Speciation
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Speciation
the origin of new species is at the focal point of Darwin’s evolutionary theory
Evolutionary theory must explain
how new species originate and how populations evolve
Microevolution
Consist of adaptations that evolve within a population, confined to one gene pool
Macroevolution
refers to evolutionary change above the species level
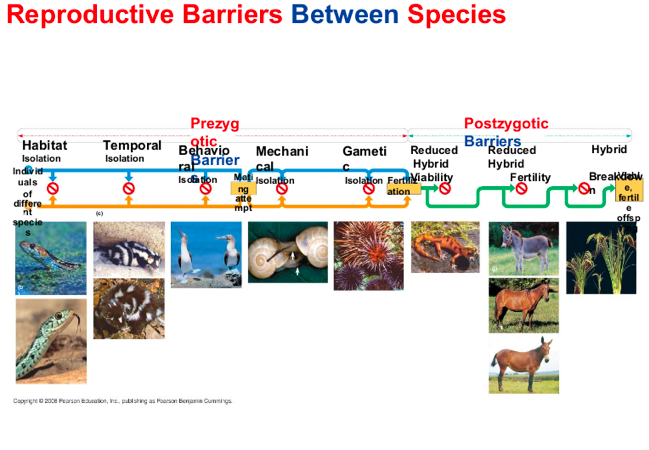
Reproductive isolation
is the existence of biological factor(barriers) that impede two different species from producing viable, fertile offspring.

Hybrids
are the offspring of crosses between different species

Reproduction isolation can be classified by
where factor act before or after fertilization
Prezygotic Barries
block fertilization from occurring by:
Impeding different species from attempting to mate
Preventing the successful completion of mating
Hindering fertilization if mating is successful.
Prezygotic barries
maintain reproductive isolation and includes
Temporal habitat, Behavioral, Mechanical, and gamete isolation
Habitat isolation
two species(genetically similar) encounter each other rarely because they occupy different habitats even though not isolated by physical barriers.
Temporal Isolation
Species that breed at different timed of the day, different seasons, or different years cannot mix their gametes
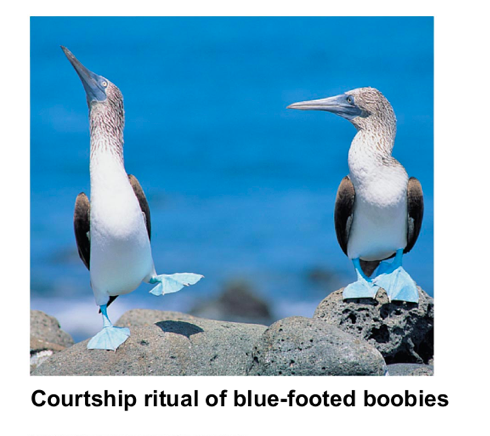
Behavioral isolations
Courtship ritual and other becahiors unique to a species are effective barriers

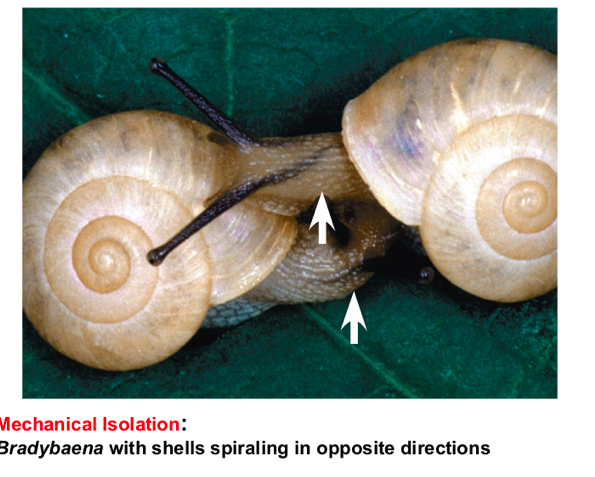
Mechanical Isolation
Morphological difference can prevent successful mating (shells)
