Lecture 25: Measles, Mumps, RSV, Rabies, and Rubella
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
There is not a link between vaccinations and autism (true/false)
True
Monogavirales
order of viruses that have negative single-stranded genomes
Where do all viruses in the Paramyxoviridae family infect?
respiratory tract
How are all viruses in the Paramyxoviridae family transmitted?
saliva or respiratory secretions
What are the five types of viruses in the Paramyxoviridae family?
1)parainfluenza
2)respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
3)metapneumovirus
4)mumps
5)measles
Which viruses in the Paramyxoviridae family are localized to the respiratory tract?
1)parainfluenza
2)respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
3)metapneumovirus
Which viruses in the Paramyxoviridae family cause systemic infections?
mumps and measels
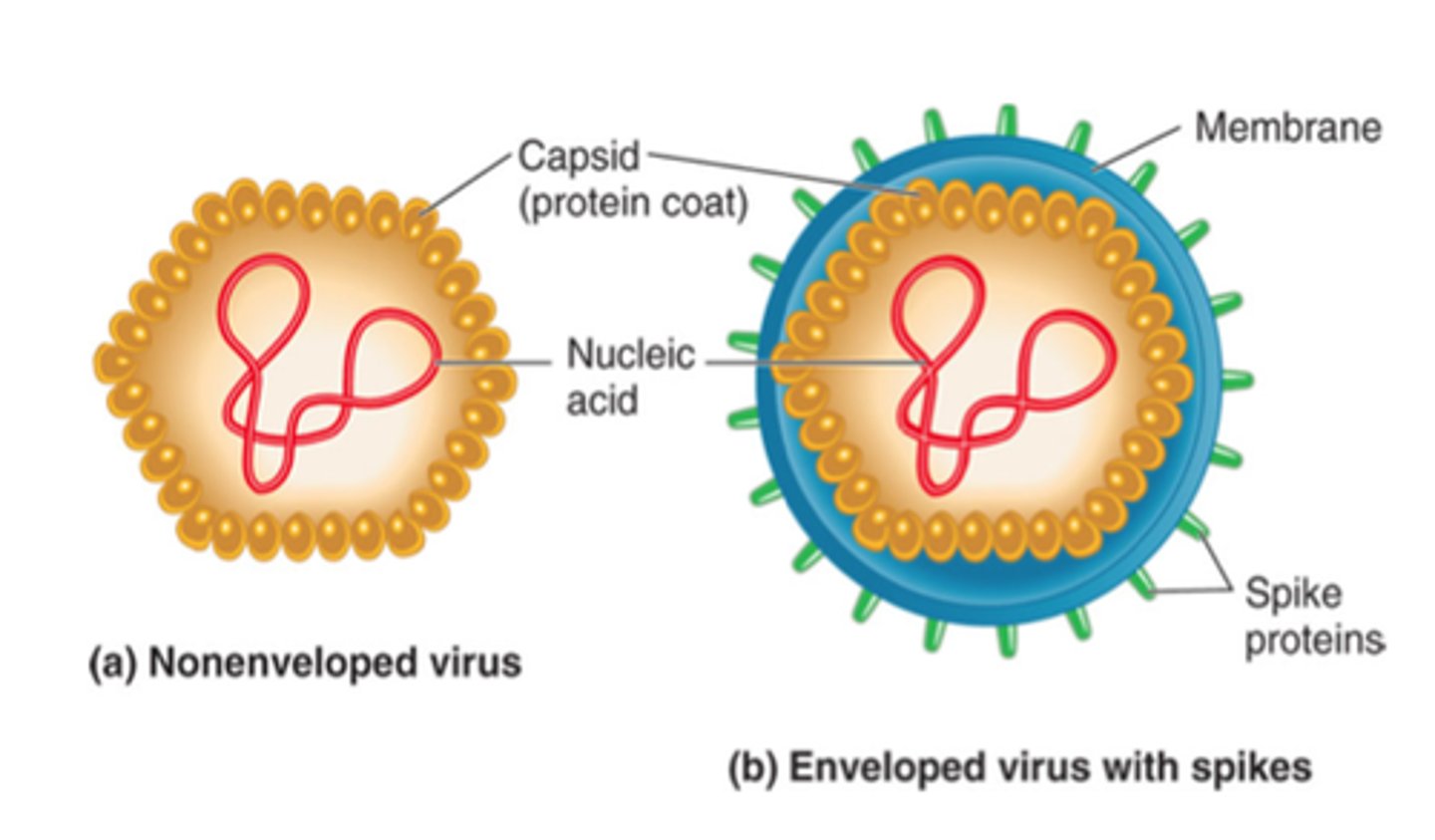
What is the virion structure of Paramyxoviruses?
