Module 4 Terms (Prevention and Management of Catastrophe and Unusual Occurrences)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
EAP (Employee Assistance Program)
A referral service that employees can use to seek professional treatment for emotional problems or substance abuse
covered by your works insurance
RACE (fire safety)
rescue, alarm, contain, extinguish/evacuate

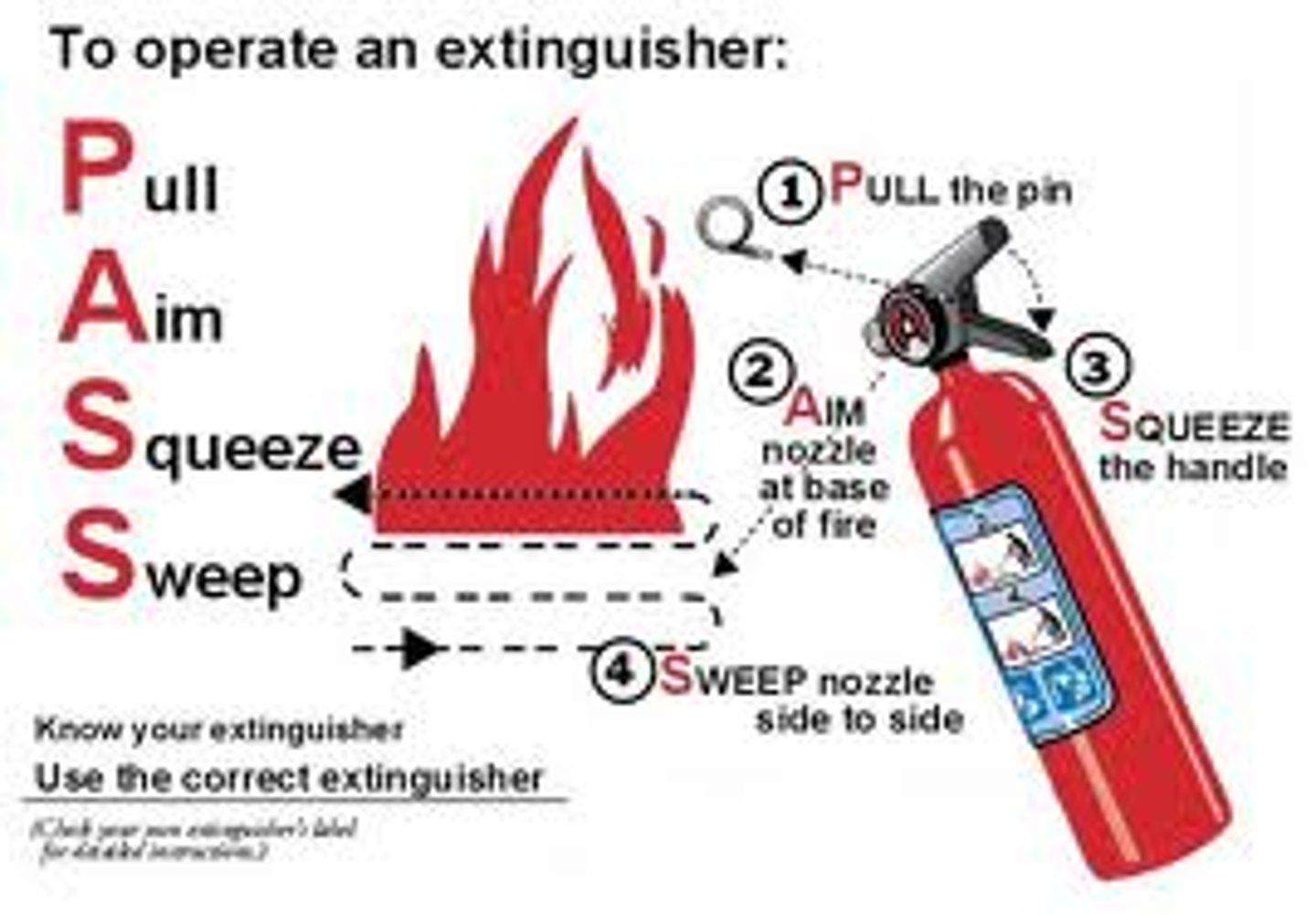
PASS (Fire Safety)
P - Pull the pin.
