Bacteria: the Sequel
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Salmonella, Shigella, Typhoid fever, Tetanus, Botulism, Campylobacter Jejuni, Cholera, C.diff, Diphtheria, Group B strep
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Salmonellosis
A leading cause of foodborne illness in the US that is most common in children under 5 and adults above 70 linked to contaminated food, poor hygiene, and pet exposure
Salmonella enterica (S. enteritidis, S. typhimurium) incubates in 12-48 hours; transmitted via fecal oral lives in the GI tracts of animals
Etiology and transmission of Salmonellosis
Clinical diagnosis BUT confirmed by stool culture, PCR GI panel in moderate/severe cases, blood culture if febrile or immunocompromised, CBC, CMP
7 y/o male presents to the ED for abdominal pain with N/V/D. Mom states that the diarrhea was loose and watery but without blood. Vitals are stable with the exception of 100.2 temp. What is your workup?
Thug it out, Hydration and electrolyte replacement, NO antidiarrheals
7 y/o male presents to the ED for abdominal pain with N/V/D. Mom states that the diarrhea was loose and watery but without blood. Vitals are stable with the exception of 100.2 temp. What is your treatment plan?
Ceftriaxone, cipro, azithromycin
Abx choices for Salmonellosis - may prolong carrier states or open patients up to C. Diff
Infants under 3 months, immunocompromised, severe illness, invasive disease
Who are abx recommended for for Salmonellosis
Osteomyelitis (sickle cell), meningitis or endocarditis (neonates), bacteremia (immunocompromised or high risk), reactive arthritis, chronic carrier state, dehydration, electrolyte abnormalities
Complications of Salmonellosis
safe food handling, wash hands, avoid raw/undercooked eggs, poultry, and meat
Prevention of Salmonellosis
Typhoid fever
A systemic illness that is rare in the US, but associated with international travel - report in 1 week
Salmonella enterica serotype typhi and paratyphi A, B, C - Humans are the ONLY reservoir
Etiology for Typhoid fever
travel to South Asia, Africa, and parts of Latin America, ingestion of contaminated food or water, close contact with a carrier (shed bacteria for 12 months), chronic biliary disease/structural GI issues, inadequate hand hygiene
