Chapter 27 THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Testes
Organs that produce sperm and testosterone; located in the scrotum.
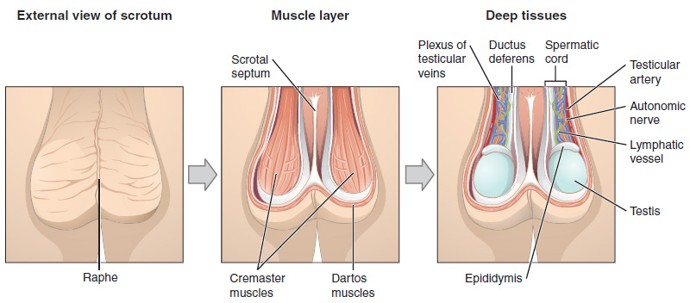
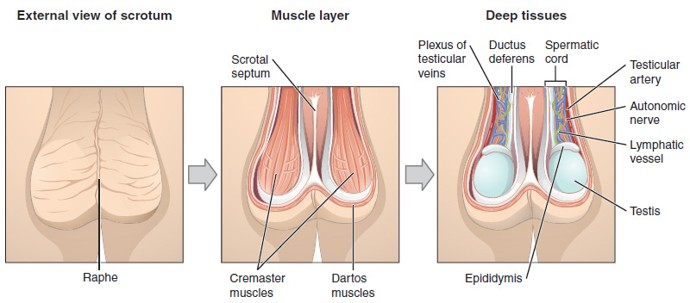
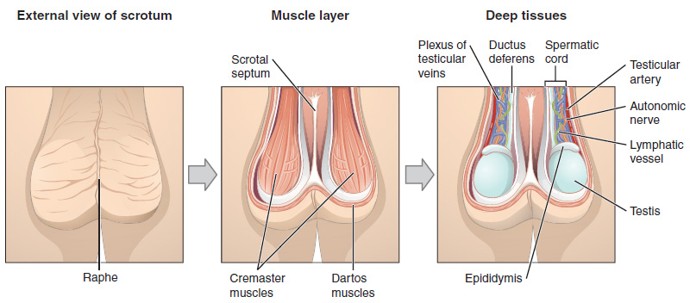
Scrotum
Sac of skin that holds the testes outside the body to maintain a cooler temperature for sperm production.
Sperm
Male reproductive cell
Requires temperature slightly below body temperature to develop properly
Tunica Dartos
Smooth muscle layer in the scrotum that wrinkles or relaxes the skin to help regulate testicular temperature.
Epididymis
