Tissue Structure and Composition
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Tissue types, bone, and muscle
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Epithelium
Thin layer of tissue that essentially covers all free surfaces of the body
Principle Function: Epithelium
act as a barrier between tissues and external environment or internal body cavities
Sensory communication
Endothelium
_____ Covering the innermost
surfaces of capillaries
Controls nutrient flow into
underlying tissues, such as: Oxygen, hormones, proteins
Epithelial Tissues: Secretory Cells
Contain extensive Endoplasmic reticulum
Composition of cell products vary depending on substance needed at the cell surface
Responsible for packing and transporting products to cell surface for release
Epithelial Tissues: Secretory Cells Example
Enzymes released from digestive tract
Epithelial Tissues: Secretory Cells Example
Goblet cells secrete Mucus,
muscus secretion respiratory tract or reproductive tract
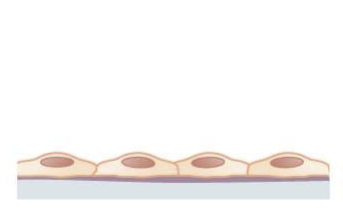
Simple Epithelial tissue
single layer of cells
Located where maximal secretion or absorption is necessary
Delicate structure
Simple Epithelial tissue
Stratified Epithelual tissue
two or more cell layers
Found where there is friction with outer environment
Chemical and mechanical perturbations
Protect underlying tissues
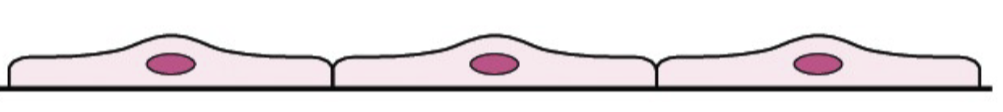
Types of Epithelium Cells: Squamous
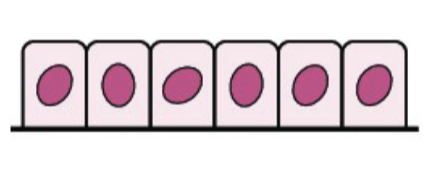
Types of Epithelium Cells: Cuboidal
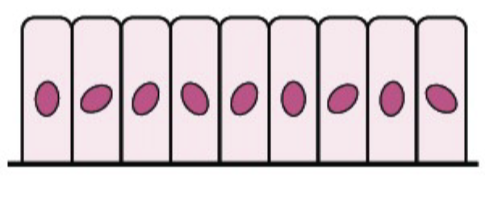
Types of Epithelium Cells: Colummnar
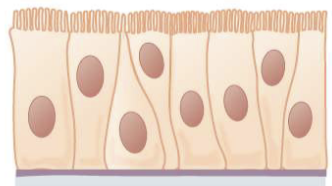
Pseudostratified
cells that are there but not reaching the next membrane
Google Def: type of epithelial tissue that appears to be stratified (arranged in layers) but actually consists of a single layer of cells.
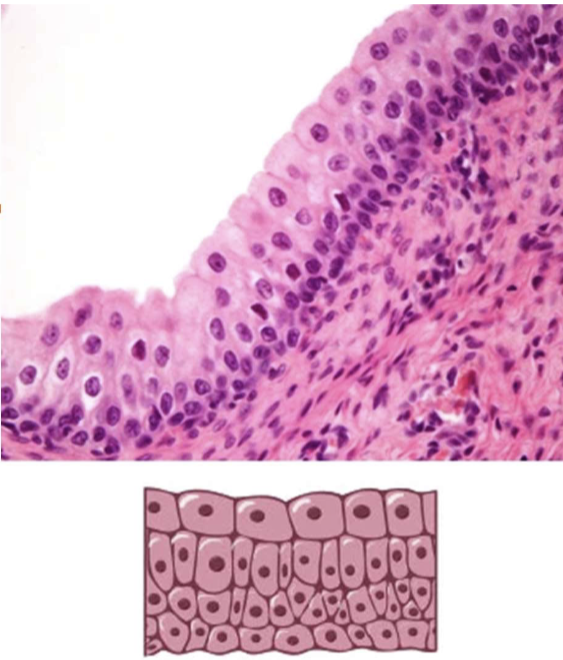
Translational Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal epithelium but changes dramatically with distention of the underlying tissues
Located in: Bladder and parts of urinary tract
Nervous Tissue
Central nervous system: brain & spinal cord, non-voluntary
Peripheral nervous system: sensory and motor neurons
Sensory-direct stimuli
Motor delivers a response message
Neurons
specialized cells that transmit signals throughout the body
Axon
projection of the cell to allows the transmission of a signal deep within a tissue
Cell body
contains the nucleus
Dendrites
where synaptic junctions are formed to perceive signals from other cells
Schwann Cell
