urinalysis 2.5
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
which elements are birefringent?
uric acid, calcium oxalate, triple phosphate, fatty casts, oval fat bodies,
if glucose +, or the patient has diabetes mellitis or vaginal moniliasis look for what?
yeast
what condition do you see renal tubular epithelial cells?
tubular injury: heavy metal exposure, drug-induced toxicity, viral infections, pyelonephritis, malignancy
hematuria, menstrual contamination
what condition do you see increased cuboidal cells?
renal transplant rejection, acute tubular necrosis (diuretic), injuries interrupting kidney blood flow, acute glomerulonephritis with tubular damage
drug ingestion causing significant shedding
salicylate intoxication
what conditions do you see increased cast formation?
acidic pH, increased solute concentration, urinary stasis, increased plasma protein
what conditions do you see the Tamm-Horsfall protein?
stress and exercise, underlying renal condition
in which conditions do you see hyaline casts?
CHF, in renal disease
in which condition do you see coarsely granular casts?
urinary stasis, glomerular and tubular disease
in which condition do you see finely granular casts?
amyloid disease, Chronic renal disease
in which condition do you see waxy casts?
blocked nephron, chronic renal failure, acute/chronic renal rejection, LAST stage of cast degeneration
in which condition do you see unusual broad waxy casts?
ESRD
in which condition do you broad casts?
extreme urine can’t leave collecting ducts
in which condition do you see fatty casts?
nephrotic syndrome, severe crush injuries, toxic tubular necrosis, diabetes mellitis, degenerative tubular disease, heavy proteinuria
in which condition do you see cylindroids?
similar to DCT casts
in which condition do you see cellular casts- RBC?
nephron bleeding, glomerulus damage (glomerulonpehritis), strenuous exercise
in which condition do you see cellular casts- WBC?
infection/inflammation of the nephron
pyelonpehritis, acutei nterstitial nephritis
in which condition do you see WBCs in urine?
pyuria (pus in urine), UTI
in which condition do you see cellular casts- RTE casts?
tubular damage: heavy metal, chemical, drug-induced toxicity, viral infection, graft rejection
in which conditions do you see oval fat bodies?
nephrotic syndrome, preeclampsia, DM
which conditions do you see uric acid in urine?
increased purine metabolism, chemotherapy (cell turnover), gout
which conditions do you see calcium oxalate in urine?
eating foods with oxalic acid (tomatoes, asparagus)
oval shape with ethylene glycol poisoning
renal calculi (kidney stones)
discrepancy in + RBC strip but none on the microscope?
cell lysis- hypotonic/alkaline urine
Hgb or myoglobin presence
strong oxidizing agents (bleach, peroxide)
discrepancy in = RBC strip but they’re present on the microscope?
mis ID RBCs, measurement is below strip sensitivity, ascorbic acid, high SG crenating the cells, unmixed specimen for strip analysis
discrepancy in + strip leukocyte esterase and no WBCs on microscope
cell lysis
discrepancy in = strip leukocyte esterase and WBCs on microscope
misID WBCs, lymphs, etc don’t contain LE
6 steps to prepare urine specimen
mix well
12mL into urine centrifuge
centrifuge 5 min at 2000RPM
consistent speed and time
pour off supernatant (except last 0.5-1mL)
resuspend sediment
which substances are an ultra filtrate of plasma?
CSF, interstitial fluid?, glomerular filtrate?
purpose of 2% acetic acid stain
removes interfering RBCs (lysis), enhances nuclei of WBC and epis
purpose of Sternheimer-Malbin stain
delineates structure and contrasting color of nucleus and cytoplasm. used to ID WBC, epithelials, and casts
purpose of toluidine blue stain
nuclear structure differentiation
WBC vs renal epi cells
purpose of sudan III or oil red O lipid stains
stains triglycerides and neutral fats orange-red to ID lipid containing cells
purpose of gram stain
bacteria gram rxn
purpose of hansel stain
methylene blue and eosin stain, stains eosinophilic granule to ID eosinophils
purpose of prussian blue stain
stains iron granules blue, hemosiderin granules are yellow until stained
purpose of brightfield microscope
parafocal objectives to maintain focus on object, subdued light to see structures better
purpose of phase-contrast microscope
ID translucent elements like casts
purpose of polarized light microscopes
ID crystals and lipids
acetic acid helps identify what?
nuclei of WBC and epi
yeast won’t dissolve in acetic acid
what’s the significance of ghost cells?
alkaline urine causes RBCs to lyse, so they appear “ghosty”
where are collecting tubule cells formed? sloughed off?
convoluted tubule (proximal, distal)
where is the squamous epithelial cell found? sloughed off?
lines the entire female urethra and distal portiion of urethra in males
can easily contaminate urine specimen
where is transitional epi cell found? slughed off?
bladder, ureters, renal pelvis
where is renal tubular epi cell found? slughed off?
each renal tubule has this
present in vascular injury
significance of Tamm-Horsfall protein
aka uromodulin
it’s ALWAYS abnormal
could be a cellular cast containing RBC, WBC, RTE, or a mix of cells
homogenous casts
hyaline and waxy
pigmented casts
bilirubin (brown/yellow), hemoglobin (pink), myoglobin
size of casts
broad (broad and waxy go together)
which part of the urinary tract are casts formed?
