AUBF 311: Renal Function
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Nephron
Functional unit of kidney
Cortical: 85%; filtration and reabsorption
Juxtamedullary: 15%; concentration
1 - 1.5 million
Amount of nephrons per kidney
25%
Approximately how much blood (pumped by the heart) does the kidney receive?
Renal Blood Flow + Urinary Filtrate Flow
Renal artery (blood enters)
Afferent arteriole
Glomerulus (bowman’s capsule)
Efferent arteriole
Proximal convoluted tubule + Peritubular capillaries (reabsorption)
Loop of Henle (descending then ascending) + Vasa recta (maintains osmotic/salt gradient)
Distal convoluted tubule + Peritubular capillaries (final adjustment of urine)
Renal vein (clean blood leaves kidney) + collecting duct (concentration of urine)
Renal pelvis
Renal calyces
Ureter
Bladder (temporary storage of urine)
Urethra
UGHHHHH
1200 mL / min
Average renal blood flow
600 - 700 mL / min
Average renal plasma flow
Glomerular Filtration Barrier
Consists of a coil of approximately 8 capillary lobes
Bowman’s Capsule
Where the glomerulus is located
<70, 000 MW
Glomerulus acts as a nonselective filter, allowing plasma substances with molecular weights of _____ to pass into the nephron
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
System that responds to changes in blood pressure and plasma sodium content
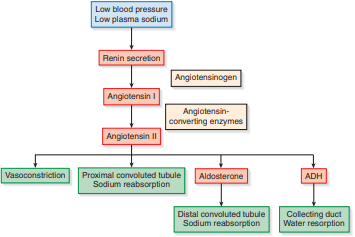
Aldosterone
Sodium-retaining hormone that is released by adrenal cortex
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Water-retaining hormone that is release by the posterior pituitary gland
Vasopressin
Other name of ADH
Ascending Loop of Henle
Passive reabsorption of water takes place in all parts of the nephron except the ____, the walls of which are impermeable to water
“Countercurrent mechanism”
160 - 180 mg/dL
Plasma renal threshold of glucose
Inversely Proportional
Relationship of body hydration to ADH in terms of urine volume
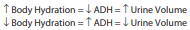
Urea Clearance
Earliest glomerular filtration test
Creatinine Clearance
Measures the waste product of muscle metabolism
Unreliable for Px with muscle-wasting diseases or athletes taking specific supplements
False positive in heavy meat diet
Cystatin C Clearance
Measures a small protein (13, 359 MW)
Screening + monitoring of glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
Recommended for:
Pediatrics
Diabetics
Geriatrics
Critically ill Px
β2-Microglobulin Clearance
Measures a small protein (11, 800 MW)
Distinguish kidney disorders as glomerular/tubular
Identify end-stage renal disease and early rejection of kidney transplant
Increased amount = Tubular damage
Concentration Test
Test to determine tubular reabsorbability
Fishberg Concentration Test
Concentration test where Px is deprived of fluids for 24 hrs before measuring SG
Mosenthal Concentration Test
Concentration test that compares day and night urine spx in terms of volume and SG
3:1
Urine to serum ratio that indicates normal tubular reabsorption
p-aminohippuric acid (PAH) Test
Most common test associated with tubular secretion and renal blood flow
Measures exact amount of plasma flowing through the kidney
Night
Lowest pH / Most acidic urine is found at what time of the day?
Renal Tubular Acidosis
Inability to produce acid urine in presence of metabolic acidosis
Caused by impaired tubular secretion of Hydrogen ions
Phenolsulfonphthalein (PSP) Test
A tubular secretion test that uses a dye
may produce anaphylactic shock