Microbio UNIT 7 (last exam)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Staphylococcus Background and Morphology
Commensal
grape elike cluster
facultative anaerobe
gram positive
for clinical purpose (Coagulase + and -) —> enzyme that clots fibrin in blood
Commensal
one organism benefits, other is unaffected
Staphylococcus
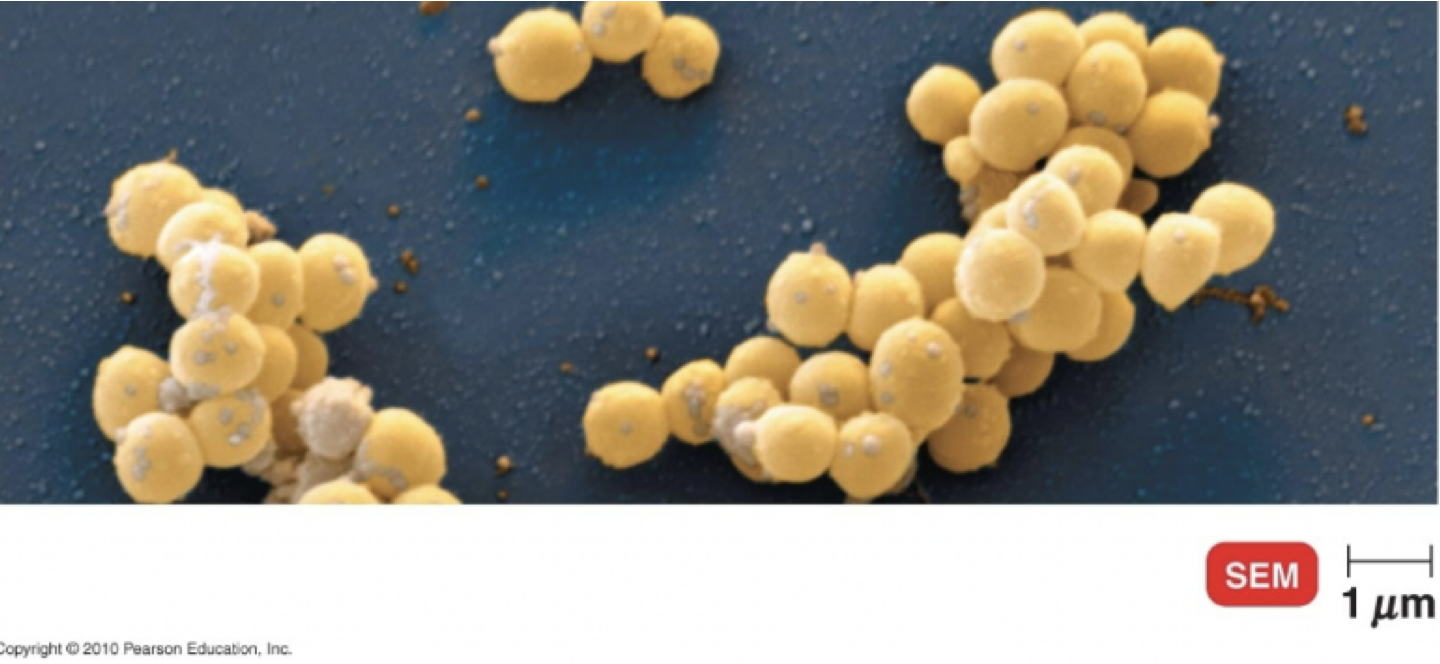
Staphylococcus epidermis
normal flora
Staphylococcus infections
pimples
boils
Pneumonia
Food poisoning
surgical wound infection
hospital associated infection
scalded skin syndrome
S. aureus
produces yellow colony (aureu = gold)
involved in 16% nosocomial infection caused by microorganisms
60% resistant to antibiotics
most frequent cause of pneumonia
Staphylococcus aureus local infections
pimples
folliculitis
furuncle/ carbuncle
abscesses
outer ear infection
impetigo
S. epidermis
Coagulase negative: causes very common skin infection
pathogenic when skin barrier broken or medical invasive procedures (catheters)
History of drug resistance of S. aureus
Penicillin-resistant S. aureus in hospital (1950s)
Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA)
S. aureus showed less sensitivity vancomycin- VISA
Vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA)- 2002
Staphylococcus aureus growth conditions
can grow well under:
high osmotic pressure
low moisture
they can grow in nasal secretions, skin, low moisture food, food with high osmotic pressure (ham, cured meat)
have a yellow pigment which protects them from anti-microbial effects of sunlight
Staphylococcus produces toxins
toxins cause pathogenicity
increases ability to invade body or damage tissue
toxin causes toxic shock syndrome (high fever, vomiting, even death)
produces enterotoxin (in the intestines): most common cause of food poisoning (a superantigen that affects intestine like Vibrio enterotoxin)
Staphylococcus superantigen causes
secretion of fluids, electrolytes from capillaries
thus decreases blood volume
lowers blood pressure
Plasmid and pathogenicity
resistance factors for antibiotics are encoded here
staphylococcal enterotoxin are encoded here
Bacteriophage genes contribute to staphylococcal enterotoxin
plasmid
small circular DNA separate from bacterial chromosome
Neisseria Background and Morphology
Gram Negative Cocci (resembles coffee beans)
inhabit the mucous membranes in mammals
representative of normal microbiota inside the mouth
Pathogenic species of Neisseria
N. gonorrhoeae - gonorrhoea
N. meningitides - meningococcal meningitidis
N. gonorrhoeae
genitourinary tract
N. meningitides
respiratory tract through aerosol
produces endotoxin
Gonorrhea
STI
incubation period for symptoms —> few days
fimbriae attaches to columnar epithelial cells
this causes pus formation due to infiltration of leukocytes
untreated gonorrhea causes endocarditis or arthritis (1%)
Ophthalmia neonatorum
infected infants eyes
can lead to blindness
acquired during vaginal birth
common type of gonorrhea
Pharyngeal gonorrhea
resembles septic sore throat
common type of gonorrhea
Anal gornorrhea
itching, painful, pus
common type of gonorrhea
Vaccines
can prevent serotype A, C, Y, and W - 135 meningococcal infections
purified polysaccharide
development of gonococcal _____ is remote
