Bilateral Disc Edema
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
priciple pathophysiologic finding in optic disc edema?
blockage of axonal transport
what 2 factors cause axonal flow blockage?
where does the blockage usually occur?
mechanical
vascular
occurs at the level of the lamina & results in intr-axonal swelling
what causes optic disc edema (2 possible things)
any event that:
increases venous pressure at or near the lamina cribrosa
anything that mechanically or physically blocks axoplasmic flow
what are the 3 bilateral optic disc edemas
malignant papilledema
idiopathic intracranial hypertension
neuromyelitis optica
papilledema is referred exclusively for ____
when the optic disc edema is secondary to elevated intracranial pressure
increased intracranial pressure can be caused by what 5 mechanisms?
when the skull is too small for brain (craniostynoses - birth)
brain volume too large for skull (space occupying lesion or brain edema)
obstruction of CSF flow
increased production of CSF
reduced absorption of CSF
optic disc appearance changes in papilledema (3)?
changes at ONH - RNFL opacification, elevation of the margins, hyperemia, obliteration of the cup
vascular congestion - venous dilation, vascular tortuosity, hemorrhages, cws, exudates
mechanical features - retinal folds (paton’s lines), choroidal folds due to posterior globe deformation
what do spontaneous venous pulsations (SVPs) tell you
if present, ICP not high —> nerves are not elevated bc of high IP
if absent, ICP is high —> but not necessarily causing elevated disc
stages of ODE
stage 0 - normal ON with blurred margin
stage 1 (very early) - nasal border of disc obscured, no elevation of borders, radial NFL arrangement disrupted, gray opacity accentuating NFL bundles, normal temporal disc margin
stage 2 (early) - obscuration of all borders, elevation of nasal border, complete peripapillary halo
stage 3 (moderate) - obscuration of all borders, increased diameter of ONH, obscuration, peripapillary halo-irregular outer fringe with finer-like extensions.
stage 4 (marked) - obscuration of all borders, elevation of the entire nerve head, total obscuration on the disc of a segment of a major vessel.
stage 5 (severe) - dome-shaped protrusions (represents anterior expansion of the ONH), peripapillary halo is narrow & smoothly demarcated, total obscuration of a segment of a major BV may or may not be present. Obliteration of the optic cup.
symptoms of papilledema
may be asymptomatic
may have systemic symptoms (nausea, vomiting, headaches, pulsatile tinnitus)
may have visual symptoms (transient visual obscuration, peripheral VF loss that can progress to central, double vision from 6th nerve palsy)
signs
normal VA
enlarged blind spot on VF
6th nerve palsy
RNFL thickness map would show what?
thick NFL layer
what neuro imaging would you do?
immediate and urgent CT scan to rule out space occupying lesion
lumbar puncture to confirm elevated CSF & analyze its composition
MRI & MRV (less urgent) to confirme elevated CSF
management
manage underlying cause of elevated IP
medication to lower IP
chronic edema leads to ____
axon loss with the development of secondary optic nerve atrophy
what is the primary ocular finding in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
papilledema
idiopathic intracranial hypertension more likely among?
