Static Occlusion (objectives + highlights + quiz)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Another name for centric cusps? (5 answers)
-working cusps
-functional cusps
-occluding
-supporting
-stamp
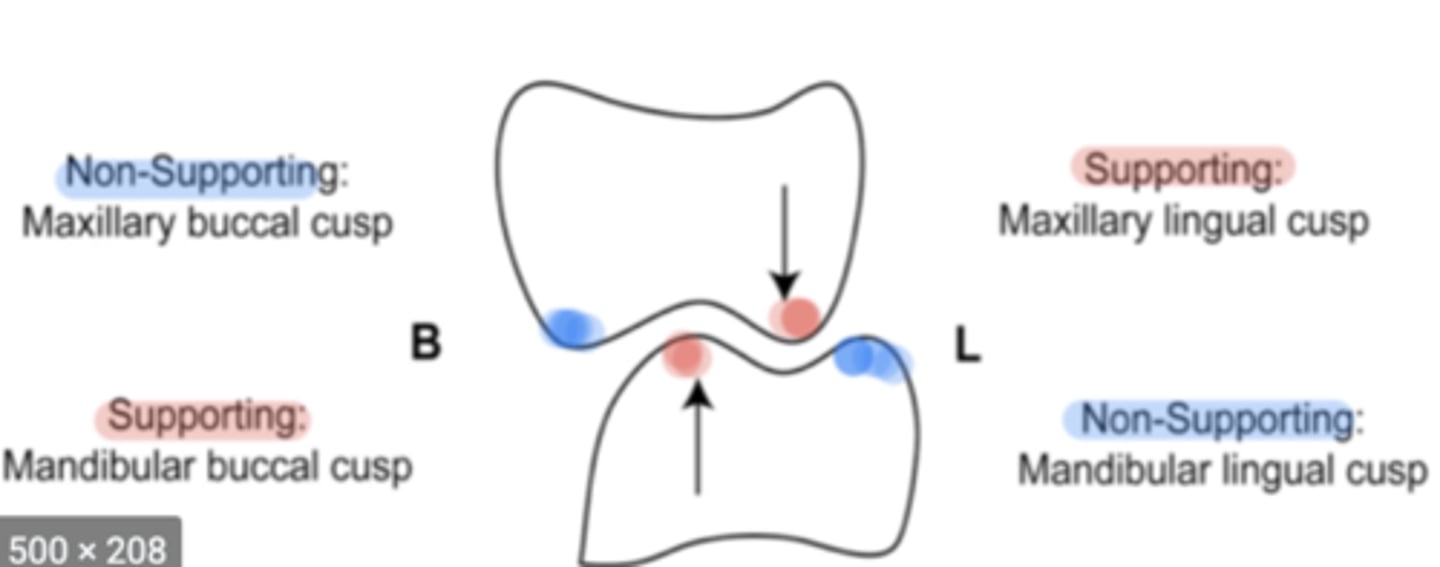
Which cusps are centric cusps?
maxillary lingual cusps and mandibular buccal cusps
The ________ of the centric cusp is the only area of an outer incline with functional significance.
functional outer aspect (FOA)
Another name for non-centric cusps? (4 answers)
-non-working cusps
-non-functional cusps
-shear
-guiding
Which cusps are non-centric cusps?
maxillary buccal cusps and mandibular lingual cusps
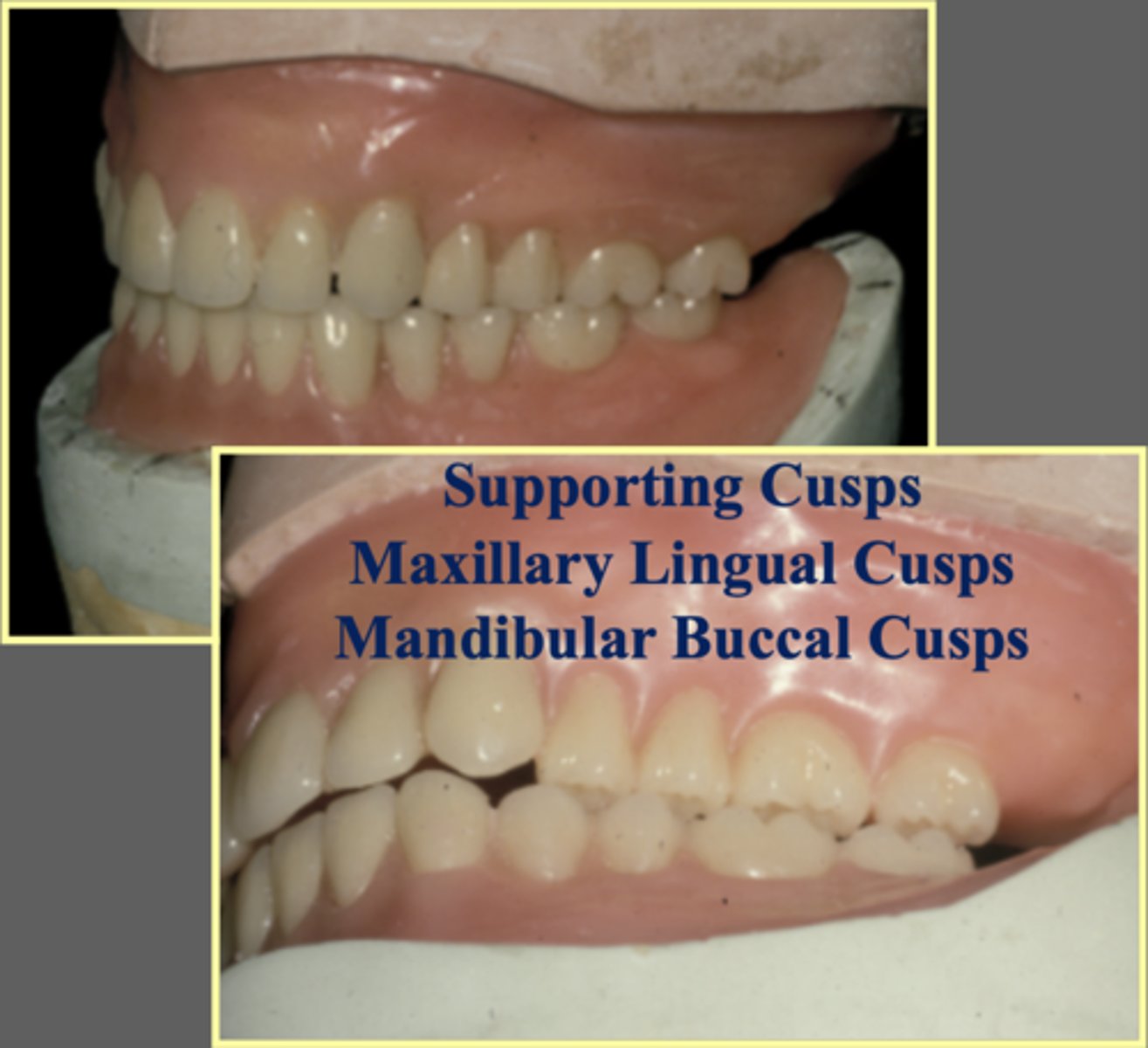
What do centric cusps look like? Function?