i may need a more specific answer
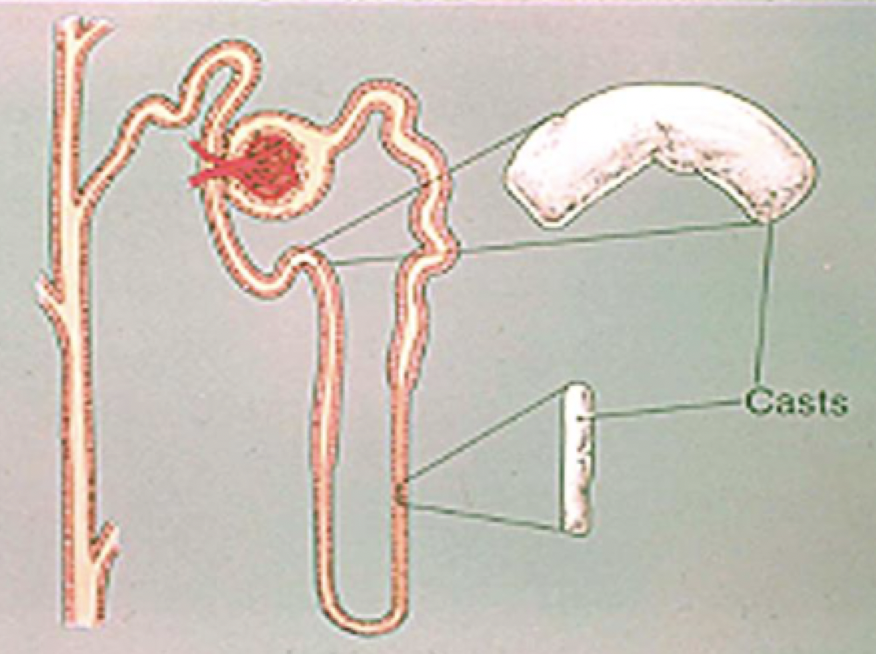
which crystals can be seen in alkaline urine?
calcium oxalate
amorphous phosphate
triple phosphate
ammonium biurate
calcium carbonate
which crystals are formed in acidic urine?
amorphous urate
uric acid
calcium oxalate
how to differentiate uric acid crystals from cystine?
cystine is nonpolarizing
uric acid is birefringent
what condition do you see amorphous urate in urine?
uroerythrin on crystal surface
what condition do you see ammonium biurate in urine?
neutral urine
****when looking at alot of crystals, amorphous material, or cells, how do you clarify urine sediments?
by centrifuging, pouring off supernatant, and then resuspending the sediment?
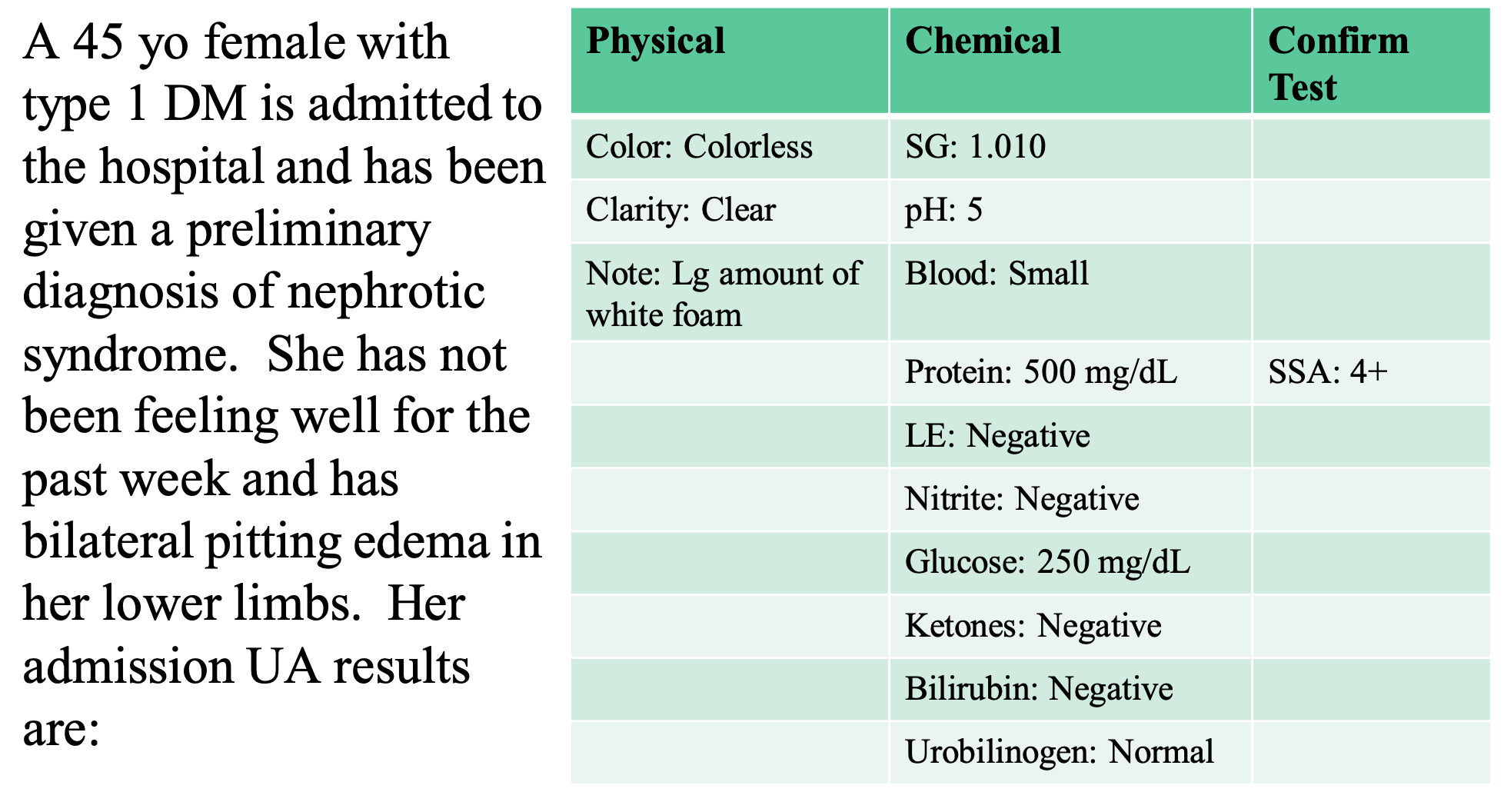
SSA used for the protein; it’s clear, and then adding equal parts