women of childbearing ages with HIGHER BMIs
risk factors for idiopathic intracranial hypertension
systemic conditions: obstructive sleep apnea, hypothyroidism, anemia, addison disease, SLE, behcet’s, polycystic ovary syndrome, coagulation disorders
certain medications: tetracyclins, oral contraceptives, vitamin A, lithium, anabolic steroids
idiopathic intracranial hypertension symptoms
headache- MOST COMMON symptom
transient vision loss
pulsatile tinnitis (whooshing sound)
visual disturbance
horizontal diplopia (if 6th cranial nerve palsy)
idiopathic intracranial hypertension diagnostic criteria
signs/sx of ICP (headaches, nausea, vomiting, transient visual obscurations, papilledema)
no localizing neurologic signs, except unilateral or bilateral 6th cranial nerve palsy
CSF opening pressure >25 cm
no evidence of hydrocephalus, mass, structural, or vascular lesion on imaging
no other cause of ICP identified
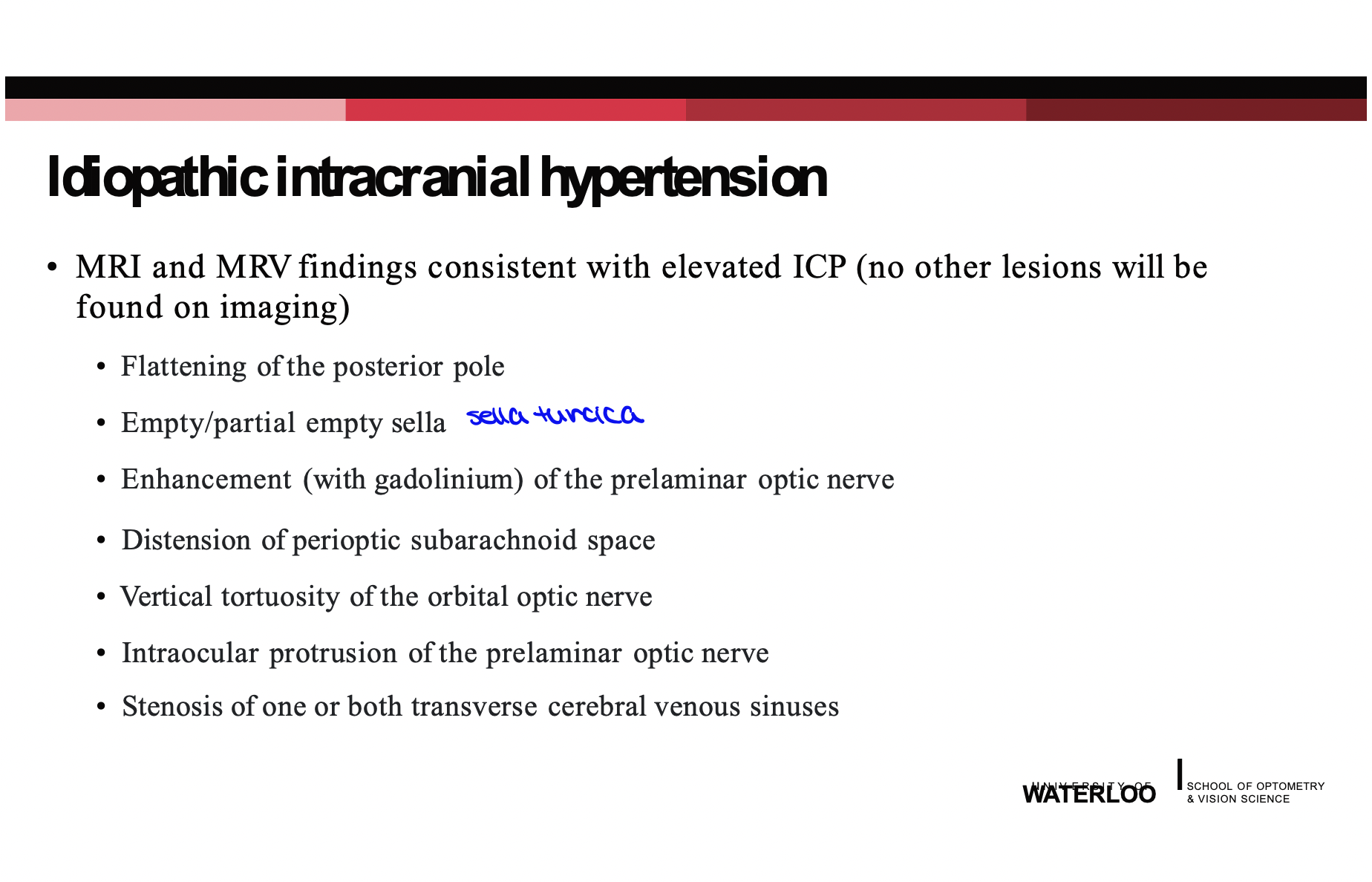
MRI and MRV findings consistent with elevated ICP
idiopathic intracranial hypertension management
lower ICP
weight loss if higher BMI
surgical intervention (CSF shunt or venous sinus shunting)
prognosis of idiopathic intracranial hypertension
permanent vision loss is possible depending on severity of papilledema
recurrence may occur in 3-8% of ppl within weeks-years of initial presentation