-appearance: broad and rounded
-Function: chewing food
(Picture: red = centric/functional cusps)
What do non-centric cusps look like? Function?
-appearance: sharper with defined cusp ridges and tips
-function: mandible stability in occlusion
(Picture: green = non-centric/non-working cusps)
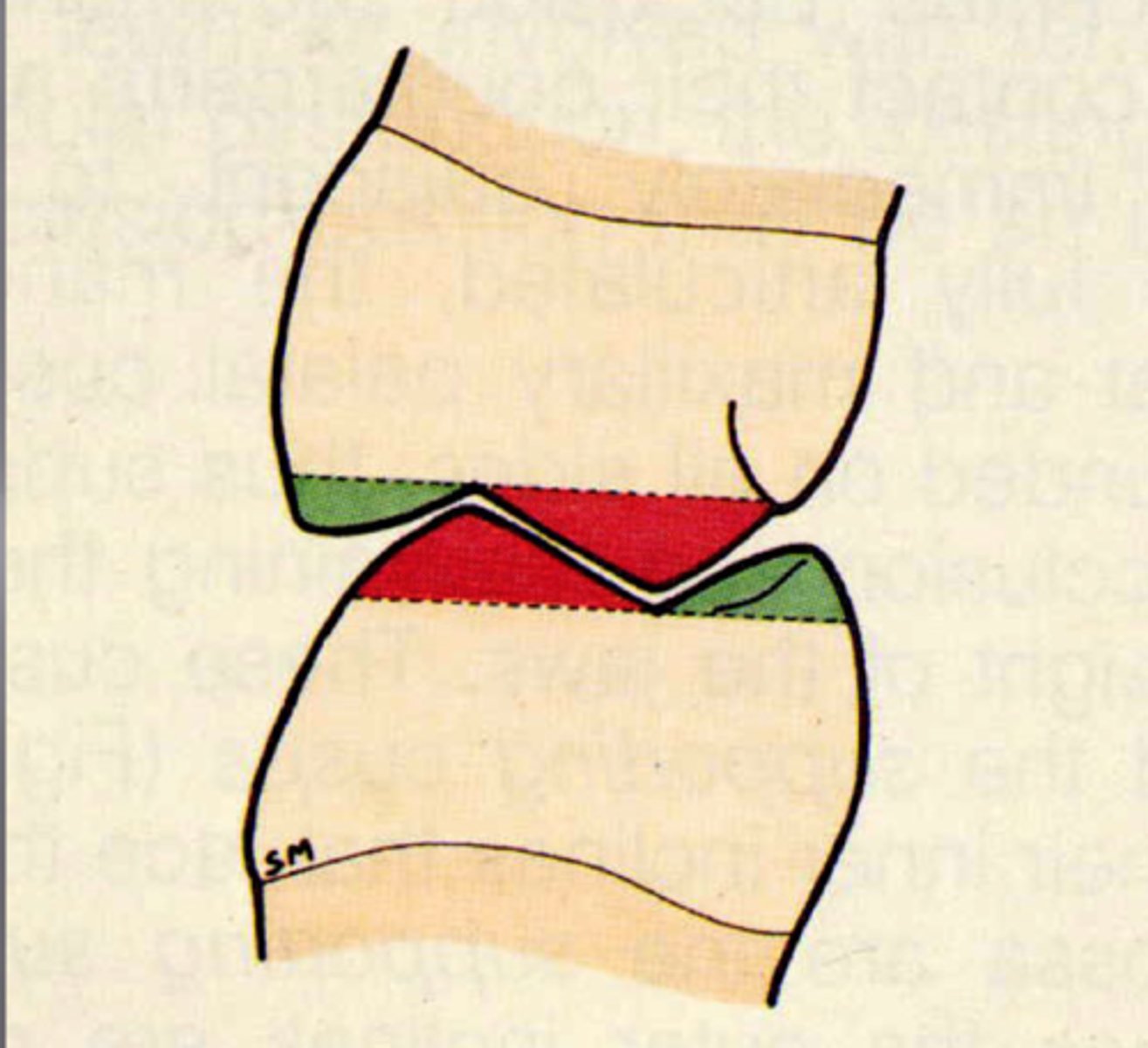
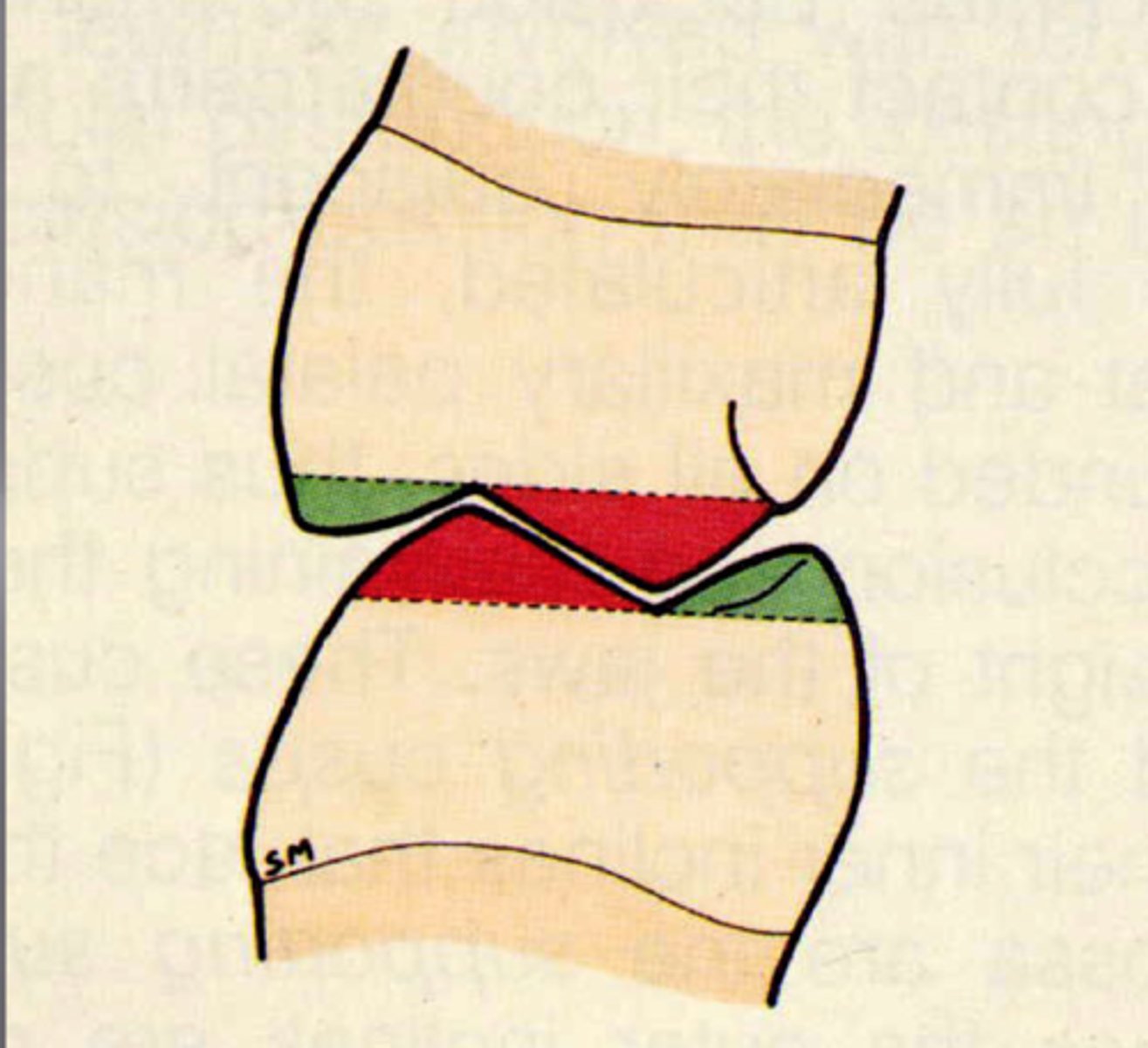
What are centric stops?