A - Aim at the base of the fire, not at the flames.
S - Squeeze the lever.
S - Sweep the nozzle from side to side.
Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
An OSHA-required document that explains the hazards of a chemical product

CMS
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
Disaster plan
Disaster plan is an actively maintained document containing procedures and information needed to prevent, mitigate, prepare for, respond to, and recover from emergencies
Emergency
The term emergency is often used interchangeably with disaster, although emergency generally connotes an event smaller than a disaster. For example, an emergency could become a disaster if not contained right away, or multiple emergencies could compound into a disaster.
Escape routes
Escape routes - An exit route is a continuous and unobstructed path of exit travel from any point within a workplace to a place of safety.
Emergency codes
Code words/colors to determine level of emergency
announcements using codes to inform staff of certain emergencies, and preventing panic among residents and visitors

External disaster
External disasters occur at locations separate from the hospital, such as transportation incidents or industrial accidents. Disasters can be both internal and external disasters concomitantly, such as natural disasters that cause mass casualties as well as damage hospital structure.
Fire plan
This fire plan sets out the standard response for all staff within the hospital buildings, to an alarm, or to conditions, which indicate, or seem to indicate the presence of a fire in the hospital.
Internal disaster
Internal disasters are events that occur within the walls of the hospital itself, such as an active shooter, power outage, or radiation exposure.[2] External disasters occur at locations separate from the hospital, such as transportation incidents or industrial accidents.
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)
The MSDS lists the hazardous ingredients of a product, its physical and chemical characteristics (e.g. flammability, explosive properties), its effect on human health, the chemicals with which it can adversely react, handling precautions, the types of measures that can be used to control exposure, emergency and first aid procedures, and methods to contain a spill. When new regulatory information, such as exposure limits, or new health effects information becomes available, the MSDS must be updated to reflect it.

