nurse cheung: mitosis vs meiosis and gentetics teas
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
mitosis
cell division that results in 2 daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes
starting cell in mitosis (diploid cell) 2n
meiosis
cell division that results in 4 daughter cells each half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell
starting cell meiosis (diploid cell) 2n
primary spermatocyte (males)
primary oocyte (females)
(mitosis and meiosis) both have 2 sets of chromosomes
46 total chromosomes
23 from mom
23 from dad
mitosis
PMAT
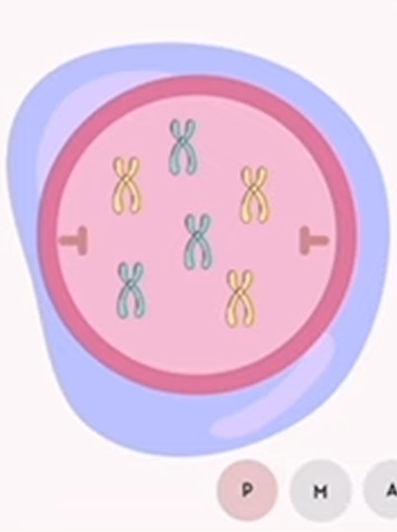
mitosis: prophase
pro=before
chromosomes become visible as they condense and thicken
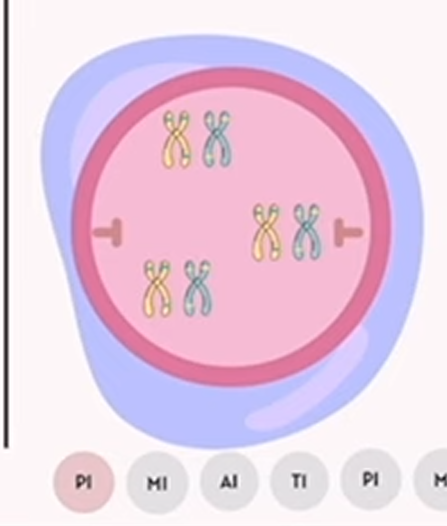
meiosis: prophase 1
chromosome condensation and pairing of homologous chromosomes
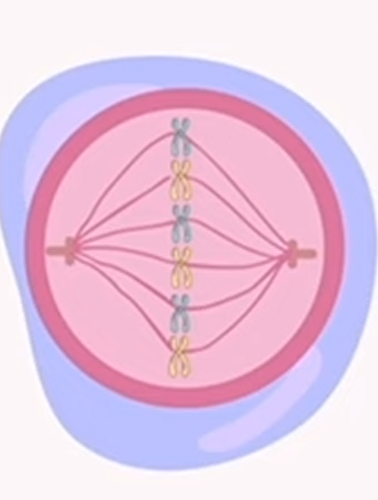
mitosis: metaphase
m = middle
chromosomes align in the middle of the cell’s center, forming a single row
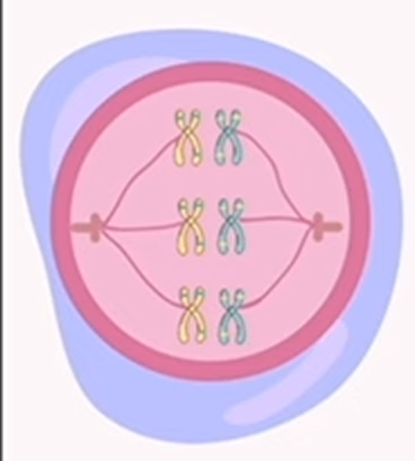
meiosis: metaphase 1
chromosomes align in the middle of the cell’s center, maintaining their homologous pairs
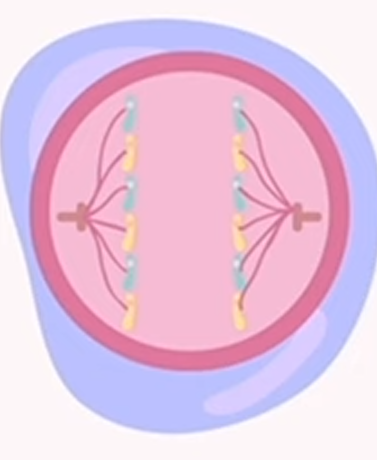
mitosis: anaphase
a = away
chromatids are separated and drawn to the opposite ends of the cell by spindle fibers
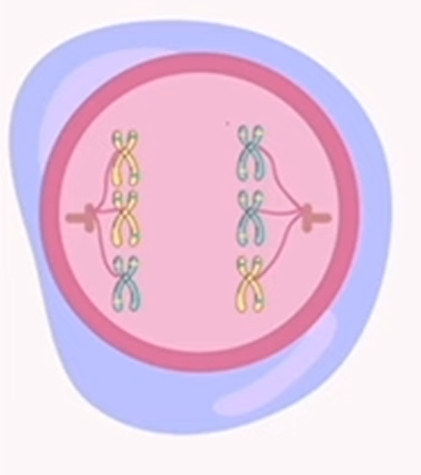