Areas of occlusal contact that a supporting cusp makes with opposing teeth in centric occlusion
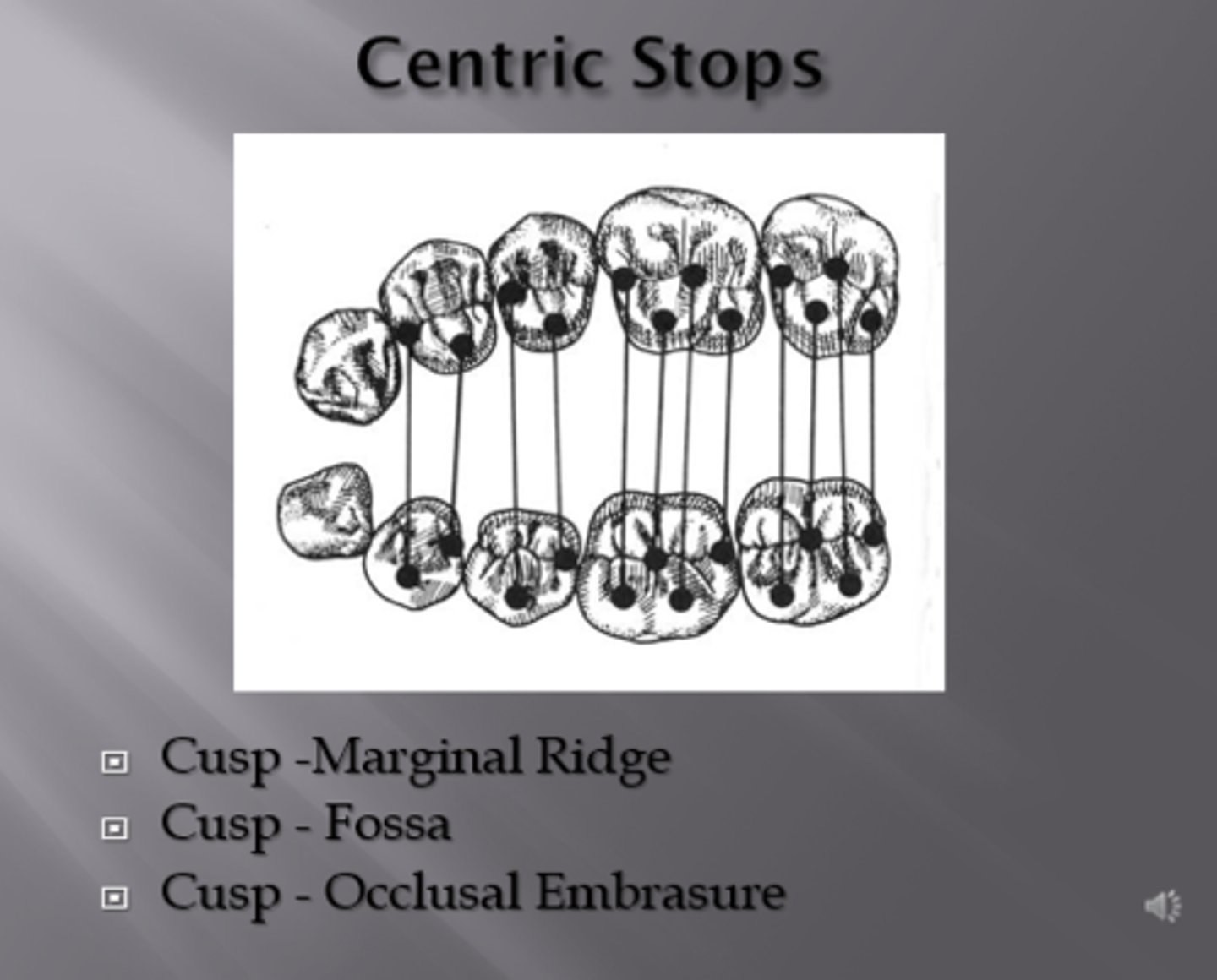
Typically, which centric stop of opposing arches contribute to occlusal stability? (2 answers)
central fossa or marginal ridges