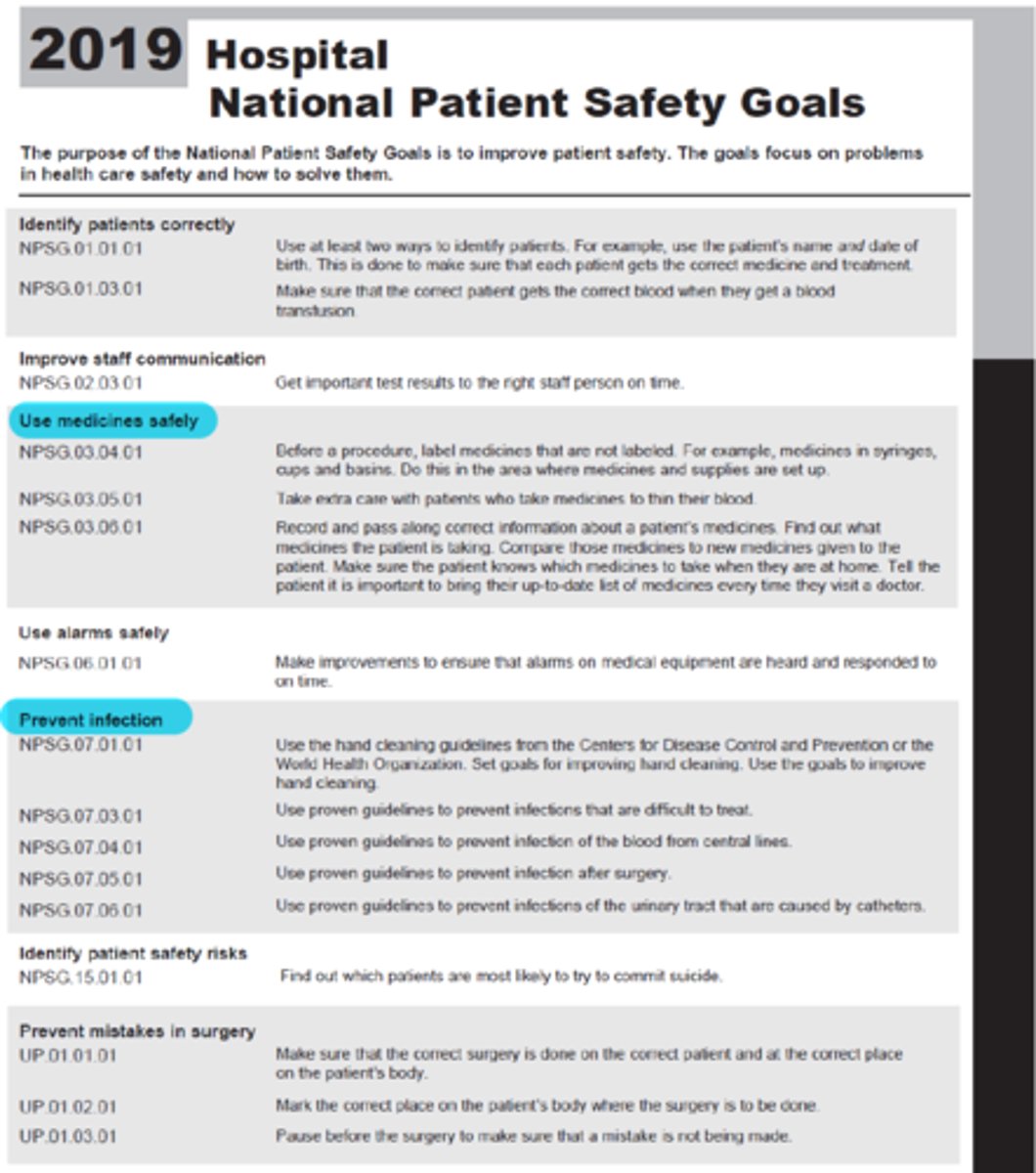
National Patient Safety Goals
The purpose of the National Patient Safety Goals is to improve patient safety. The goals focus on problems in health care safety and how to solve them. This is an easy-to-read document. It has been created for the public. The exact language of the goals can be found at www.jointcommission.org.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
With the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970, Congress created the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) to ensure safe and healthful working conditions for workers by setting and enforcing standards and by providing training, outreach, education and assistance.

Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA)
The Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA), also known as the Nursing Home Reform Act of 1987, has dramatically improved the quality of care in the nursing home over the last twenty years by setting federal standards of how care should be provided to residents.
Oxygen (O2)
Medical oxygen is high purity oxygen that is used for medical treatments and is developed for use in the human body. Medical oxygen cylinders contain a high purity of oxygen gas; no other types of gases are allowed in the cylinder to prevent contamination.
Oxygen precautions
Place "Oxygen in Use" signs in visible areas. Never place the tank or machine near an open flame (e.g., matches, lit candles, a stove in use). Keep the oxygen tank at least six feet away. Always turn your oxygen off when not in use. Always check the oxygen levels on your oxygen tank.

Postural supports
Postural support means an appliance or device used to achieve proper body position and balance, to improve a resident's mobility and independent functioning, or to position rather than restrict movement, including, but not limited to, preventing a resident from falling out of a bed or chair.
Quality Assurance (QA)
According to the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA), quality assurance (QA) measures compliance against certain necessary standards, typically focusing on individuals, whereas quality improvement (QI) is a continuous improvement process focused on processes and systems.