1)enveloped, helical, negative-sense RNA
2)non-segmented genome
3)VAP is H or HN proteins (contains both HA and N activity)
4)separate fusion proteins (F) that fuse at neutral pH
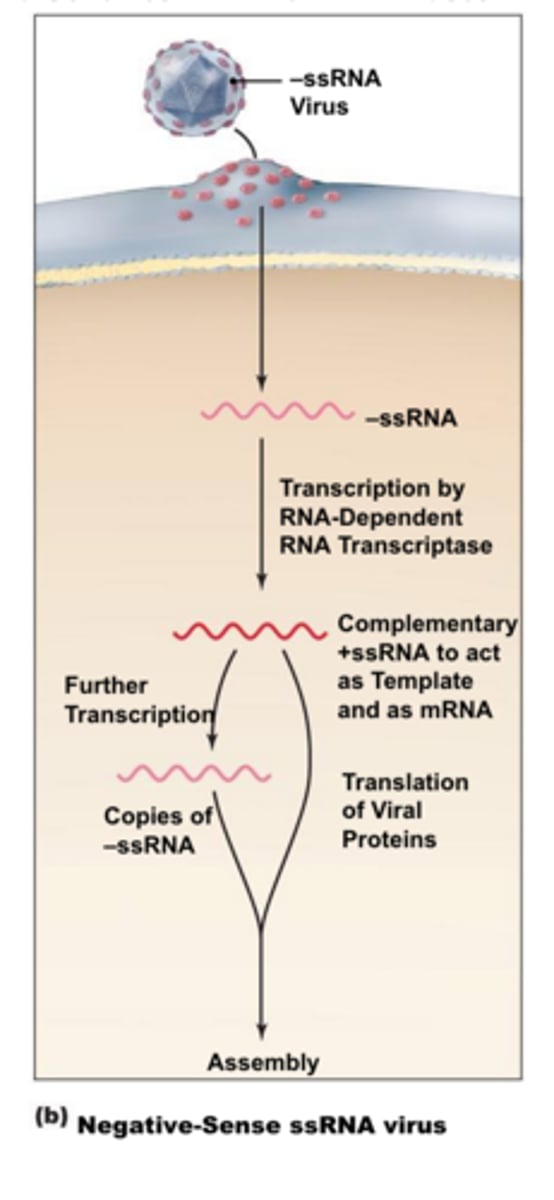
What is the replication cycle of Paramyxoviruses?
1)attachment and fusion through HA binding and F fusion
2)uncoating and release of the negative-stranded genome into the cytoplasm
3)RDRP transcribes positive-strand RNA from negative-strand RNA
4)positive-strand RNA translated into proteins
5)positive-strand RNA made into negative-strand RNA by RDRP for amplification and packaging