A coiled tube on the back of each testis where sperm mature and are stored.
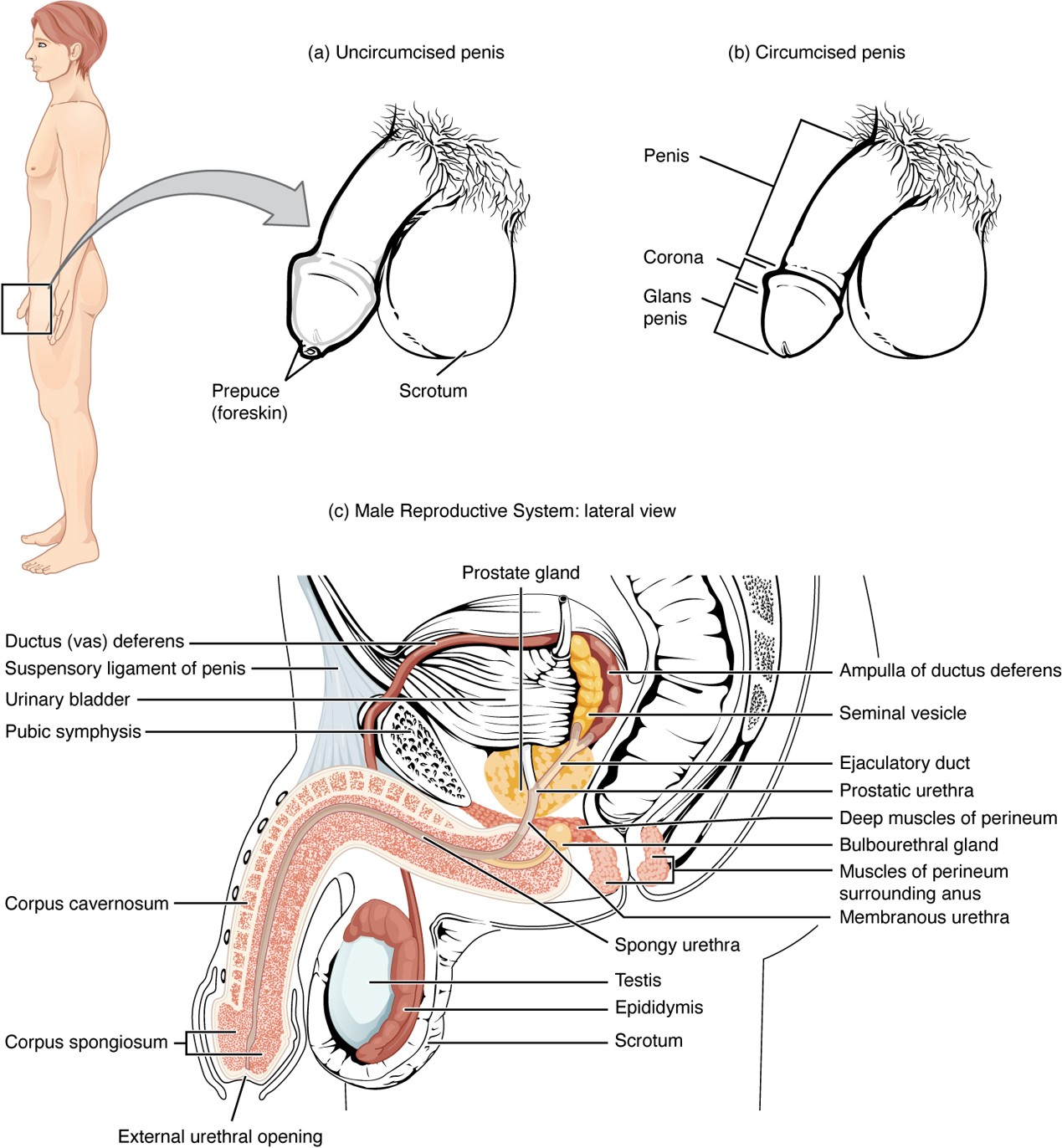
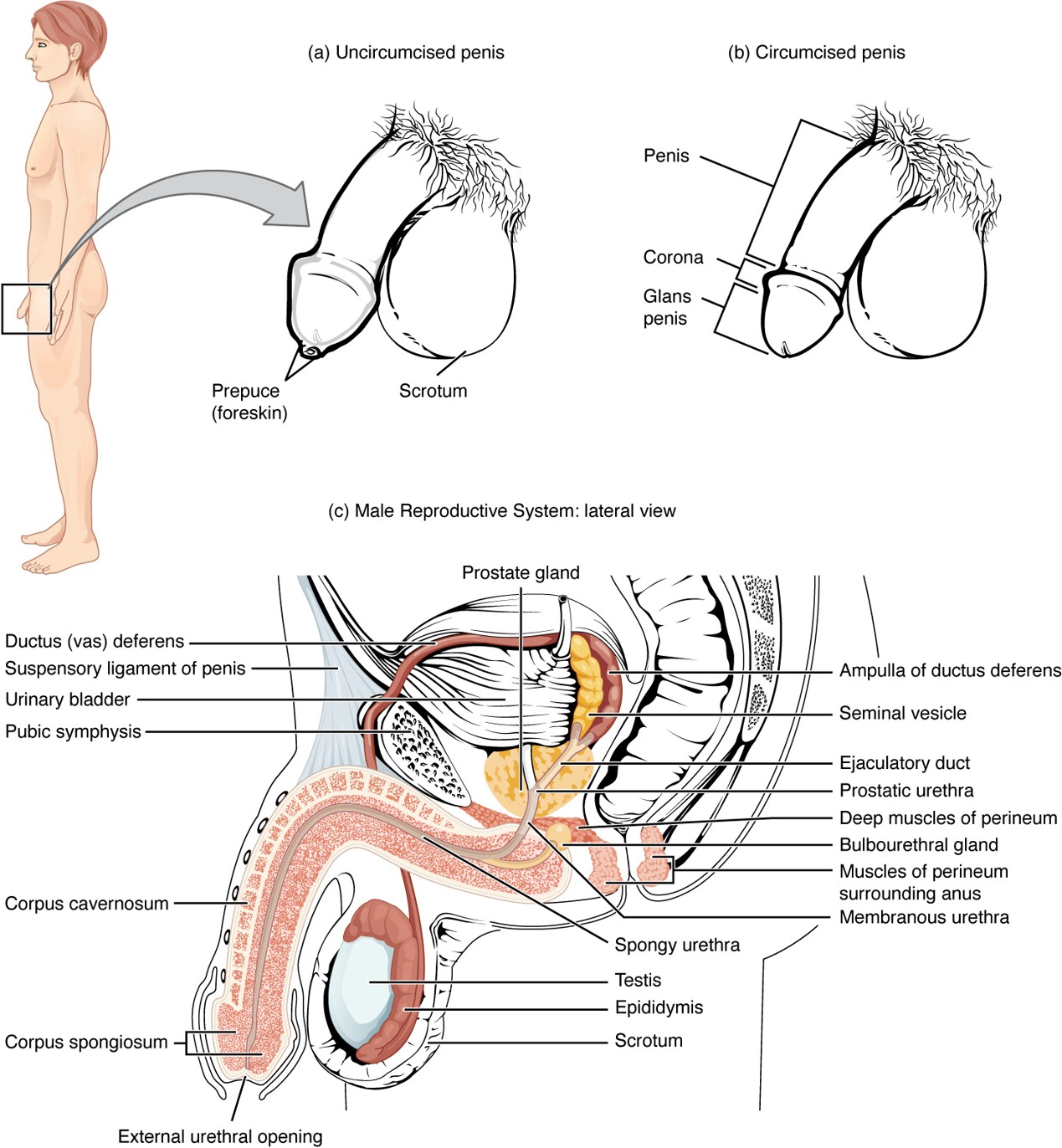
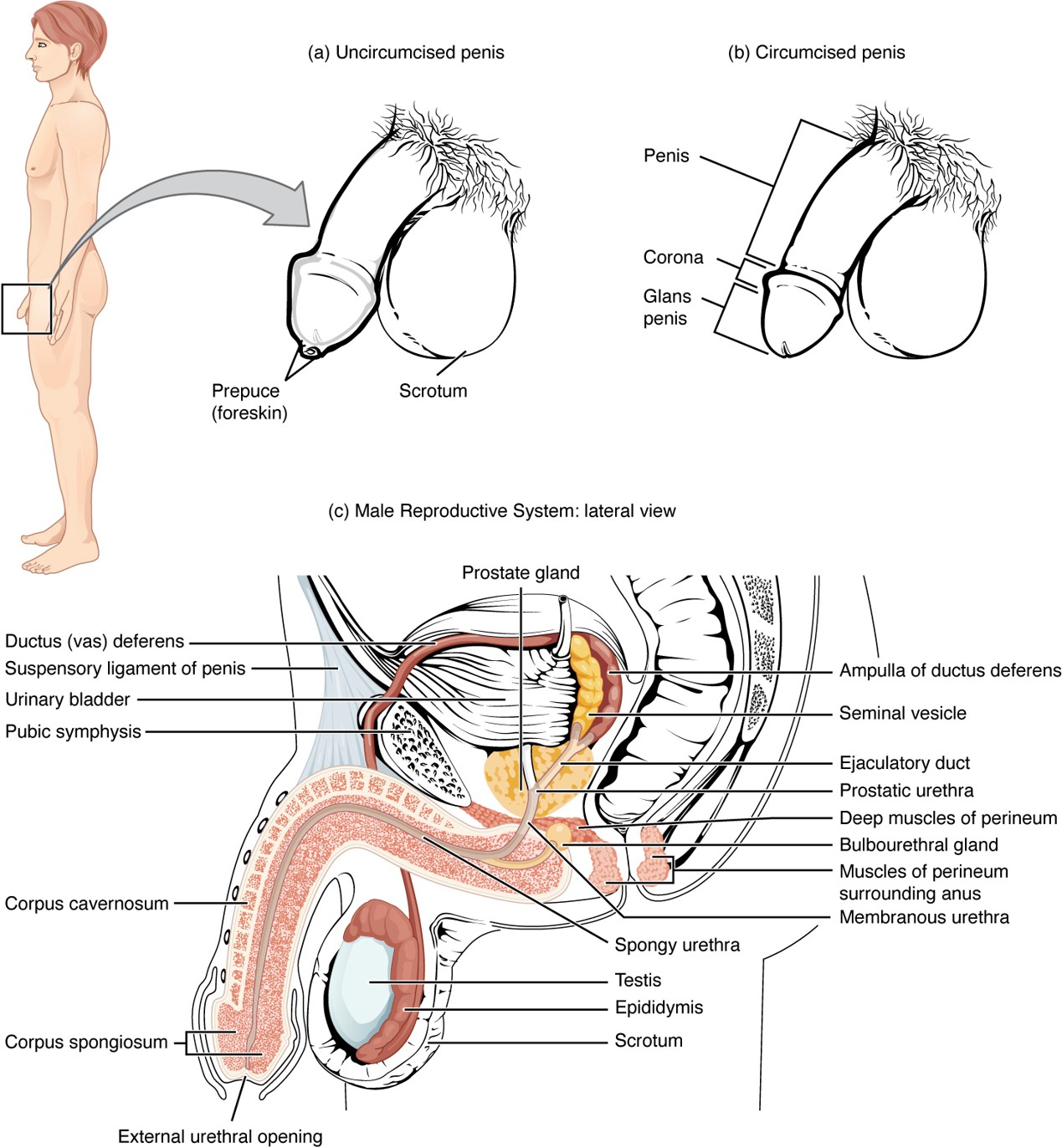
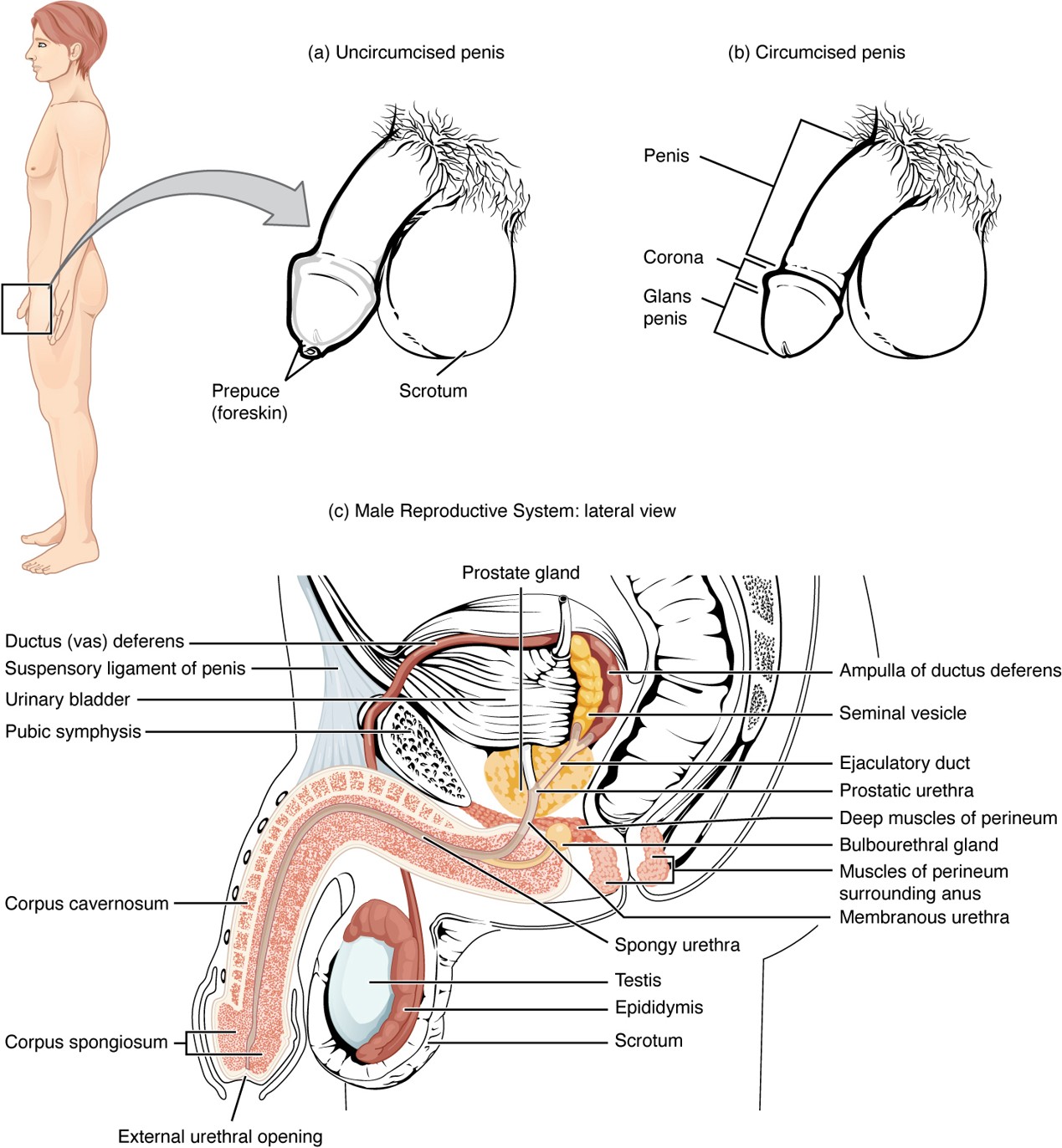
Vas Deferens
A muscular tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct; part of the spermatic cord.
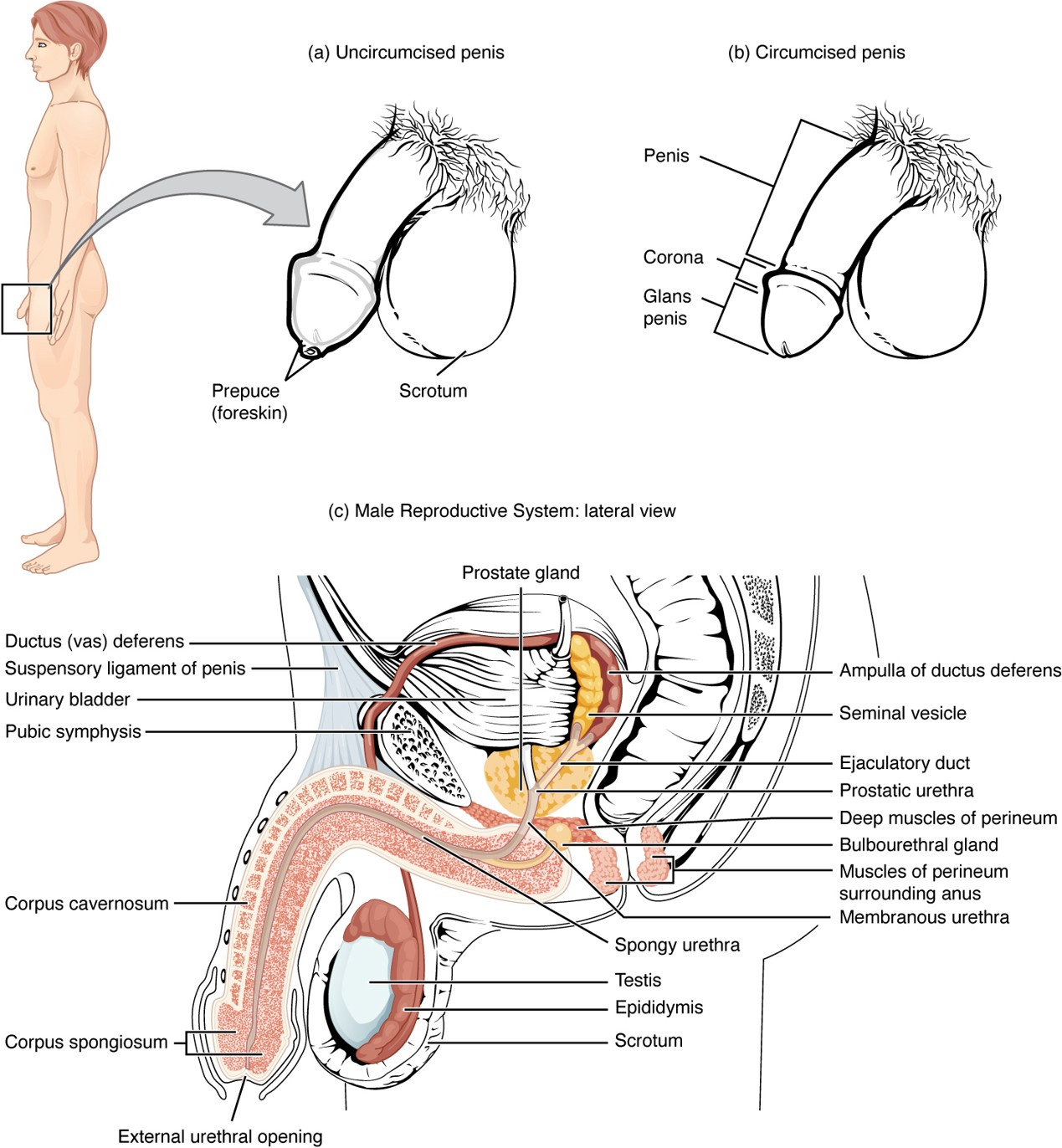
Spermatic Cord
Bundle of structures (including the vas deferens, blood vessels, nerves) that pass through the inguinal canal into the scrotum.
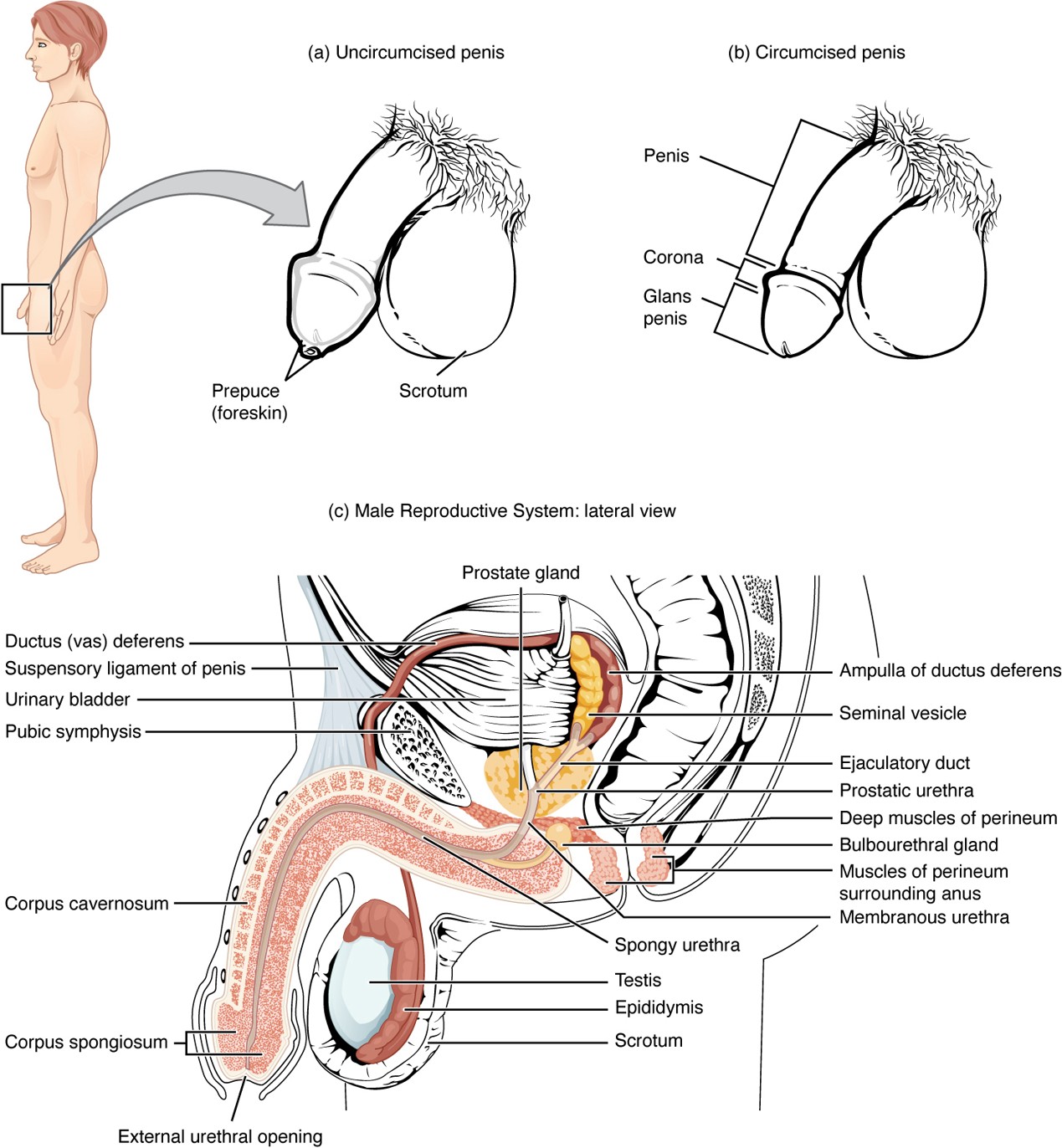
Seminal Vesicle
Gland that contributes fructose and water to nourish sperm and form part of semen.
