Social Psych: Final Exam (mc review)
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Social Psychology
The scientific study of how people about, influence, and relate to one another
Focus of social psychology
psychology of the individual
Social psychology compared to related fields
Social psychology manipulates various kinds of contact between individuals and different groups and examine the effect of the manipulation on the degree of topic exhibited
Psychological theories vs. common sense
Theories are always put to the test
Who was credited with the creation of social psychology as a distinct fiend
McDougall, Ross, and Allport
[Class lecture] Had the most dramatic impact on social psychology.
Adolf Hiltet
When social psychology was established as a distinct field
nineteenth century to early twentieth century
“I knew it all along” phenomenon
Phenomenon that makes people question how social psychology is different from common sense
Basic research
attempt to increase understanding human behavior
Applied Research
attempt to understand naturally occurring events
Random Sampling
Selecting participants to be in study so that everyone from the population has an equal chance of being a participant in the study
Advantage if cross-cultural or multicultural research methods is that they allow better tests of
External validity
Dogmatism
Pitfalls of theories: do not allow for questions, doubts, and new information. Stuck to what worked in the past, and tend to make circular arguments
Neologisms
“New Words”; when theory is developed, may have concepts that have not had names before, and find words that name them
Nature vs. Nurture
What degree is what we are due to genetics/ upbringing, or experience
Self= me and I
William James’s theory on self; me is what is known, I is specific to your self
Looking Glass self
American sociologist Charles Horton Cooley made this concept to argue that people in our close environment serve as “mirror” that reflect ourselves
Self-concept
Sum total of beliefs that people have about themselves
Self-schemas
Make up our self-concept; is the belief about oneself that guide processing of self-relevent information
Information Processing Model
Encoding, Storage, Retrieval
Salience
1 of 2 things that captures our attention; unusual and out of context
Vividness
1 of 2 things that captures our attention; emotionally interesting, imagery provoking, proximate
ABCs of self
Affect, Behavior, and Cognition
Random Assignment
Assigning participants to the various conditions of the experiment so that each participant has an equal chance of being in any of the conditions
Individualistic culture
Oriented around the self, independent instead of identifying with a group mentality. They see each other as only loosely linked, and value personal goals above that of the group.
Collectivist cultures
Usually focus on community, society, or nation. They emphasize family and work group goals above individual needs or desires.
Self-esteem
This is the affective component of self, consisting of a person’s positive and negative self-evaluations.
Self-verification
Desire to have others perceive us as we truly perceive ourselves
Mechanisms to raise self-esteem
Self-serving bias, self-handicapping, downward social-comparison
Availability heuristic
a cognitive rule that judges likelihood of things in terms of availability in memory
Peripheral route
People are persuaded on the basis of superficial, peripheral cues. Influences by attitude-irrelevant factors and simple-minded heuristics
Base-rate fallacy
People tend to be relatively insensitive to numerical base rates ir probabilities. Influenced by media and the portrayal of graphic and dramatic events.
Stereotypes
Beliefs about personal attributes of a group of people; cognition/ thoughts or beliefs. Think representative heuristics
Confirmation bias
Seek, interpret, and create information that verifies existing beliefs
Selective exposure
tendency to seek information and media that agree with one’s views and to avoid disharmonious information
Representative heuristic
Tendency to presume someone/somethings belongs to a particular group; they resemble a typical member
Central Route
Assumption that recipients are attentive, active, critical, and thoughtful; a thoughtful process
Out-group homogeneity effect
Tendency to assume that there is greater similarity among members of outgrips than among members in the in-groups
LaPiere (1934)
This researcher went on cross-country trip with a Chinese couple. Although prejudice against Chinese was high at this time, only one out of 251 establishments refused service. Afterwards, a letter was written to each establishment after the trip asking if they would serve a Chinese visitor and over 90% said they would not.
Aronson and Mills (1959)
These researchers proved a person who goes through much pain to get something value it more than someone who obtains the same thing with minimum effort.
Impression formation
The process of integrating information about a person to form a coherent impression.
Discrimination
Unjustified negative behavior toward a group or its members
Cognitive dissonance
Tension that arises when one is simultaneously aware of two inconsistent cognitions
Trait Negativity Bias
Negative information weighs more heavily on our impressions than positive information.
Illusory correlation
The tendency for people to overestimate the link between variables that are only slightly or not at all correlated. The variables are already expected to go together.
Just-world phenomenon
The tendency of people to believe that the world is just, and people get what they deserve.
Categorization
Process of thinking of a person as a member of a group on the basis of physical characteristics or other types of categories.
Social identity theory
The “we” aspect of our self-concept. The part of our answer to “Who am I?” that comes from our group memberships
Ingroup
Groups with which an individual feels a sense of membership, belonging, and identity
Outgroup
Group that doesn’t feel sense of belonging, membership, or identity
Social perception
The process by which people come to understand one another. The three major elements are persons, situations, and behavior.
