L9 - Synthesis of AAs, purines, pyrimidines
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
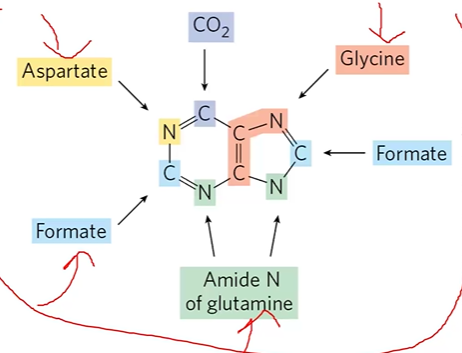
origin of ring atoms
C CO2, N aspartate, NCC glycine, C formate x 2, N glutamine x 2
de novo synthesis begins with
PRPP
de novo synthesis 1
glutamine (N) + PRPP (C1) > 5PRSA + glutamate + PPi
de novo 2
4PRSA + glycine (C) + ATP > GAR + ADP + Pi
de novo steps 3-11
***overall: use glutamine asp fumarate folate HCO3- , ATP, 1C donors
**** energy expensive
PRPP > 5PRSA > GAR > FGAR > FGAM > AIR < N5CAIR > CAIR > SAICAR > AICAR > FAICAR > IMP
de novo step 3-5
GAR > FGAR > FGAM > AIR
uses folate, glutamine, ATP, makes H2O
ring closure
de novo steps 6-7
are 1 step un eukaryotes
AIR > N5-CAIR > CAIR
de novo steps 8-10
CAIR > SAICAR > AICAR > FAICAR
uses Asp, folate, ATP
makes fumarate
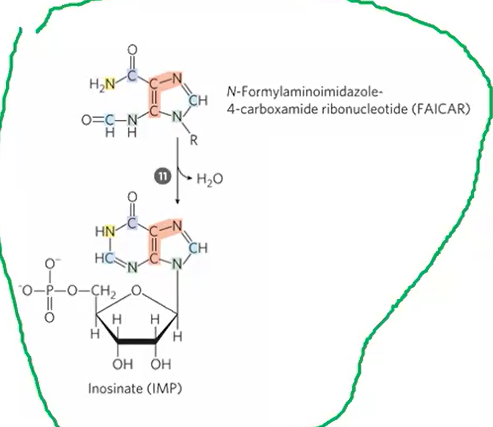
de novo step 11
FAICAR > IMP + H2O
first purine ring closure
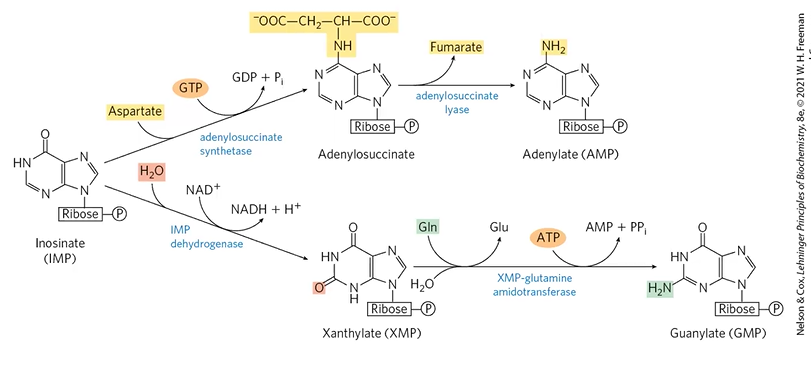
IMP turns into ___ or ____ via ____ or _____.