6)egress by budding
7)virus picks up viral envelope proteins at the cell membrane at the exit
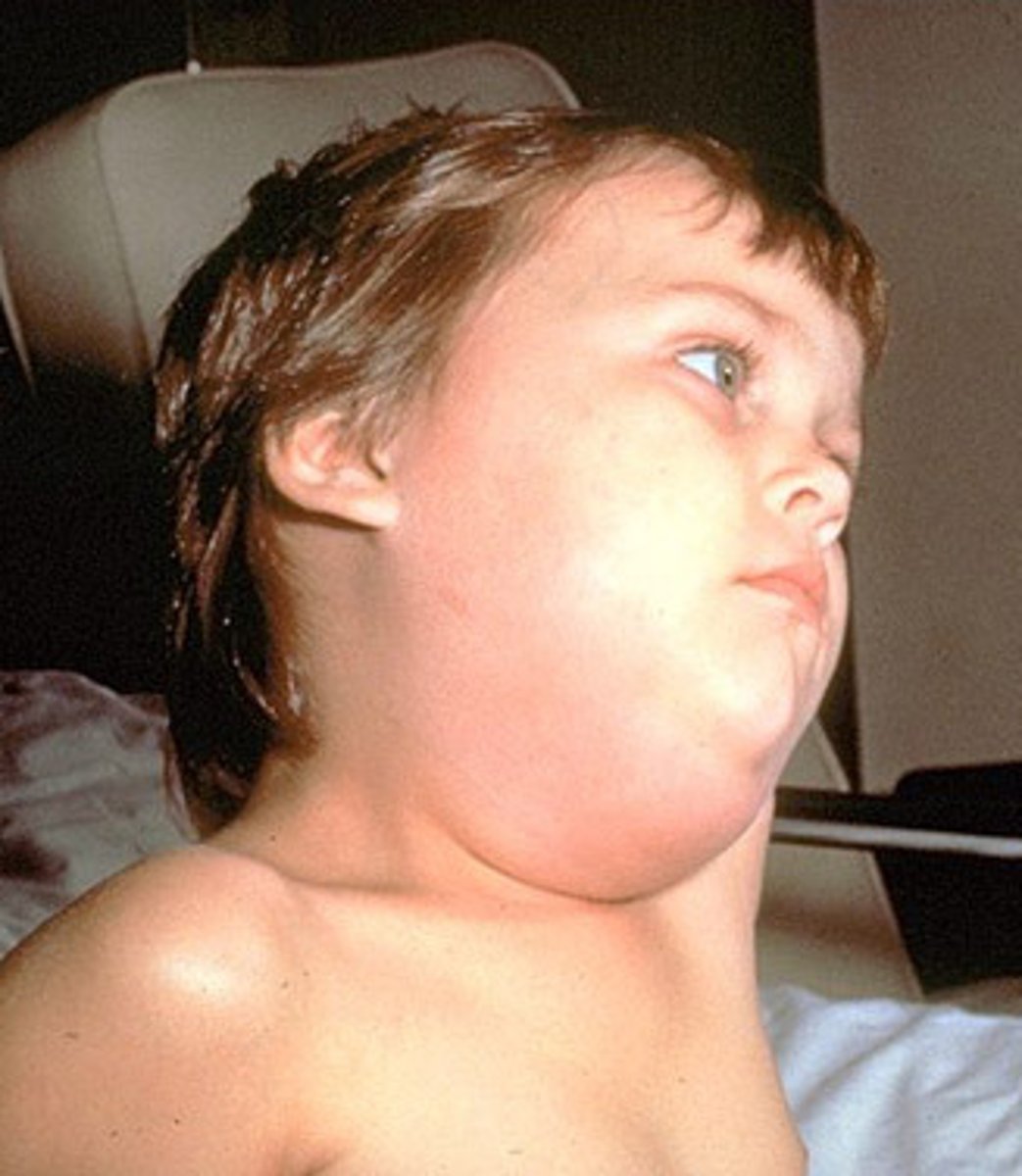
What are symptoms of mumps?
Headache, anorexia, malaise, parotitis (swelling of the parotid gland bilateral), and low to moderate grade fever

What is the incubation period for mumps?
12-24 days of incubation
How long does it take for mumps to affect the salivary glands?
12-24 hours later, salivary gland involvement (peaks on 2nd day and lasts 5-7 days)
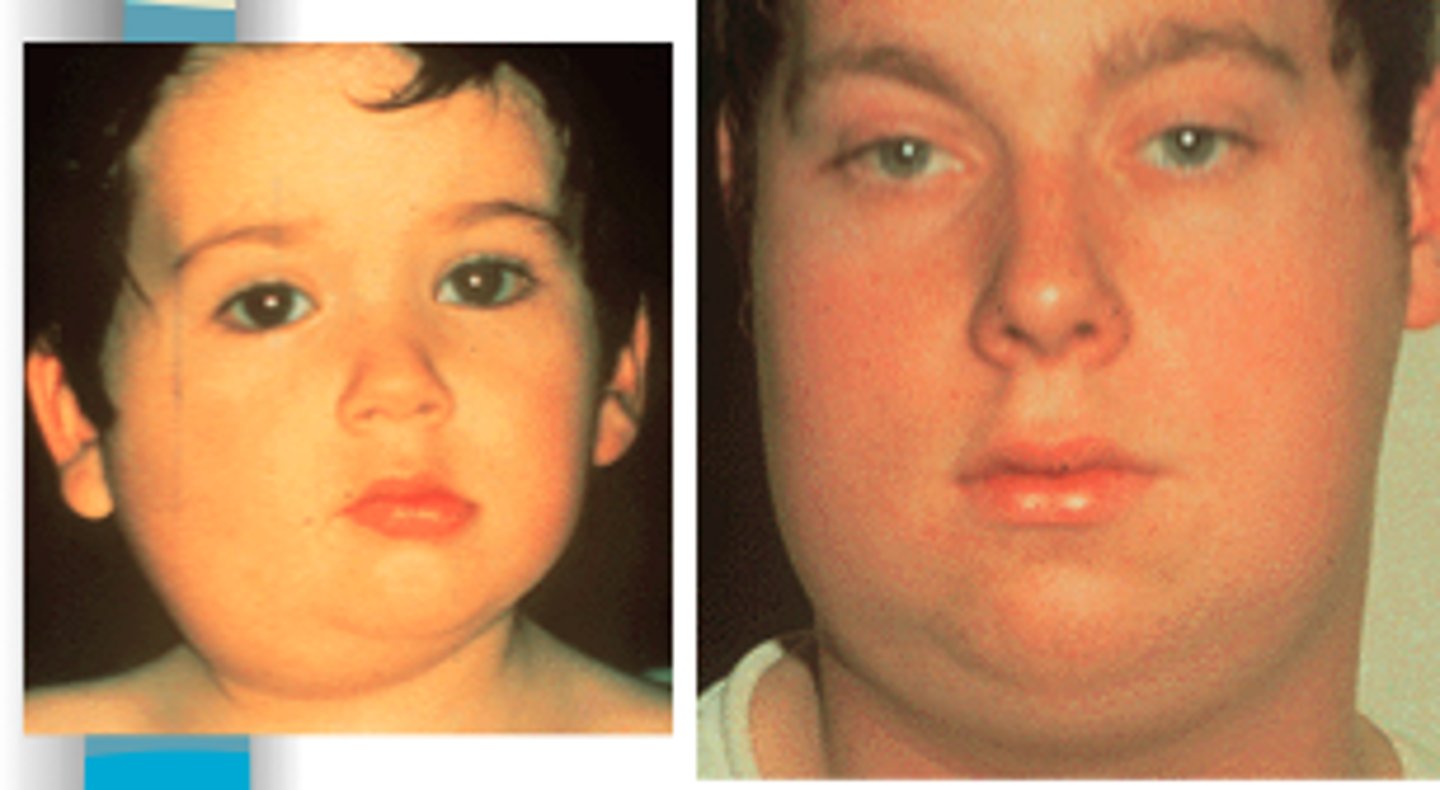
What are complications of mumps?
