Unit 4: Cellular Energy and Metabolism
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that consume other organisms for energy.
Activation Energy
Minimum energy required for a chemical reaction.
Exergonic Reaction
Releases energy during the reaction process.
Endergonic Reaction
Absorbs energy from surroundings during reaction.
Temperature
Measure of thermal energy in a system.
Entropy
Measure of disorder or randomness in a system.
Metabolism
All chemical reactions in an organism.
Cellular Respiration
Process of converting glucose into ATP.
Photosynthesis
Process of converting sunlight into chemical energy.
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
Energy currency of the cell.
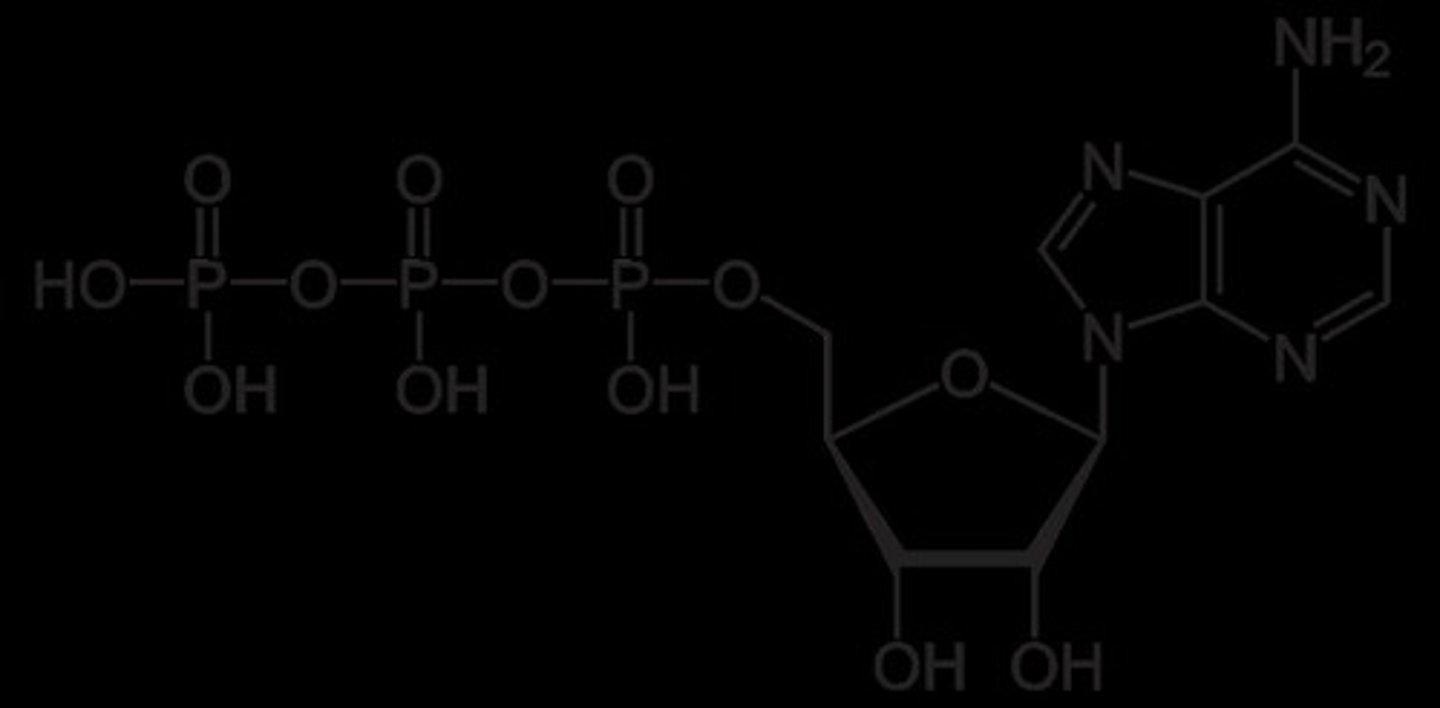
ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate)
Formed when ATP loses a phosphate group.
Energy Coupling
Using energy from exergonic reactions to drive endergonic reactions.