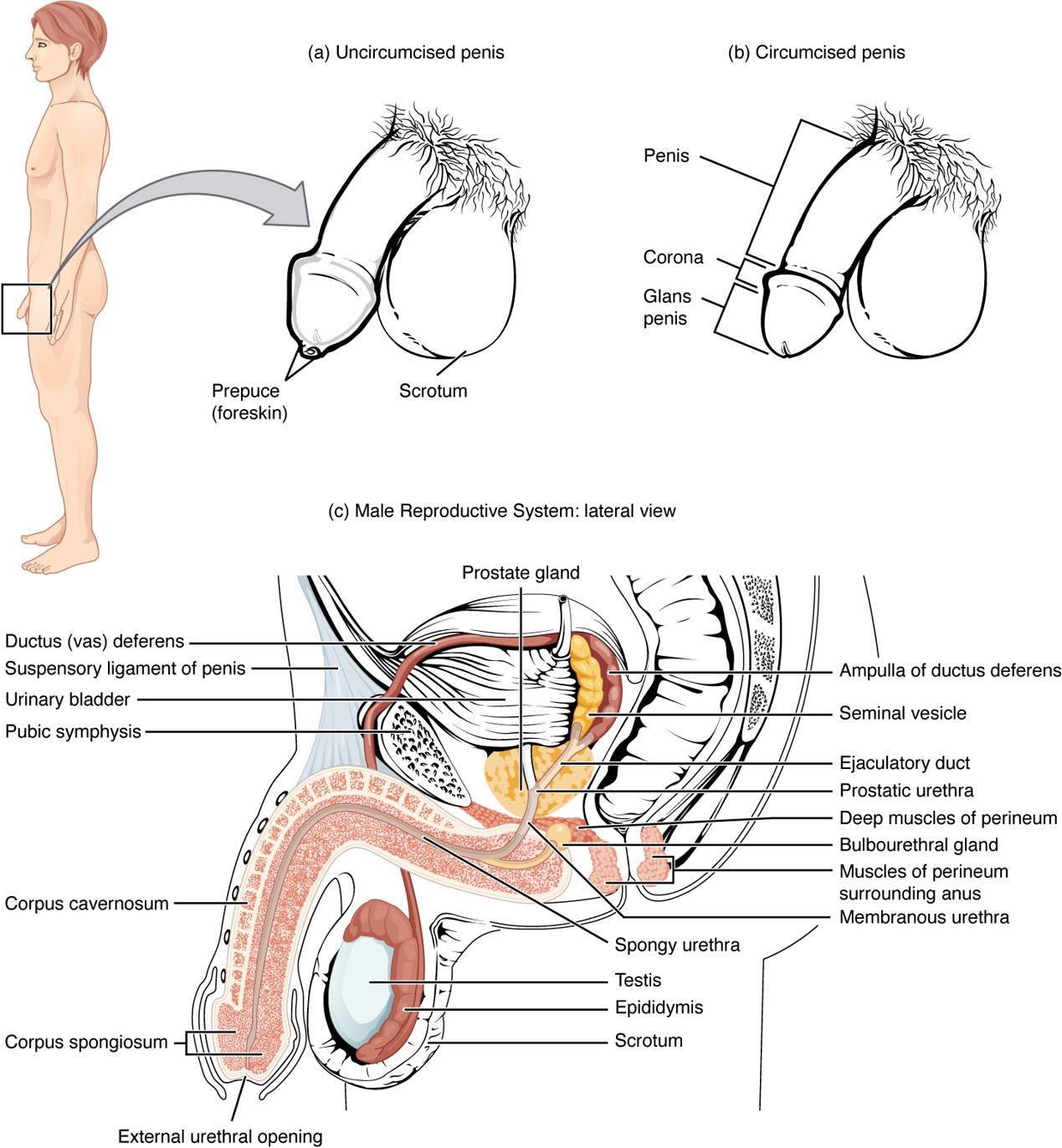
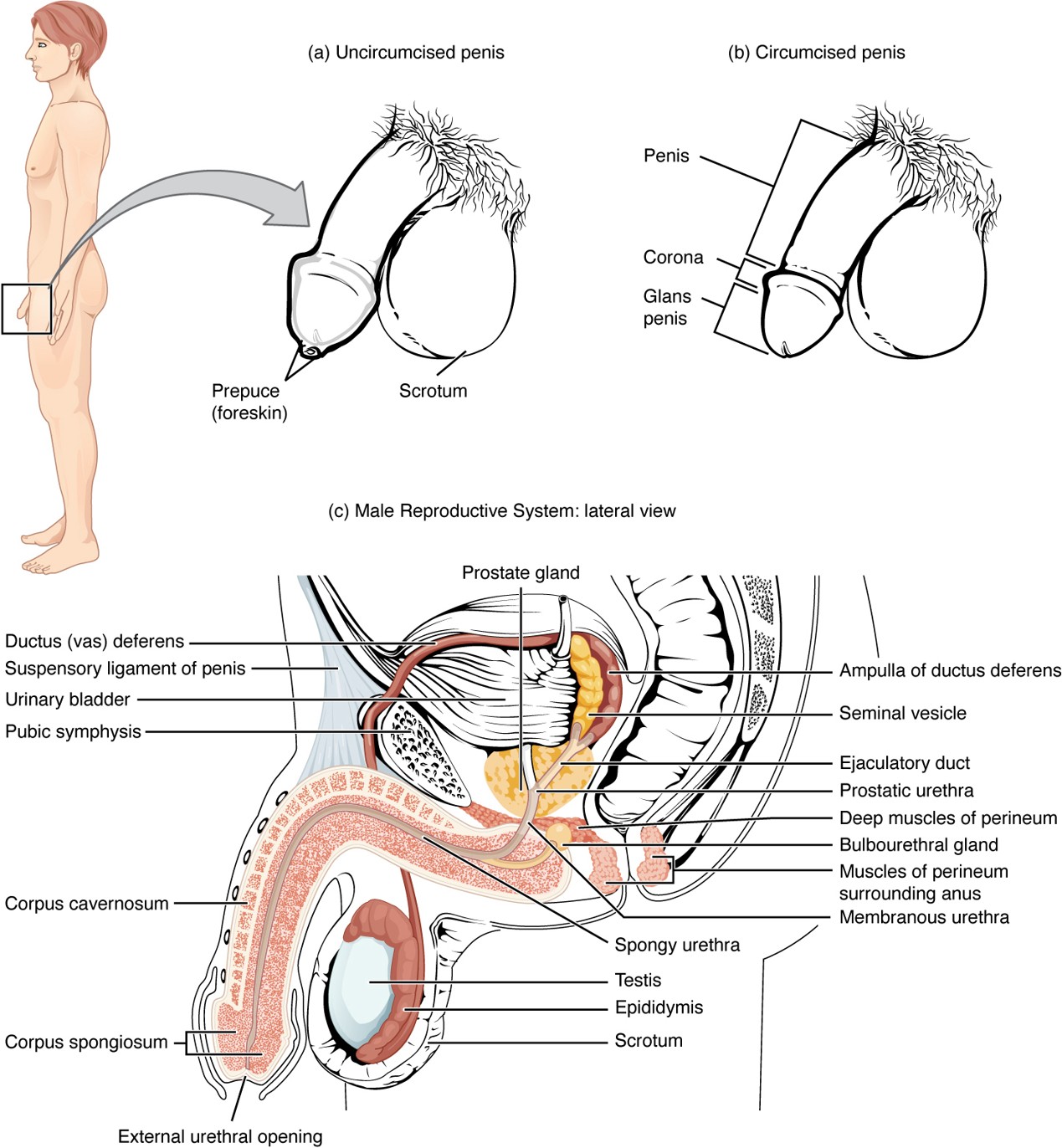
Prostate Gland
Secretes alkaline fluid that helps sperm survive in the acidic environment of the vagina.
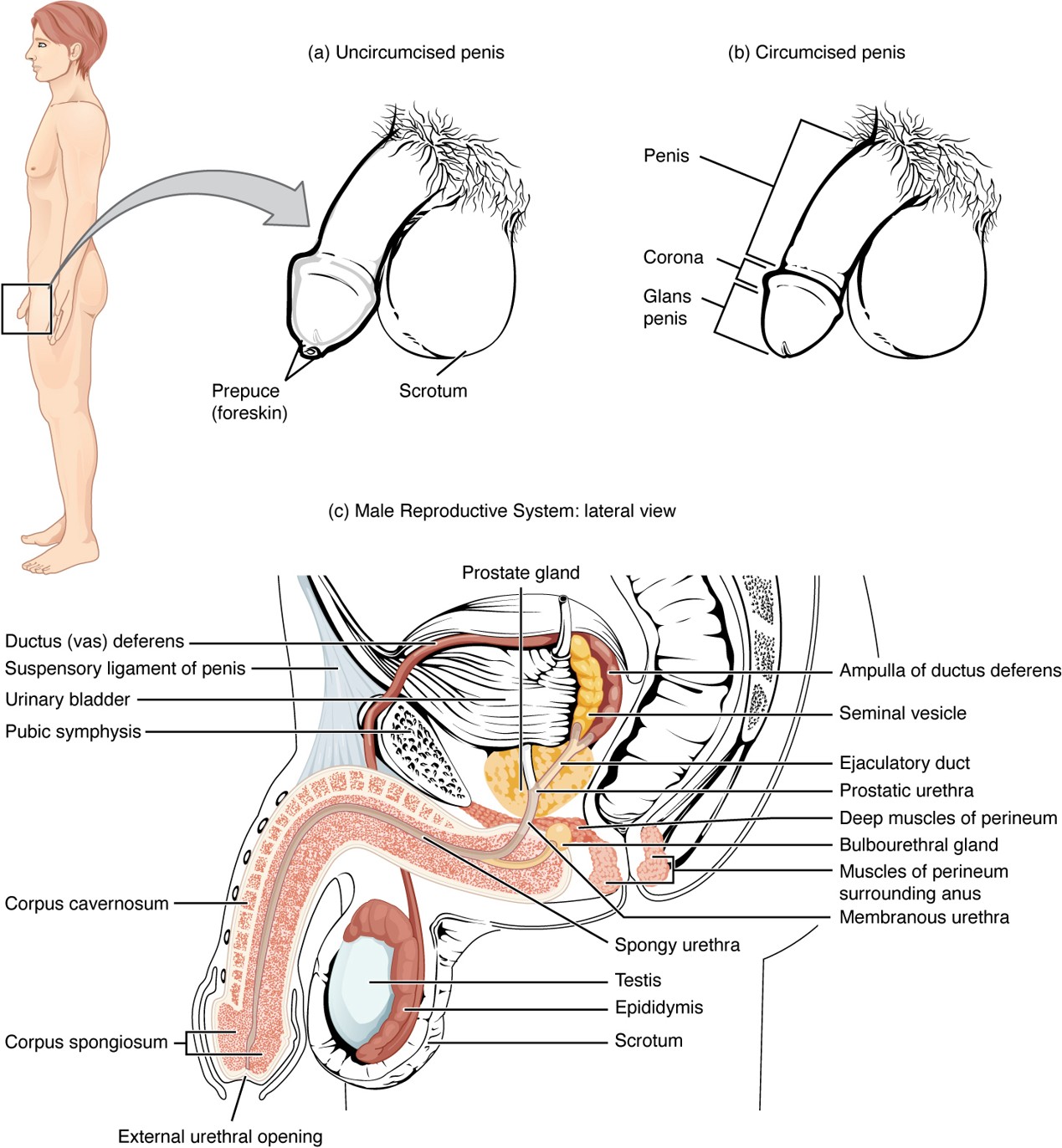
Bulbourethral Gland
Secretes mucin (pre-ejaculate) to lubricate and neutralize the urethra before sperm passes through.