1)gonad involvement (males more common but also females)
2)meningitis (inflammation of meninges covering brain)
3)encephalitis (inflammation of brain)
4)pancreatitis
5)inflammation of other organs
6)hearing loss
orchitis
inflammation of the testes
parotitis
inflammation of the parotid gland
menigitis
inflammation of the meninges covering the brain and spinal cord
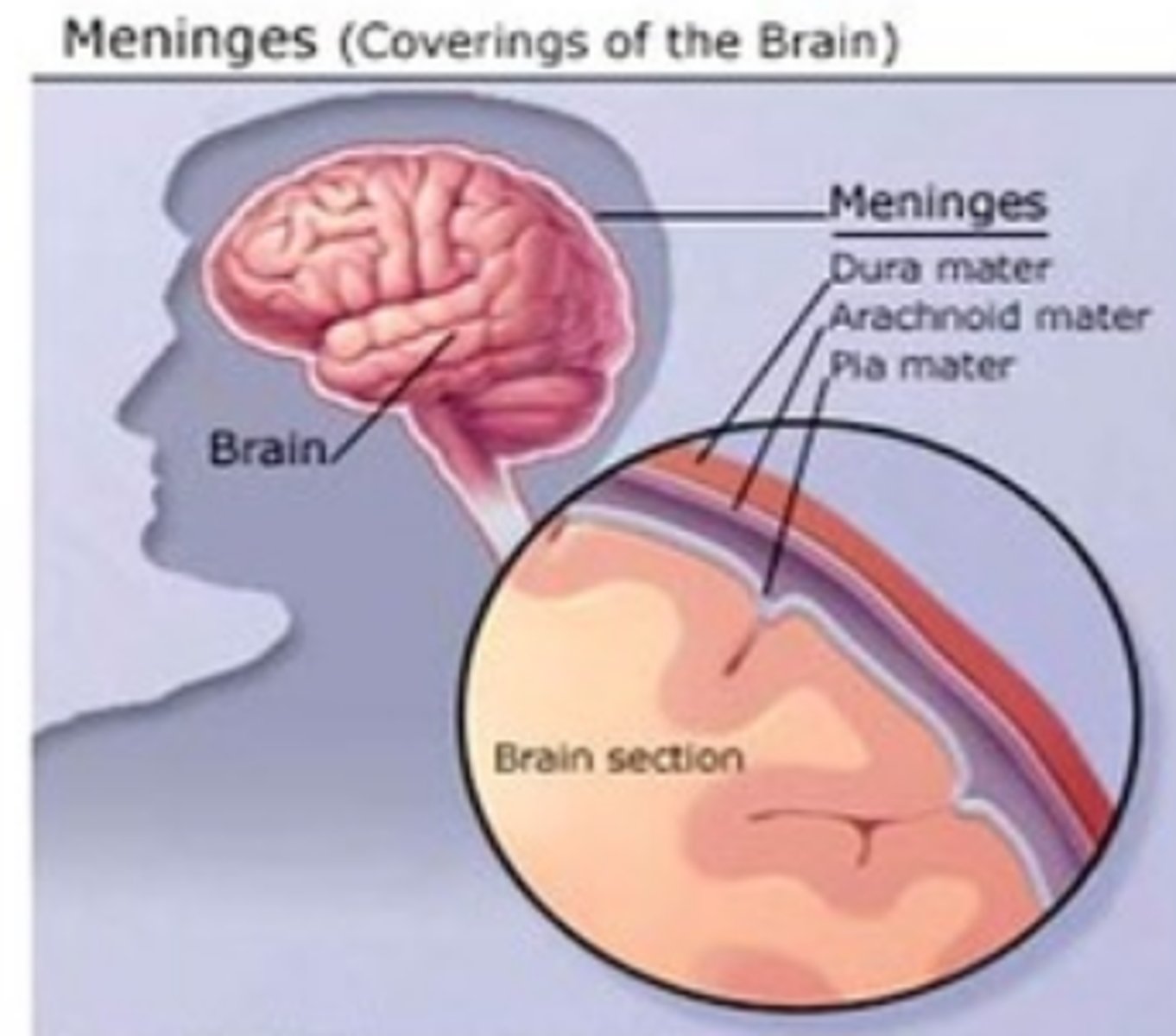
encephalitis
inflammation of the brain

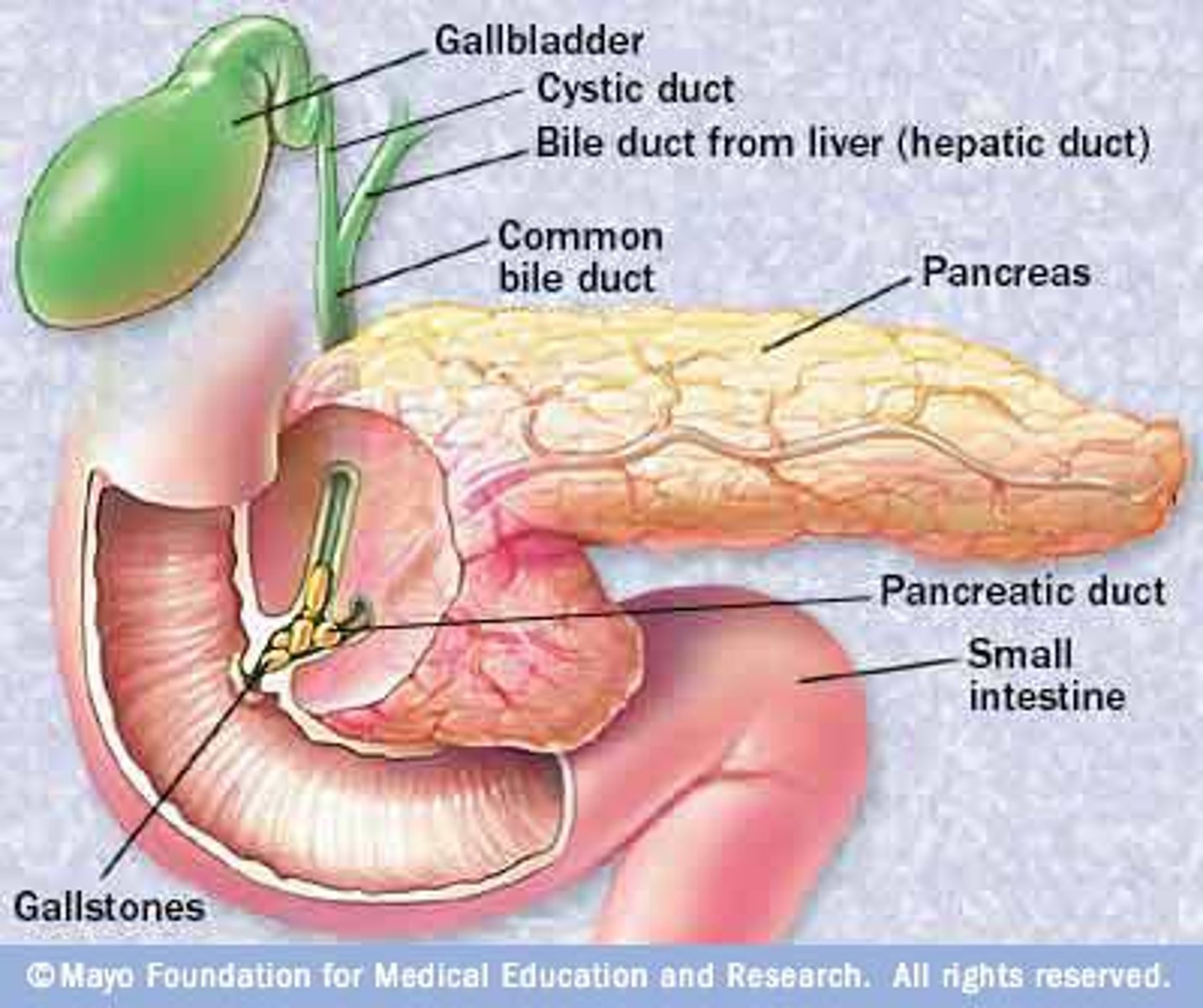
pancreatitis
inflammation of the pancreas
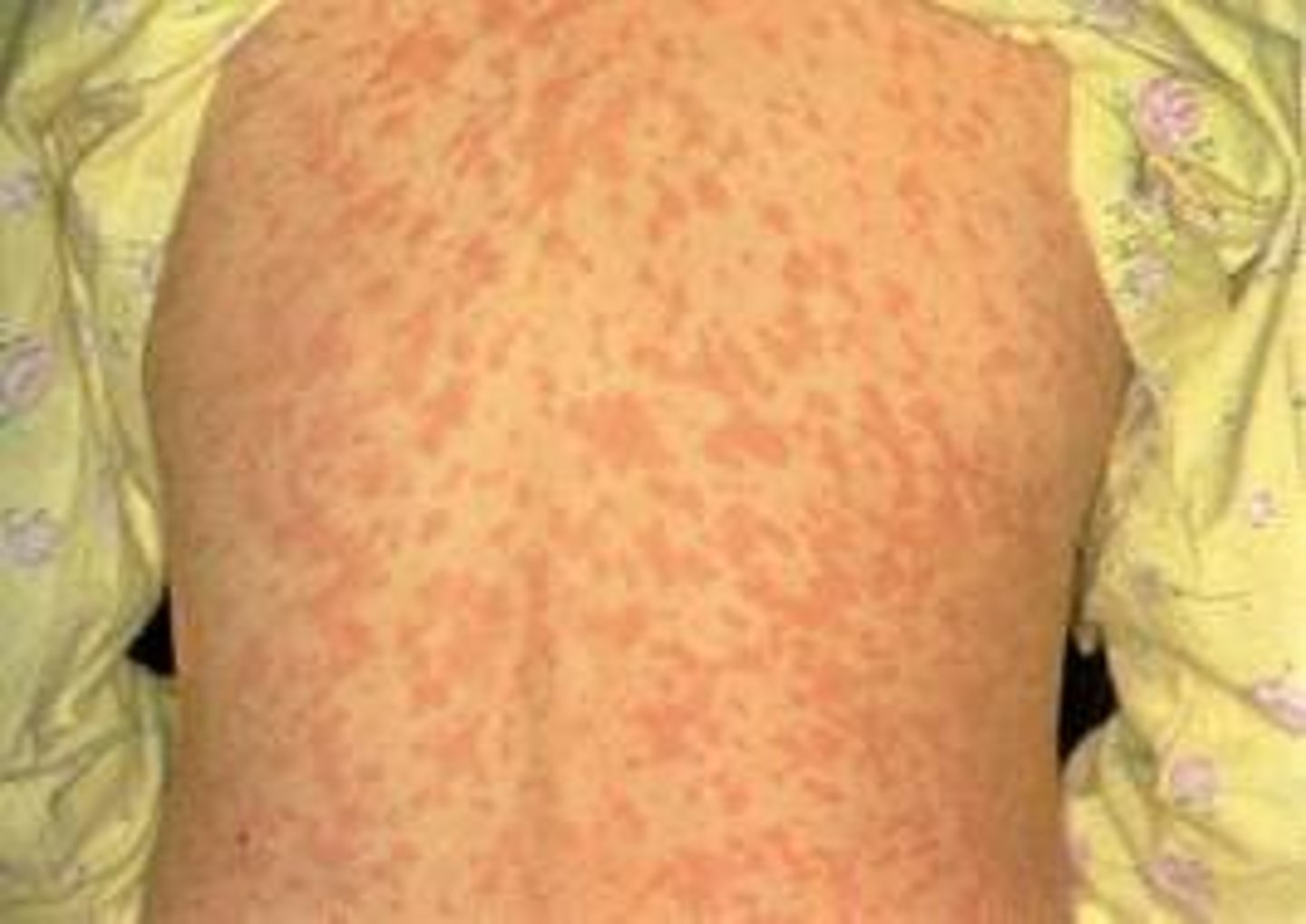
What are symptoms of measles?