meiosis: anaphase 1
chromosomes are separated and drawn to the opposite ends of the cell by the spindle fibers
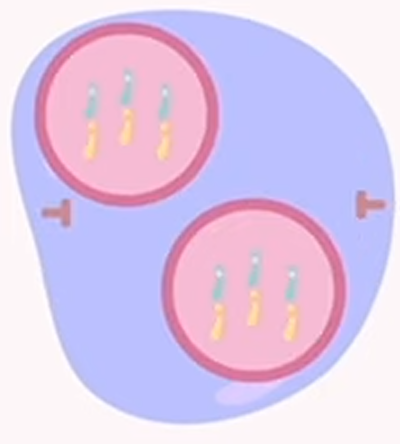
mitosis: telophase
chromosomes reach the opposite sides if the cell, forming new nuclear envelopes around the chromosomes
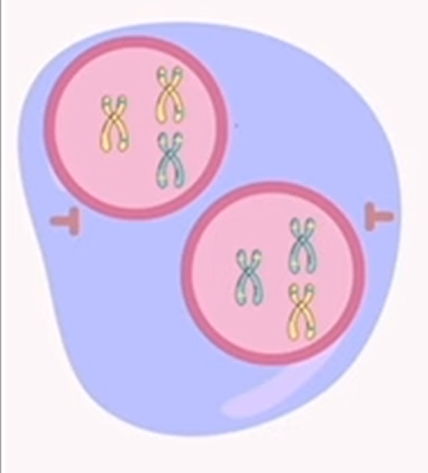
meiosis: telophase 1
chromosomes reach the opposite sides of the cell, forming new nuclear envelopes around the chromosomes
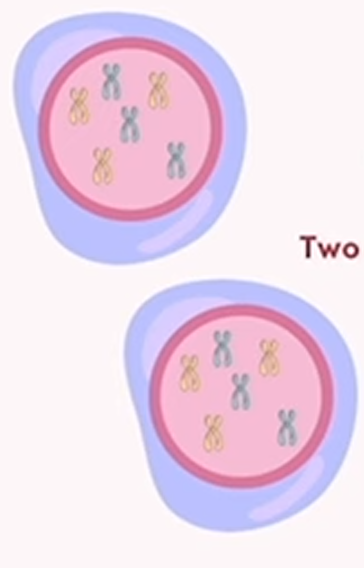
mitosis: cytokinesis
splits the cytoplasm of the cell
2 identical, diploid cells
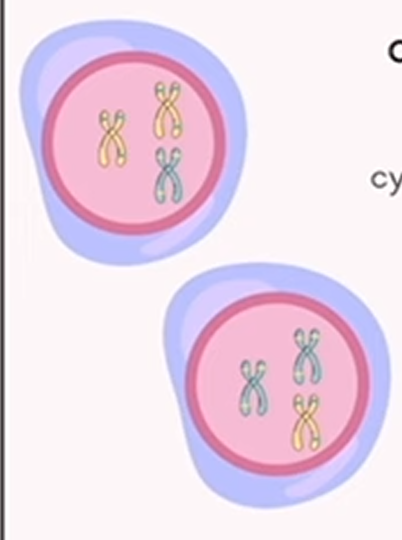
meiosis: cytokinesis
splits the cytoplasm of the cell
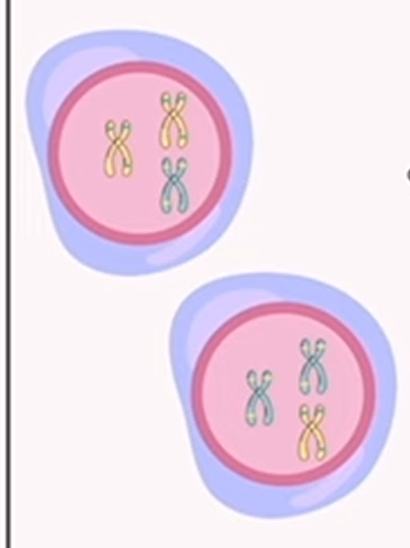
meiosis: prophase 2
chromosome condensation in both cells
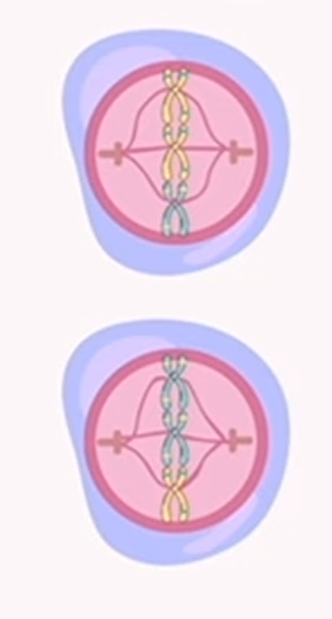
meiosis: metaphase 2
chromosomes align in the middle of the cell’s center, forming a single row
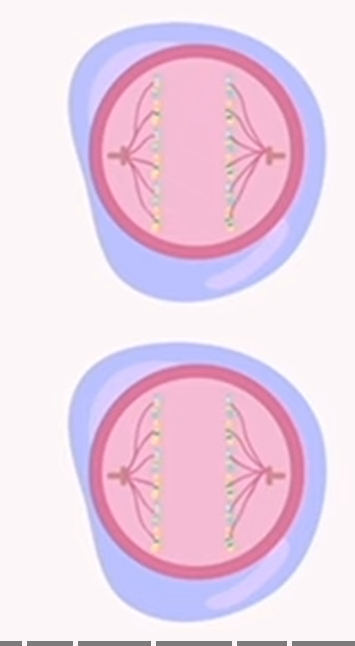
meiosis: anaphase 2
chromatids are separated and drawn to the opposite ends of the cell by spindle fibers
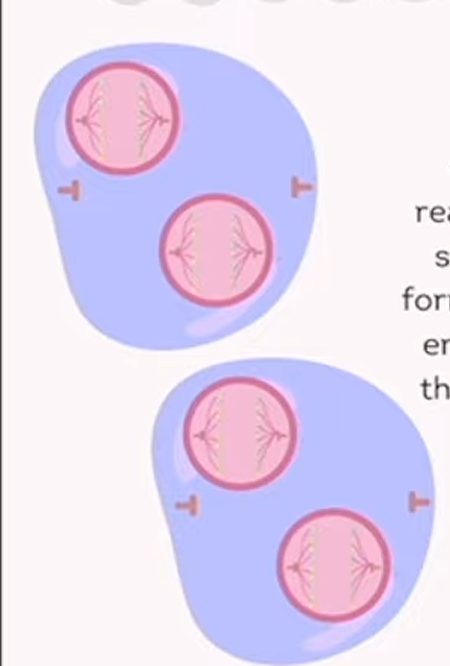
meiosis: telophase 2
chromosomes reach the opposite sides of the cell, forming new nuclear envelopes around the chromosomes
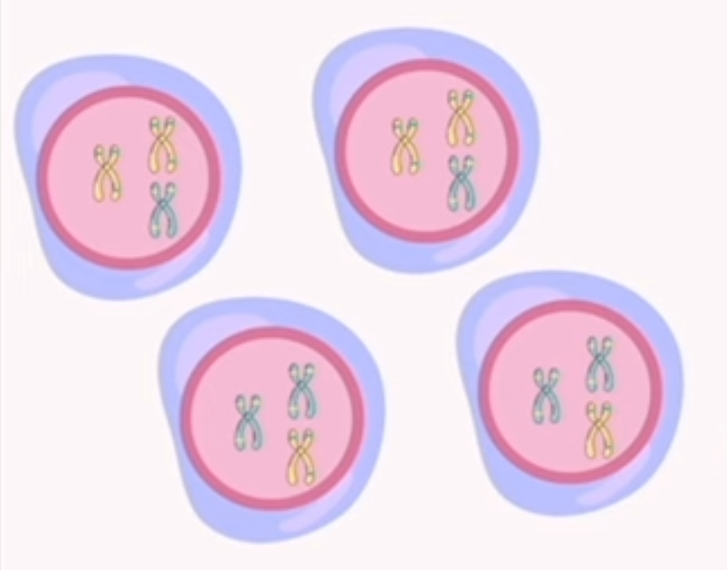
meiosis: cytokinesis
splits the cytoplasm of the cell
4 non-identical cells (gametes)
23 chromosomes
haploid cells
heredity
the passing on of physical or mental characteristics genetically from one generation to another
(height, eye color, risk for certain diseases, hair color)
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
self replicated material that is present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes
composed of phosphate, deoxyribose (a sugar), and nitrogenous base (code for traits)
nucleotide bases
held together with hydrogen bonds
DNA nucleotide bases
adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine
adenine
thymine
cytosine
guanine
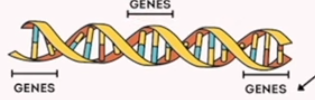
genes
a unit of heredity which is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristics of the offspring
protein can code for genes
structural genes
eye/hair color
transport
structure
enzymatic activity
defense mechanisms
plus more
regulatory genes/gene regulation
used to control the timing, location, and amount in which genes are expressed
genes can be activated and deactivated through various mechanisms
chromosomes
a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes
-made up of DNA
-humans have 46 chromosomes
-23 chromosomes from mom
-23 chromosomes from dad
which of the following best describes the function of regulatory genes in gene expression?
