EXAM 2- Hussein (REVIEW+ SG)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Helicobacter pylori is known to cause what condition?
peptic ulcer


For H. pylori, list 2 virulence factors and 3 tests that can be used for diagnosis.
virulence factors
VacA (vacuolating cytotoxin A)
CagA (cytotoxin-associated gene A)
tests
urea breath test
stool antigen test
confirmation tests (for urease, catalase, and oxidase)
How do VacA and CagA act as virulence factors? What allows CagA to get into cells?
VacA- causes cell death of gastric epithelium
CagA- disrupts tight junctions between cells
TSS4 allows CagA to get into cells
For Brucellosis what is found in animal placentas that stimulates this bacteria’s growth?
erythritol
For each of the following list the host they infect:
Brucella melitensis
Brucella abortus
Brucella suis
Brucella melitensis- goat, sheep
Brucella abortus- cow
Brucella suis- sow (female pig)

Francisella tularensis causes what zoonotic disease (zoonosis)? How is it transmitted? Why would there be a lab alert?
causes TULAREMIA (sounds similar to bacteria name)
transmission- rabbit, tick, ingestion of contaminated meat, aerosols
lab alert—> BC EXTREMELY infectious

What are the symptoms of tularemia caused by Francisella tularensis?
splenomegaly (enlarged spleen)
hepatomegaly (enlarged liver)
How is Rickettsia rickettsii transmitted?
What disease does it cause?
Symptoms?
transmission: tick
disease: rocky mountain spotted fever
symptoms: rash on the palms

How is Rickettsia prowazekii transmitted?
FYI: What disease does it cause?
transmission: lice
FYI not in the sg—> disease: epidemic typhus

How is Orientia (Rickettsia) tsutugamushi transmitted?
FYI: What disease does it cause?
transmission: mite (chiggers)
FYI not in the sg—> disease: scrub typhus

How is Coxiella burnetti transmitted?
You can’t have what?
What disease does it cause?
transmission: inhlation, direct contact, handling of fetal tissue/products of conception
no vector milk products
disease: Q fever
There are 3 main strains of Bartonella bacteria—> quintana, baciliformis, henselae. List the disease(s) each of them cause:
B. quintana- TRENCH fever
B. baciliformis- PERUVIAN fever, MASSIVE anemia
B. henselae- CAT SCRATCH fever

How are B. quintana and B. baciliformis transmitted?
B. quintana- lice feces
B. baciliformis- sandfly
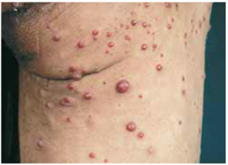
Bartonella henselae is associated with what condition, common in immunocompromised, characterized by the proliferation of small blood vessels? HOW IS IT TREATED?
bacillary angiomatosis—> erythromycin
Chlamydia trachomatis is the leading cause of…
preventable blindness
Some subtypes of chlamydia trachomatis can cause what infection? What are the symptoms?
LGV!!!
symptoms:
groove’s sign
buboes (enlarged lymph nodes)
vesicles on penis
Which is the most common and second most common STI?
chlamydia—> most common
gonorrhea—> 2nd most common
WHAT can C. trachomatis cause in INFANTS? transmitted how?
inclusion conjunctivitis (eye infection)
infant pneumonia syndrome
transmitted mom—> baby during vaginal delivery

What is the cause of vancomycin resistance in E. faecalis or S. aureus? Does it use acquired or intrinsic resistance?
the terminal D-alanine changed to D-lactate- acquired in the cell wall
Resistance can either be acquired or intrinsic. Describe acquired resistance:
by using plasmids or genetic transfer mechanisms like transposon, horizontal spread (conjugation, transduction, transformation)
Answer the following about beta-lactam antibiotics:
examples
most effective during _____ phase
mechanism of resistance in e.coli?
exs: penicillins, cephalosporins
most effective during log phase
mechanism of resistance in E.COLI—> make new porins
= decreases beta-lactam permeability
Augmentin is a combination of what? Which one is a suicide inhibitor?
Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid
clavulanic acid—> suicide inhibitor of beta-lactamase
Answer the following about Rifampin:
mechanism of action
mechanism of resistance
MOA: RNA polymerase inhibitor (stops transcription)
MOR: RNA polymerase becomes insensitive= Rifampin can’t bind to RNA polymerase
Answer the following about Quinolone:
mechanism of action
mechanism of resistance
MOA: Gyrase inhibition (deals with coiling of DNA)
MOR:
mutation of gyrase genes
alteration of membrane permeability to quinolones (can’t get in)
efflux
mobile elements with qnr gene (encodes a protein that protects DNA gyrase from quinolones)
REVIEW (not in sg):
What does “efflux” have to do with resistance to antibiotics?
basically overexpression of efflux pumps= pumps the abx out of the cell = aka then it won’t work!!!!!