Each tooth opposes 2 teeth in the opposite arch, EXCEPT: (2 answers)
-mandibular central incisors (hits only the maxillary central incisors)
-maxillary third molar (hits only the mandibular 3rd molar)
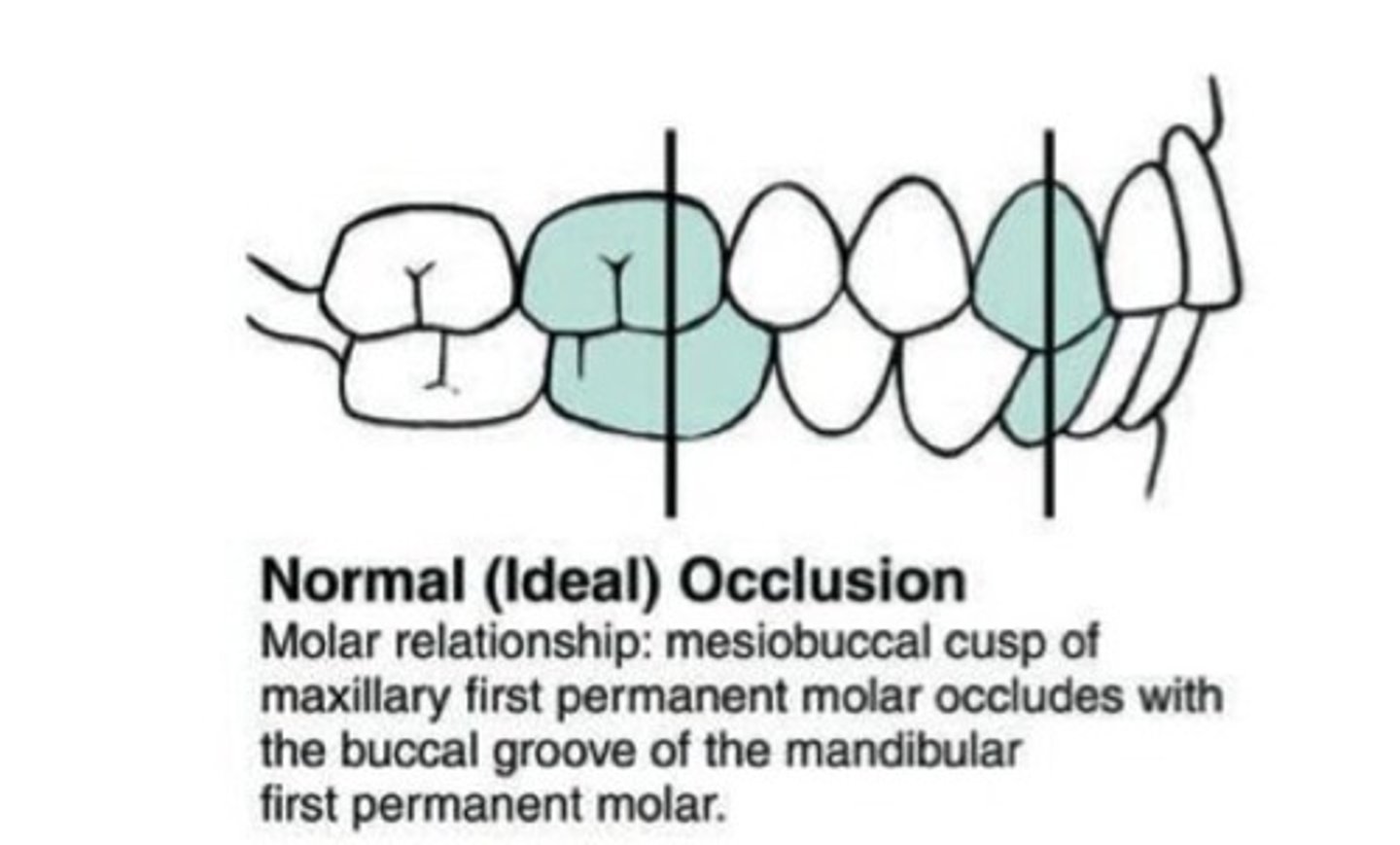
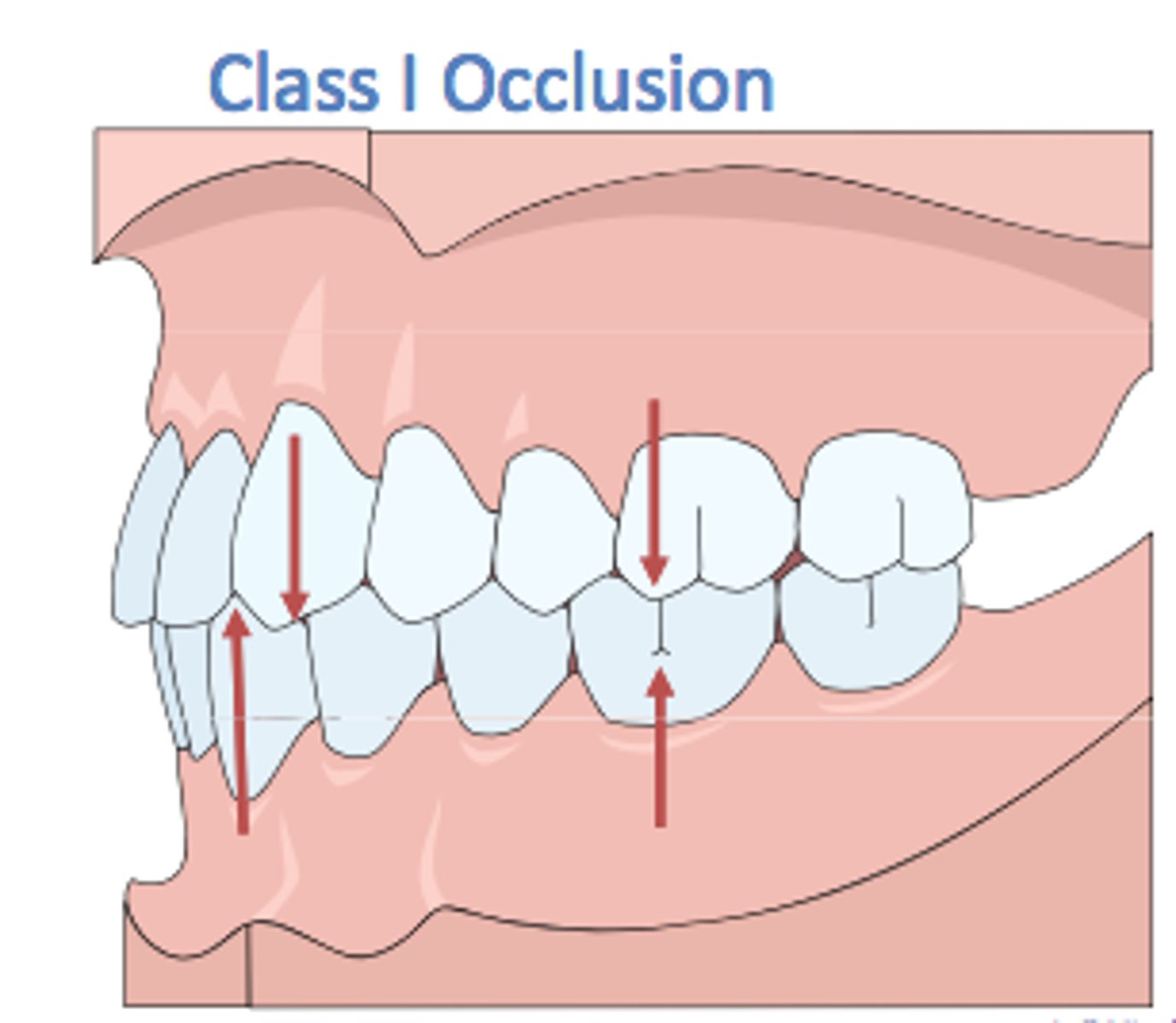
What is a Class 1 occlusion?