Gram positive bacilli
non endospore formers
Listeria Background and morphology
gram positive
bacili
opportunist pathogen
commonly found in sewage, stream water, plants, food, soil etc
can grow in temp 4-37 C
depicts tumbling motility
Listeria monocytogenes
listeriosis
caused by eating contacted food (uncooked meat, vegetables, unpasteurized milk and products)
Listeria monocytogenes susceptible population
infants
pregnant women
immunocompromised
Listeria monocytogenes Mechanism of infection
survive within phagocytes and proliferates primary in liver
can escape from phagosome before fusing to lysosome
can move from phagocyte to adjacent cells
Listeria monocytogenes disease in infected adults
mild, sometimes causes mengitidis (50% mortality)
invade bloodstream - sepsis
Listeria monocytogenes disease in fetus and newborns
more severe form
can infect fetus via placenta-abortion, still birth
sometimes manifested in infants after birth (meningitis)
60% mortality infants
Listen-P100
reduces L. monocytogenes in food by using bacteriophages to kill them
Brucella background and morphology
small, non-motile, aerobic, gram-negative
coccobacilli (coccoid rods)
obligate parasites of mammals
causes Brucellosis (Undulant fever)
reservoir - domestic livestock
transmission - contained milk, meat, or animals
Brucella survival and pathogenesis
can survive phagocytosis
it persists in reticuloendothelial system leading to evade host defensed allowing long term survival and replication
disease often becomes chronic and can affect other organs
Brucella
easily airborne and dangerous to handle
a bioterrorism agent
BSL 4 facility
B. abortus
found primarily in cattle but also infects camels, bison, and several other animals
brucella
B. suis
infects swine but is known to infect cattle when kept in close contact with swine herd
humans with close contact with carcasses are any risk
brucella
B. melitensis
causes most serious cases in humans
most commonly found in goats, sheep
brucella
Brucellosis
previously most human cases were attributed to B. abortus (now seldom)
testing and vaccination eliminated brucellosis in cattle (no human vaccines)
most commonly caused by B. melintensis (predominantly in hispanics)
disease endemic in Mexico imported unpasteurized food like soft cheese made form goat milk
Symptoms of Brucellosis
incubation period: 1-3 weeks but could be longer
symptoms depend on stage and organ affected
rising and falling fever
Malaise (night sweats)
muscle aches
Diagnosis of Brucellosis
serological test (but need a definitive test)
ultimate proof (isolation from tissue/ blood of patient)
starts with an interview
no resistance to antibiotics reported
Pseudomonas Background
Aerobic, gram-negative, motile, rods
polar flagella- single or tufts
depicts twitching motlity
common in soil and other natural environemnts
responsible for 1 in 10 nosocomial infection (hospital acquired)
P. aeruginosa
produces soluble blue-green pgiment
in immunocompromised host - infected urinary tracts, burns, wounds, sepsis (blood infection), abscesses, meningitis
species of Pseudomonas
P. syringae
occasional plant pathogen
species of Pseudomonas
bioremediation
What does Pseudomonas use for breaking down harmful pollutants?