Answer the following about Tetracycline:
mechanism of action
mechanism of resistance
MOA: binds to 30S subunit—> blocks binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to mRNA translation complex—> protein synthesis is inhibited
(basically: blocks the step in protein synthesis from transcription to translation)
MOR: efflux pump
Answer the following about Chloramphenicol:
mechanism of action
mechanism of resistance
MOA: binds to the 50S subunit—> no peptide bond formed—> protein synthesis is inhibited
MOR:
resistance is PLASMID mediated
acetylation of CAT
(basically these bacteria add acetyls to the ribosome where the abx binds—> this make it so the binding affinity of the abx is reduced)

Answer the following about Macrolides and Lincosamides:
mechanism of action
mechanism of resistance
MOA: inhibit peptide chain elongation
MOR:
resistance is PLASMID mediated
ribosome methylation
(basically these bacteria add methyls to the ribosome where the abx binds—> this make it so the binding affinity of the abx is reduced)
Answer the following about Sulfonamides:
mechanism of action
mechanism of resistance
MOA: competitive PABA inhibitor—> inhibits dihydropteroate synthase
(by inhibit dihydropteroate synthase—> messes with folic acid synthesis needed for DNA synthesis)
MOR:
PABA overproduction (outcompetes the abx)
making insensitive enzyme (reduces binding affinity of abx)
making more enzyme (overcomes abx)

Answer the following about Trimethoprim:
mechanism of action
mechanism of resistance
MOA: competitive inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase (needed for DNA synthesis)
MOR:
PABA overproduction (outcompetes the abx)
making insensitive enzyme (reduces binding affinity of abx)
making more enzyme (overcomes abx)
Answer the following about Aminoglycosides:
mechanism of action
mechanism of resistance
MOA: inhibit f-Met-tRNA—> inhibit protein synthesis
MOR: drug modification by the bacteria—> can’t get inside the bacteria/ inactive (transport inhibition)
Answer the following about Mycobacterium tuberculosis:
cause of what disease?
what test to detect?
what is found in its cell wall?
virulence factor? result?
tuberculosis
PPD test
mycolic acid
virulence: cord factor —> inhibits phago-lysosome fusion in macrophages
MRSA occurs because of
synthesis of PBP with a lower affinity for b-lactams
Borrelia recurrentis is responsible for what disease? how is it transmitted?
responsible for relapsing fever
transmission—> lice
Answer the following about Pseudomonas aeruginosa:
gram +/-
oxidase +/-
resistance mechanism?
causes what infections in what pt. populations?
gram -
oxidase +
resistance due to membrane IMPERMEABILITY
Cystic fibrosis pts. suffer severe respiratory infections
burn wound pts. susceptible

What does Chlamydia psittaci cause? transmission? why is it a hazard?
causes respiratory infections
transmission: parrots
occupational hazard for bird handlers/pet shop workers, etc.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae both can cause what disease? WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THEM?
both cause protracted (long) WALKING PNEUMONIA
difference
M. pneumoniae has NO INCLUSIONS
C. pneumoniae HAS INCLUSIONS
FYI: inclusions are aggregates of bacteria in respiratory samples
What characteristic of M. pneumoniae makes it resistant to beta-lactams?
no peptidoglycan
M. genitalium is the cause of what infection? Describe the infection? What characteristic of M. genitalium makes it resistant to beta-lactams?
causes NG (non-gonococcal) urethritis
recurrent
grows in cell-free media
NO PG like M. pneumoniae
M. hominis AND U. urealyticum are the cause of what disease in what population? where?
causes meningitis in preterm infants
where? CSF