Scripts
We often have preset notions about certain types of situations. They help us understand other people’s verbal and nonverbal behavior.
Nonverbal behavior
Facial expressions, body language, eye contact, and touch
Attitude
Feelings, often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond favorably or unfavorably to objects, people, and events.
Attitude can be strengthen by
An attack against it from a persuasive message
Subtyping
Accommodating individuals who deviate from one’s stereotype by thinking of them as “exceptions to the rule”
Self-fulfilling prophecy
Perceiver’s expectancy about a target influences the perceiver’s behavior toward that target.
Fundamental Attribution Error
When explaining other people’s behavior, we tend to overestimate the role of personal factors, and overlook the impact of situations.
Priming
The tendency for recently used words or ideas to come to mind easily and influence the interpretation of new information
Continuum of Social Influence
Conformity, compliance, and obedience
Studies on conformity
Sherif, Asch, and Milgram
Sherif (1936)
Used autokinetic effects on “movement” of light. Separated into two experiments with same groups of men. First experiment, the men gave their own answers. Second experiment, participant heard others’ answers. Results, they would change responses based on what others have said.
Asch (1950s)
Line test for which one matches the model. Group of confederates would say their answer (often incorrect) out loud. One participant is actually a participant. When confederates gave the same responses even when the line didn’t match the model, the participant would also say the same thing, even if they thought differently.
Milgram (1961)
Participant would be given responsibility to text a confederate on a memory test. If the confederate got it wrong, the participant would “shock” them, increasing the voltage for each incorrect answer. If the participant wanted out or stopped, the “researcher” would encourage participant to keep going: “the experiment must go on”.
Three features of the Milgram experiment
(1) framing of shock-giving as a social norm. (2) Opportunity to deny responsibility. (3) Limited time to reflect on decision
Reasons to go along with a group
(1) fit in with group and (2) normative influence
Request strategies
(1) low balling, (2) foot-in-the-door, (3) door-in-the-face
Assertive: say no
(1) be diligent, (2) not feel indebted by norm of reciprocity
Social impact theory
3 factors: (1) strength of source, (2) immediacy of the source to the target in time and space, (3) number of sources
Aggression
verbal or physical behavior intended to cause harm
Hostile aggression
Springs from anger; spur of the moment
Instrumental aggression
is means to some other ends; planned and pre-medicated
Positive reinforcement
aggression produced desired outcomes; Directed to boys that engage in aggression
Negative reinforcement
Aggression prevents or stops undesirable outcomes; directed to girls who engage in aggression
Altruism
motive to increase another’s welfare without conscious regard for one’s own self-interests
Reciprocity norm
expectation people will help those who helped them
Social responsibility
Expectation people will help those who need it
Evolutionary theory on “Selfish gene”
Help to protect their own kin selection to help genetic relatives; biological stakes are high
Empathy
Understand a vicariously experiencing another’s individuals perspective and feeling sympathy and compassion for that individual
Egoistic
Motivated by desire to increase own’s welfare
Social-exchange theory
theory that human interactions are transition that aim to maximize one’s rewards and minimze one’s costs
Bystander effect
the finding that a person is less likely to provide help when there are other bystanders
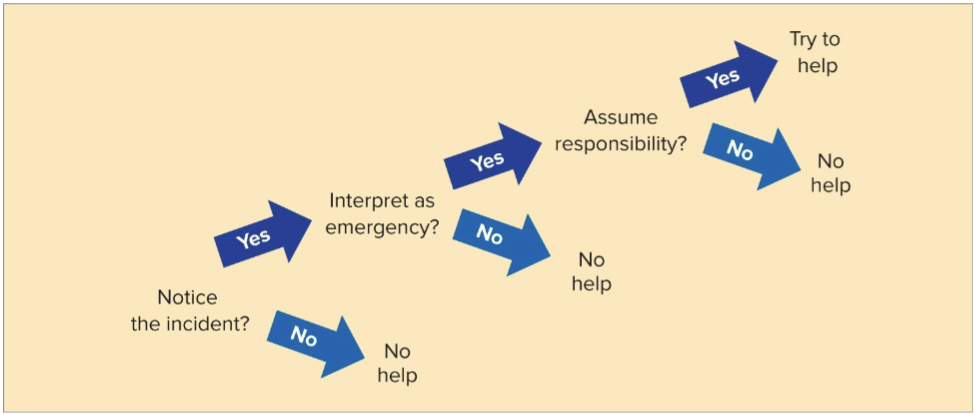
Decision Tree
Only one path up the tree leads to helping. At each fork of the path, the
presence of other bystanders may divert a person down a branch toward not
helping.