a normal relationship between the upper and lower teeth and jaws
(mesial buccal cusp of maxillary 1st molar in the buccal groove of the mandibular 1st molar)
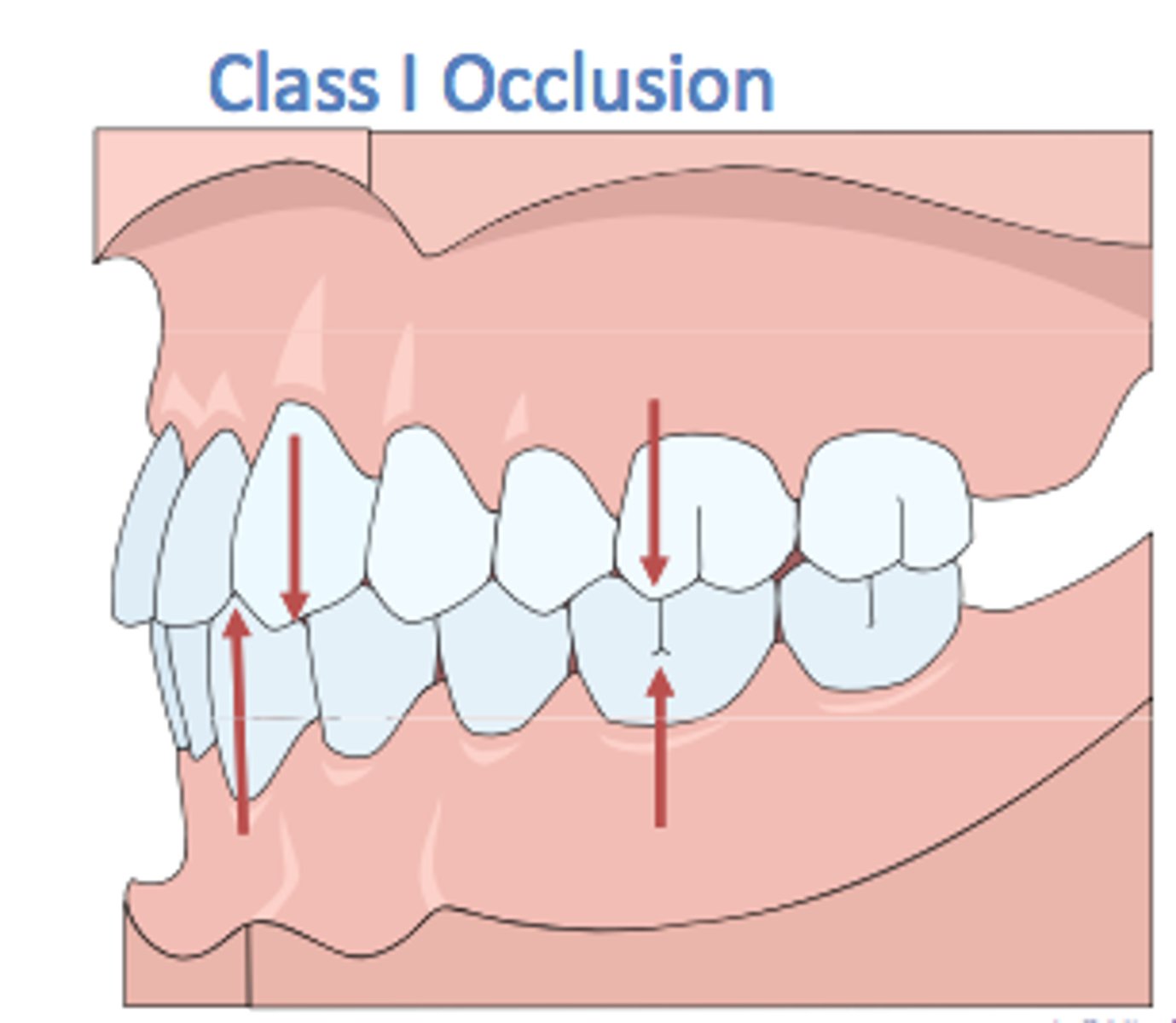
What percentage of people have a normal Class 1 occlusion?
30%
Which class of malocclusion is MOST common?
Class 1
What percentage of people have class 1 malocclusion?
55%
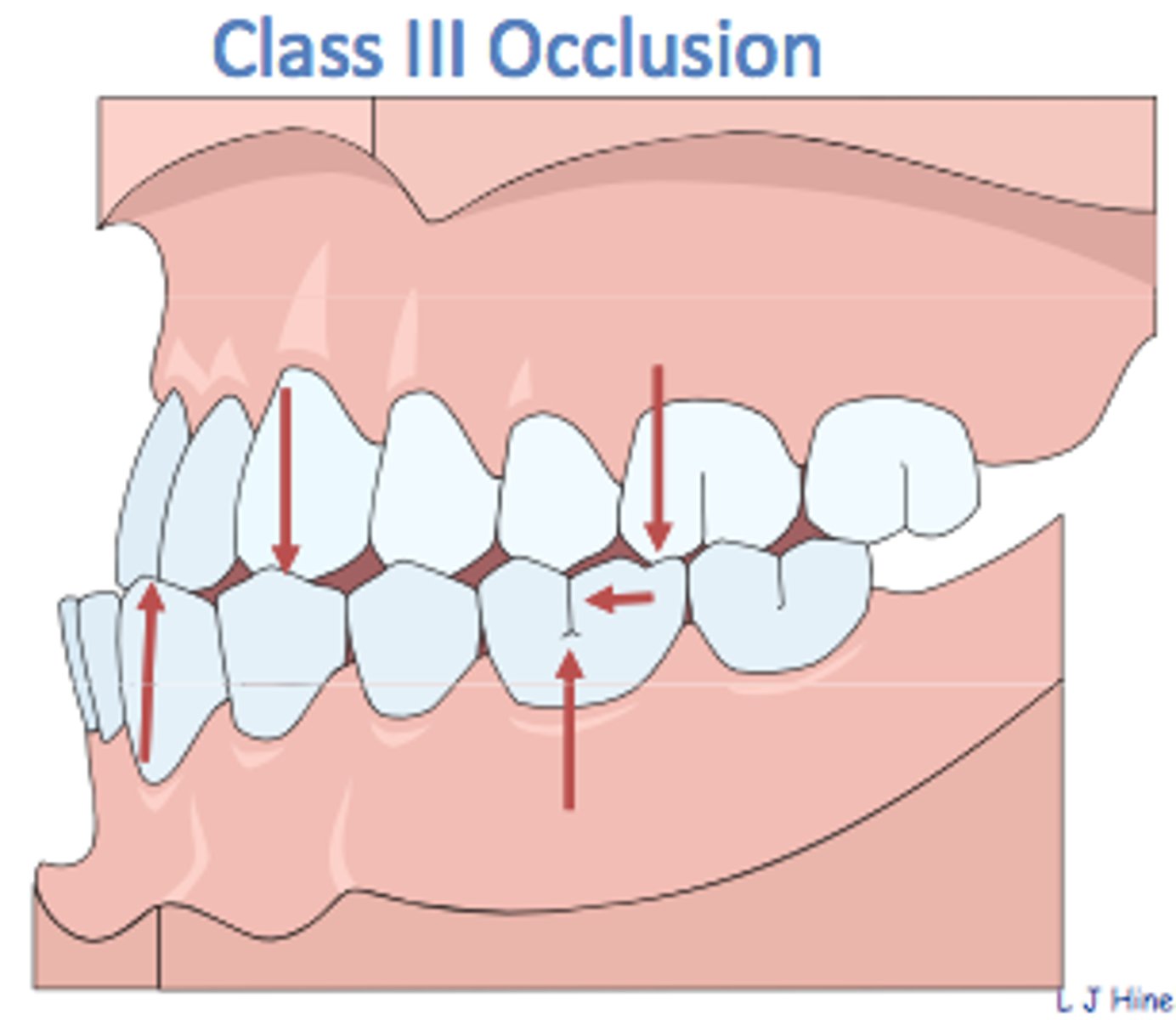
Which class of malocclusion is LEAST common?
