Anaerobic/Aerobic Respiration 1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Describe the structure of mitochondria.
1-10um in size
Mitochondria have a double-membrane structure with an outer smooth membrane and a highly folded inner membrane forming cristae, which increases surface area for ATP production. These membranes enclose the intermembrane space and the inner matrix, a gel-filled space containing enzymes, ribosomes (For protein synthesis), and mitochondrial DNA, essential for cellular respiration.
What are mitochondrial networks?
Mitochondrial networks are complex, dynamic, interconnected structures formed by mitochondria constantly fusing and dividing within a cell, acting as central hubs for energy production, metabolism, and cell signaling.
Describe the differences between Nuclear DNA vs. Mitochondrial DNA.
Nuclear DNA
Double helix, large
Encodes 20,000 protein coding genes
Located inside the nucleus
Mitochondrial DNA
Circular, double-stranded DNA, extracellular source of DNA, found within the mitochondria
mtDNA contains 37 total genes, not all protein-coding
13 protein-coding genes
Components of the oxidative phosphorylation (Ox Phos) system
22 tRNA genes
2 rRNA genes
Explain the Endosymbiosis Theory.
The endosymbiosis theory says that mitochondria were once free-living bacteria that were swallowed by a larger cell and eventually became a permanent part of it.
Step-by-step, very simply:
A large primitive cell engulfed a small aerobic bacterium.
The bacterium was not digested.
Instead, it:
Made ATP (energy) for the host cell
Got protection and nutrients from the host
Over time, the bacterium lost independence and became the mitochondrion.
Why scientists believe this:
Mitochondria still look like bacteria because they:
Have circular DNA
Have their own ribosomes
Divide by binary fission - similar to bacteria
Have a double membrane - similar to bacteria
How is mitochondrial DNA inherited?
Mitochondrial DNA is inherited only from the mother.
Why?
The egg contains many mitochondria
The sperm contributes almost none (and those are destroyed after fertilization)
So:
All offspring get their mitochondrial DNA from their mother
Both males and females inherit it, but only females pass it on
Why is paternal mtDNA eliminated
Maternal mitochondrial DNA that enters with the sperm during fertilization is destroyed and not passed on.
What actually happens:
Sperm do carry a few mitochondria in the midpiece
After fertilization:
These paternal mitochondria are tagged
They are broken down and eliminated inside the embryo
What structures does the mitochondrial membrane have allowing transport within the structrure?
Porins
Channel proteins in the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM)
Form large, water-filled pores
What they do:
Allow small molecules and ions (≤ ~5 kDa) to freely pass, passively.
Examples:
ATP, ADP
Pyruvate
Ions
TOM = Translocase of the Outer Membrane
Located in the outer mitochondrial membrane
TIM = Translocase of the Inner Membrane
Located in the inner mitochondrial membrane
Both actively import nuclear-encoded proteins across the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes into the matrix, respectively.
What occurs in the inner mitochondria membrane?
Site of oxidative phosphorylation (ATP production)
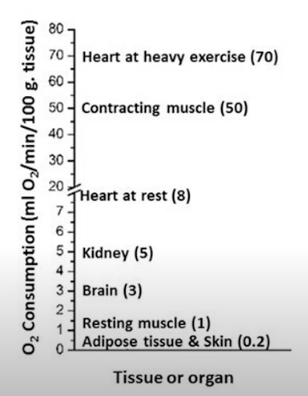
How do mitochondria reflect the energetic needs of particular tissues?
Low metabolic rates = adipose tissue, skin, resting muscle, brain
High metabolic rates = contracting muscle, heart at heavy exercise
Reflects the number of mitochondria
What does it mean in saying “mitochondria are dynamic” (Aka mitochondrial dynamics)?
Mitochondrial dynamics refers to the fact that mitochondria are not static—they are constantly changing shape, size, and number to meet the cell’s needs.
It involves two opposite but coordinated processes:
Fusion → mitochondria join together
Fission → mitochondria split apart
These processes help with:
Energy efficiency
Quality control
Adaptation to stress
Cell survival and apoptosis
What is mitochondrial fussion and why does it happen?
Mitochondrial fusion is when two mitochondria merge into one.