nephrotic syndrome explains the blood
the foam that doesn’t go away indicates a protein
glucose levels are 1+ or 2+
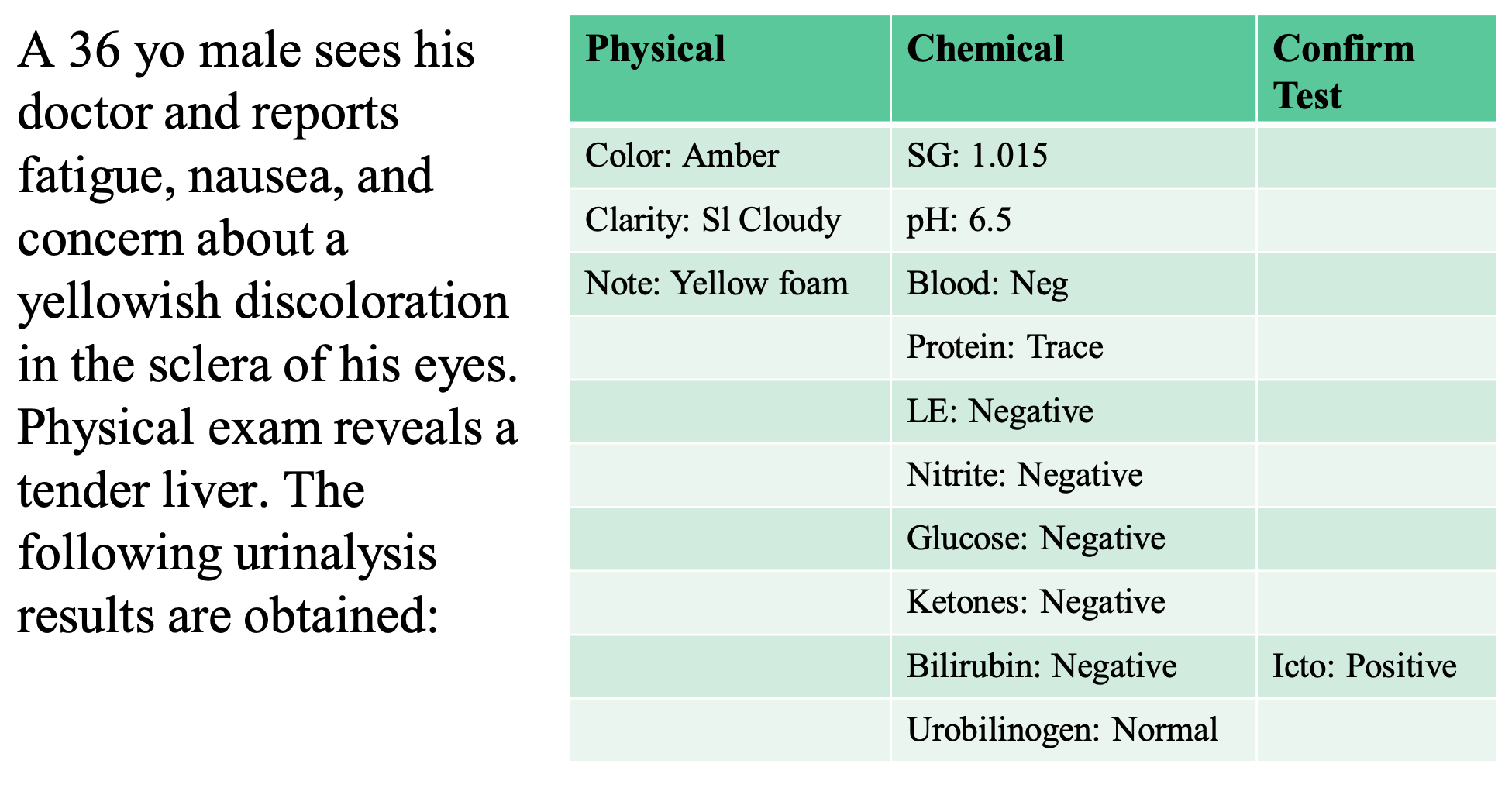
confirmatory tests are used to settle discrepancy
yellow foam indicates jaundice
bilirubin is discrepant
positive Icto is more sensitive to Bilirubin, so you report a positive Bilirubin
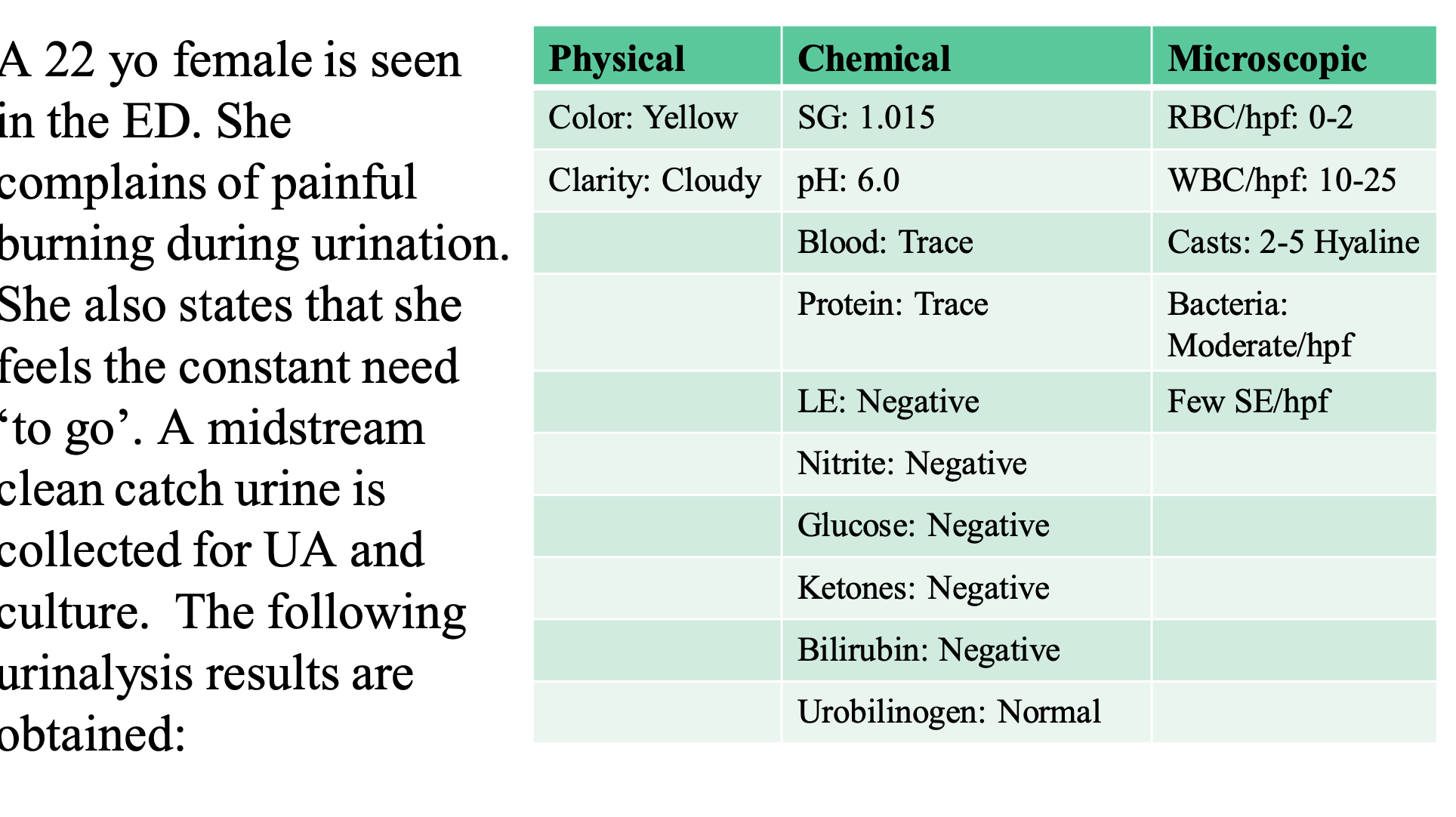
trace of blood goes with RBC levels
cloudy is cloudy and white cells are seen, so there is a descrepancy in the LE test
there’s some type of interfering substance
G+ doesn’t reduce the nitrates, 4 hrs?
there are more hyaline casts than usual
which stain is helpful for fats?
lipid stains: Oil Red O and Sudan III
used to identify neutral fats
what’s the significance of fat in your urine? (4 clinical applications)
it polarizes with the maltese cross
it’s seen in nephrotic syndrome, severe crush injuries, toxic tubular necrosis, and DM
why is sperm in urine significant?
should always be reported when seen
which contaminant looks like oval fat bodies?
lubricants, creams, and lotions
significance of hemosiderin granules
macrophages contain these large brown/black granules ~48 hrs after a hemorrhage
erythrophagia occurs, where the macrophage eats the RBC
glitter cells
neutrophils exposed to hypotonic urine → they absorb water and swell
you get cytoplasm brownian movement
but it has no pathological significance
clue cells indicate what?
some type of bacterial vaginosis
>20%
also no/few WBCs
Trichomonas vaginalis
a flagellated protozoan (single-celled) parasite of the urogenital tract. The cells are motile, have 4 flagella and a single nucleus.