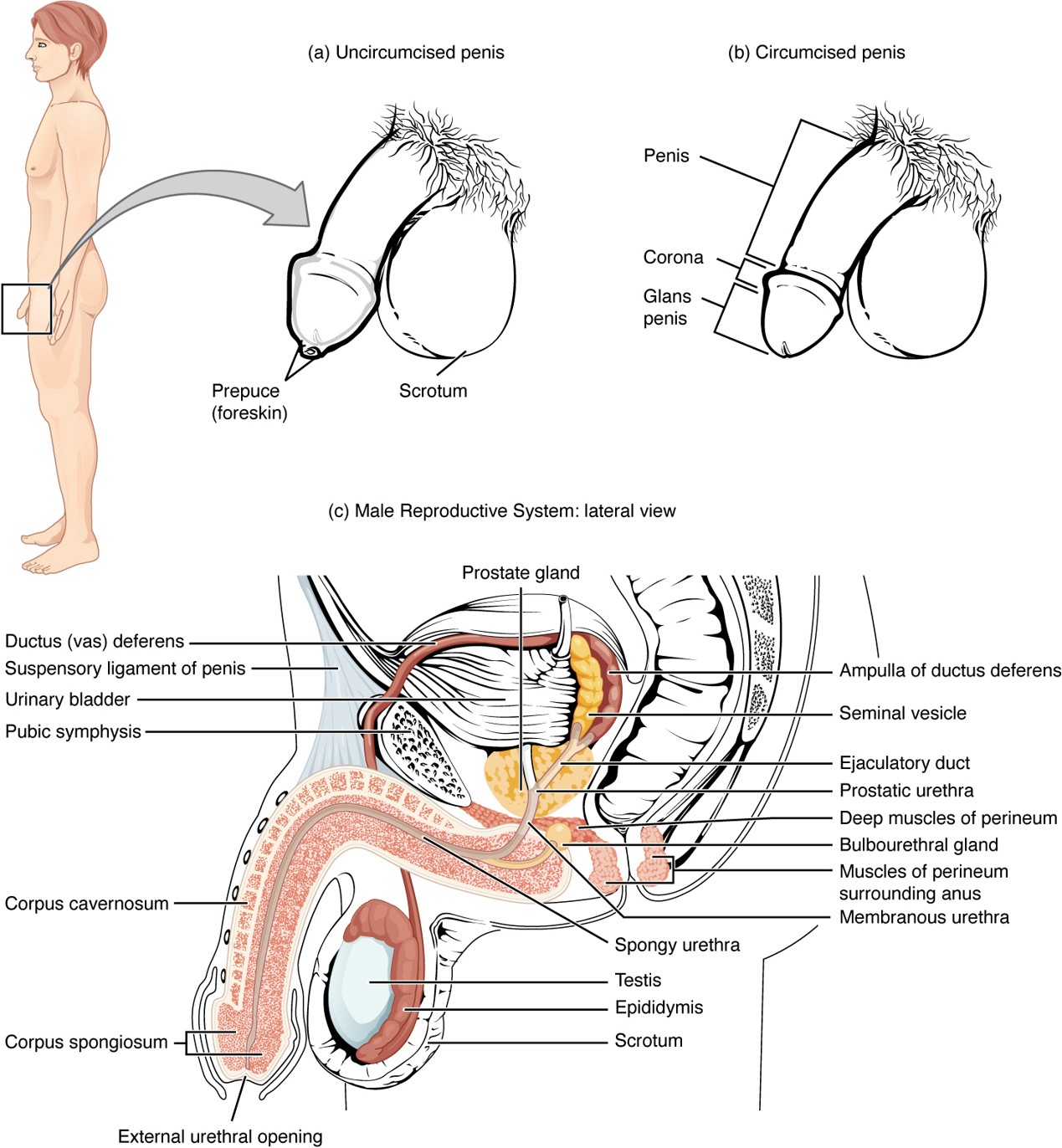
Semen
Fluid containing:
Sperm
Fructose (energy source)
Water
Prostaglandins (aid sperm motility and help sperm enter the uterus)
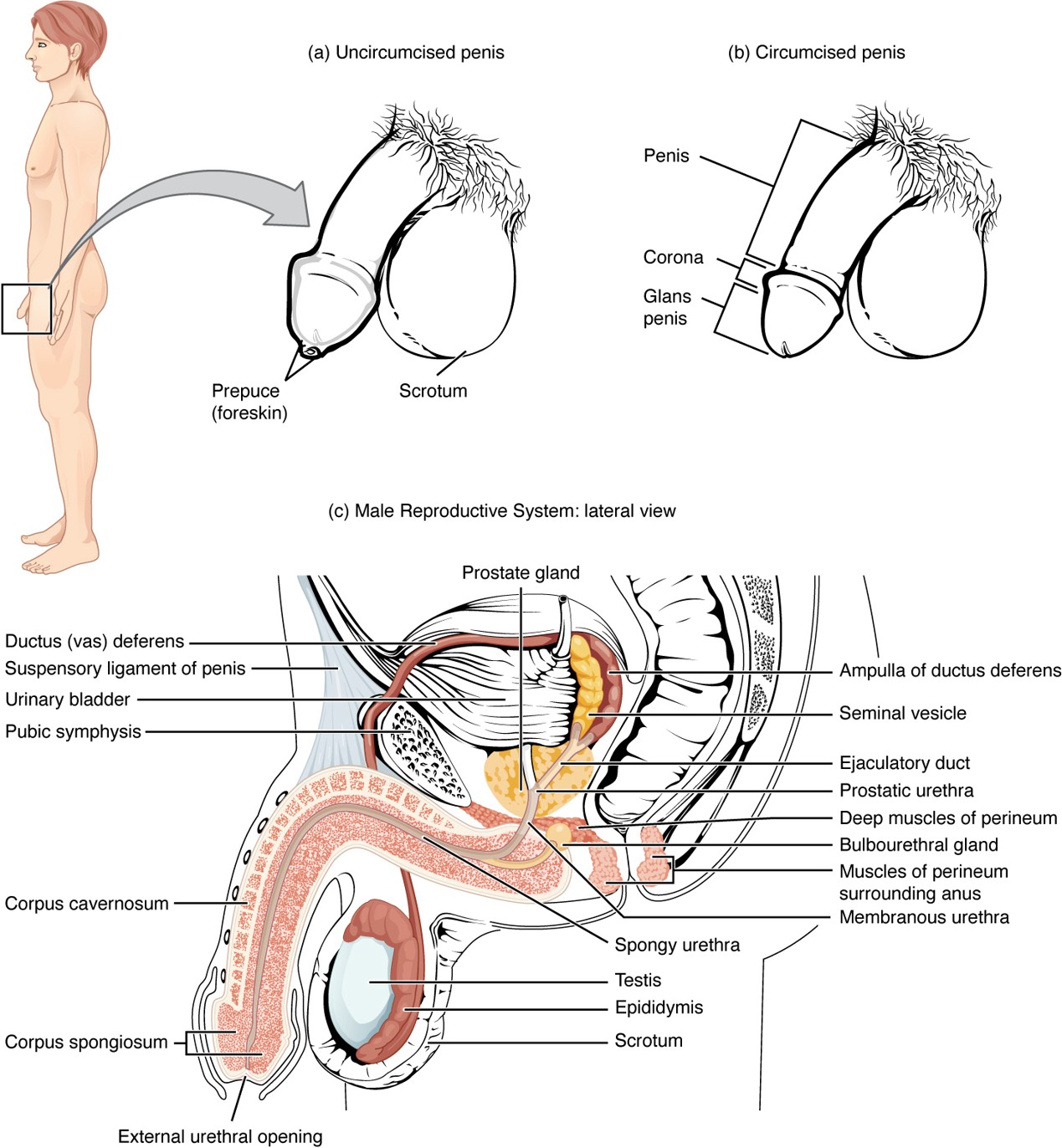
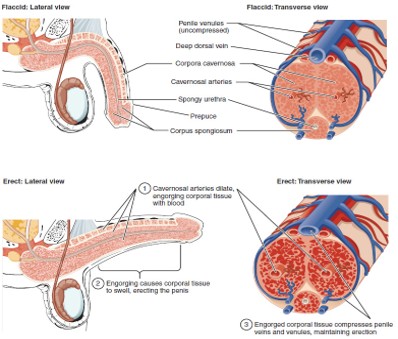
Corpus Cavernosum
Two erectile tissue columns in the penis that fill with blood during an erection.
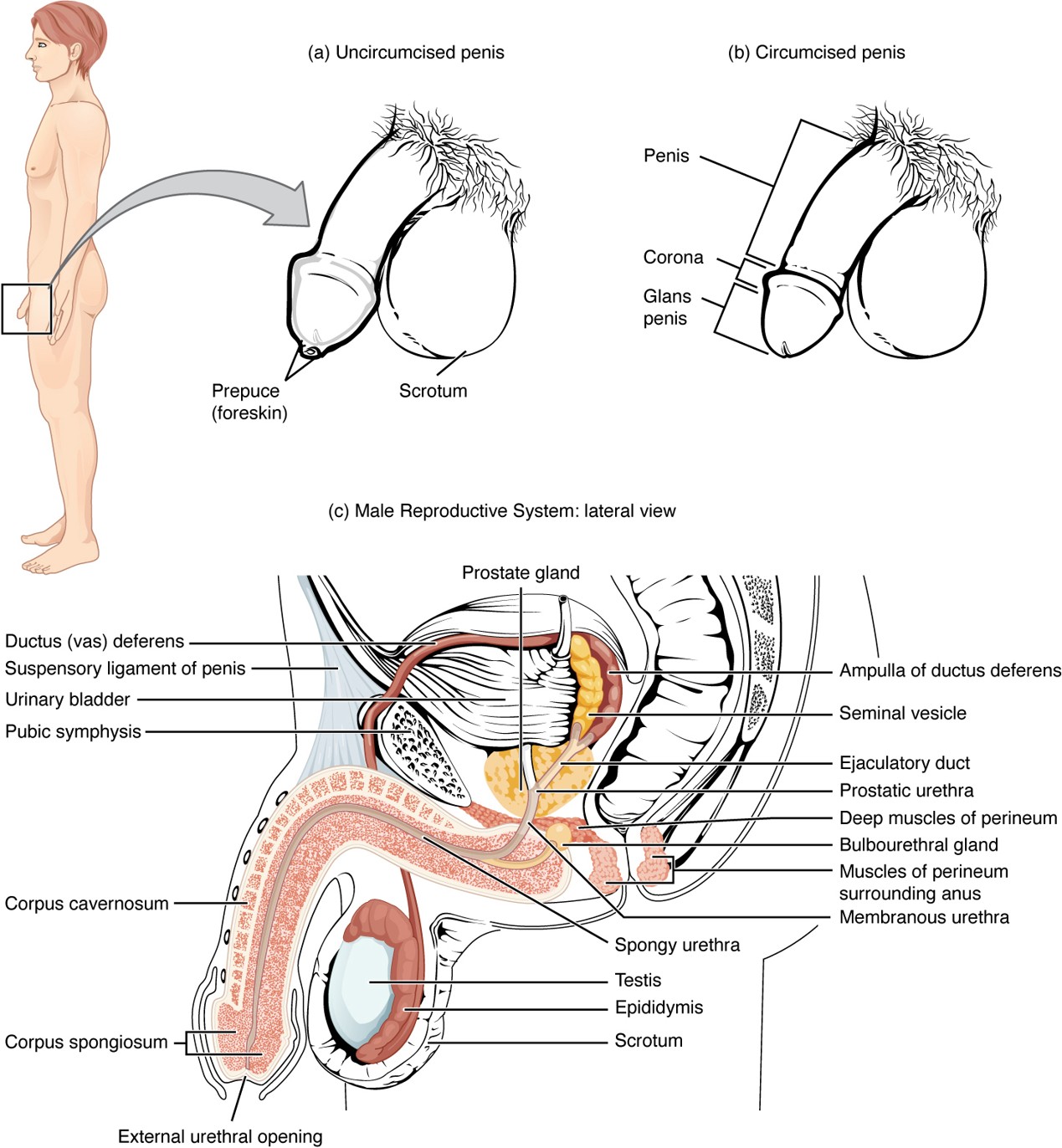
Corpus Spongiosum
Erectile tissue surrounding the urethra that prevents the urethra from collapsing during erection.