they produce proteins or RNAs that control the expression of other genes
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
a nucleic acid present in all living cells whose principal role is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling synthesis of proteins
present inside and outside the nucleus
-different sugar base (ribose, a sugar)
RNA nucleotide base
adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine
(messenger) mRNA
carries genetic information to make proteins
(ribosomal) rRNA
serve as a location for protein sytheisis
(transfer) tRNA
an adaptor molecule that decodes a mRNA into a protein
polypeptide chain
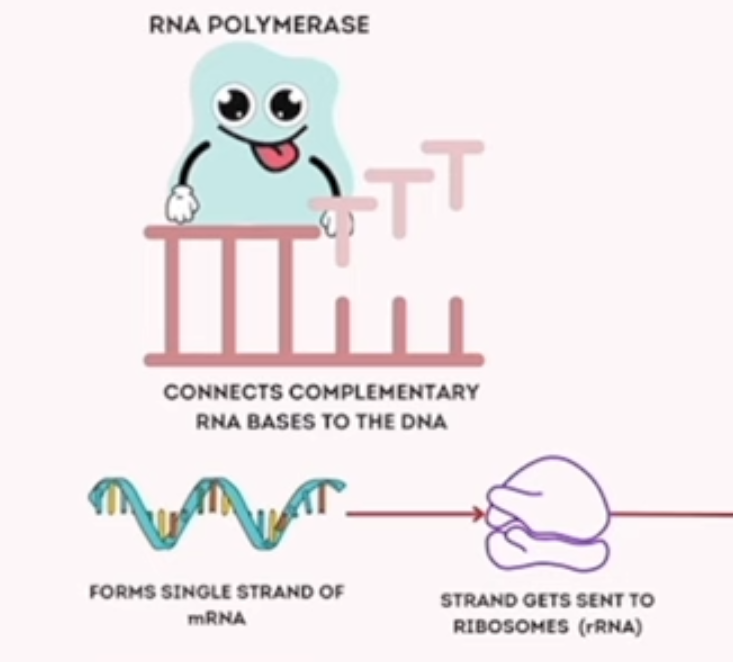