fever, cough, runny nose, and maculopapular rash
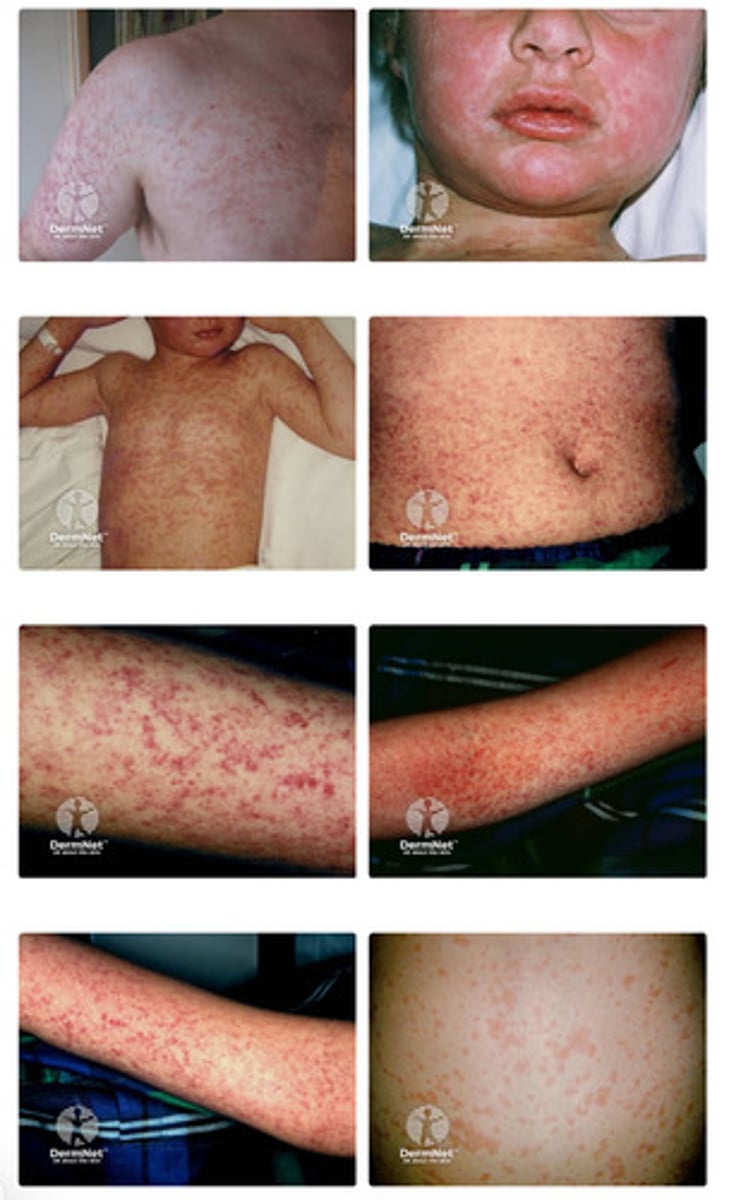
maculopapular rash
A rash that appears 1-3 days later to initial symptoms and is caused by a T-cell response to infected capillary endothelial cells
macule: flat red spots
papule: small, raised bumps
