science (heating and cooling curve)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
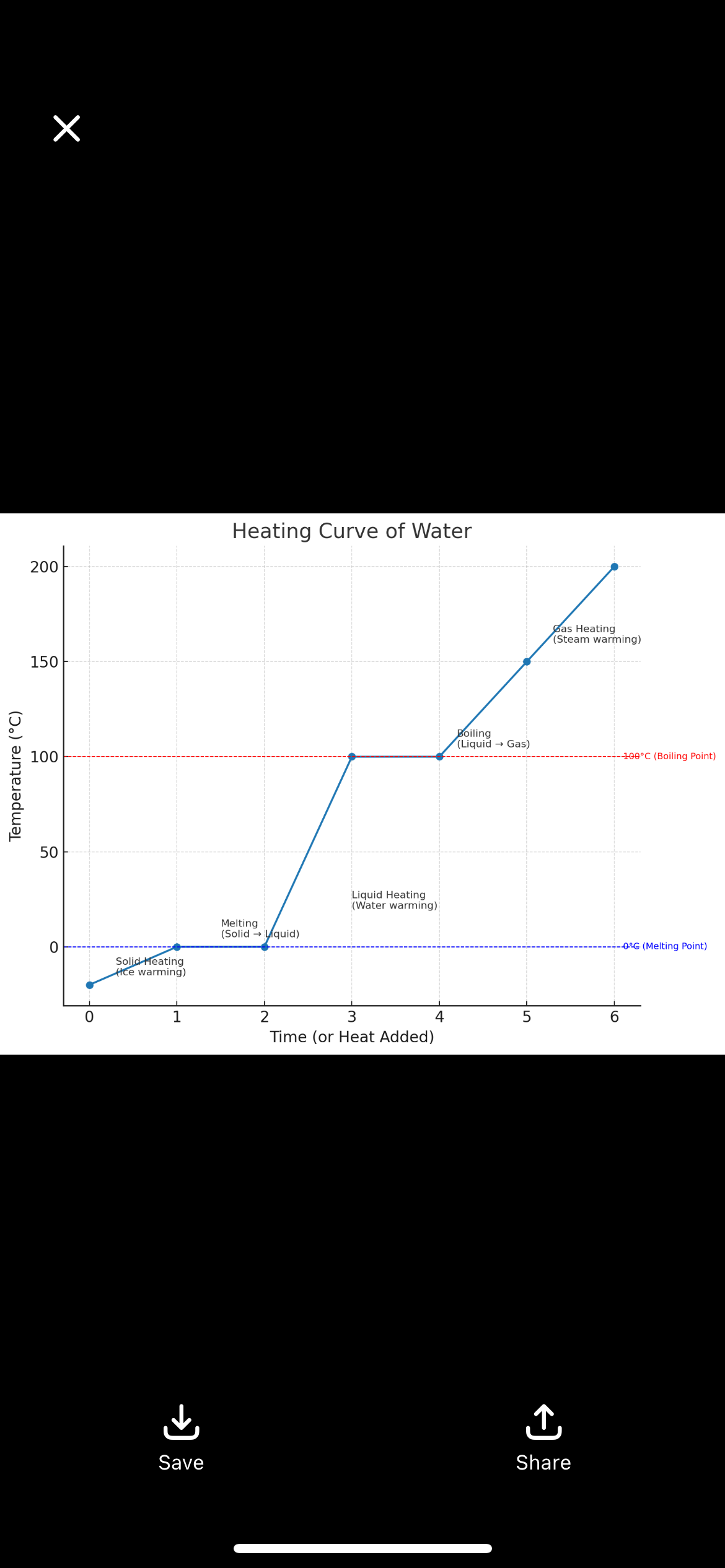
What is a heating curve
A graph that shows how temperature changes as heat is added to a substance, illustrating phase changes (solid → liquid → gas).
What does the flat part of a heating curve represent?
A phase change, where heat energy goes into changing the state of matter instead of raising temperature.
What happens at 0°C for water on a heating curve?
Ice begins to melt (solid → liquid). Temperature stays constant until all ice is melted.
What happens at 100°C for water on a heating curve?
Water begins to boil (liquid → gas). Temperature stays constant until all water turns to vapor.
Why does temperature stay constant during melting and boiling?
Because heat energy is being used to break bonds between particles rather than increasing kinetic energy.
What are the five main segments of a heating curve for water?
Heating solid
Melting (solid → liquid)
Heating liquid
Boiling (liquid → gas)
Heating gas
What type of energy is involved in temperature increase?
Kinetic energy (movement of particles).
What type of energy is involved in phase changes?
Potential energy (breaking or forming intermolecular bonds).
0°C
melting/freezing point (solid ↔ liquid).
100°C
boiling/condensation point (liquid ↔ gas).
What is a cooling curve?
A graph that shows how temperature changes as heat is removed from a substance, illustrating phase changes (gas → liquid → solid).
What happens at 100°C for water on a cooling curve?
Water vapor (gas) condenses into liquid water. Temperature stays constant until all gas has turned to liquid.
What happens at 0°C for water on a cooling curve?
: Liquid water freezes into ice. Temperature stays constant until all liquid turns into solid.
Why does temperature stay constant during condensation and freezing?
Because heat energy is being released to form stronger bonds between particles, instead of changing their movement speed.
What are the five main segments of a cooling curve for water?
Cooling gas
Condensation (gas → liquid)
Cooling liquid
Freezing (liquid → solid)
Cooling solid
What type of energy is released during phase changes?
Potential energy is released as particles form stronger bonds.
What type of energy changes when temperature drops (no phase change)?
A: Kinetic energy, because particle movement slows down.
100°C
Cooling curve
Condensation point
0C cooling curve
Freezing point
Label
Solid melting boiling gas