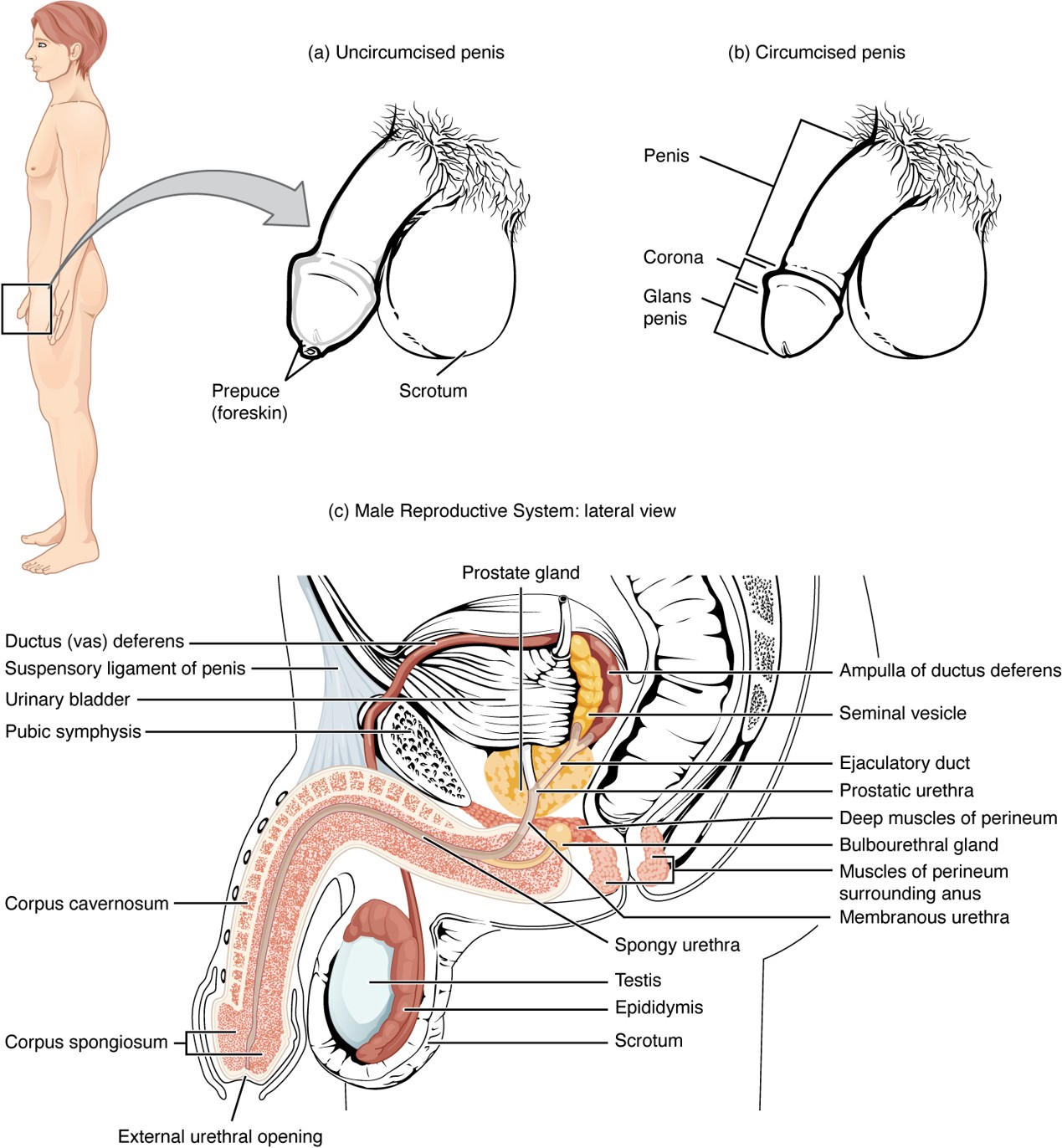
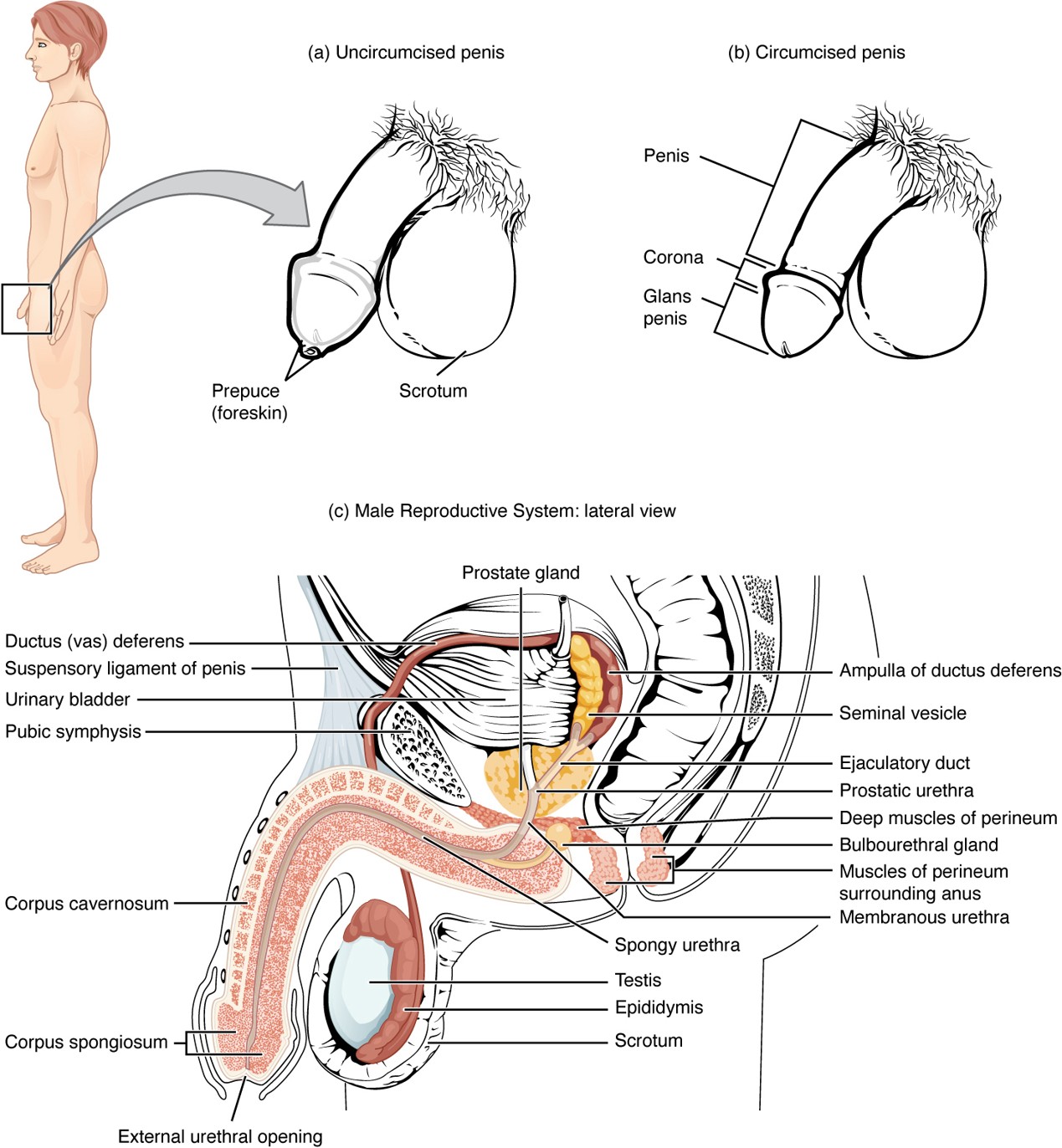
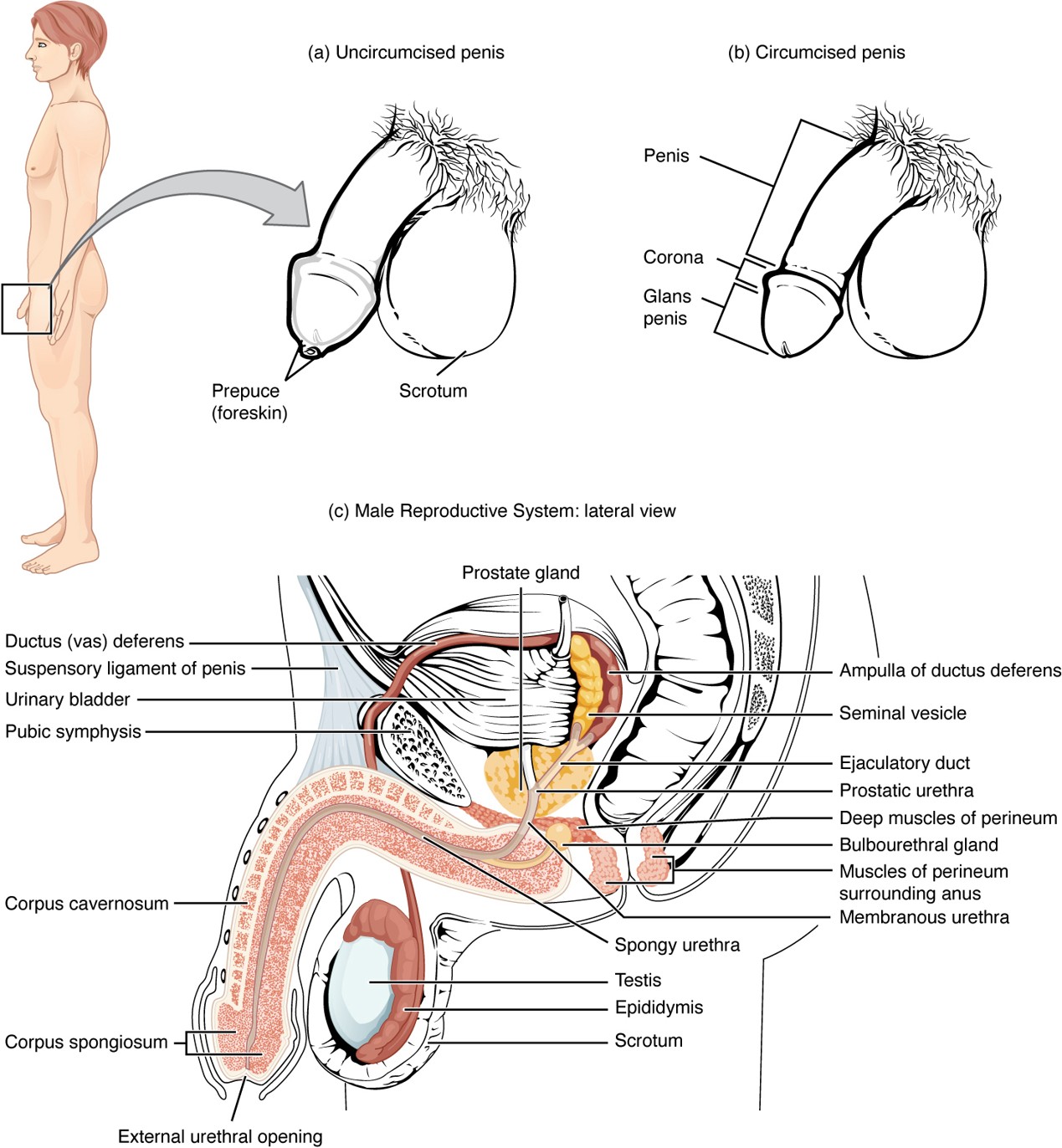
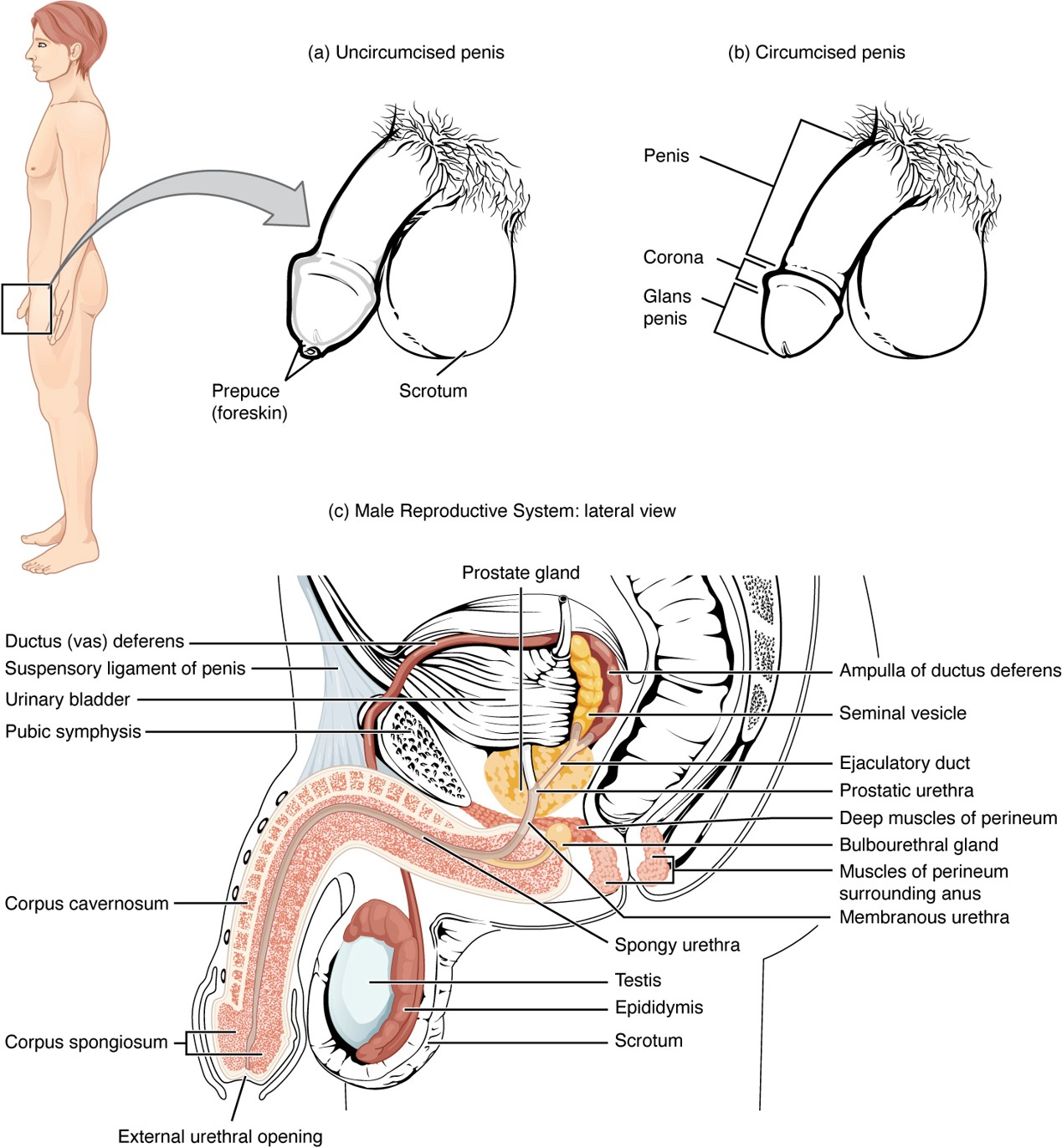
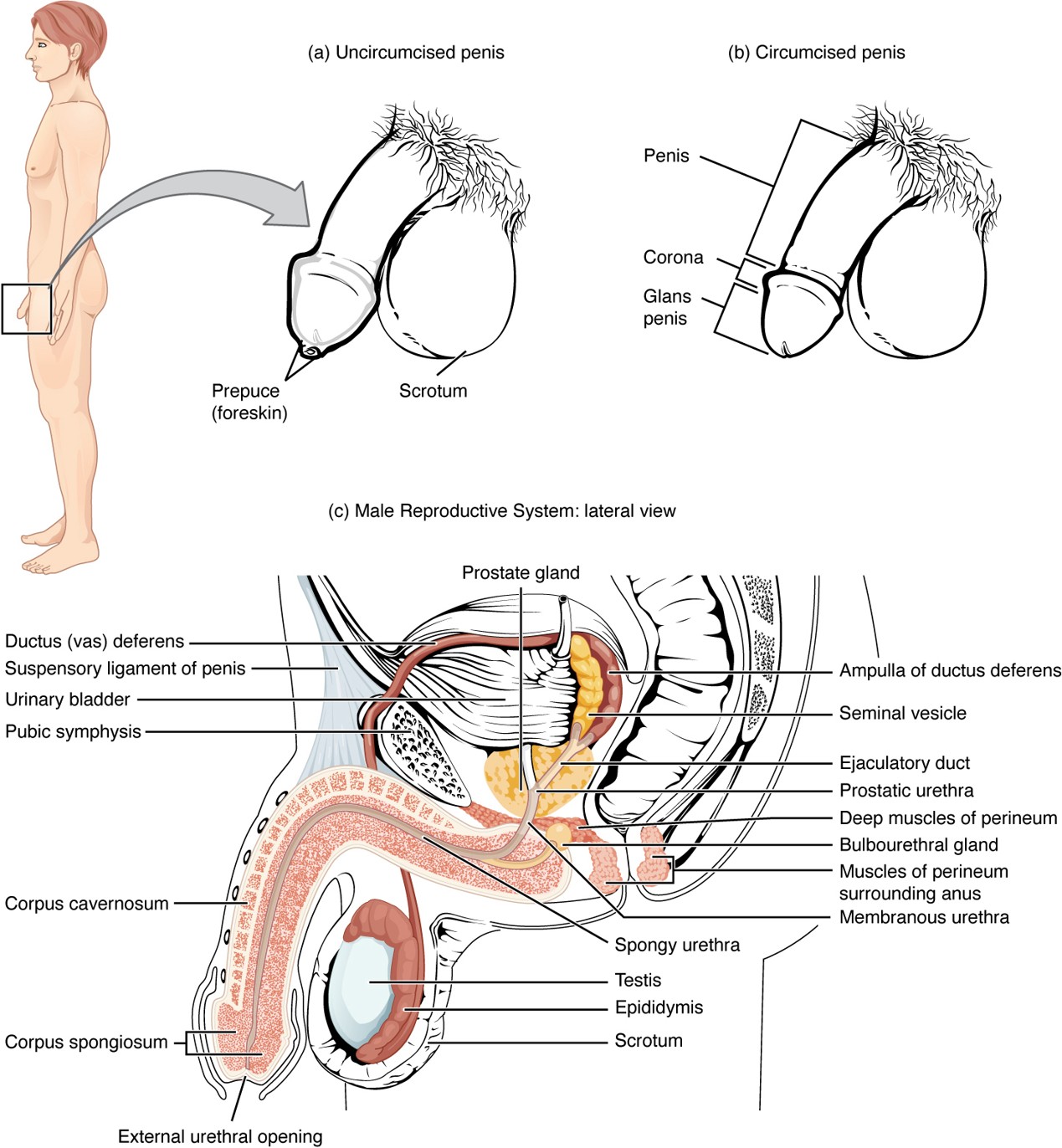
Prepuce (Foreskin)
Skin covering the glans penis; removed during circumcision.
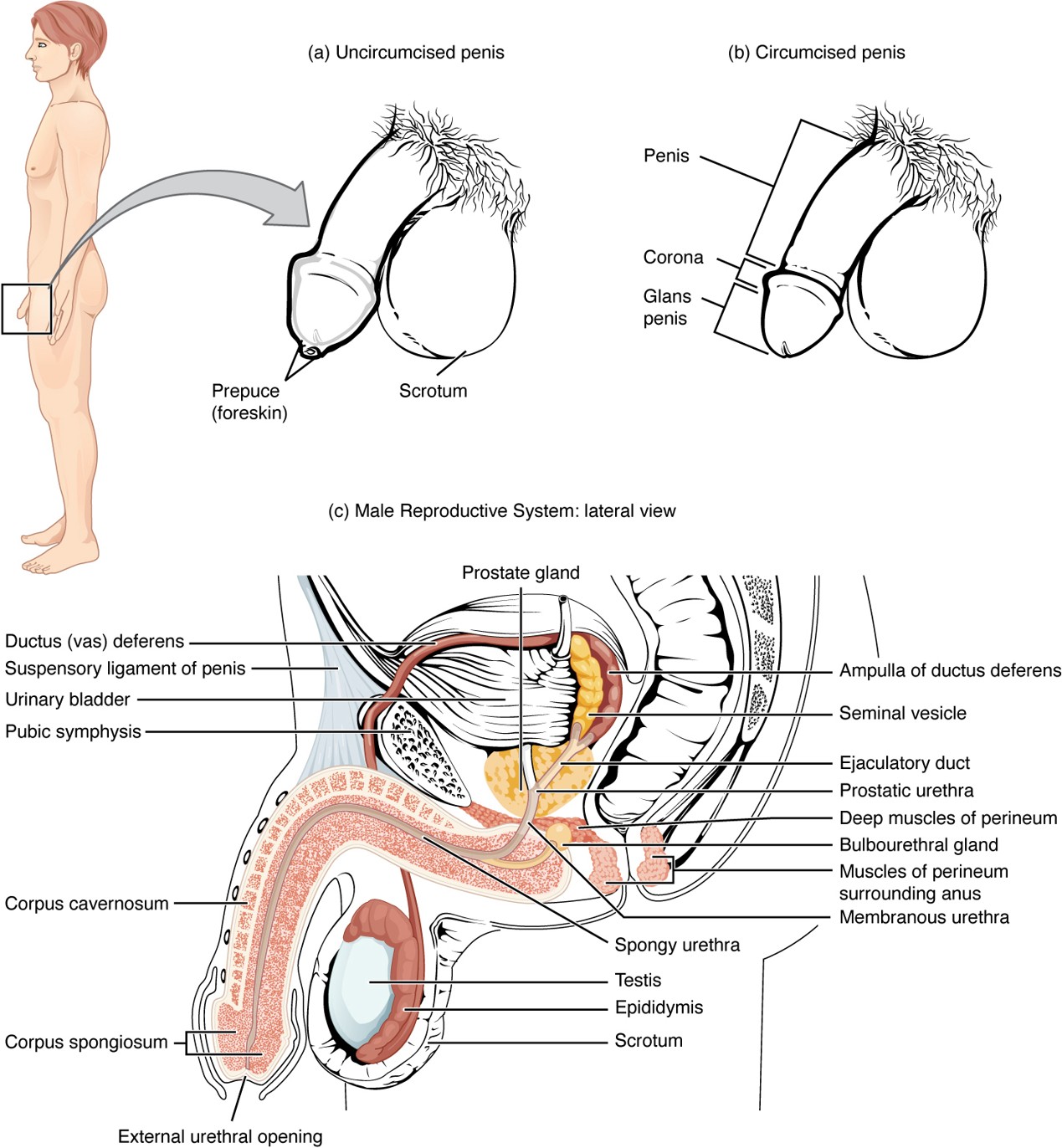
Circumcision
Surgical removal of the prepuce (foreskin).
Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Inability to achieve or maintain an erection; may be due to blood flow, nerve, or hormonal issues.
Inguinal Hernia
When abdominal contents push through the inguinal canal, potentially into the scrotum.
Prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate gland; may cause pain, urination problems, or swelling.
Scrotum
A sac of skin and muscle that houses the testes and helps regulate their temperature.
Testes (Testicles)
Male reproductive organs that produce sperm and testosterone.
