Machine Learning
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
is machine learning AI?
Machine learning is a subset of AI
what is hypermarameter
a parameter whose value must be set by the researcher before learning begins
what is labeled data
also called training data; used in supervised learning
unsupervised learning
1) does not use labeled data 2) a set up inputs (x) is used for analysis with no corresponding target (y) 3) the algorithm discovers underlying structure in data
dimension reduction
reducing the number of input, complexity of data. Kinda like if I eat and work I carpool and eat I have less to do
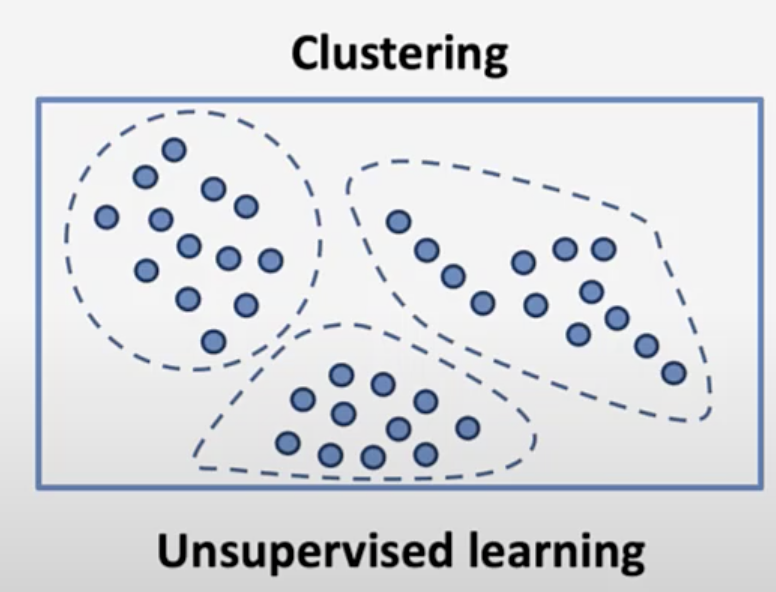
clustering
reducing data by categorizing them. Example, putting kids going to soccer and going to piano together and then drive them. * observation with a cluster are similar and different accross clusters.
deep learning
self teaching system which a computer learns from interacting with itself. can be supervised, unsupervised or reinforcement learning (train and error)
overfitting
the ML fits the training data too well, unable to generalize new data
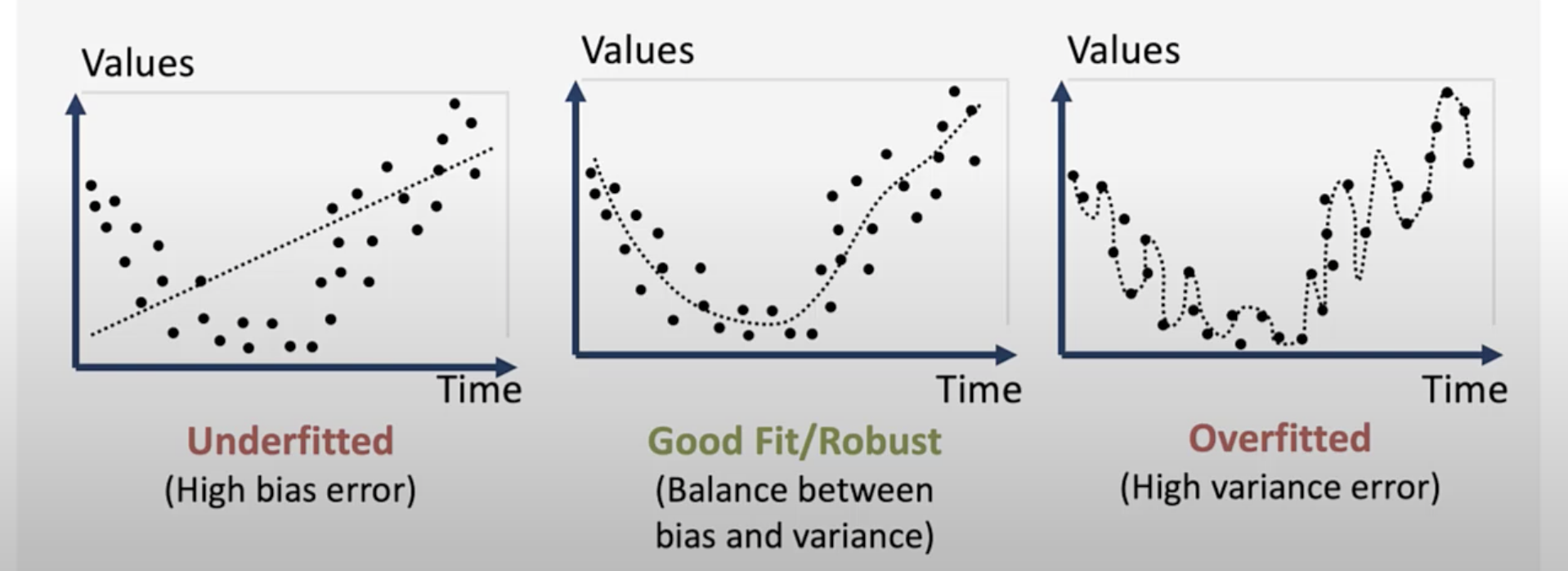
descriobe in sample error
1) regarding training sample 2)bias arises from underfitted models
out of sample errors
1) prediction erros in validation and text sample 2) variance error from over fitted models
residual errors
results from randomness in the data
complexity reduction and cross validation solves
overfitting
a type of cross validation — K fold
1) split the data set into K number of sections/folds 2) first section is used to test the model, and the test are used to train model 3) this reduces the problem of holdout sample (data not used to train the sample). * usually K = 5 or 10 (sections)
random forests are a special case of
bagging ( a ensemble methods)
Random forest
large number of uncorrelated tress operating as a group outperform any of the individual consistent tress (wisdom of crowds)
what is good for factor based investment strategies
random forest
Dimension reduction and clustering are examples of supervised or unsupervised machine learning
unsupervised
lower dimensional dataset benefit
reduce overfitting, easy to train and interpret
divisive clustering is a
top down approach , hierachrial is bottom up approach
which model to use “In some cases, their fear of loss seems to increase at an increasing rate when some scenarios are presented.”
the relationship is not linear, so neural net work
if the out put of data is not specified
unsupervised learning