Risk factors for Typhoid Fever
Blood cultures (sensitive early), Stool cultures (sensitive later), Bone marrow culture (the MOST sensitive - but rarely needed), CBC, CMP, Widal test (no longer recommended)
45 y/o male presents to the ED for abdominal pain and malaise. He states that he’s had a fever every day since getting back from Brazil and it keeps getting higher. He also reports pea soup diarrhea. On physical exam you note faint salmon colored blanching macules on the trunk and hepatosplenomegaly. Vitals are stable with the exception of 55 bpm (faget’s) and 102.5 temp. What is your workup?
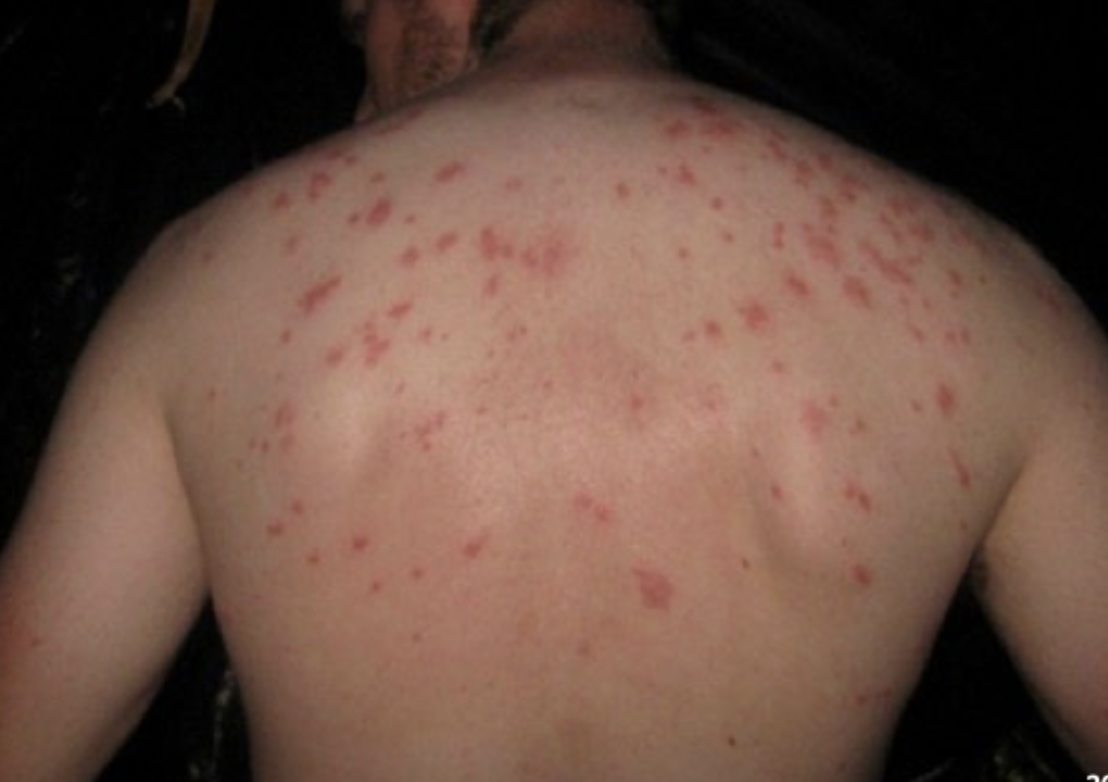
Azithro/Ceftriaxone 🥇, FQs (resistance common), fluids, antipyretics, nutrition, Corticosteroids (shock, delirium)
45 y/o male presents to the ED for abdominal pain and malaise. He states that he’s had a fever every day since getting back from Brazil and it keeps getting high. He also reports pea soup diarrhea. On physical exam you note faint salmon colored blanching macules on the trunk and hepatosplenomegaly. Vitals are stable with the exception of 55 bpm (faget’s) and 102.5 temp. What’s your treatment plan?
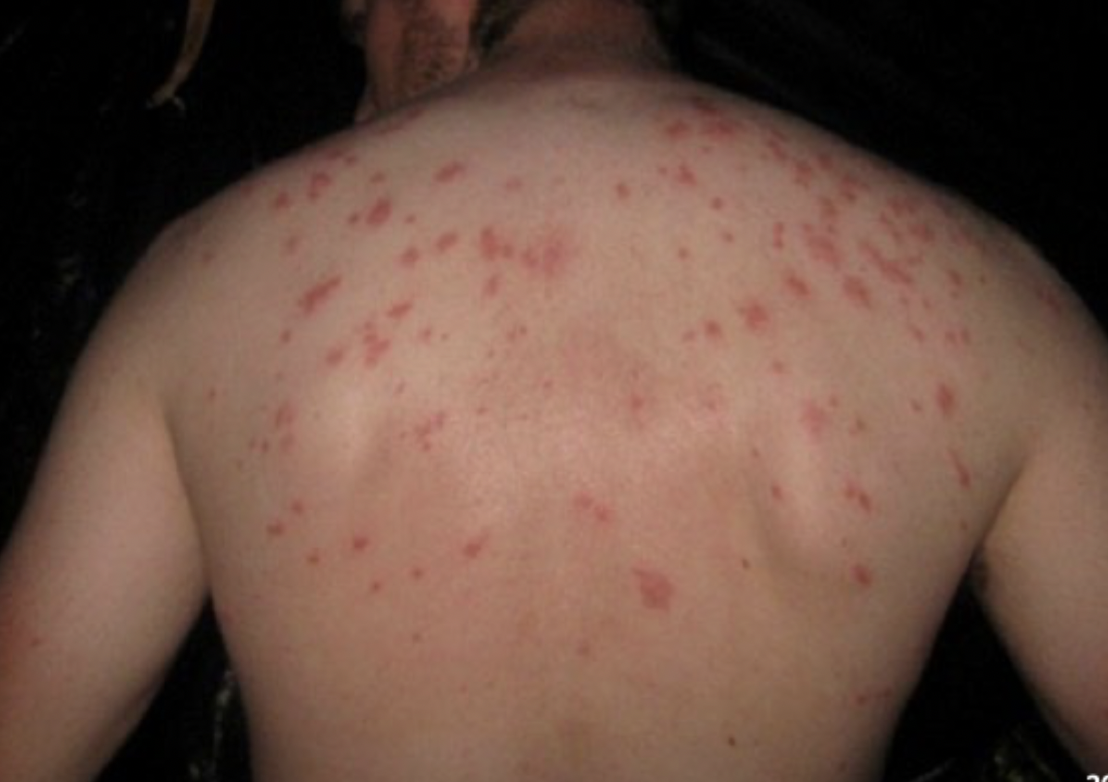
Prolong Abx, maybe cholecystectomy
Game plan for chronic carriers of Typhoid Fever
Intestinal perforation, Hemorrhage (peyer’s patches), encephalopathy (AKA typhoid state), hepatitis, myocarditis, carriage, sepsis
Complications of Typhoid - mortality up to 15% if untreated
Vaccines available (live oral and injectable), food and water precautions, treat chronic carriers, investigate outbreaks
Prevention of Typhoid fever
Shigelllosis
A common cause of inflammatory diarrhea that has a LOW infectious dose and is an important cause of daycare, institutional, and MSM outbreaks
Children under 5, poor sanitation, contaminated food and water, travel to endemic regions, MSM, homelessness
Risk factors for Shigellosis
Shigella sonnei (most common), flexneri, dysenteriae, boydii (gram neg rod 1-3 day incubation); fecal-oral human only pathogen that invades the colonic mucosa
Etiology and transmission of Shigellosis