What happens:
Outer membranes fuse
Inner membranes fuse
Contents (proteins, mtDNA, metabolites) mix
Why fusion is important:
Helps dilute damaged components
Allows sharing of mtDNA
Improves ATP production
Supports cell survival during stress
Why it happens:
Mitochondrial fusion occurs to maintain mitochondrial function by mixing contents, improving ATP production, and protecting against cellular stress.
What is an example of diseases which affect mitochondrial fusion?
MFN2 mutations and Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease
Most common inherited neuromuscular disorder. No current drug therapy
In humans: muscle weakness, muscle wasting, hammer toes/fingers
In dogs: Mini snauzzers: mega-esophagus: can get regurgitations, inspiratory dyspnea
What are some of the ways that mitochondria are dynamic?
Cellular migration, fusion, fission, turnover
Can also respond to damage by mitophagy
Respond to energetic requirements: Exercise, hypoxia
Where are mitochondria found within the muscle fiber?
Periphery - to reduce diffusion distance of nutrients and oxygen for cotracting muscles
How does exercise training change mitochondrial health?
Exercise training
Mitochondrial density increased with exercise (OXPHOS increased), you can produce more ATP
Number of capillaries increased
Diffusion index decreased
Correlation between mitochondrial density and max. O2 consumption VO2 max
Correlation between mitochondrial density and run time (treadmill), longer time to exhaustion = greater mitochondrial density
What is the primary function of the mitochondria?
Powerhouse of the cell - generating ATP
Net production = 38mol A TP/mol glucose
Glycolysis in the cytosol produces 2 ATP/mol glucose
Within mitochondria:
Krebs / Citric Acid Cyle
Beta-Oxidation - fatty acids into Acetyl CoA
Formation of components of sex hormones
Formation of components of heme
Calcium homeostasis
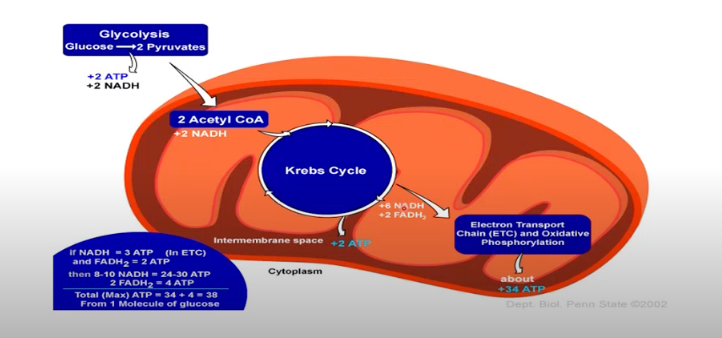
What occurs within glycolysis?
Happens in the cytoplasm
Does not require oxygen
Breaks one glucose into two pyruvate
Makes a small amount of ATP (energy) and NADH
Glycolysis is the cytoplasmic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, producing ATP.
Why is glycolysis called substrate-level phosphorylation?
Glycolysis - substrate level phosphorylation
ATP is made by directly transferring a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP.
Breaking that down simply:
A substrate = an energy-rich molecule made during metabolism
That substrate already has a phosphate attached
The phosphate is directly passed to ADP
This makes ATP, without any membranes or oxygen
What and how does anaerobic metabolism occur?
When oxygen is limited, cells rely on glycolysis in the cytoplasm to produce ATP. Glucose is converted to pyruvate, generating 2 ATP per glucose. Because mitochondria cannot use pyruvate without oxygen, lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate, regenerating NAD⁺ so glycolysis can continue. Lactate accumulates in muscles, causing temporary fatigue, and can later be transported to the liver to be converted back to glucose via the Cori cycle.
More rapid then aerobic metabolism
Used in fight or flight
How do lactate concentrations change with training?
Increasing exercise and work increases level of lactate
But more training produces less lactate over time
What is Type A Lactic Acidosis?
Build-up of (typically) L-lactate in blood leading to excessively low pH
Leading to:
Tissue hypoperfusion and hypoxia
Oxygen consumption/delivery mismatch leading to anaerobic metabolism
Associated with:
Hypovolemia - blood loss
Cardiac failure
Sepsis
Cardiac arrest
What is Type B Lactic Acidosis?
Occurs under normoxia, with no evidence of organ hypoperfusion
Usually drug or toxin interference of cellular metabolism
For Instance:
Cyanide poisoning/alcoholism
Metformin - common drug used to treat diabetes, affects complex I within mitochondria
Mitochondrial disease
Excessive exercise to exhuastion
What is another way Type B Lactic acidosis may manifest within cattle?