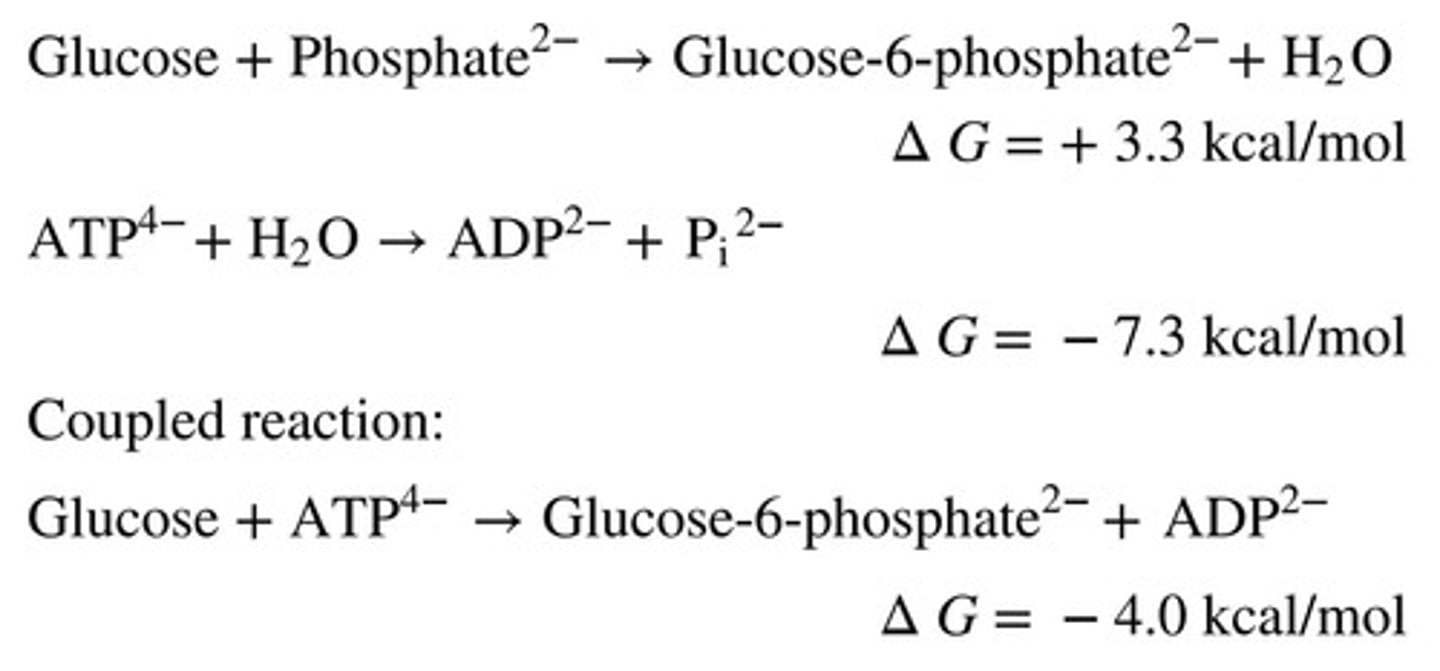
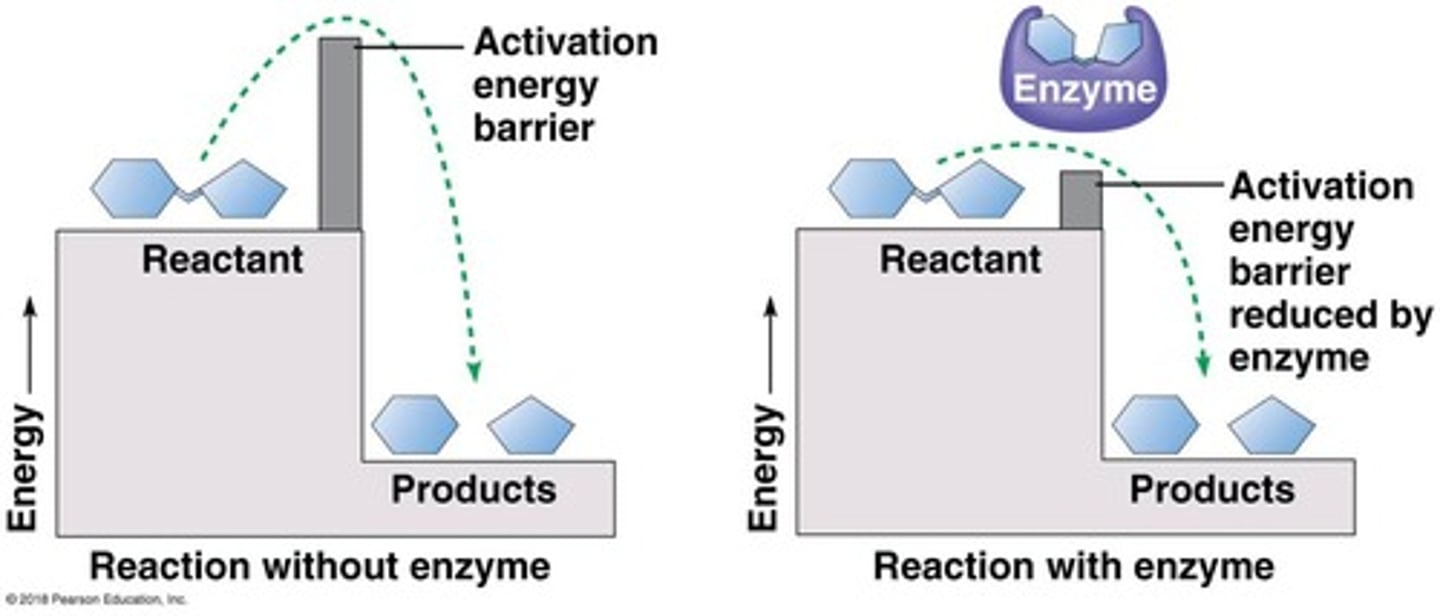
Catalyst
Substance that lowers activation energy of a reaction.