form myelin sheath creating Nodes of Ranvier
Rapid action potential firing
Components of Connective Tissue
Fibers
Ground Substance
Cells
Connective Tissue: Extracellular Matrix
Ground substance
Chondritin
Ground substance
fluid-like structure of the Extracellular Matrix consisting of soluble proteoglycans
Chondroitin sulfates
Hyaluronic acid
proteoglycans
proteins linked to carbohydrates
Connective Tissue Fibers
Collagen Fibers
Reticular Fibers
Elastin
Collagen Fiber
Most abundant protein in animals (20-30%)
Support
Crosslinking
Type 1-most abundant connective tissue in the body (80% of total _____)
Skin and Muscle
Procollagen
Collagen Precursor that is secreted from the fibroblast
Reticular Fibers
Small and Delicate
High proportion of ground substance
Loose connective tissue
Surround's organs
Elastin Fiber
Reversibly stretched
Secreted from fibroblasts
Precursor molecule: tropelastin
Abundant in blood vessels, ligaments, lungs and skin
Loose Connective Tissue
Porous, flexible
Structure to blood vessels and nerves
Few collagen and elastic fibers
Highly vascularized with relatively large number of cells
Dense Connective tissue
Many fibers
Strength
Fibroblast cells producing fibers
Two types
Irregular
Regular
Specialized connective tissue
Blood
Cartilage
Adipose
Blood
Very fluid ground substances with little to no extracellular fibers
Cartilage
Structural support for other tissues
Perichondrium
Chondrocyte
Interstitial growth
Appositional growth
no blood vessels
Perichondrium
thin membrane
Chondrocyte
cells responsible for producing matrix
found in lacunae
Interstitial growth
growth within that results in an increase in length
Appositional growth
addition of a new layer between cartilage and perichondrium increases thickness
Adipose Tissue
Adipocytes
Triglyceride storage
Highly vascularized
Located around critical organs
Endocrine organ: adipokines
Insulation
Cartilage
Large amounts of extracellular fibers or matrix
Densely packed
Types of Bone
Long,Short, Irrgular, flat
Types of Bone Tissue
Compact, Spongy
Compact Bone Tissue
Dense
Osteon
Found on the outside of bones
Spongy Bone Tissue
Bone arranged in the small structures' spicules and trabeculae
Help in resisting stress to bone
Spicules (bone structure)
elongated cylindrical structures
Trabeculae (bone structure)
long, flattened structures
Long Bone
Bone growth occurs at epiphyseal plate (growth plate) or appositional growth (between periosteum and compact bone)
Osteoblast
Osteoclast
Osteoblast (long bone)
populations found between periosteum and bone