Clinical BUT confirm with stool culture (species ID and sensitivity) or PCR panel, imaging if concerned for toxic megacolon, CBC/CMP (monitor systemic effects)
49 y/o female presents to the ED for sudden onset abdominal cramps and mucoid, bloody diarrhea. She also reports tenesmus and urgency. Vitals are stable with the exception of 101.7 temp. What is your workup plan?
Thug it out → fluids and electrolytes, NO ANTIDIARRHEALS
49 y/o female presents to the ED for sudden onset abdominal cramps and mucoid, bloody diarrhea. She also reports tenesmus and urgency. Vitals are stable with the exception of 101.7 temp. What is your treatment plan?
Children, MSM, elderly, institutional settings, immunocompromised
Abx (azithromycin and ceftriaxone) may shorten illness and shedding in Shigellosis but who’s getting them?
Seizures (kids), Toxic megacolon, dehydration, HUS (dysenteriae), reactive arthritis, prolonged carriage and shedding, IBD flares
Complications of Shigellosis
Handwashing 🥇, safe water and food practices, quarantine symptomatic patients
Prevention of Shigellosis
fever, cramps, bloody diarrhea
Classic triad of Shigellosis
1 week
Is Shigellosis reportable in Tx?
Tetanus (report in 1 week)
What can cause life-threatening muscle rigidity and spasms, especially in unvaxxed or elderly adults
developing countries, puncture wounds, crush injuries, burns, injection drug use, chronic wounds/ulcers, lack of vax, non-steril deliveries (neonatal)
Tetanus risk factors
Tetanospasmin toxin formed by Clostridium tetani found in soil, dust, and animal feces that enters through a break in skin (incubators in 3-21 days)
Etiology and transmission of Tetanus
trismus (lockjaw), dysphagia, neck stiffness
Early signs of Tetanus
ICU admit!! Tetanus immune globulin (TIG), Metro/Pen G, Benzo (muscle spasms), Beta blockers/Mg (autonomic instability), begin tetanus vaccine, intubate and vent at 1st sign of resp compromise
38 y/o male presents to the ED for generalized muscle rigidity. His wife states he pulled a rusty nail out of his foot a week ago, but they don’t believe in vaccines. On physical exam you note opisthotonos, trismus, skin is diaphoretic, and spasms are triggered by pain and noise. Vitals are stable with the exception of 158 bpm and 159/98. What is your management plan?