What is the incubation period for measels?
10-14 days
What are Koplik spots?
An indicative sign of measles infection that appears as tiny erythematous macules with white necrotic centers on the buccal mucosa
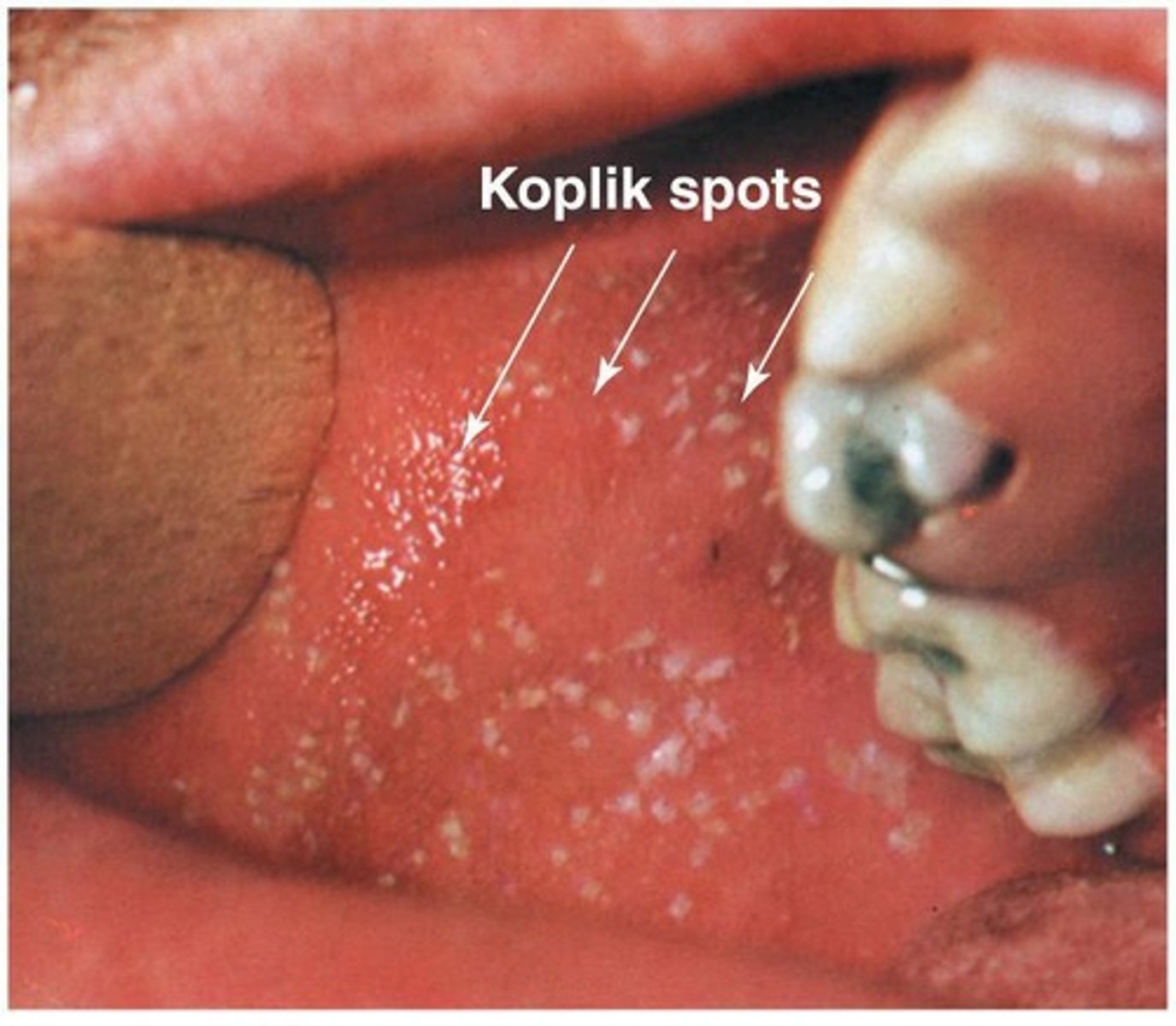
What are complications of measels?