Gametic(sperm and egg) isolation
Sperm of one species may not be able to fertilize to fertilize eggs of another species
Postzygotic barriers
prevent the hybrid zygote from developing into a viable fertile adult
reduced hybrid viability (weak)
Reduce hybrid fertility( sterile )
Hybrid breakdown

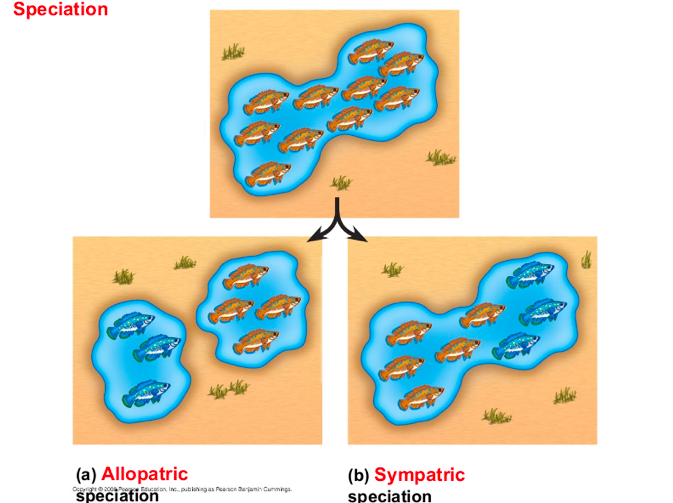
Speciation occurs in two ways
Allopatric speciation: geographic barrier operates populations
Sympatric speciation: no geographic barrier
In allopathic speciation gene flow is
interrupted or macroevolution is the cumulative effect of many speciation and extinction events
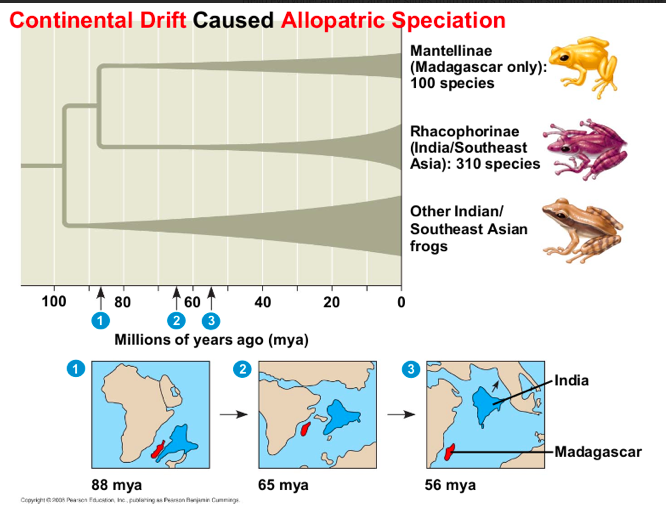
Reduced when a population is divided intro geographically isolation subpopulations
A geographic barrier separated the original population
Separate population may
evolve independently through mutation, natural selection, and genetic drift
Barriers to repoduciron are insteisci(naturally happens)
seperation itself is not a biological barrier
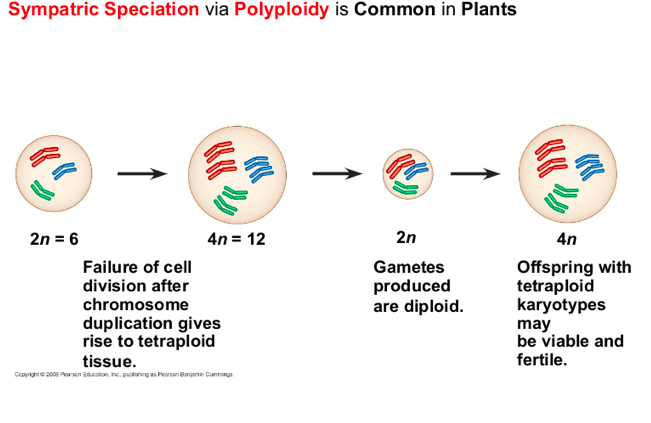
Autopoluloid is a species with
multiple steps of chromosomes(always have to been even) derived from different species
Polyploidy
is common in plants
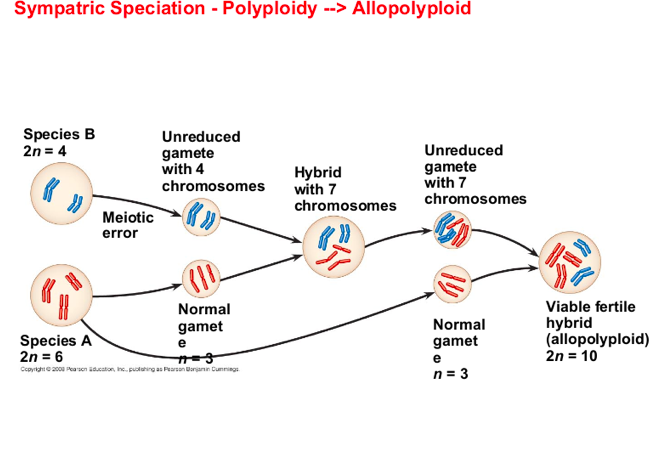
Sympatric speciation
can also result from the appearance of new ecological niches
For example
the North American maggot fly can live on notice hawthorn trees as well as more recently introduces apple trees
Sexual selection
can drive sympatric speciation
Sexual selection form aged of different color has
likely contribute to the speciation in cichlid fish in lake Victoria.