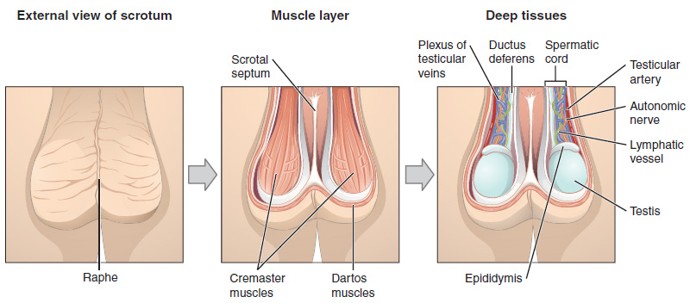
Cremaster Muscle
Skeletal muscle that raises or lowers the testes to regulate temperature.
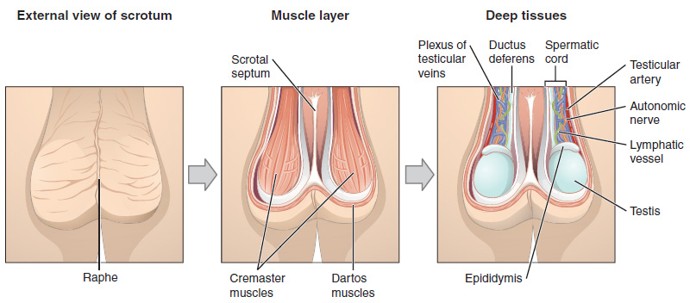
Dartos Muscle
Smooth muscle in the wall of the scrotum that wrinkles or relaxes the scrotal skin to conserve or release heat
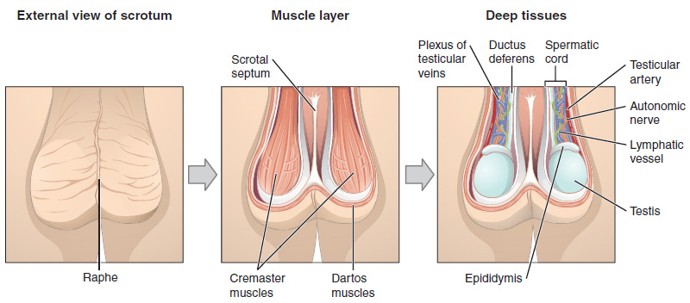
Spermatic Cord
A bundle that includes the vas deferens, blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and cremaster muscle; runs through the inguinal canal into the scrotum.
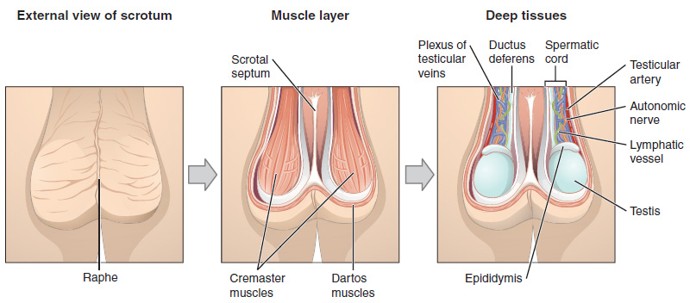
Pampiniform Plexus
A network of veins surrounding the testicular artery that helps cool the arterial blood before it reaches the testes.
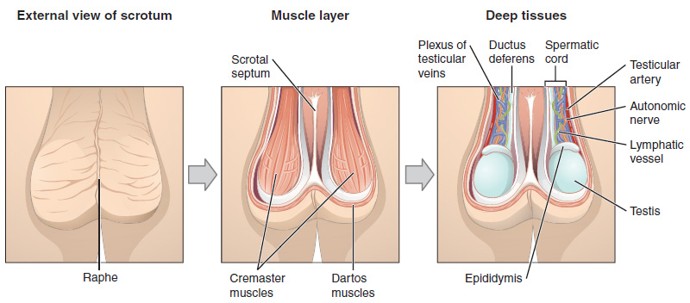
Inguinal Hernia
Occurs when abdominal contents push through the inguinal canal, potentially entering the scrotum; may cause a bulge and discomfort.