Osteoclast (long bone)
populations found under endosteum
Osteoblast
Bone cell precursor
Bone matrix production
Divide
Osteocyte
Mature osteoblast (mature bone cell)
Bone matrix production
Reside in lacunae (surrounded by the bone matrix)
Bone Matrix Production and Maintenance
Osteoblast and Osteocyte
Bone Resorption
Osteoclast
Osteoclast
Bone resorption (breakdown)
Mutli-nucleated cells that are formed from the fusion of cell of the monocyte macrophage lineage
Osteon
Osteocytes
Cylindrical (oriented parallel to
the long axis of the long bone)
Haversian canal
Osteocytes
ocated in lacunae
Haversian canal
contains blood vessels to provide blood flow to the cells in the osteons
contract
The major organelles within a muscle will always have the ability to ______ due to the myofibril
Avascular
lacking blood vessels
Smooth muscle
involuntary, non-striate= extremely elastic and pliable, single centrally located nucleus (1 per cell)
Cardiac Muscle
involuntary, striated, highly vascularized, one or two nuclei per cell, intercalated discs
(Can’t regen it’s self)
Skeletal Muscle
voluntary, striated, multi-nucleated=cells merge together, varying metabolic characteristics, bulk (35-65%) of carcass weight
(can repair and regen)
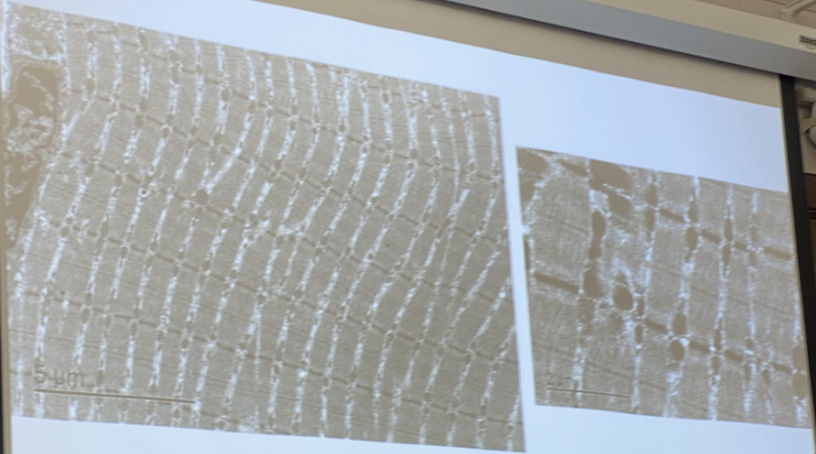

What are the horizontal lines?
striations
Origin
the part of the muscle that does not move during contraction
insertion
moves towards the origin during contraction
Origin, insertion
effect the speed of an contraction
push, contract
Muscle does not ____ anything it only _____
myofibril
The major organelles within a muscle will always have the ability to contract due to
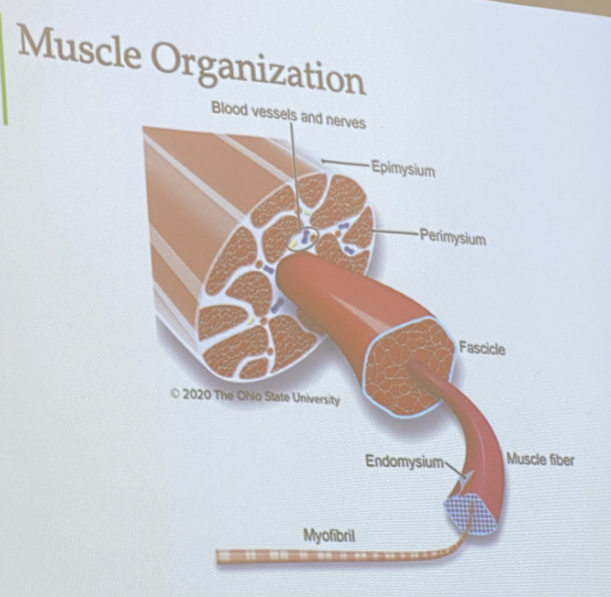
Epimysium
Outermost layer of connective tissue
Surrounding outside of the muscle and organ
Strong piece of connective tissue
provides avenues for nerves and blood vessels to enter and exit muscles
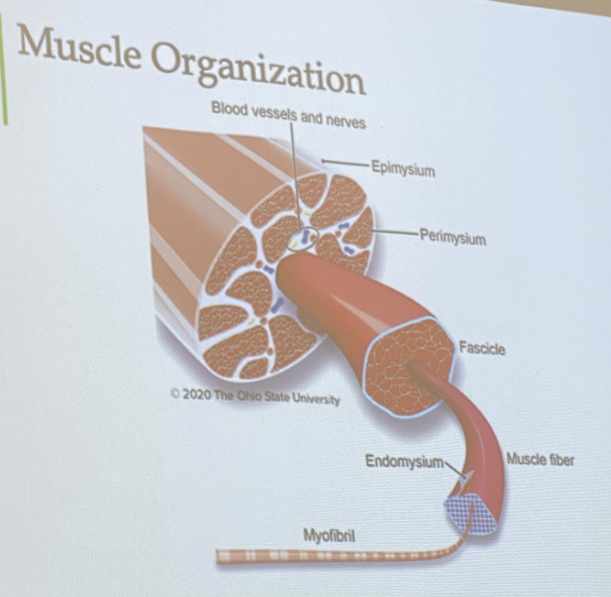
Perimysium
Conective tissue that surrounds the fascicle
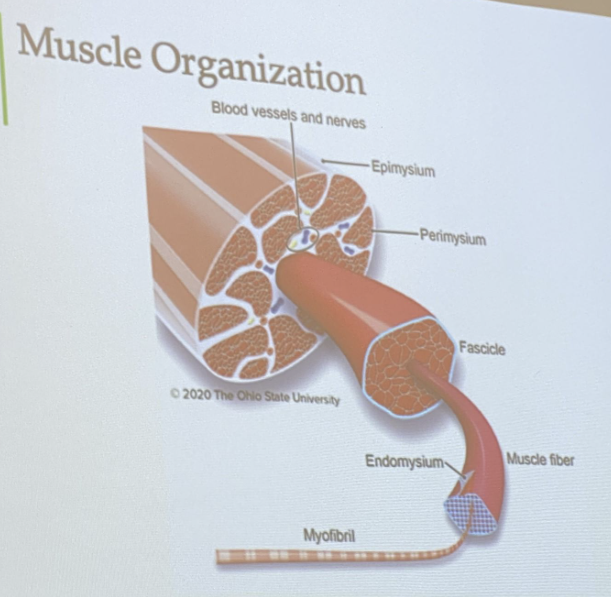
Endomysium
connective tissue surrounding myofibers
major connective tissue component responsible for meat tenderness and changes with age
immediately adjacent to the muscle cell membranes
Sarcolemma
is an cell membrane (made out of a phospholipid by layer) and not a connective tissue
sarcomere
smallest contractile unit of muscle
Made up of actin and myosin along with other structural and regulatory proteins
Like the endoplasmic reticulum that is made up of lipids?
Web like for increased surface area
