Genetics: Chapter 1.2 Genome and Genetic Variation
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
genome
the complete set of genetic information for an organism
the human genome
the 23 pairs of chromosomes and all the genetic material contained therein
all the genes (and their alleles) present in an organism and other DNA sequences that do not encode genes (make a protein)
what is included in the genome?
1.5%
only ___% of the DNA in the human genome encode protein (of about 24,000)
noncoding DNA
highly repeated sequences with unknown functions in DNA
proteomics
area of science that looks at the expression of that 1.5% of DNA that encodes protein
proteomics
allows us to look at the expression of what specific enzymes and proteins are expressed within cells and then understand what specific cells create, used to understand cancer. Looks at the 3D structure and expression.
1.5%
protein-coding genes make up ___% of the genome
variation
produced by mutation and “shuffled” by recombination
evolution
variation is important for…
polymorphisms
variations in the DNA sequence in individuals or groups that occur in at least 1% of the population; can be 1 to 1000’s of bases; may or may not have an effect
single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
single base sites that differ among individuals and are important as markers
substitution, deletion, addition
3 types of mutations
substitution
type of mutation where one pair is replaced by another
deletion
type of mutation where one pair is deleted from the sequence
addition
type of mutation where one pair is added to the sequence
gametes
a mutation is only passed on during reproduction if it happens to the _____
crossing over
creates new combination of genes; occurs between two homologous chromosomes
atom → molecule → macromolecule → organelle → cell → tissue → organ → organ system → organism
type out the levels of organization within the body from atoms to organism
same
all cells with a nucleus in the body contain the _____ (same/different) genetic information
stem cells
type of cell that are less specialized and can become many different cell types
differentiation
______ causes ells to differ in appearance and function
variation in gene expression
differentiation is controlled by…
toti-potent stem cells
very early in development; involved in the placenta and the creation of the other types of stem cells
pluri-potent stem cells
can be converted into just about any cell in the body
endoderm line
type of cell that becomes lung and pancreas cells
mesoderm line
type of cell that becomes heart muscle and red blood cells
ectoderm line
type of cell that becomes skin and neurons
multi-potent stem cells
stem cells that break off into three different lines (an endoderm line, mesoderm line, or an ectoderm line)
genotype
the unique combination of alleles they carry
phenotype
visible trait
dominant alleles
alleles expressed if the individual carriers one or two copies of the allele
recessive alleles
the alleles only expressed if the individual carries two copies of the allele
pedigree
indicates the structure of a family schematically
population
a group of interbreeding individuals
gene pool
the total of all the alleles in a population
evolution
the changing allelic frequencies in populations over time
mendelian traits
traits that are determined by a single gene pair
multifactorial traits
traits that are not controlled by a singe gene
multifactorial
are most traits mendelian or multifactorial?
gene; environment
multifactorial traits are influenced by more than one ____ and the _______
True
True or False: some illnesses may occur in different forms such as mendelian, multifactorial, and non-inherited
simple inheritance
mendelian traits are also called…
ok
BRCA1 gene can make you more susceptable to cancer, but it isn’t the sole determining factor. There are other environmental factors that play into it. Example of multifactorial traits.
mendelian inheritance
refers to the inheritance of traits controlled by a single gene with two alleles, one of which may be dominant to the other (example is whether you have attached earlobes or free-hanging earlobes)
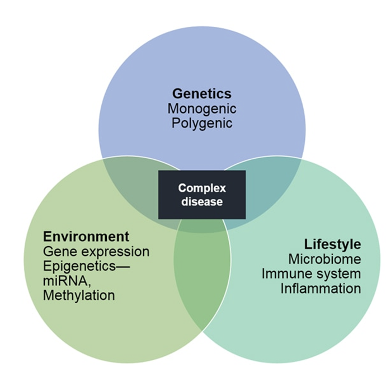
genetics + environment + lifestyle
How multifactorial traits allow disease to occur