Testicular Torsion
A medical emergency where the spermatic cord twists, cutting off blood supply to the testicle; causes sudden severe pain and swelling.
Seminiferous Tubules
Highly coiled tubes inside the testes where sperm are produced through a process called spermatogenesis.
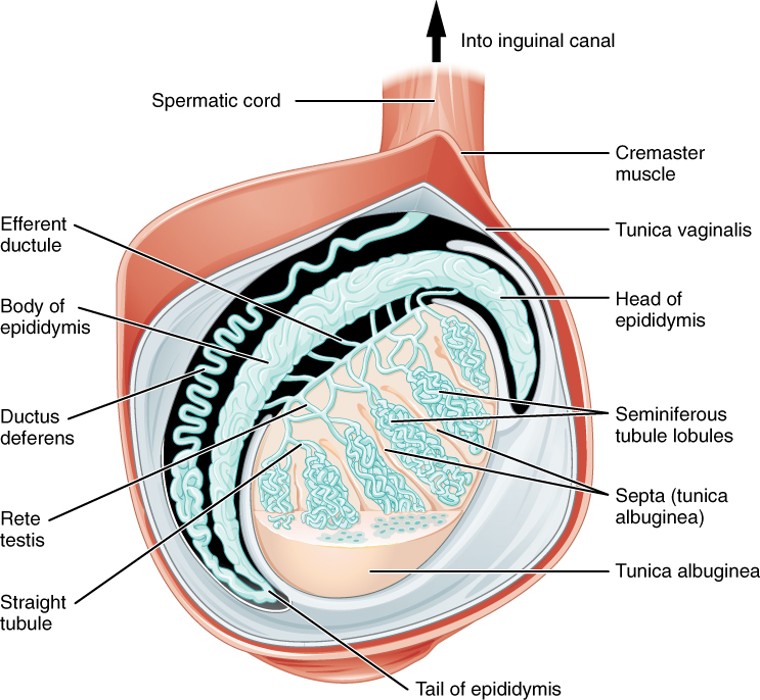
Rete Testis
A network of tubules that collect sperm from the seminiferous tubules and transfer them to the epididymis.
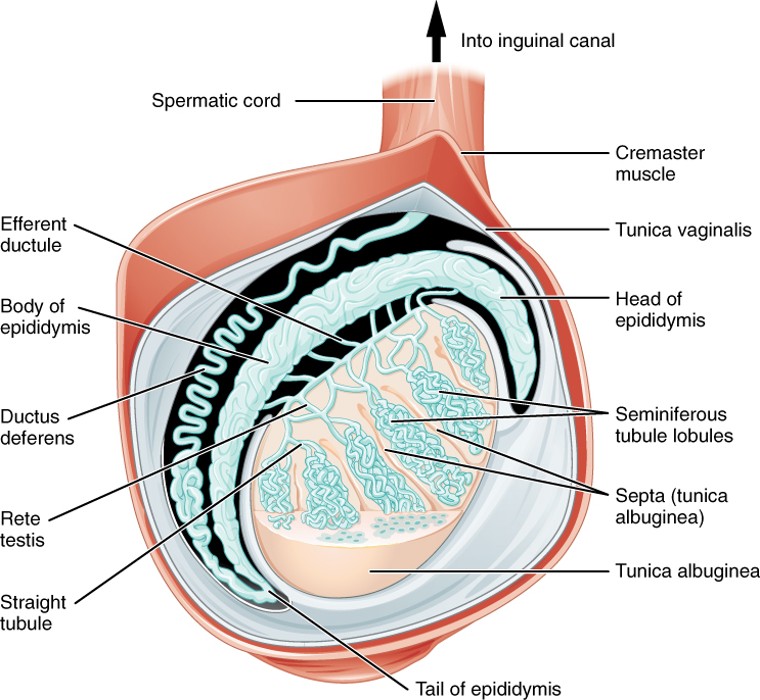
Epididymis
A long, coiled tube on the back of the testis where sperm mature and are stored before ejaculation.
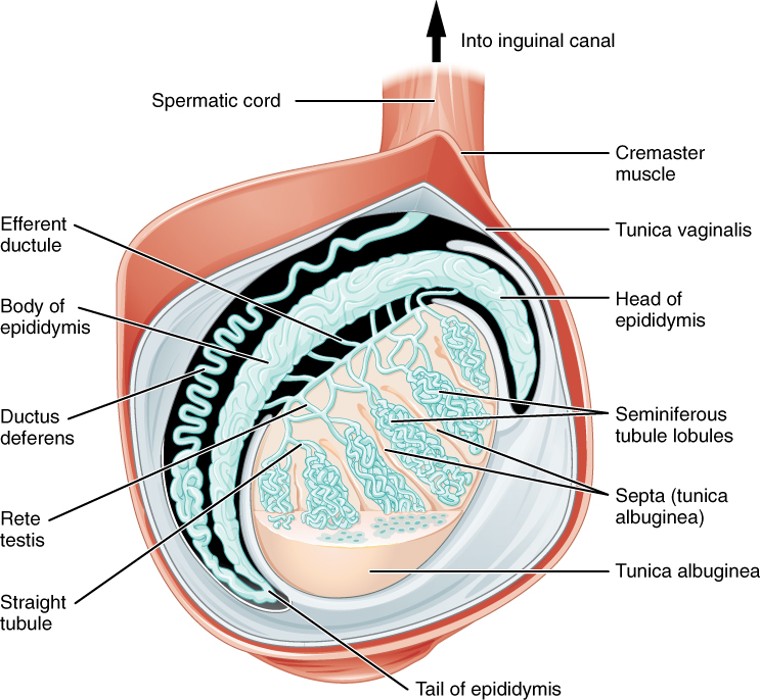
Vasectomy
A surgical procedure that cuts or seals the vas deferens, preventing sperm from mixing with semen (a form of male sterilization).
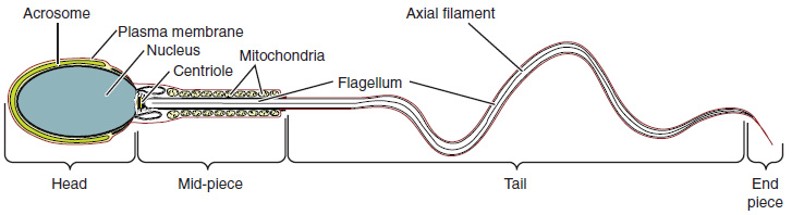
Structure of Sperm
are divided into a head, containing DNA; a mid-piece, containing mitochondria; and a tail, providing motility. The acrosome is oval and somewhat flattened.
Urethra (Penile)
Runs through the corpus spongiosum; carries urine and semen out of the body.
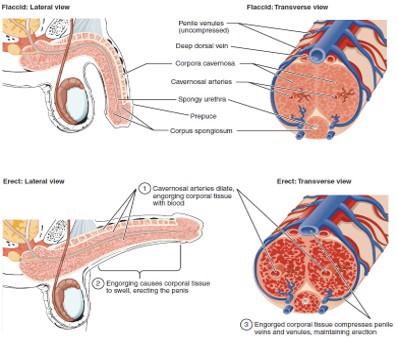
Flaccid State
Occurs when erectile tissue is not filled with blood.
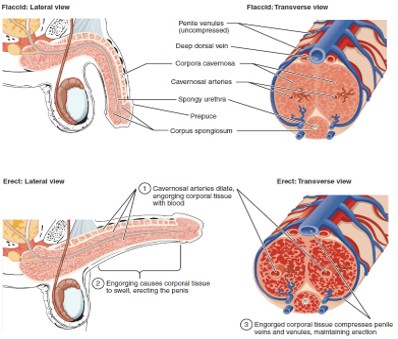
Nitric Oxide (NO)
A chemical messenger that triggers vasodilation by stimulating cGMP production → leads to erection.
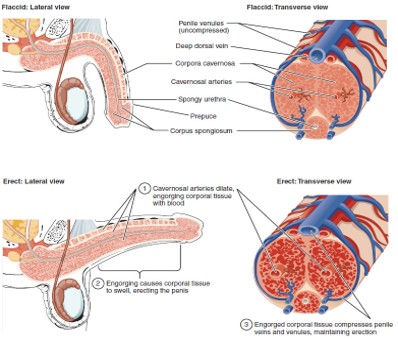
cGMP (Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate)
A chemical that relaxes smooth muscle, allowing blood to fill erectile tissue, producing an erection.
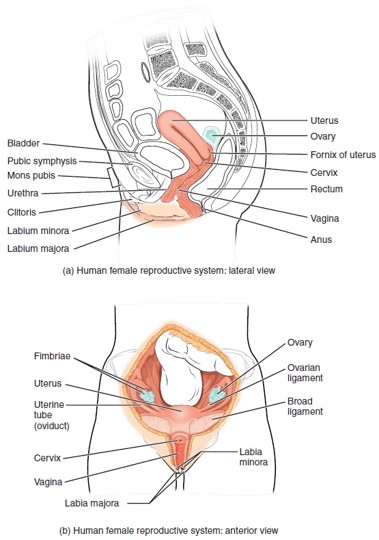
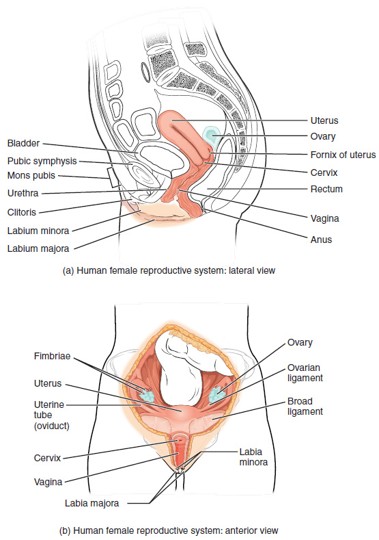
Ovary
Female gonad that produces eggs (oocytes) and secretes estrogen and progesterone.
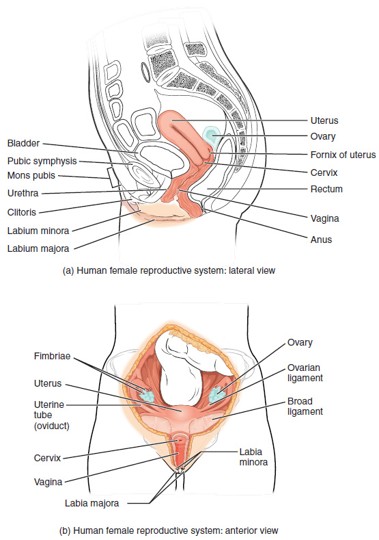
Urethra (Female)
A short tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside; located anterior to the vagina.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
More common in females due to the short urethra and close proximity to the anus; bacteria can easily enter the urinary tract.
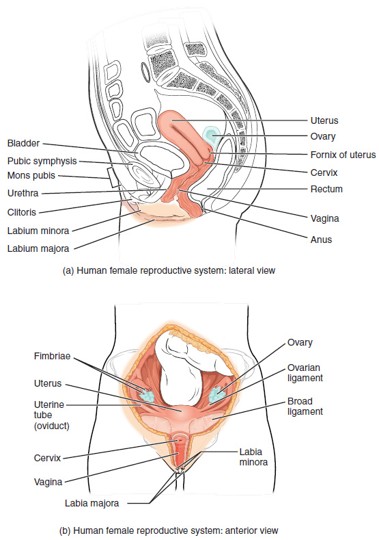
Urinary Bladder
Hollow organ that stores urine; located just behind the pubic symphysis.
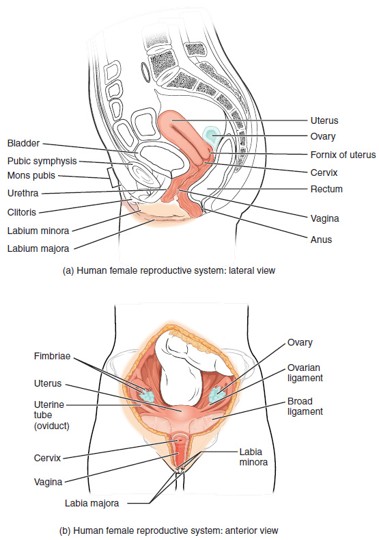
Pubic Symphysis
A cartilaginous joint connecting the two pubic bones; softens during childbirth to allow for passage of the baby.