Rapid Response Team (RRT)
A rapid response team, also known as a medical emergency team and high acuity response team, is a team of health care providers that responds to hospitalized patients with early signs of deterioration on non-intensive care units to prevent respiratory or cardiac arrest
Restraints
To physically restrict voluntary movement or use chemicals to revise/restrict resident behavior
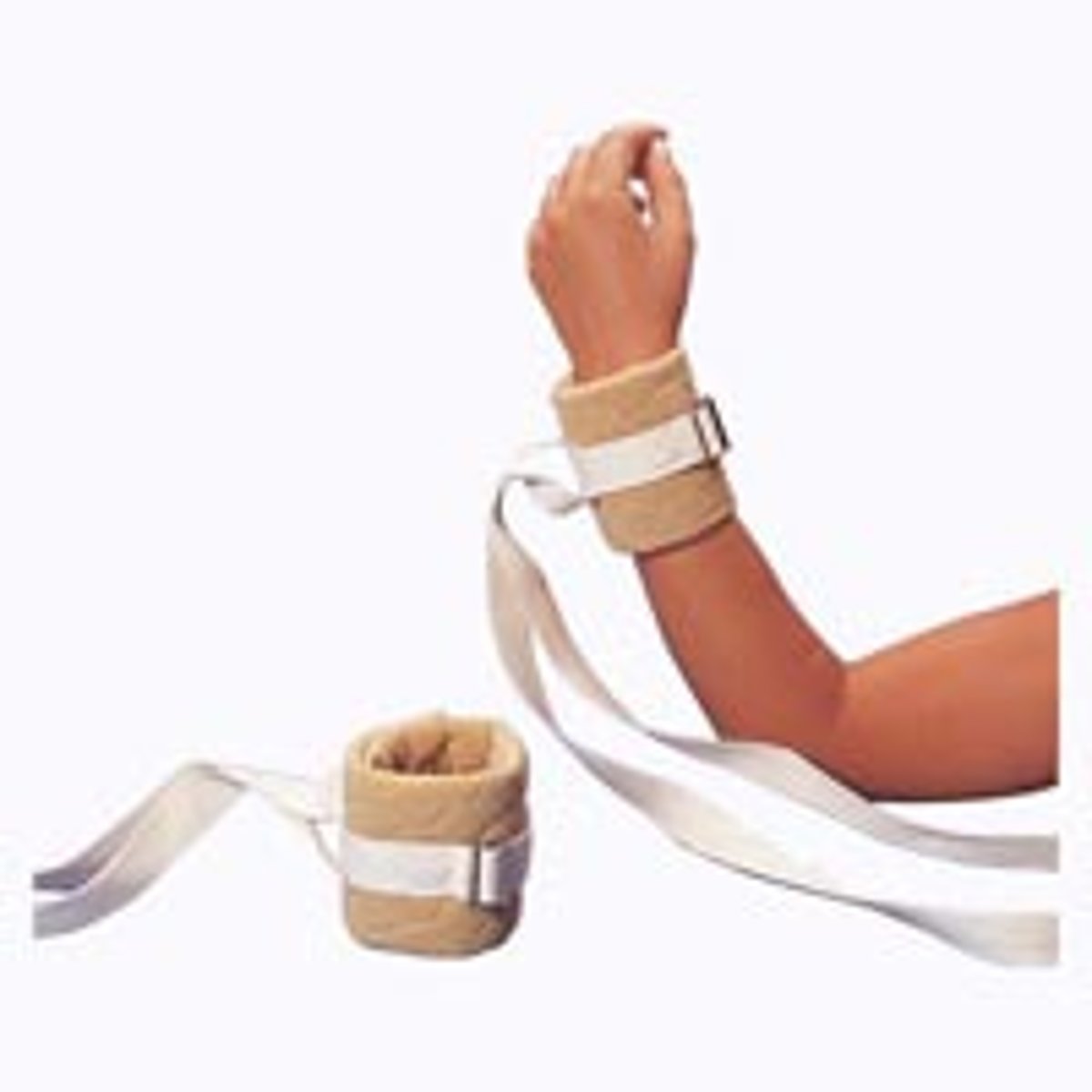
Safety Device Reminders (SDR)
Safety Reminder Device (SRD) any of the numerous devices used to immobilize a patient or part of the patient's body, such as arms or hands' formerly referred to as restraints.
Soft protective device
A device used to protect the resident from injury
STAT
Stat, used as a directive to medical personnel during in an emergency situation, is from the Latin word statim, which means "instantly" or "immediately."
Total Quality Improvement (TQI)
Total quality improvement (TQI) advocates that all staff members in an organization develop their own ideas on job improvement about their own specific jobs. This process helps to improve staff performance and to build continually on those improvements.
Workplace violence
Workplace violence (WPV) is a recognized hazard in the healthcare industry. WPV is any act or threat of physical violence, harassment, intimidation, or other threatening disruptive behavior that occurs at the work site. It can affect and involve workers, clients, customers and visitors.