Class 3
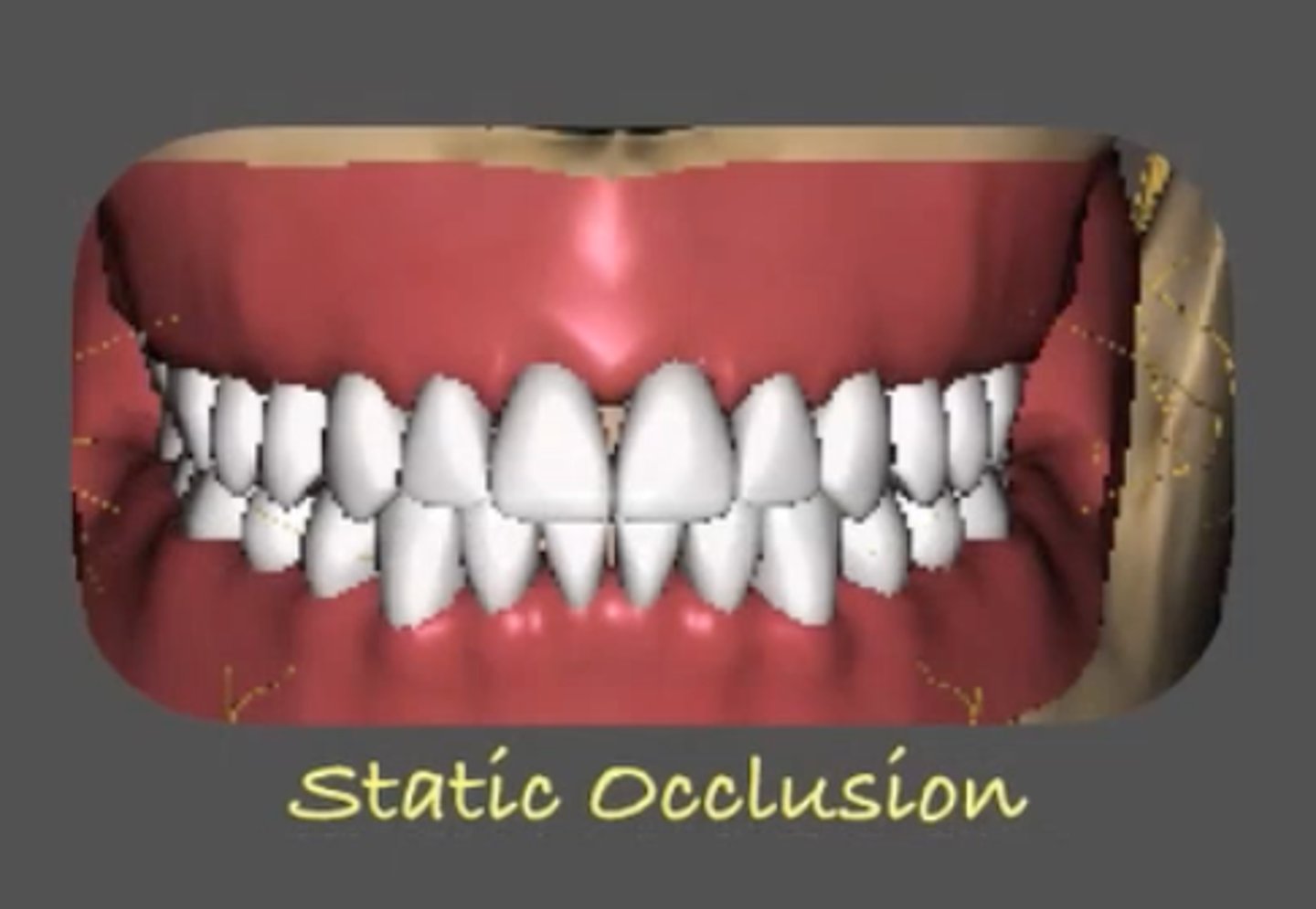
What is static occlusion?
How the teeth contact when closing in centric occlusion or centric relation
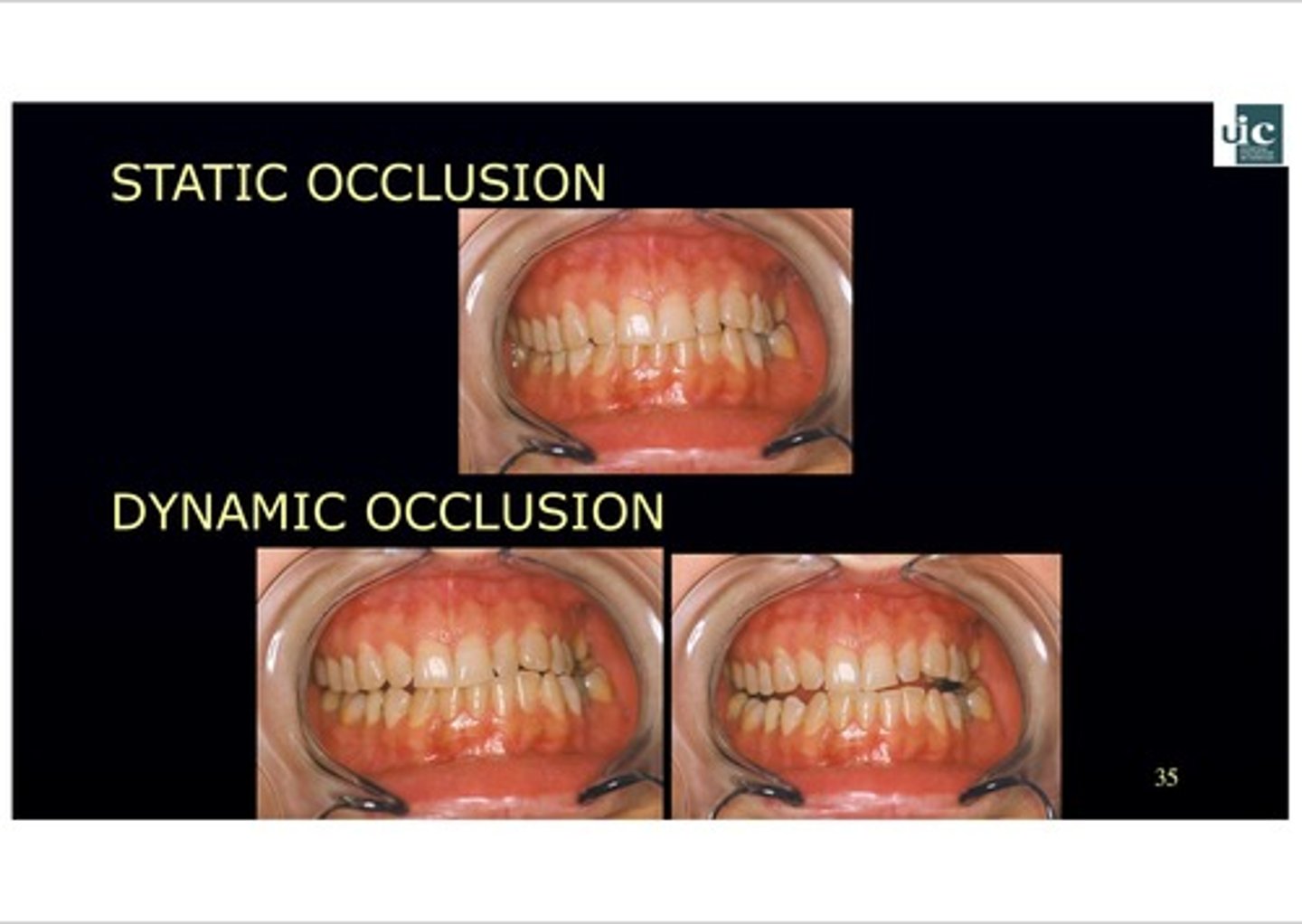
What is dynamic occlusion?