Sudden, unaccustomed ingestion of CH-rich feeds in ruminants Grain or concentrates usually (Highly fermentable, lots of sugars, increase the VFAs which alter bacterial growth rates, increasing bacterial which produce lactic acid - leading to a decrease in pH, get dying off of other microbes, increasing lactic acid more).
Leads to:
Colic
Tooth grinding - common sign of pain
Cattle weak and may fall
Laminitis
Profuse diarrhoea
Recumbency
May die in 24-48hrs
What dietary deficiencies may cause lactic acidosis?
Thiamine (Vitamin B1) Deficiency
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex - is a multi-enzyme mitochondrial matrix complex which catalyzes conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA
Deficiency in B1 can reduce ability of Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) which is a cofactor for PDC, which is critical for movement of pyruvate from cytosol into the mitochondria
Can therefore reduce ability of transport protein to get pyruvate into cell, so aerobic metabolism not possible
Causing:
Lactic acidosis, anorexia, cardiac hypertrophy, muscle weakness, convulsions, Opithotonos (star gazing)
How is lactic acid distinct from metabolic acidosis?
In metabolic acidosis, a metabolic processes that produce/manage acids break down is impacted
Example: Antifreeze (Ethylene glycol) ingestion
Is a competitive inhibitor of Alcohol dehydrogenase
Sweet tasting, toxic even if feet/coat contaminated
Breakdown of antifreeze metabolites highly toxic
Glycolic and oxalic acid
Calcium oxalate crystals within the kidney- renal failure
Treatment- ethanol or 4-MP (Fomepizole)
‹ 3hrs for cats
‹ 8-12 hrs for dogs
Summarize the processes of aerobic and anaerobic metabolism and when each occurs.
1. Why aerobic metabolism occurs
Aerobic metabolism is the main way cells make ATP when oxygen is available.
Key points:
Location: mitochondria
Starting molecule: glucose → pyruvate
Process: Pyruvate enters mitochondria → converted to acetyl-CoA → Krebs cycle → NADH/FADH₂ → electron transport chain → oxidative phosphorylation
Oxygen’s role: Final electron acceptor in the ETC (O₂ + e⁻ → H₂O)
ATP yield: ~30–32 ATP per glucose (much higher than glycolysis alone)
Summary:
Aerobic metabolism efficiently converts glucose to ATP because oxygen allows pyruvate to enter the mitochondria and fully oxidize into CO₂ and H₂O.
2. When anaerobic metabolism takes over
Anaerobic metabolism occurs when:
Oxygen is limited (e.g., intense exercise, hypoxia, ischemia)
Mitochondria cannot use pyruvate in the Krebs cycle/ETC
Result: Cells rely on glycolysis alone to generate ATP.
Glucose → 2 pyruvate (glycolysis, 2 ATP)
Problem: Glycolysis uses NAD⁺ → must be regenerated
Solution: Pyruvate → lactate (via lactate dehydrogenase), regenerating NAD⁺ so glycolysis can continue
ATP yield: 2 ATP per glucose (much less than aerobic)
Describe the Krebs Cycle.
Occurs within Mitochondrial Matrix
Pyruvate (Glycolysis) from CHO, fats, protein
transformed to Acetyl CoA
Acetyl group oxidised in Krebs cycle
Produces high energy electron donors- 3 NADH, 1 FADH2 (For ETC in oxidative phosphorylation)
Describe the features of ATP.
Adenosine triphosphate
Nucleoside phosphate- ~45 atoms (Small)
Highly unstable molecule - cannot be stored in this form, has to store: ADP+Pi- (ATP synthase) → ATP and H2O
ATP hydrolysed to ADP+Pi (Hydrolization is what produces release of energy)
1. Location
Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane
Complexes I–IV are embedded in this membrane
ATP synthase (Complex V) uses the proton gradient produced by the ETS
2. Main purpose
The complexes transfer electrons from NADH and FADH₂ to oxygen
Pump protons (H⁺) into the intermembrane space → creates a proton gradient (proton motive force), pass through complex V
This proton gradient is then used by ATP synthase to produce ATP (oxidative phosphorylation)
Taking ADP → ATP