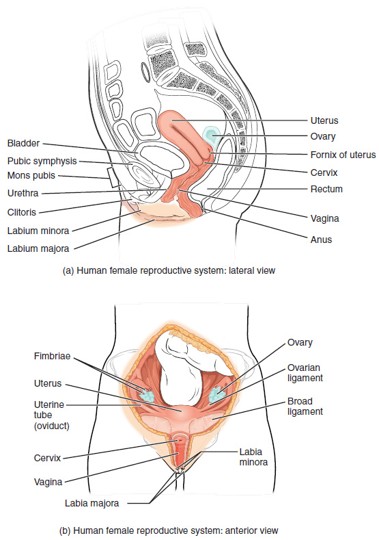
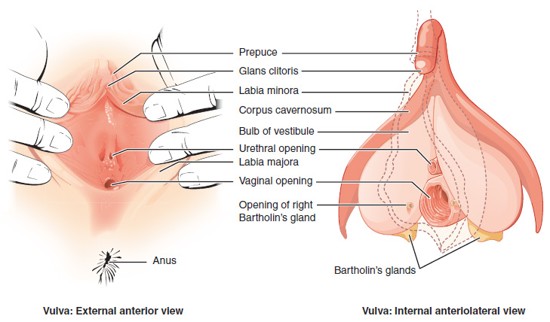
Labia Majora
Outer, larger folds of skin that protect the external genitalia; contain fat and sweat glands.
Labia Minora
Inner, thinner folds of skin; surround the vaginal and urethral openings; contain sebaceous glands.
Clitoris
A small, sensitive organ made of erectile tissue, located at the top of the vulva; homologous to the penis.
Female Circumcision (FGM)
The removal or alteration of the clitoris or other external genitalia; considered a harmful and non-medical practice with serious physical and emotional consequences.
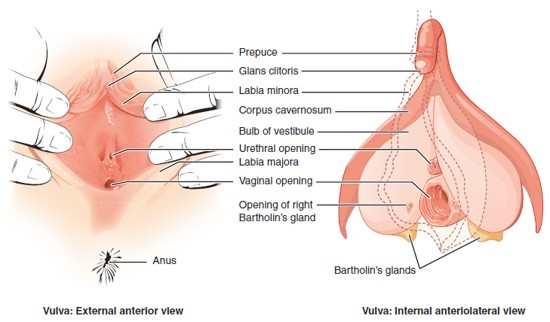
Vulva
The collective term for the external female genitalia, including the labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, prepuce, vestibule, and external openings of the urethra and vagina.
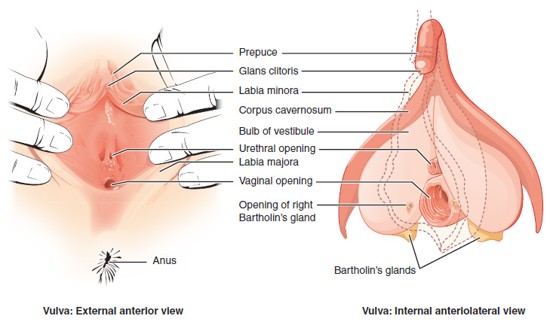
Prepuce (of the Clitoris)
A fold of skin that partially covers the clitoris; formed by the merging of the labia minora; similar in function to the male foreskin.
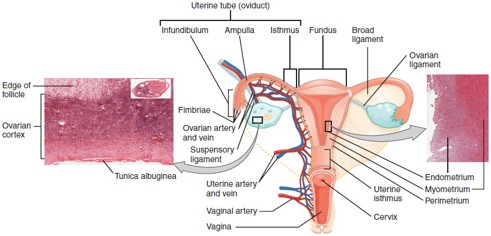
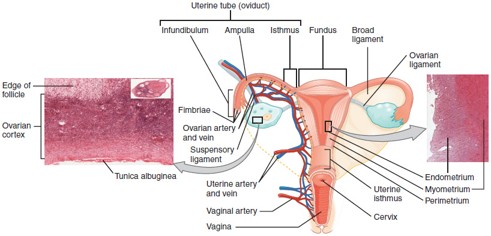
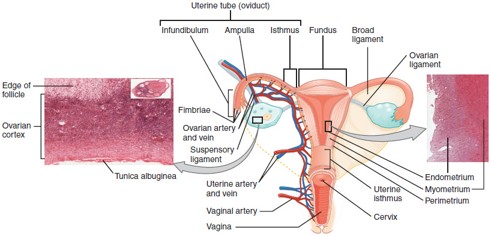
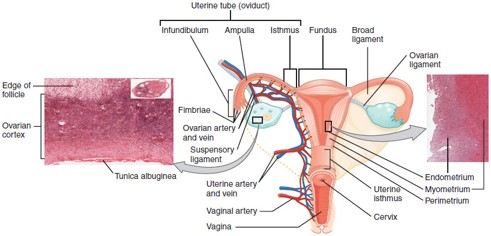
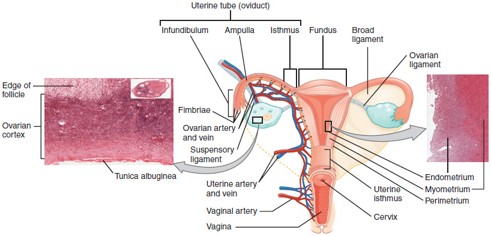
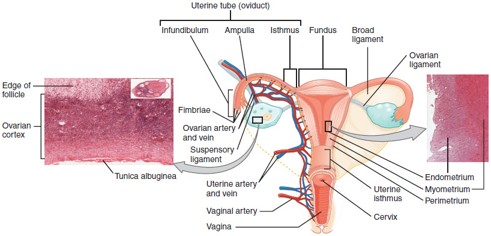
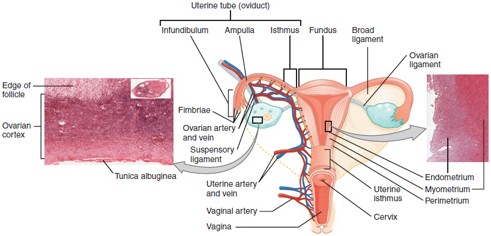
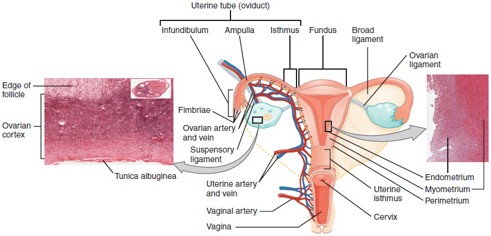
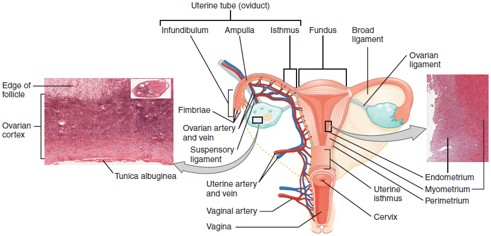
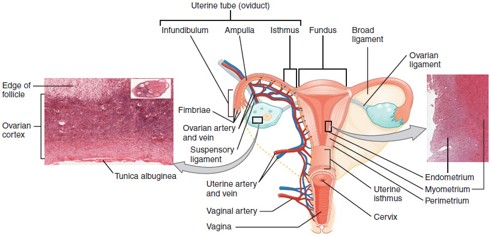
Fallopian Tube (Uterine Tube/Oviduct)
Carries the oocyte from the ovary to the uterus; fertilization typically occurs in the ampulla, the widest part of the tube.
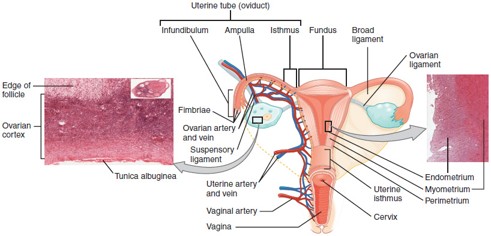
Uterus
Hollow, muscular organ where a fertilized egg implants and grows into a fetus.
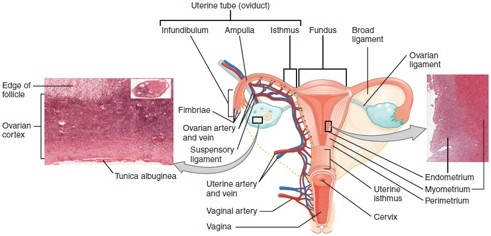
Cervix
The lower, narrow part of the uterus that opens into the vagina; produces cervical mucus and dilates during childbirth.
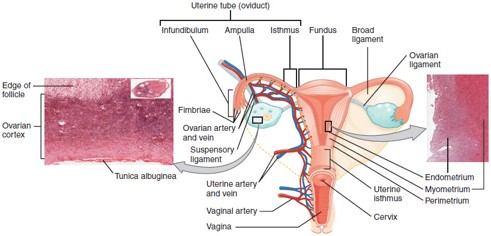
Vagina
Muscular canal that receives the penis, serves as the birth canal, and allows menstrual flow to exit the body.
Ampulla
The widened part of the fallopian tube where fertilization usually occurs.
Implantation
The process by which a fertilized egg (zygote) sticks to the endometrium, beginning pregnancy.
Tubal Pregnancy
A type of ectopic pregnancy where the embryo implants in the fallopian tube—life-threatening if untreated.
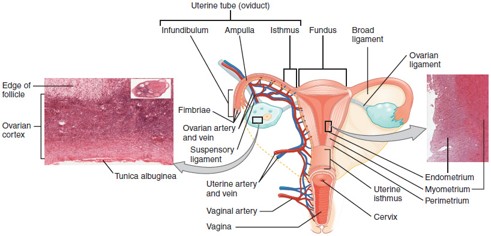
Ectopic Pregnancy
A pregnancy that occurs outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes.
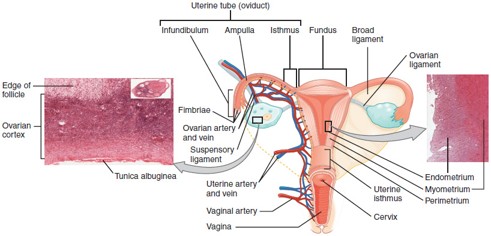
Endometrium
The inner lining of the uterus that thickens monthly and sheds during menstruation if implantation doesn’t occur.
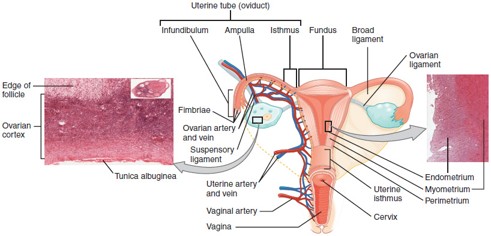
Myometrium
The middle muscular layer of the uterus, made of smooth muscle; contracts during labor and menstruation.
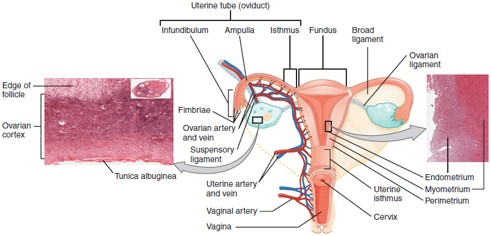
Fornix
The recessed area around the cervix at the upper end of the vagina.
Ovarian Cancer
Cancer that arises from the ovaries; often detected late due to subtle symptoms.
Breast Cancer
Cancer of the breast tissue, often involving the milk ducts or lobules; early detection improves prognosis.
Cervical Cancer
Cancer of the cervix, often caused by HPV infection; can be detected early by Pap smear.
PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome)
Physical and emotional symptoms occurring before menstruation, such as cramps, bloating, irritability, and fatigue.
Endometriosis
A condition where endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus, often causing pain, infertility, and irregular bleeding.
Uterine Prolapse
Occurs when the uterus drops into or out of the vagina due to weakened pelvic floor muscles.
Ovarian Cycle
The monthly cycle of events in the ovary that leads to ovulation and potential pregnancy; divided into:
Follicular phase
Ovulation
Luteal phase
Follicular Phase (Days 1–13)
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) stimulates growth of follicles in the ovary
Estrogen increases as follicles develop
Endometrium rebuilds during this time
Ovulation (Around Day 14)
Triggered by a sharp LH (Luteinizing Hormone) surge
A mature follicle releases an egg (oocyte) into the fallopian tube
Luteal Phase (Days 15–28)
The ruptured follicle becomes the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone
Progesterone thickens and maintains the endometrium
If no fertilization occurs, corpus luteum degenerates, progesterone drops → menstruation
Menstruation (Days 1–5)
Shedding of the endometrial lining
Caused by drop in estrogen and progesterone
Secretory Phase (Lining Events – Days 15–28)
Endometrium becomes thick and vascularized, ready for implantation
Driven mainly by progesterone from corpus luteum
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
Stimulates development of ovarian follicles during the follicular phase
LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
Triggers ovulation and stimulates formation of the corpus luteum
Estrogen
Produced by developing follicles
Helps regrow the endometrium
Promotes LH surge
Progesterone
Secreted by the corpus luteum
Maintains the endometrium for possible pregnancy
Drops if no fertilization, leading to menstruation
Alveoli (in Breast Tissue)
Small glandular sacs in the breast that produce milk during lactation.
Lactiferous Ducts
Tubes that carry milk from the alveoli to the nipple.
Nipple
The external opening through which milk is released from the breast.
Areola
The pigmented area surrounding the nipple; contains sebaceous glands that help lubricate and protect the skin during breastfeeding.
Suspensory Ligaments (of Cooper)
Fibrous bands that support the breast tissue and help maintain breast shape.