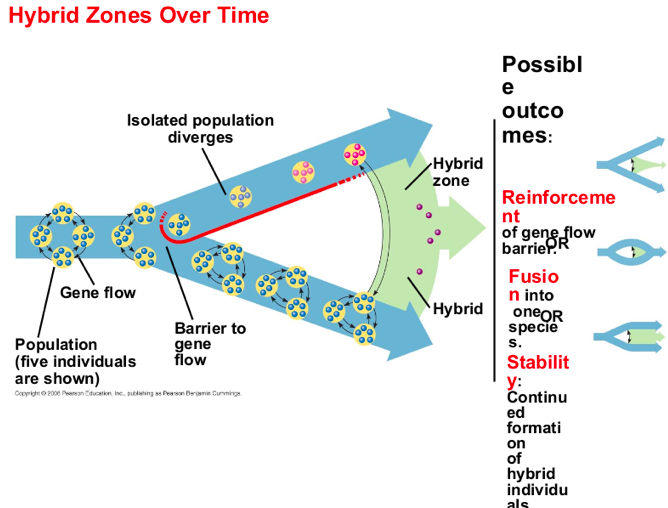
hybrid zone
is a region in which members of different species mate and produce hybrids.
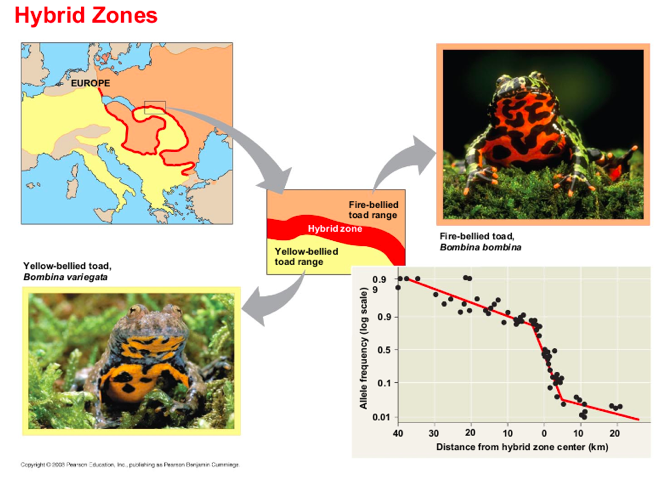
where adjacent species meet?
A hybrid zone can occur in a single band
Hybrids often have
reduced fitness compared
with parent species.
The distribution of hybrid zones can be more
complex
if parent species are found in multiple
habitats within the same region.
When closely related species meet in a hybrid
zone, there are three possible outcomes:
Reinforcement -- Strengthening of reproductive barriers reducing gene flow.
Fusion -- Weakening of reproductive barriers with eventual fusion into one species.
Stabilizing -- Continued formation of hybrid individuals.
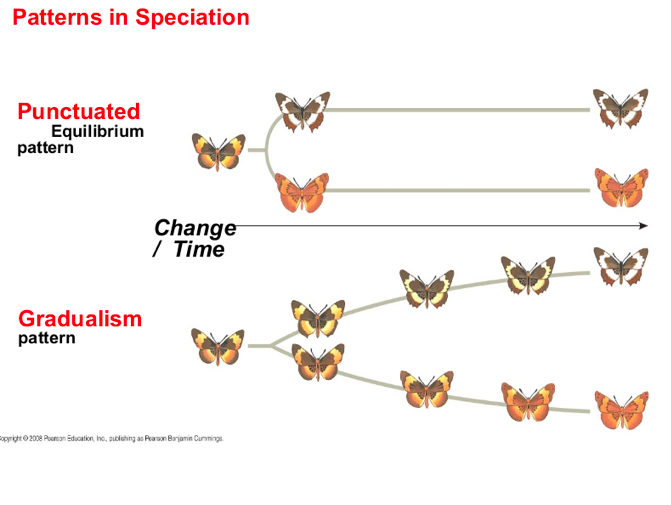
The Time Course of Speciation
Broad patterns in speciation can be studied using the fossil record, morphological data, or molecular data.
The fossil record includes
examples of species that appear suddenly, persist essentially unchanged for some time, and then apparently disappear
punctuated equilibrium
to describe periods of apparent stasis (no change) punctuated by brief periods of rapid change.
The explosion of genomics is
enabling researchers to identify specific genes involved in some cases of speciation. (speciation might require the change of only a single allele or many alleles.)