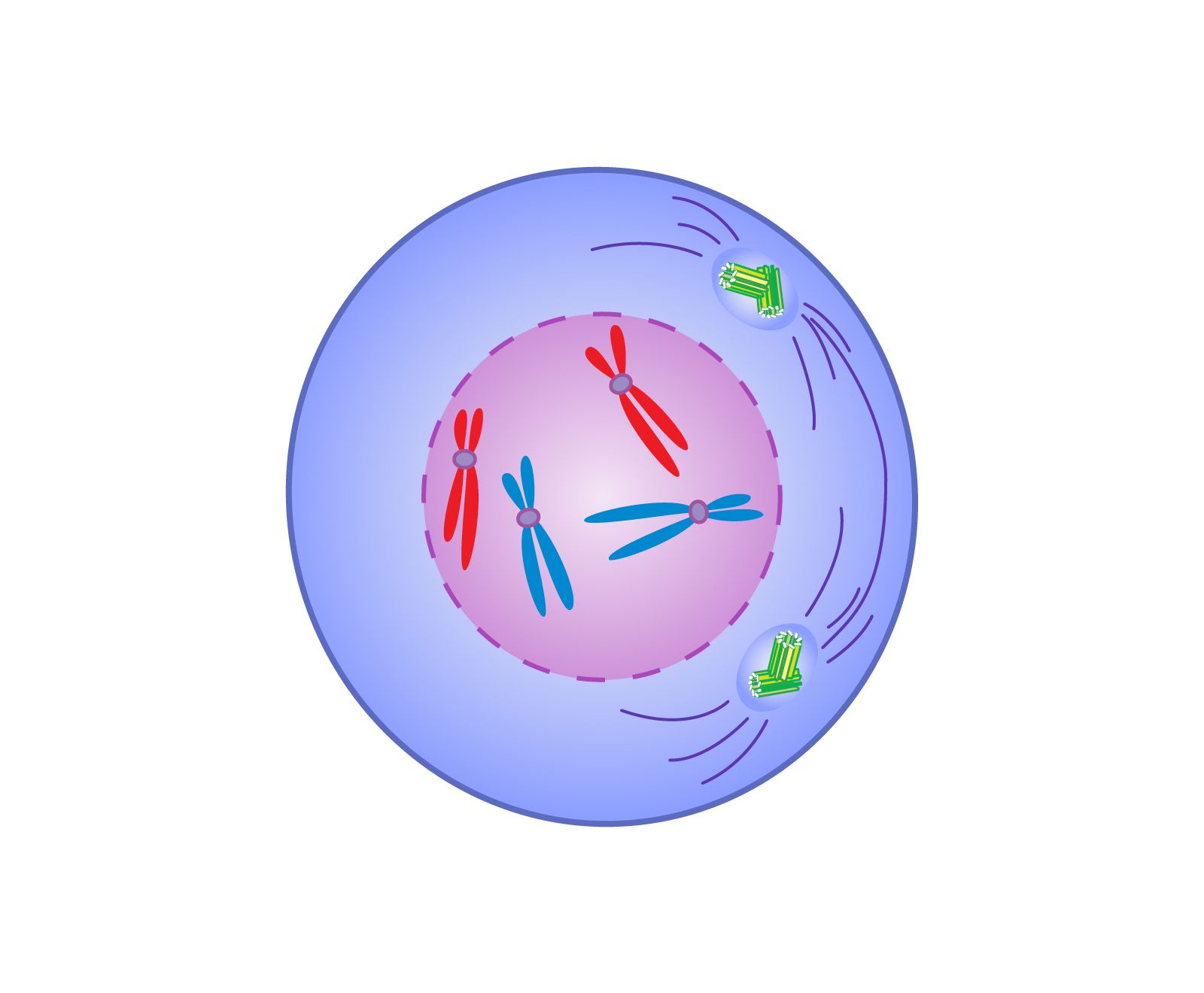
What happens in Metaphase?
Chromosomes line up along the middle (equator) of the cell.
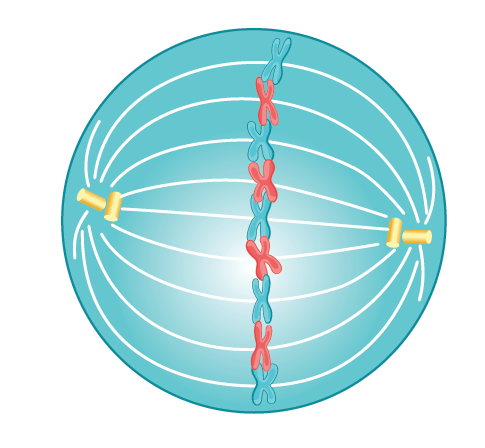
What happens in Anaphase?
Sister chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite sides of the cell.
What happens in Telophase?
Nuclear membranes reform around chromosomes, spindle fibers disappear, chromosomes uncoil.
What is cytokinesis?
Division of the cytoplasm, forming two identical daughter cells.
What is apoptosis?
Programmed cell death, removing damaged or unnecessary cells.
How can uncontrolled cell division cause cancer?
Mutations disrupt the cell cycle, leading to uncontrolled division and formation of tumors.
Define benign tumor.
A non-cancerous tumor that does not spread.
Define malignant tumor.
A cancerous tumor that can invade surrounding tissues.
What does metastasis mean?
The spread of cancer cells from the original site to other parts of the body.
What is a carcinogen? Give examples..
A substance that can cause cancer. Examples: tobacco smoke, radiation, UV light, asbestos, certain chemicals.
What lifestyle choices can increase cancer risk?
Smoking, poor diet, lack of exercise, excessive sun exposure, alcohol use.
What is a zygote?
A fertilized egg formed when sperm and egg combine.
What is a stem cell?
An unspecialized cell that can divide and develop into specialized cell types.
What is cellular differentiation?
The process by which stem cells become specialized cells with specific functions.
What is the difference between embryonic and tissue stem cells?
Embryonic stem cells: can become any cell type in the body.
Tissue (adult) stem cells: limited to producing certain types of cells (e.g., blood stem cells → blood cells).
Which body parts can regenerate? Which cannot?
Skin and blood can regenerate well; nerves, heart muscle, and brain tissue cannot easily regenerate.
What are two ethical issues with stem cell research?
Use of human embryos in research, and concerns about cloning or genetic manipulation.