XMP or adenylsuccinate;
IMP DHase + H2O + NAD+
ASStase + Asp + GTP
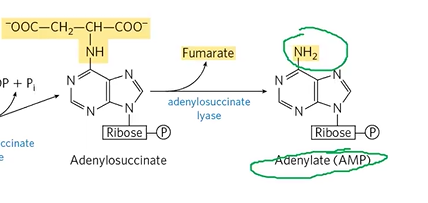
adenylosuccinate
turns into AMP via adenylosuccinate lyase, also makes fumarate
*structure
xanthylate XMP
turns into GMP via XMP-GluAmidoTransase, Gln, ATP
*structures
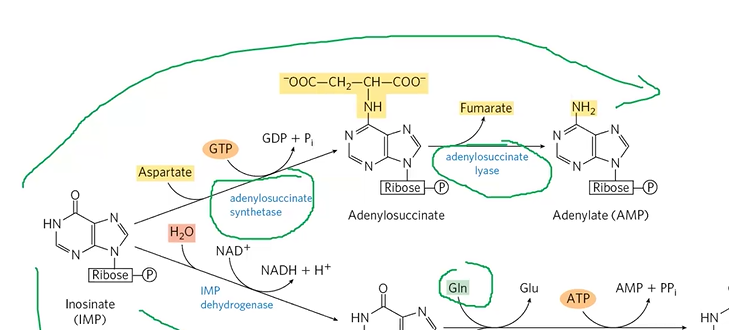
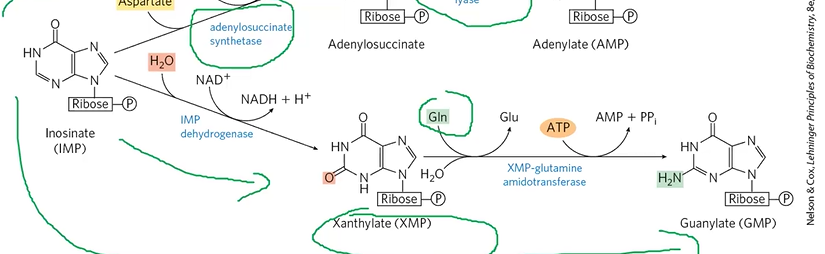
AMP formation
IMP + Asp + GTP + AdenylSStase > adenylosuccinate
adenylosuccinate + adenylosuccinate lyase > AMP
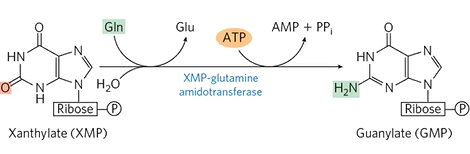
GMP formation
IMP + H2O + NAD+ + IMPDHase > XMP
XMP + Gln + ATP > GMP
IMP regulation by feedback inhibition
Ri5P > PRPP
X by ADP
PRPP > 5PRsA = inhibited by main products
X AMP, GMP, X IMP
5PRSA > IMP
IMP > adenylosuccinate > AMP inhibited by end product
X AMP
IMP > XMP > GMP inhibited by end product
X GMP
AMP and GMP push each other when they are inhibited
purine salvage pathway
HGPRT = free guanine and hypoxanthine (adenine deam product)
Adenosine PRsTransase = ( free adenine with PRPP > AMP + PPi)
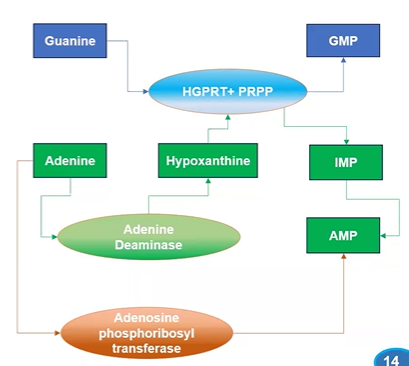
HGPRT
hypoxanthine-guanine phosopribosyl transferase
cat. salvage of free guanine and hypoxanthine (deam product of adenine)
adenosine phosphoribosyl-transferase
cat. rxn of adenine + PRPP > AMP + PPi
lesch-nyhan syndrome
coord, brain, hostile, compulsive;
lack of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase activity
cant do purine salvage
ribonucleotide reductase
deoxyribonucleotide
ribo > deoxyribo
thioredoxin
deoxyribonucleotide
intmd. H-carrying protein
glutaredoxin
deoxyribonucleotide
transfers power from GSH > ribonucleotide reductase
thioredoxin reductase