transcription
process of making an RNA copy of a gene’s DNA sequence
C comes before L
transcription comes before translation
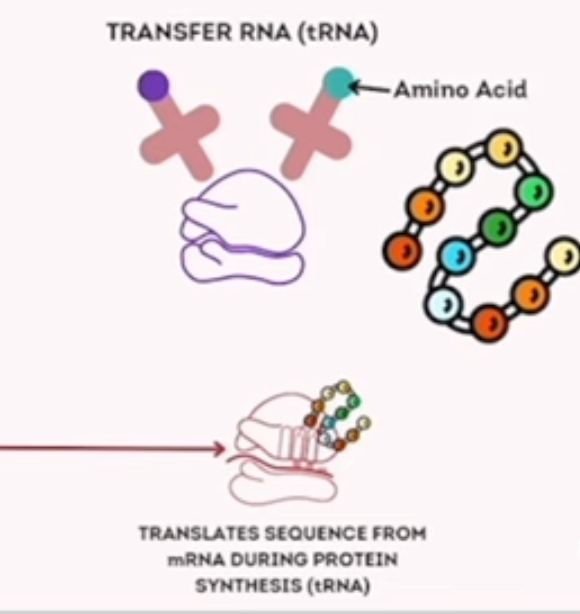
translation
process of translating the sequence of a mRNA to amino acids during protein synthesis
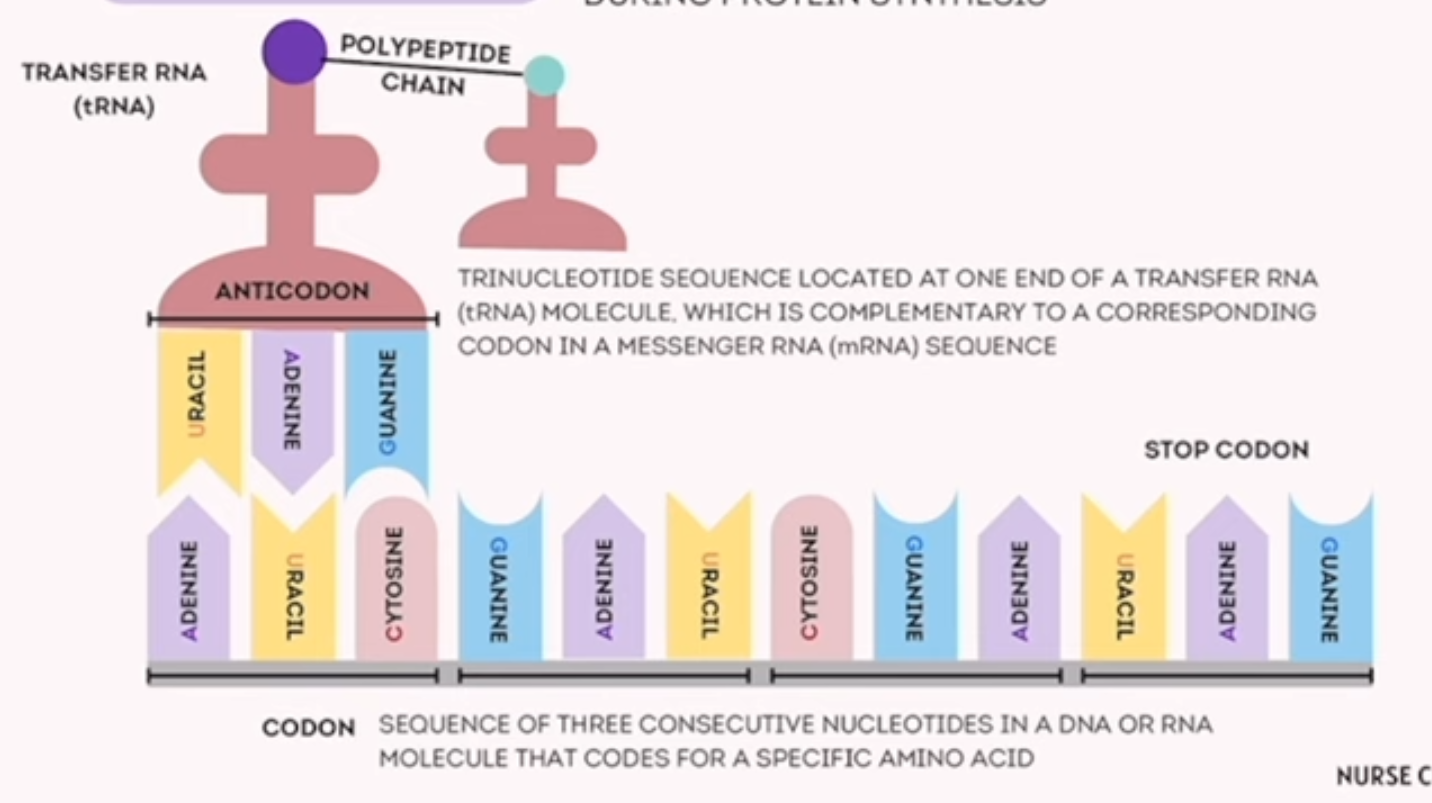
codon
sequence of 3 consecutive nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule that codes for a specific amino acid
which component is essential for initiating the transcription of a gene into mRNA in eukaryotic cells
RNA polymerase
what is the role of mRNA in protein synthesis?
it serves as a template for assembling amino acids into proteins