Internet Protocol Version 6
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
module 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Advantages of IPv6
Scalability: Supports a vast number of devices.
Efficiency: Simplified processing improves performance.
Security: Enhanced by default with IPsec.
Flexibility: Auto-configuration and multicast improve network management.
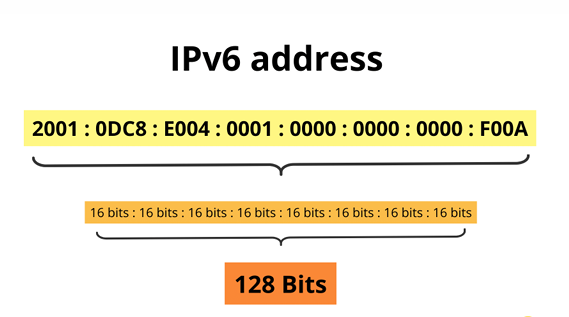
IPv6 Address Types
Unicast: Identifies a single device.
Anycast: Assigned to a group, with packets reaching the nearest device.
Multicast: Sent to multiple devices in a group.
IPv6 Address Allocation
Global Unicast: Publicly routable addresses.
Unique Local Addresses (ULA): Private addresses used within specific sites.
Link-Local Addresses: Used for communication within a single network segment.
IPv6 Transition Techniques (Dual Stack)
enables devices and networks to run both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols simultaneously. This allows systems to communicate using either protocol and facilitates a gradual transition to IPv6 without disrupting existing IPv4 services.
IPv6 Transition Techniques (Tunneling Protocols)
6to4 encapsulates IPv6 packets within IPv4 headers to allow them to be transmitted across IPv4-only networks. This is useful for connecting IPv6 networks over an existing IPv4 infrastructure.
IPv6 Transition Techniques (Tunneling Protocols)
Teredo: Explanation: Teredo provides IPv6 connectivity through NAT (Network Address Translation) devices. It enables IPv6 packets to be tunneled through IPv4 NAT environments, which are common in many home and small office networks.
IPv6 Transition Techniques ISATAP (Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol):
ISATAP allows IPv6 packets to be transmitted over an IPv4 network by using automatic tunneling. It helps organizations with IPv4 infrastructure to connect their IPv6 enabled devices.
IPv6 Translation Mechanisms NAT64
translates IPv6 addresses to IPv4 addresses and vice versa, allowing IPv6-only devices to communicate with IPv4-only devices. It bridges the gap between the two protocols.
IPv6 Translation Mechanisms • DNS64:
works with NAT64 to provide DNS resolution for IPv6 clients. It translates IPv4 addresses found in DNS queries into IPv6 addresses that can be used by IPv6-only clients