deoxyribonucleotide
cat. red of ox. form of thioredoxin by NADPH
GMP purine degradation pathway
GMP + 5’nucleotidase > guanosine + Pi
guanosine + nucleosidase > guanine (base) + ribose
guanine + guanine deaminase > xanthine + NH3
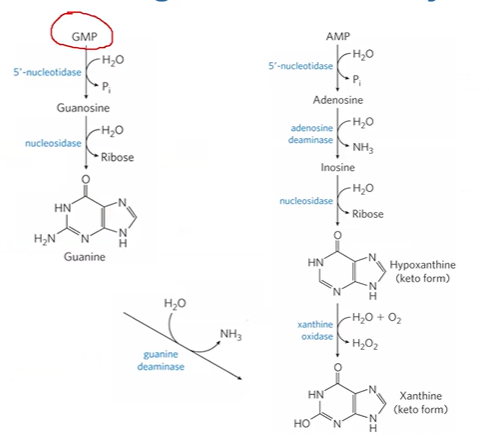
AMP purine degradation pathway
AMP + 5’Ntdase > adenosine + Pi
adenosine + adenosine deaminase > inosine + NH3
inosine + nucleosidase > hypoxanthine + ribose
hypoxanthine + xanthine oxidase > xanthine + H2O2
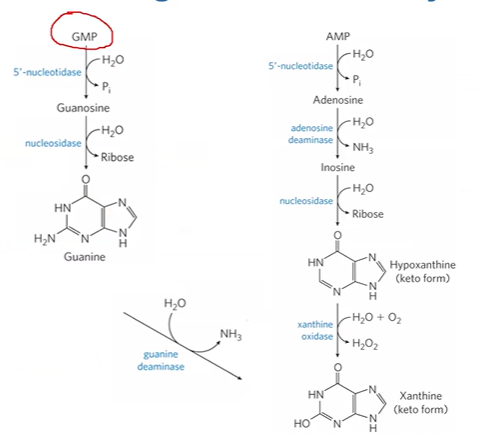
if nucleosidase fails, _____ increases which blocks ______, causing lymphocyte failure
dATP;
reductases
xanthine oxidase
flavoprotein
degrades xanthine > uric acid + H2O2
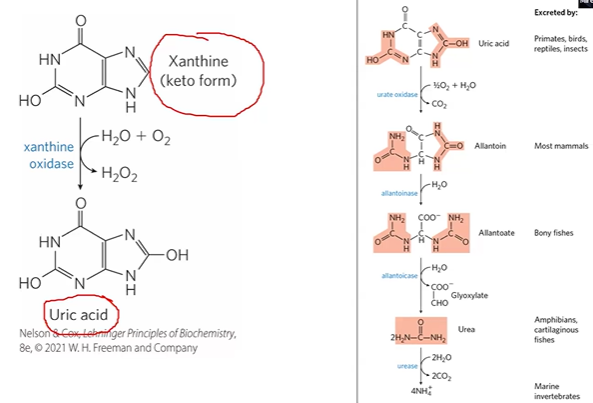
what species secretes what? primates v birds v reptiles v others mammals?
primates birds reptiles excrete uric acid
most mammals secrete allantoin
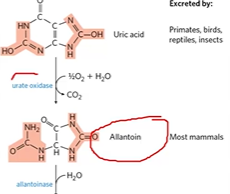
allantoin conversion
uric acid + urate oxidase > allantoin;
causes gout if fais
gout
uric acid buildup / improper breakdown of N bases, no allantoin
joint pain, crystallization,
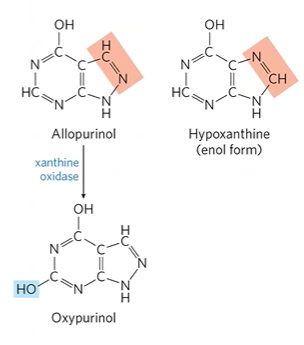
treated by allopurinol, inhibitor
how do you treat gout
allopurinol, inhibitor of xanthine oxidase
converted to oxypurinol, comp. inhibitor
important cofactors in 1C transfers
biotin (CO2)
tetrahydrofolate (oxidation)
S-adenosylmethionine (methyl)
biotin transfers
CO2
tetrahydrofolate transfers
oxidation states
SAM transfers
methyl groups
megaloblastic anemia
B12 deficiency
decline in mature blood cells, for megaloblasts (big baby cells)
replacement with macrocytes
depletion in N5N10methlyenetetrahydrofolate