Attach to mucosal and cause tissue damage
‘Jerky’ motion can be seen on wet prep
Specimen should be at RT and viewed within 2 hours to ensure motility
major functions of CSF
protects underlying CNS tissue
mechanical buffer to: prevent trauma, regulate pressure, circulate nutrients, remove CNS waste, lubricate CNS
expected CSF volume in adult
90-150mL
CSF normal appearance and composition
ultrafiltrate of plasma and active secretion of transport
how to store CSF?
room temp to preserve analytes/formed elements
should be a STAT specimen
if CSF volume is small, send first sample to _______. Other than that, the order is:
micro department
Chem and immunology
Micro
Hematology
Cytology
which CSF tube do you centrifuge and why?
micro tubes
15 min at 1500g to recover bacteria
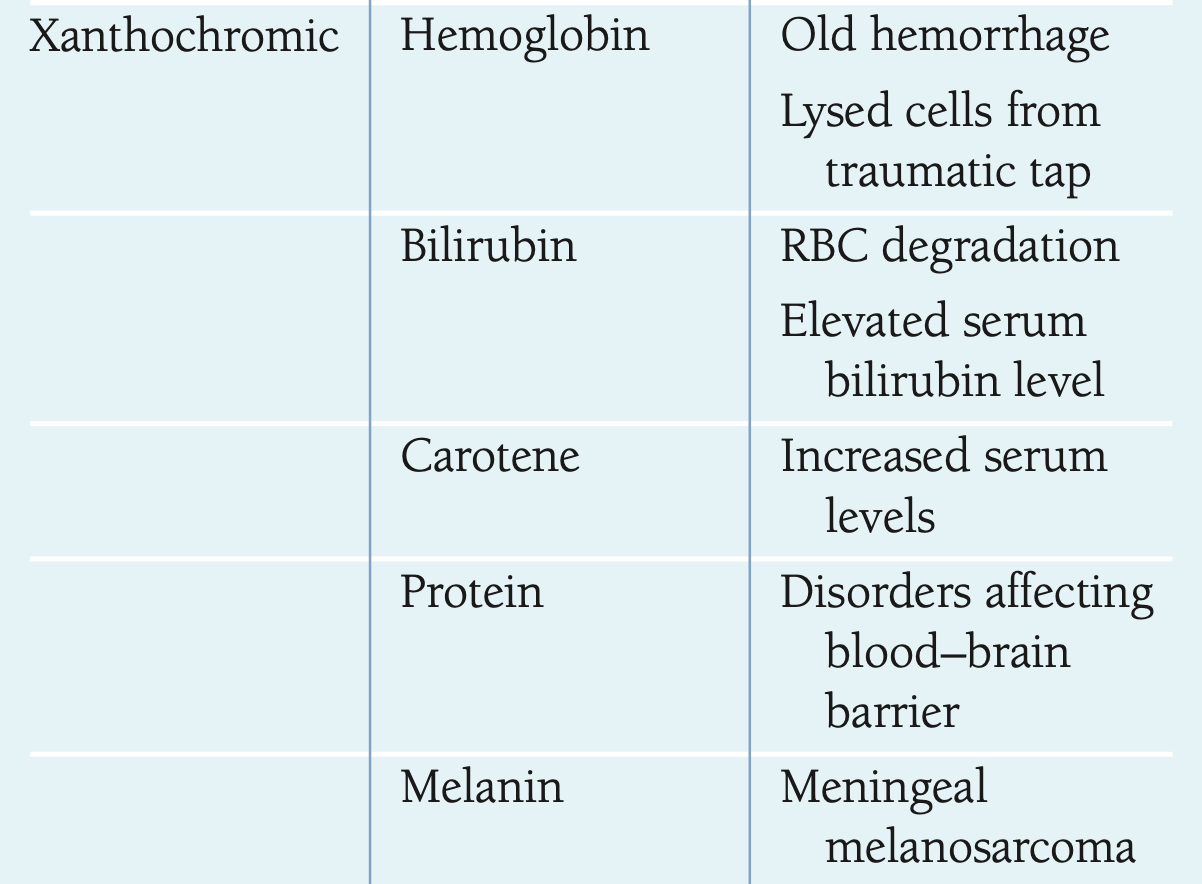
what causes xanthachromic CSF?
how to do Neubauer chamber CSF values
count all 9 squares
manual counts

chemical components of CSF
80% protein: transthyretin (prealbumin) albumin, transferrin, some IgG
20% intrathecal synthesis
60% glucose
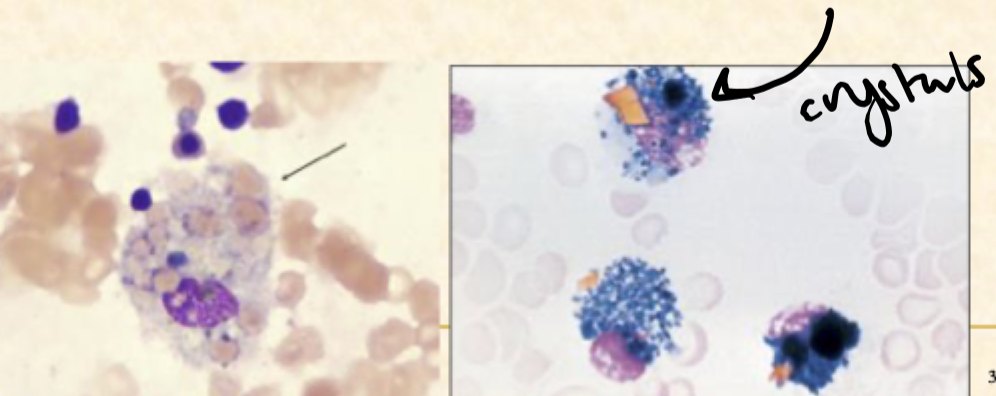
how are CSF macrophages clinically significant?