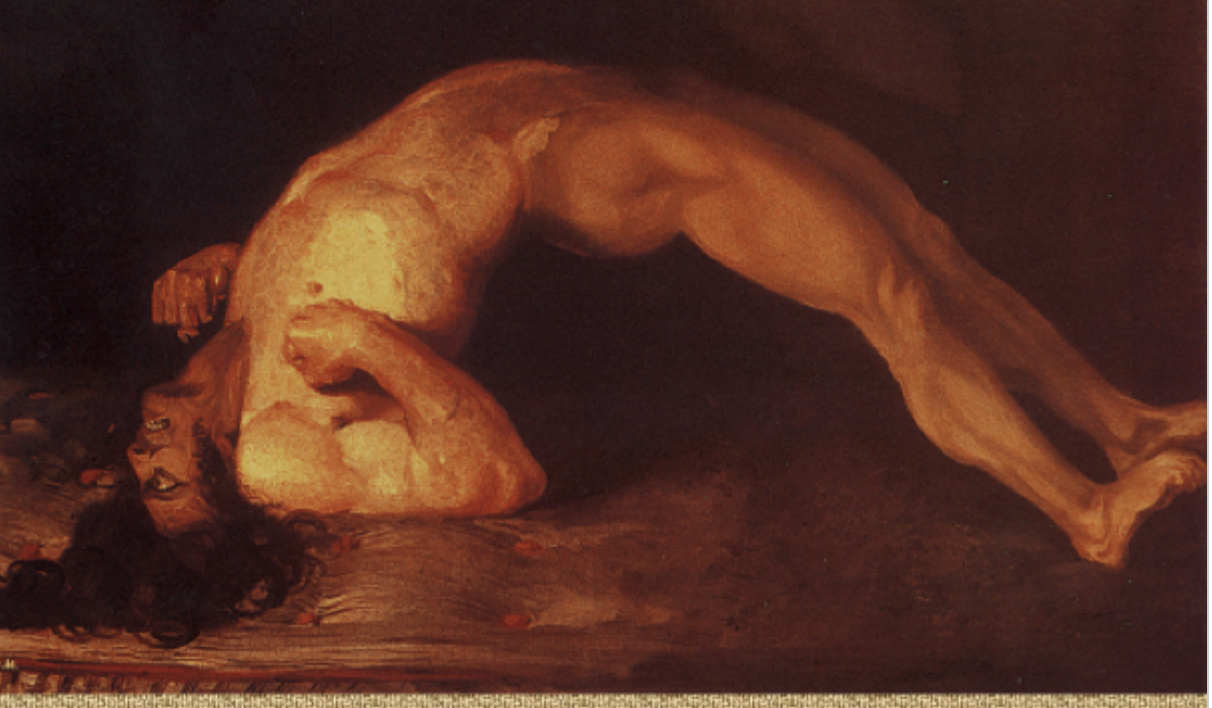

Laryngospasm, respiratory arrest, autonomic instability, aspiration pneumonia, long bone fractures, DVT, DEATH
Complications of Tetanus
clean, minor with 3 prior doses (no booster), dirty wound or 5+ years since last booster (give Tdap/Td), unknown or incomplete vaccination (TIG), boost every 10 years
Post-exposure prophylaxis rules (just stab’em tbh)
Botulism (report immediately - A$AP)
A rare but life-threatening neuroparalytic illness that presents with descending flaccid paralysis requiring urgent antitoxin administration and respiratory support
home-canned or fermented food, black tar heroin (wound), spore ingestion (honey - infant), GI surgery/abnormalities, cosmetic/therapeutic botox use
Risk factors for Botulism
Botulinum toxic (inhibits Ach) produced by Clostridium botulinum (anaerobic, spore forming gram + rod), spores are heat resistant, toxin is heat labile
Etiology for Botulism
Foodborne (ingestion of preformed toxin), infant (most common - in vivo toxin production), wound, iatrogenic (OD), NO person-person
Transmission for Botulism
respiratory failure
Leading cause of death in Botulism
Serum or stool toxin assay, wound culture, R/o mimics with CMP, CBC, ABG, CXR, CSF
Donatella Versace presents to the ED for facial paralysis after her 45th botox appointment this week. She says it started in her forehead and is moving down as well as double vision and dysphagia. On physical exam you note decreased deep tendon reflexes ptosis. What can you use to confirm your diagnosis, while we wait for the health department to bring the goods?

ICU admit!! Equine-derived heptavalent antitoxin (adults), Human botulism immune globulin (BIG -IV 👶), debridement + Pen G/Metro for wound, NO AMG, Supportive care
Donatella Versace presents to the ED for facial paralysis after her 45th botox appointment this week. She says it started in her forehead and is moving down as well as double vision and dysphagia. On physical exam you note decreased deep tendon reflexes and ptosis. Vitals are stable. What is your treatment plan?