Biofilms
P. aeuginsosa can grow inside humans without causing disease until they form _____
can overcome a host’s immune response
can colonies lungs in cystic fibrosis patients and cause deaths
can form on medical devices like catheters, implants etc
Bordetella background
non-motile
obligaeltey aerobic
gram-negative rods (coccobacillus)
virulents strain possess capsule
B. pertussis
pertussis or whooping cough
emerging infectious disease (ones that a re new or changing)
Bordetella Mechanism
specifically attaches to ciliated cells in trachea, first impeding ciliary action and the progressively destroying the cells
this prevents ciliary escalator system from clearing mucus
Bordetella transmission
droplet transmission (a type of contact transmission)
spread in droplet nuclei (mucous droplet) that travel 1 meter and are not regarded as airborne
droplets discharge in air by coughing, sneezing, laughing or talking,
Bordetella incubation period and portal of entry
6-14 days
GI tract
Francisella Morphology
small
Pleiomorphic
gram-negative, bacillus
grows only in complex media enriched with blood or tissue extract
Francisella diseases
Tularemia (F. tularensis)
aka Pahvant Valley plague, rabbit fever, deer fly fever, and Ohara’s fever
Zoonotic disease: transmitted by contact with infected animals (rabbits, squirrels, ticks, and insects)
Francisella route of entry and pathogenesis
penetration of the skin (minor abrasions, ulcer)
swollen lymph nodes containing pus
if not contained leads to sepsis and the infection of multiple organs
Francisella
agent for bioterorism
the infective dose is very small
organisms is dangerous to handle if aerosols are produced
Legionella Morphology
gram negative
bacillis
thin
pleomorphic
flagellated
aerobic
Legionella disease
legionellosis (legionnaires disease)
Legionella growth
grows suitably of artificial media
readily visualized with silver stain
common in streams
Legionella
What microbe is the exception to Koch’s postulate (the pathogen must be isolated forms he diseases hot and grown in a pure culture)
Legionella transmisison
via aerosols - th inhalation of mist droplets containing the bacteria
Legionella Incubation period
up to 2 weeks
Legionella symptoms
initial: flu-like, including fever, chills, and dry cough
advanced:
GI
the nervous system
lead to diarrhea and nausea
symptoms of pneumonia
Campylobacter Morphology
gram-negatie
microaerophillic vibrios
one polar flagellum
C. jejuni
leading cause of outbreaks of food borne intestinal disease
campylobacter disease
C. fetus
causes spontaneous abortion ind domestic animals
campylobacter disease
Vibrio morphology and background
curved rods
facultative anaerobes
gram-negatives
non-spore formers
motile, polar flagella (monotrichous) with sheath
found mostly in aquatic habitats
V. haemolyticus
less serious gastroenteritis
vibrio pathogenic strain
V. vulnificus
haemolytic
vibrio pathogenic strain
V. cholerae
causes cholera
produces A-B enterotoxin called cholera toxin
vibrio pathogenic strain
vibrio transmission
raw undercooked seafood
contaminated water
vibrio symptoms
5-10% cases develop severe illness
rice watery stool
vomiting
dry mucous membranes
drop in blood pressure
thirst
renal failure
coma
loss of skin elasticity
vibrio diagnosis
stool culture
rectal swab
mycobacterium tuberculosis background
discovered by Robert Koch
waxy coating (mycotic acid) - acid-fast stain
highly aerobic
can survive in dry conditions for weeks
can survive some disinfectants
another strain is called M. leprae
reside in alveolar macrophage
waxy cell wall prevent pahosome-lysosome fusion
can neutralize reactive nitrogen species
mycobacterium tuberculosis diagnosis
sputum test
chest x-ray
mycobacterium tuberculosis symptoms
can stay dominant for decades
10% of infected people develop tuberculosis
can spread form lungs to brain, reproductive system, kidney, bones
loss of appetite
fever
weight loss
coughing blood
chest pain
difficulty breathing
Yersinim pestis background
rod shaped
facultative anaerobe
safety pin appearance
Black Death (plague)
Yersinim pestis transmission
reservoir - several species of rodents
from flea during feeding on an infected animal
animal —> human
human —> human thought skin contact, cough, or sneezing
Yersinim pestis Mode of pathogenesis
resides in lymph nodes and avoid killing by macrophage by escaping phagocytosis
Symptoms of Bubonic plague
after incubation 2-6 days causes swollen lymph nodes (bulbo) most common
Symptoms of pneumonic plague (weaponization)
6 day incubation, spread through aerosolization, respiratory failure, septic shock
Symptoms of Septicemic plague
most dangerous
1-7 days incubation
septic shock an intravascular coagulation
gangrene “Black Death”
Yersinim pestis diagnosis
staining
culturing
Haemophilus Background
aerobic (facultative anaerobe)
previously called bacillus influenzae
gram-negative, rods
opportunistic commensal
six serotypes a-f (based on polysaccharide capsule)
Haemophilus Pathogenesis
affects the immunocompromised
colonizes the upper respiratory region (nasopharynx)
can spread to blood stream
Haemophilus Diseases
Otitis media (children)
adverse conditions with people with bronchitis or CF pateints
Pneumonia
Haemophilus transmission
aerosolization of droplets
Helicobacter pylori background
microaerophilic
gram negative
helix shaped (curved rods)
4-6 lophotrikhous flagella (highly motile)
can form biofilms
Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis
bacteria can be present for decades in the stomach without the patient knowing
causes chronic low-level inflammation in the lining of the stomach
individuals are often asymptomatic
they go through he mucoid epithelium and reside in the inner surface of stomach epithelial cells
Helicobacter pylori disease
duodenal and gastric ulcers
chronic gastritis
esophagus and stomach cancer
reflux esophagitis