during erythrophagia, the macrophage eats the RBC in a hemorrhage
the macrophages have large brown/black hemosiderin granules that are present around 48 hours after the hemorrhage
normal CSF differential cell counts (adult and baby)
lymph
mono
neutrophil

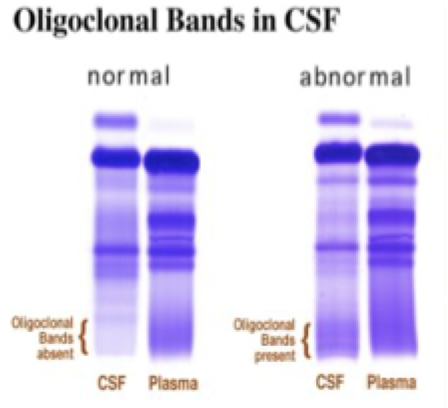
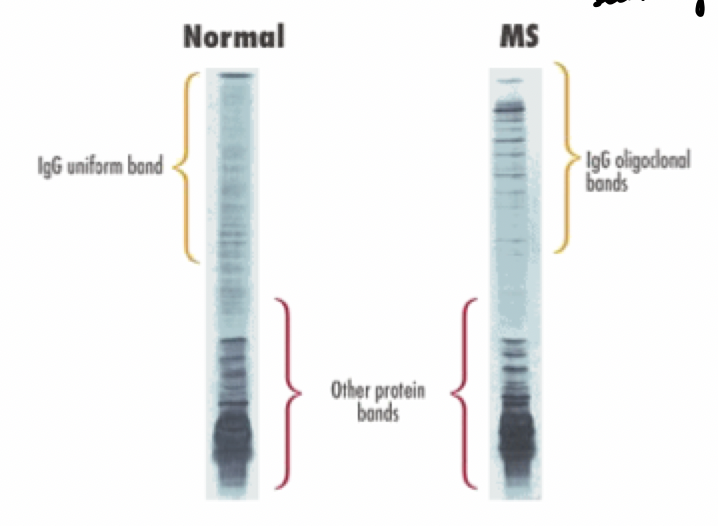
3 pathalogical conditions causing elevated CSF protein
MS, chronic meningoencpehalitis (from viruses), bacterial/viral meningitis/poliomyelitis/encephalitis inflammation
increased CSF protein can be caused by what 2 things?
BBB
IgG intrathecal synthesis
BBB CSF protein increase detected by:
albumin
intrathecal synthesis CSF protein increase detected by:
protein content of myelin sheath
CSF/serum Ig concentration ratio
CSF electrophoresis for MM
which organism has a positive india ink test
Cryptococcus