Different for each muscle type, due to each one having different needs
Function of Satellite cells
Detect damage
Adipose tissue
Specialized connective tissue
Intramuscular Fat (marbling): Deposited within the muscle
Hyperplasia (muscle growth)
increase in number of fibers
Hypertrophy (muscle growth)
increase in size of existing fibers (bigger)
Atrophy
decrease in size
Muscle stem cells
capable of proliferating, differentiation, and fusing w. muscle fibers, contributing more than 95% of total myonuclei in mature myofibers
Satellite Cells Location
between the basement membrane and sarcolemma of myofibers
Glycolic and Oxidated
Major types of energy metabolism
Glycolic
Strong and quick contractions, fatigable
White because=No mitochondria? So little need for oxygen?
ADP, ATP, glycolysis
Oxidated
Terminal electronic receptor= oxygen
Comes from krebs cycle
Hemoglobin (red color) bound
Transports oxygen into muscle and to myoglobin => to the mitochondria as thermal electron receptor
White muscle
speed and contraction but limited amount, short distance
Red muscle
oxygen based, longer times, fatigue resistant, greater need for ATP
Difference in muscle fiber type?
Will effect muscle turn over
Why is there more fat in the muscle of Breast verses Thigh?
You don’t deposit fat in glycolic muscles (no mitochondria)
The breast use oxidated muscle and thigh use glycolic
Tonic
nerve is moving all the time
Contraction
slower like waves (phasing contract and relax)
Basement membrane
structure made up of interwoven fibers connecting the endomysium to the sarcolemma
Nuclei
multinucleated due to large size of myofiber to regulate cellular functions (multiple nuclei)
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of myofiber
Myofibril
the unique microfilamentous organelles of myofibers
How does it know for the nerve to release Action Protentional?
The T tubule, made up of cell membrane where the AP goes into the cell to the terminal cisterna which creates the release of calcium
Calcium is needed for contraction
Calcium
needed for contraction
T-tubules
small invaginations of the sarcolemma surrounding the myofibrils at the A-I band junction
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
development of the endoplasmic reticulum extending between two T-tubules; Calcium storage
Traffic things out of the cells (transport)
Sarcomere
Smallest contractile unit of muscle
made up of actin and myosin along with other structural and regulatory proteins
I band
Major protein: actin
how to length
A band
Primary protein: myosin