Enzyme
Biological catalyst that speeds up reactions.
Substrate
Reactant molecule that an enzyme acts upon.
Active Site
Region on an enzyme where substrate binds.
Coenzyme
Organic molecule that assists enzyme function.
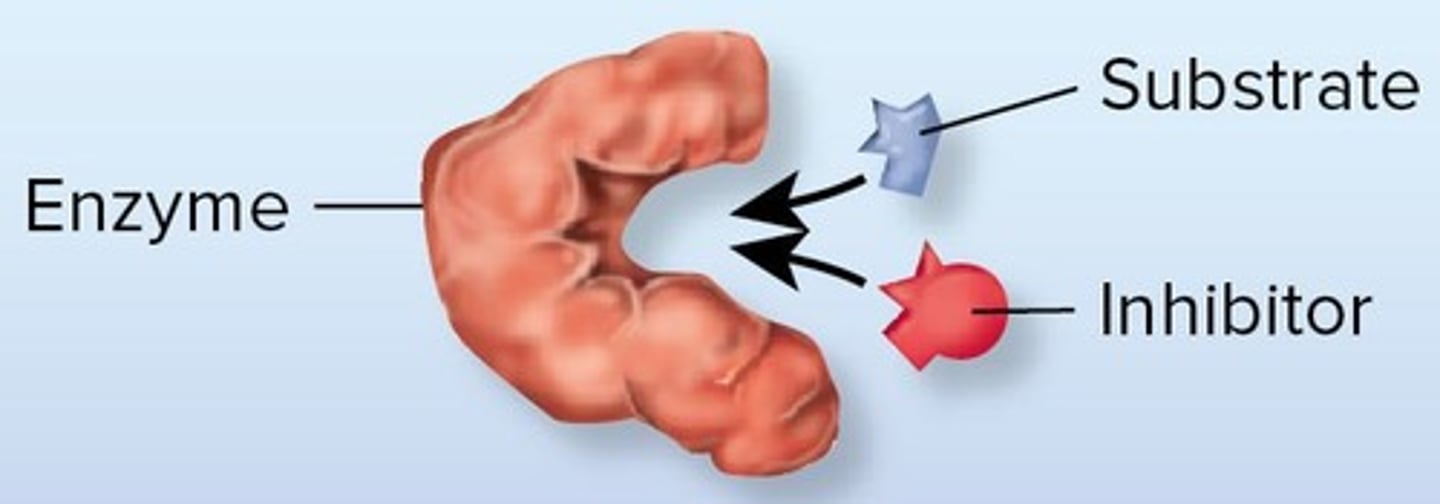
Inhibitor
Substance that decreases enzyme activity.
Allosteric Regulation
Regulation of enzyme activity through binding at a site other than the active site.
Feedback Inhibition
Process where the end product inhibits an earlier step.
Glycolysis
First step in cellular respiration, breaking down glucose.
Krebs Cycle
Series of reactions to produce energy carriers from acetyl-CoA.
Electron Transport Chain
Series of proteins that transfer electrons to produce ATP.
Chemiosmosis
Process of ATP production using proton gradient.
Fermentation
Anaerobic process to produce energy without oxygen.
Photosystems
Protein-pigment complexes in chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll
Green pigment involved in photosynthesis.