How the teeth contact when the jaw moves OUT of centric position
What are the centric holding cusps when there is a posterior crossbite?
Lingual cusps of the mandibular posterior teeth and buccal cusps of the maxillary posterior teeth
What is leeway space?
-space for permanent teeth
-allows for mesial movement of premolars
-allows for alignment of lower incisors
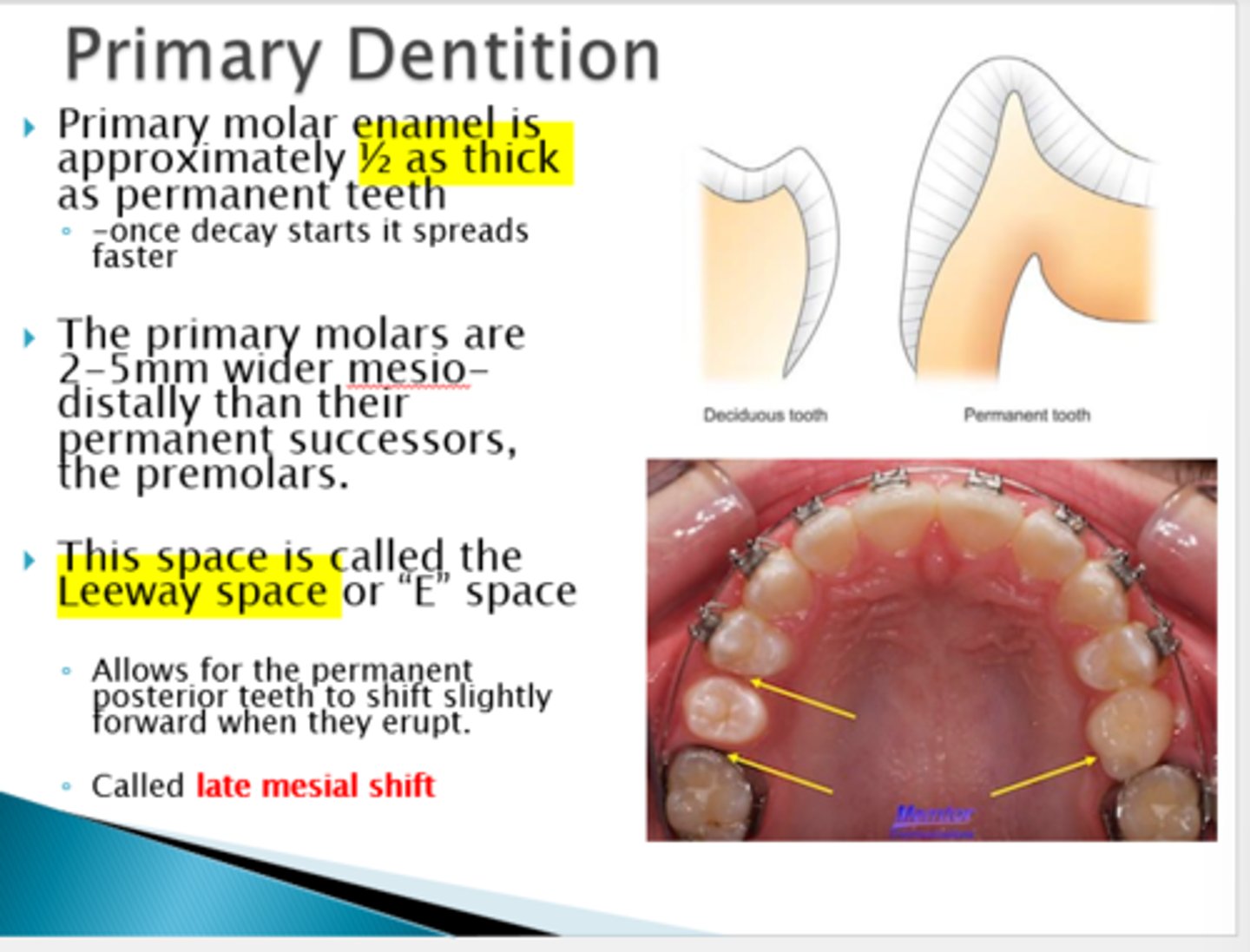
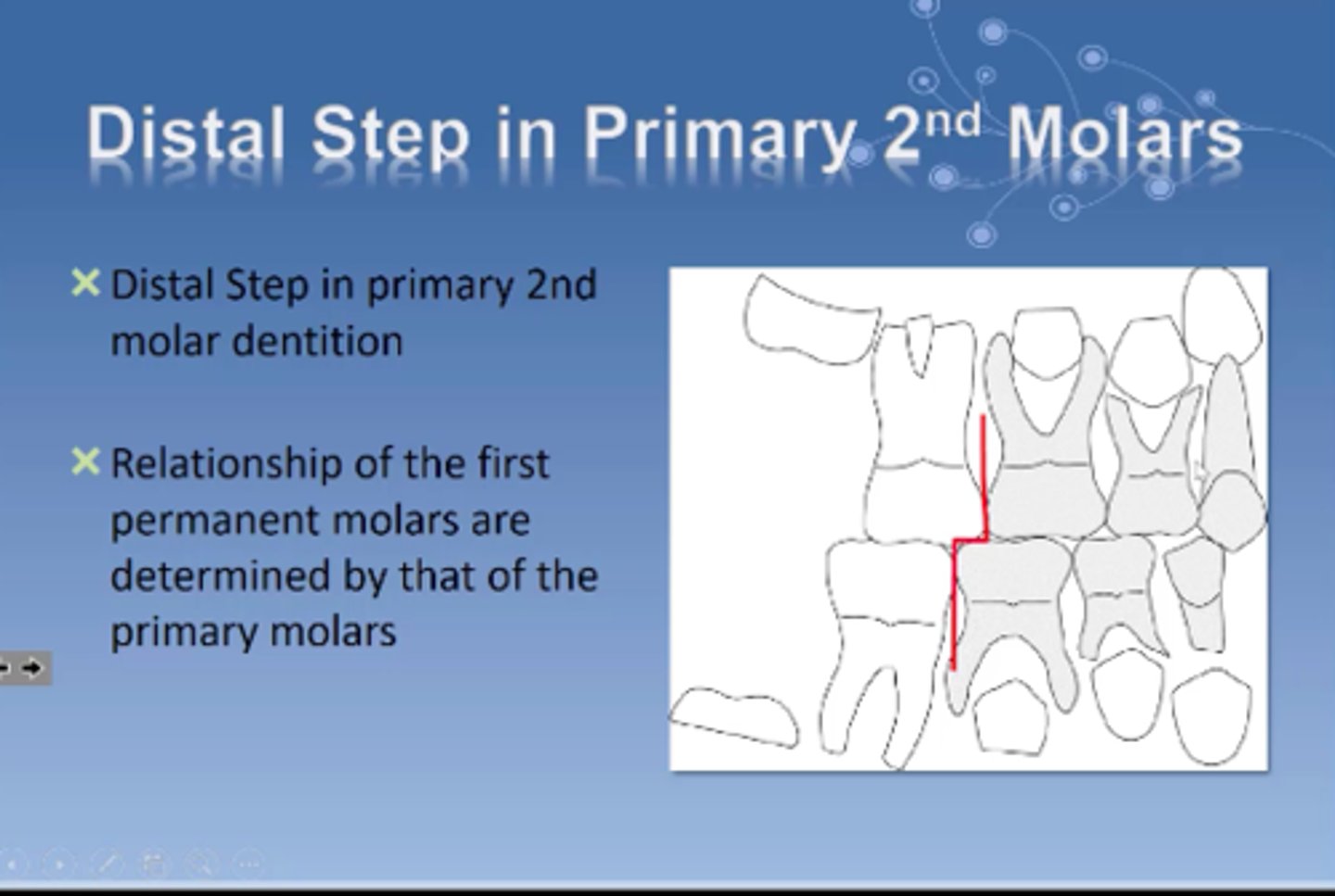
Primary molar: distal step
How does this affect the permanent molars?
may cause Class 2 occlusion
Primary molar: flush terminal plain
How does this affect the permanent molars?
end to end occlusion
(Picture: B)
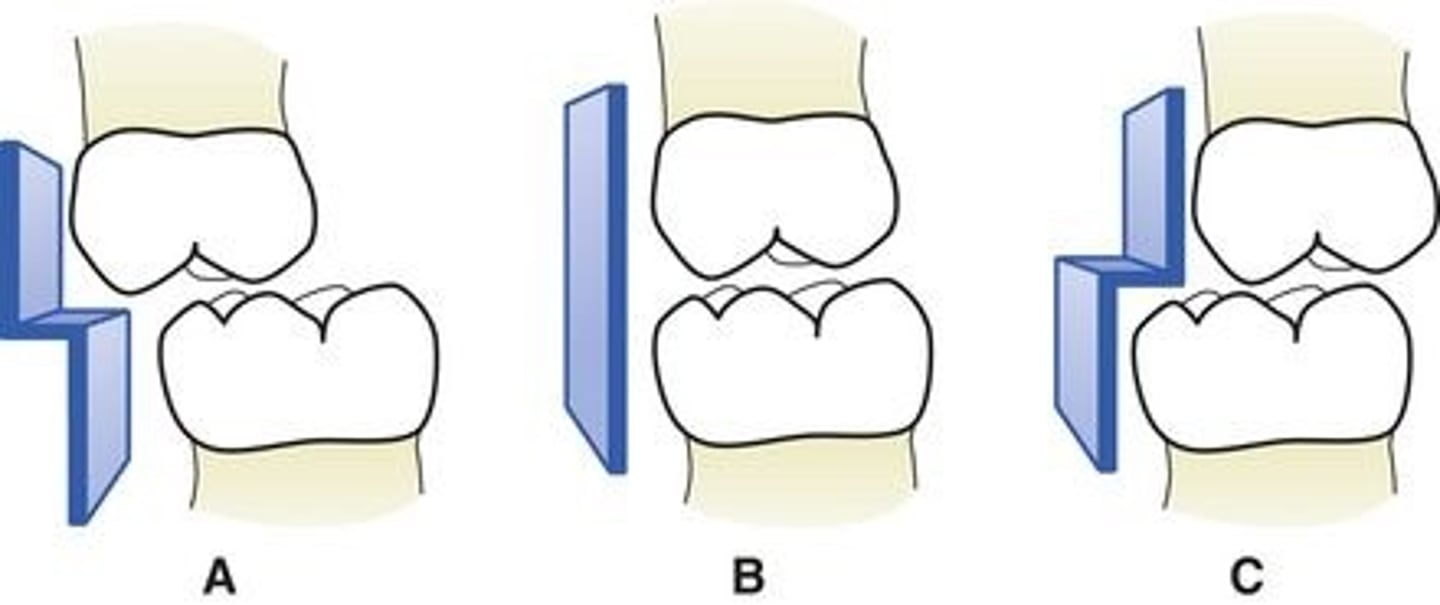
Primary molar: mesial step
How does this affect the permanent molars?
may cause Class 1 occlusion
All of the following are true about centric cusps except:
a. Support forces of occlusion
b. Oppose embrasures or grooves in the opposing dentition
c. Positioned approximately 1/3 into the total buccolingual dimension
d. Maintain vertical dimension
b. Oppose embrasures or grooves in the opposing dentition
Centric stops are areas of occlusal contact that a supporting cusp makes with opposing teeth in centric occlusion. They are typically the _______ or ________ of opposing arch.
central fossa or marginal ridges
Due to the ginglymo-arthroidal nature of the temporomandibular joint, the movements of the mandible are in _____ axes.
3
The Non-centric cusps are also know as all of the following except:
a. Non working cusps
b. Guiding cusps
c. Supporting cusps
d. Shear cusps
c. Supporting cusps
Each tooth opposes 2 teeth in the opposite arch, EXCEPT:
Maxillary third molar and Mandibular central incisor
The ______ is a main muscle of mastication.
Masseter
The centric cusps are: (2 answers)
Maxillary lingual cusps and Mandibular buccal cusps
_____ cusps are sharper cusps with defined cusp ridges and tips.
Non-centric