What’s the purpose of bacterial and cryptococcal antigen testing?
determine if a patient has bacterial meningitis (do a blood culture), cryptococcus, and TB infections
what tests to do for syphilis in CSF testing?
VDRL test and fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorption tests
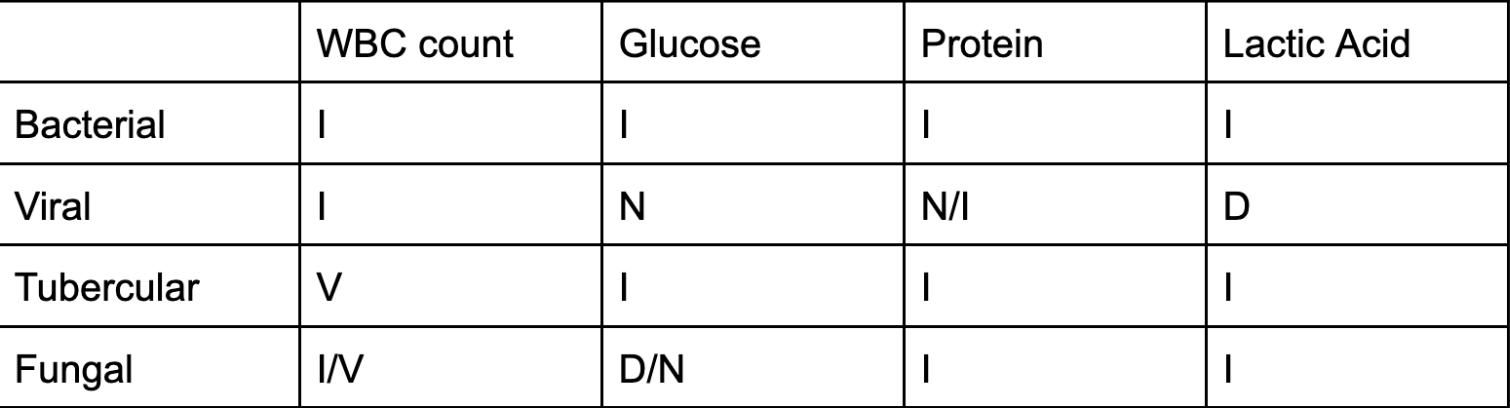
lab results of meningitis Bacterial, Viral, Tubercular, Fungal
WBC count, Glucose, Protein, Lactic Acid
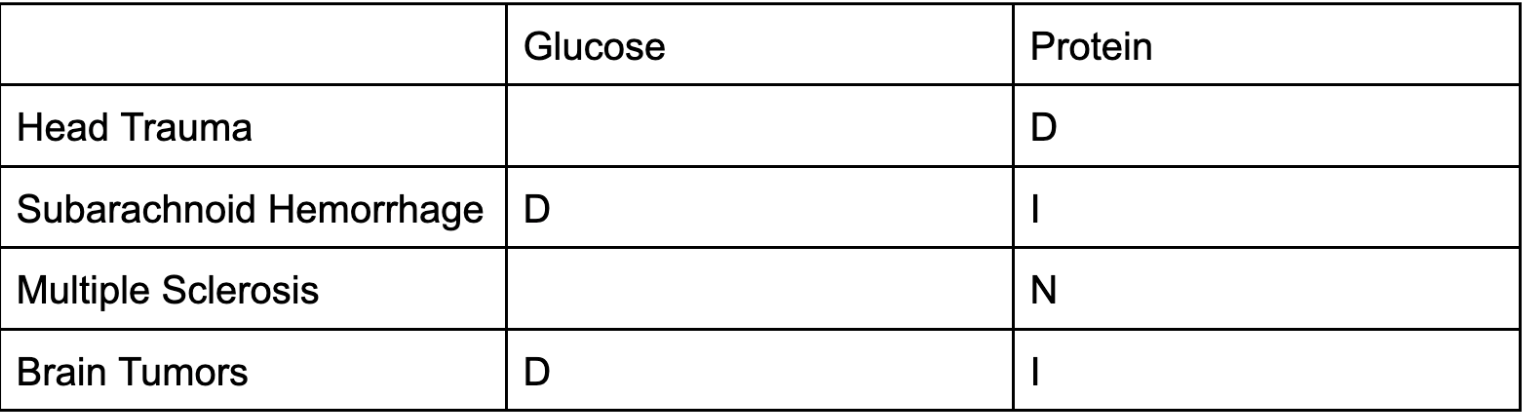
Head Trauma, Subarachnoid Hemorrhage, MS, Brain Tubors lab results
glucose
protein
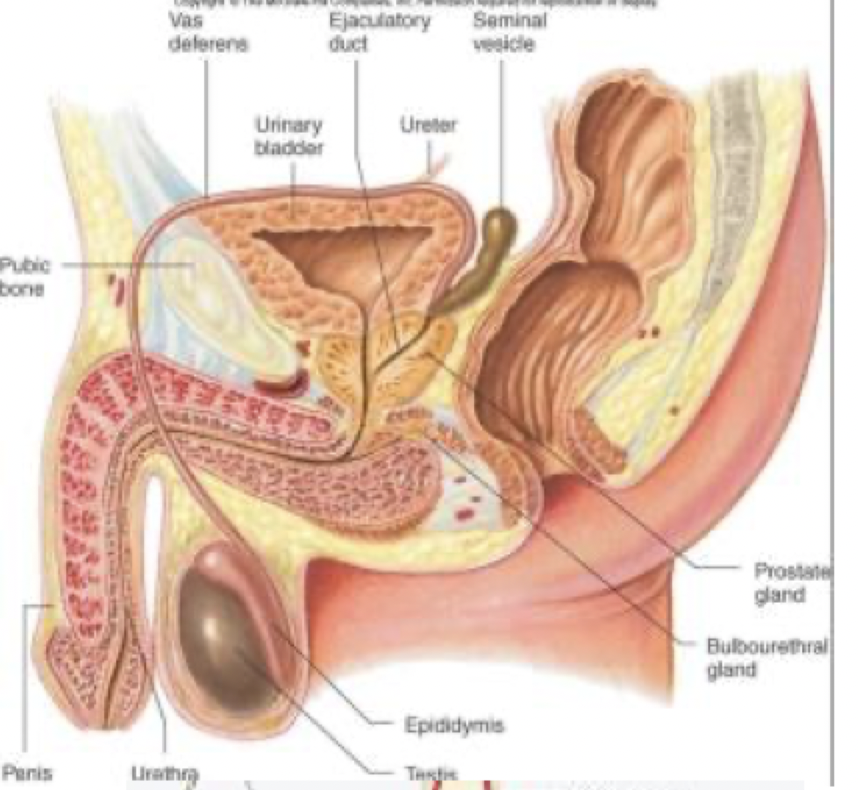
sperm production in the testes relates to which hormones
Seminiferous tubules make sperm: FSH causes germ cell maturation
Interstitial cells of Leydig make testosterone: LH stimulates Leydig
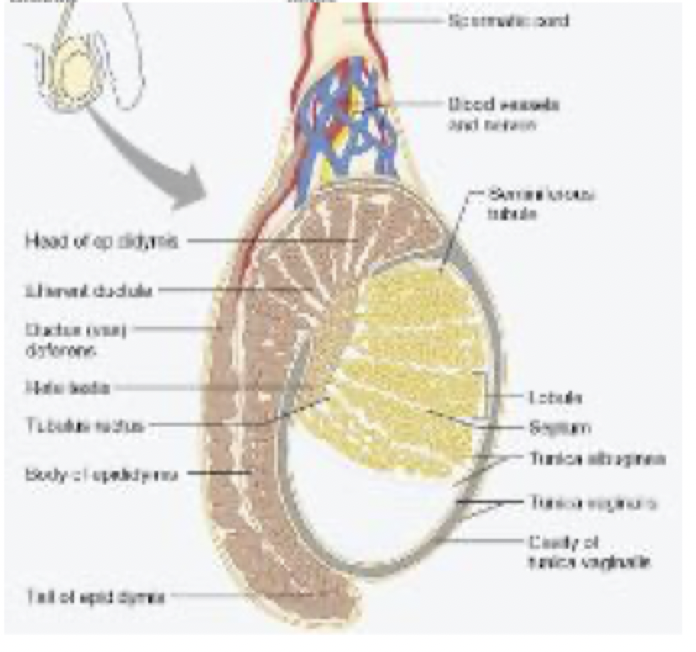
sperm maturation happens where?