Respiratory failure, aspiration pneumonia, prolonged paralysis and neuromuscular weakness, autonomic instability, secondary infections
Complications of Botulism
Proper food handling and canning, no honey until 12+ months old, prompt wound care in injection drug users,
Prevention of Botulism
Campylobacter Jejuni (report in 1 week)
One of the most common bacterial (curved gram neg rod) causes of gastroenteritis that can also trigger Guillain Barre
undercooked poultry, unpasteurized milk, contaminated water
Transmission for Campylobacter Jejuni
Stool culture, PCR, CT with contrast to r/o appendicitis
15 y/o male presents to the ER for crampy abdominal pain and watery, bloody diarrhea. He said he thinks he drank from the wrong stream on his camping trip. Vitals are stable with the exception of 103.5 temp. What are your diagnostics?
Supportive care, Azithromycin for severe/prolonged cases or high risk patients
15 y/o male presents to the ER for crampy abdominal pain and watery, bloody diarrhea. He said he thinks he drank from the wrong stream on his camping trip. Vitals are stable with the exception of 103.5 temp. What is your treatment plan?
Cholera (report in 1 day AKA immediately)
What can cause rapid, life-threatening dehydration but is rare in the US and endemic to Africa, Asia, and Haiti?
Vibrio Cholerae (gram neg comma shaped rod); fecal oral route
Etiology and transmission of Cholera

Aggressive oral/IV rehydration, Doxy may shorten the course
21 y/o male presents to the clinic for profuse, rice water diarrhea after returning from a mission trip in Africa. He also notes minor abdominal pain and vomiting. What is your treatment plan?
C. Diff (Clostridioides difficiles)
The leading cause of healthcare and antibiotic-associated diarrhea and colitis that has a risk of recurrence and complications

C. Difficile (anaerobic, spore forming gram positive rod), spread via spores
Etiology and transmission of C. Diff

Oral Vanc, fidaxomicin 🥇, NO antidiarrheals 🚫
75 y/o female presents to the ED for watery diarrhea and abdominal cramping. She states that she was recently on clindamycin. Vitals are stable with the exception of 102.3 temp. CBC shows leukocytosis. Toxins A/B are present in the stool. What is your treatment plan?

Diphtheria (report immediately)
A disorder caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae (gram positive rod) that can cause life-threatening airway obstruction and myocarditis spread via respiratory droplets
Grey pseudomembrane on pharynx (DO NOT DISTURB), sore throat, low grade fever, cervical LAD (bull neck)
Presentation of Diphtheria
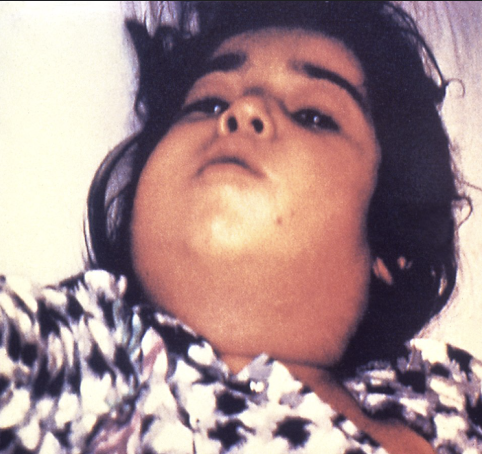
Diphtheria antitoxin + erythromycin/penicillin, quarantine patient
Management of Diphtheria
Clinical, confirm with toxin and culture
Diagnosis of Diphtheria
Group B streptococcus (GBS - report in 1 week)
A major cause of neonatal sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis but is preventable with maternal screening at 35-37 weeks
Streptococcus Agalactiae (gram pos cocci); Colonizes maternal GI/GU transmitted perinatally
Etiology and transmission of Group B streptococcus
Blood, CSF, urine culture
Diagnosis of Group B streptococcus
respiratory distress, fever, poor feeding, lethargy (early), meningitis (late)
Presentation of Group B streptococcus in neonates
Pen G 🥇, intrapatum prophylaxis reduces risk
Management of Group B streptococcus