Light : Reflection and Refraction
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What are the laws of reflection?
The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
The incident ray , reflected ray and the normal the point of incidence all lie in the same plane. Laws of reflection can be applied to all kinds of reflecting surface.
Explain real and virtual images.
Real Images
When light rays coming from a point actually meet at a point after reflection then it is called a real image.
It can be obtained on a screen
It is inverted
Virtual Images
When light rays coming from a point after reflection does not actually meet but appear to meet at a different point when traced back is called a virtual image.
It cannot be obtained on a screen
It is upright or erect.
What are the characteristics of image formation by a plane mirror.
It is always virtual and erect
It is formed behind the mirror
The size of the image is equal to the size of the object
The distance between the mirror and the image is equal to the distance between the object and the mirror.
The image is laterally inverted , ie left seems to be right and vice versa.
Differentiate between regular and irregular vision.
Regular Reflection | Diffused Reflection |
Smooth and polished reflecting surface | Rough , uneven and irregular reflecting surface |
Parallel rays are parallel after reflection | Parallel rays move in random directions after reflection. |
Differentiate between the plane and spherical mirrors
Plane Mirror | Spherical Mirror |
Virtual and Erect Image | Real and Inverted / Virtual and Erect |
Object Distance = Image Distance | Object distance may or may not be equal to the image distance |
Object Size = Image Size | Object Size may or may not be equal to image size |
Laterally Inverted | Vertical Inverted |
Differentiate between the concave mirrors and convex mirrors.
Concave Mirror | Convex Mirror |
Converging | Diverging |
Focus and centre lies in front of mirror | Focus and centre lies behind the mirror |
The magnification can be greater than , less than or equal to zero | The magnification si always less than zero |
Virtual or Real Image | Always Virtual Image |
Uses:
| Uses:
|
Explain the terms related to spherical mirrors
Centre of Curvature - it is the centre of the imaginary sphere of which the mirror is a part.
Radius of Curvature - it is the radius of the whole sphere of which the mirror is cut from.
Pole - It is the centre or mid point of the reflecting surface of the spherical mirrors.
Principal Axis - it is the line joining the pole and the centre of curvature that is normal to mirror at its pole.
Aperture - It is the diameter of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror which is equal to the straight line distance between two ends of the mirror.
Principal Focus - Principal focus is a point on the principal axis of the mirror at which light rays which come parallel to the mirror after reflection actually meet or appear to meet.
Focal Length - It is the distance between pole and principle focus of a spherical mirror and is equal to half of the radius of curvature.
Explain the sign convention for reflection by spherical mirrors.
The object is always placed to the left of the mirror meaning that the light from the objects falls on the mirror from the left hand side.
All distances parallel to principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
Distance of the left of the pole are taken as negative. Distances to the right of the pole are taken as positive.
Distances measured perpendicularly above ht principal axis are taken as positive
Distances measured perpendicularly below the principal axis are taken as negative.
The focal length of convex mirror is taken as positive and the focal length of concave mirror is taken as negative.
What is magnification? What information can we infer from the value of magnification?
Magnification produced by the spherical mirror gives the relative extent to which the image of an object is magnified with respect to the object size.
It is expressed as the ratio of the height of image to the height of object and is represented by m.
It can also be expressed as -v/u
The magnitude of magnification tells us
m=1 , image is same size as object
m<1 , image is smaller than the object
m>1 , image is greater than the object
The sign of the magnification tells us
-ve is real and inverted image
+ve is vitrual and erect image.
How is refraction different based on optical densities?
3 Cases of Refraction
Case 1 - Rarer Medium to Denser Medium - bends towards normal
Case 2 - Denser Medium to Rare Medium - bends away from normal
Case 3 - Perpendicularly to both mediums - no refraction
What are the laws of reflection?
The incident ray , the normal at the point of incidence and the refracted ray all lie on the same point.
The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is always constant for a given colour of light and a given pair of media and colour of light.
Formula for snell’s law
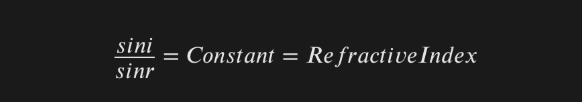
Give some examples of refraction of light
A pencil partially immersed in water appears to be bent because of the refraction of light coming from the part of pencil that is immersed inside water.
A lemon kept in water in a glass tumbler appears to bigger than its actual size when it viewed from the sides.
The bottom of a pool or tank or pond containing water appears to be raised due to refraction of light which takes place when light rays pass from the pool into the air
The letters appear to be raised when viewed through a glass slab placed over the document because of refraction of light.
Explain refraction through a rectangular slab.
When a light ray enters in a glass slab , then the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray but it is shifted sideward slightly.
In this case , refraction takes place twice , first when ray enters glass slab from air and second when eits from glass slab to air.
The extent of bending of the ray of light at opposite parallel faces AB and CD of rectangular glass slab is qual and opposite so the ray emerging from face CD is parallel to incident ray but shifted sideward slighlty.
What are the characteristics of refraction through a glass slab.
The angle of emergence = angle of incidence
If the incident ray falls normally to the surface of glass slab , then there is no bending of the ray of light , it goes straight without any deviation
The perpendicular distance between the emergent ray and incident ray when the light passes out of a glass slab is called lateral displacement.
The deviation of light will be greater , if the differences the speed of light between two medium is large.
What is refractive index? What are the types of defining refractive indexes?
Absolute Refractive Index
The refractive index of a medium with respect to vacuum or air is called absolute refractive index of the medium. The absolute refractive index of a medium is simply called its refractive index.
Relative Refractive Index
The refractive index of one medium with resepect to another medium is called the relative refractive index of the medium.

Is focus of a lens taken as positive or negative?
Focal length of a convex lens is positive
Focal length of a concave lens is negative.
What is the power of lens
The ability of a lens to converge or diverge light rays is called power of lens.
It is defined as the reciprocal of focal length.
The unit of power is diopter and focal length is always taken in meters while calculating
What happens to power when you combine lenses?
Magnification of lens in combination is the product but the power is the sum
Additive properrty of powers of lenses can be used in designing camera lenses and lesecopes.