Epididymis
sperm become motile here
4 components of sperm
nucleus/head: binds to egg
acrosome
midpiece
tail: motility
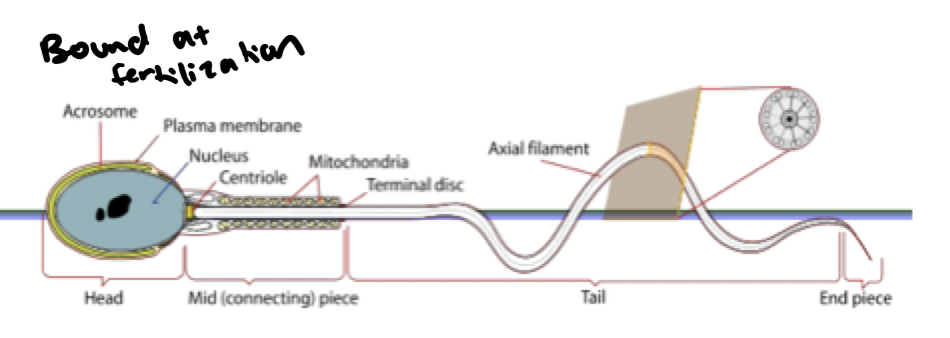
sperm acrosome purpose and source
penetrates ovum
from Golgi apparatus
sperm midpiece purpose
energy for motility is generated
macroscopic tests for routine semen analysis
viscosity, liquefaction, volume, pH
microscopic tests for routine semen analysis
count, motility, morphology, viability
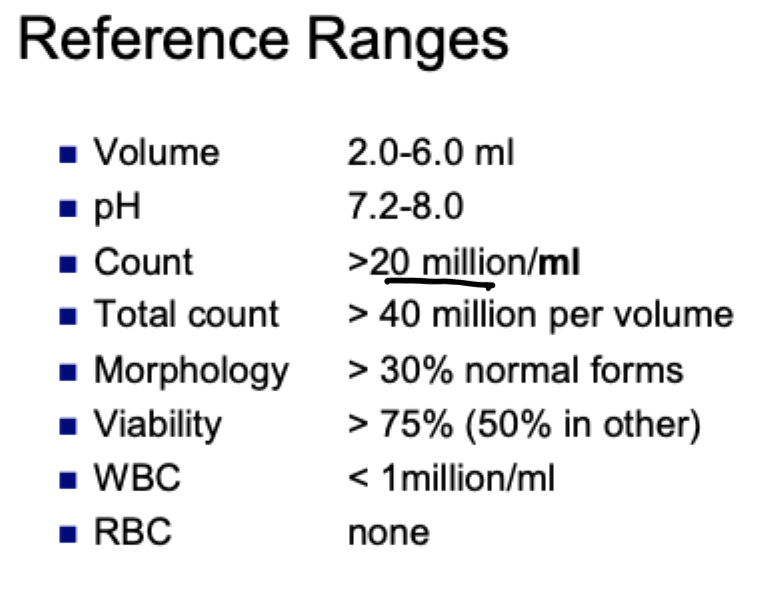
semen reference ranges
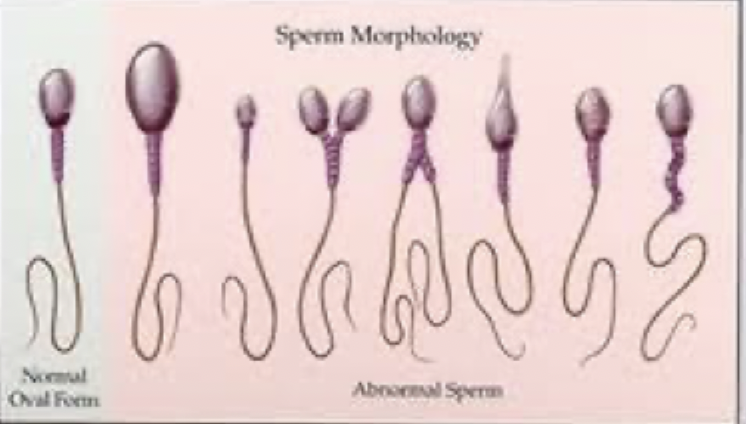
4 sperm abnormalities
head: narrow base
neck/midpiece: sharp bend
tail: coiling
cytoplasma droplets: cytoplasmic material >30% of head area

3 sperm head abnormalities
absence, double head, micro/megalo
7 causes of low semen volume?
Vasectomy
Varicocele: dilation and tortuosity of pampiniform plexus (drains testicle)
Primary testicular failure (Klinefelters)
Secondary Testicular failure
congenital vas obstruction
Retrograde ejaculation: redirected to bladder
Endocrine: prolactinemia, low testosterone
what’s the importance of semen liquefacation
enzymes from prostatic fluid break down the gel portion of the seminal plasma
what’s the implication of semen liquefaction
incomplete liquefaction has a gelatinous material in a liquid base- seen when the sample is swirled
what’s the importance of semen viscosity?
it’s the fluid nature of the whole sample, measuring how long it takes to break a thread of semen when you stretch it out