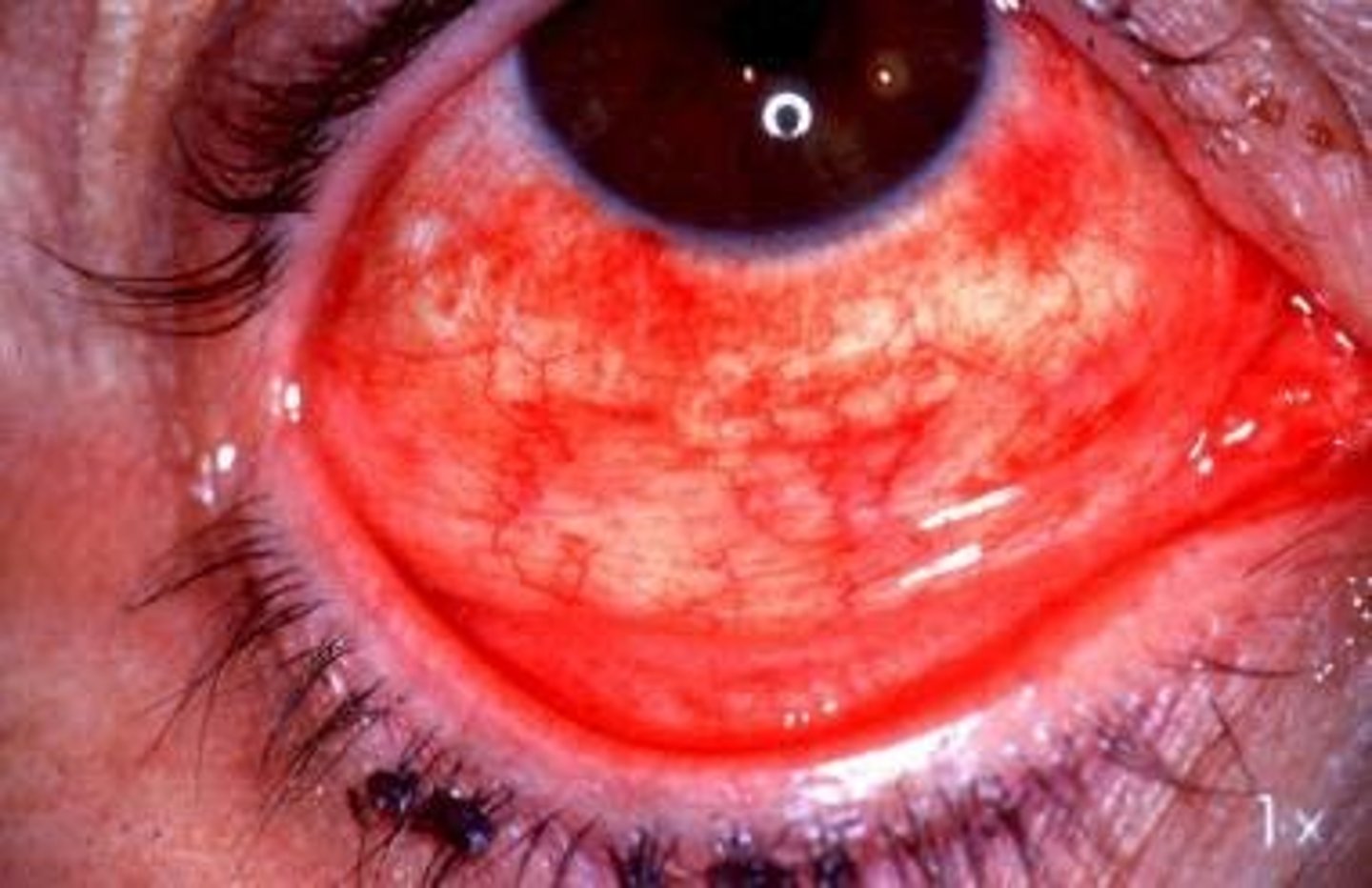
1)keratoconjunctivitis (inflammation of eye)
2)pneumonia (the most common cause of death)
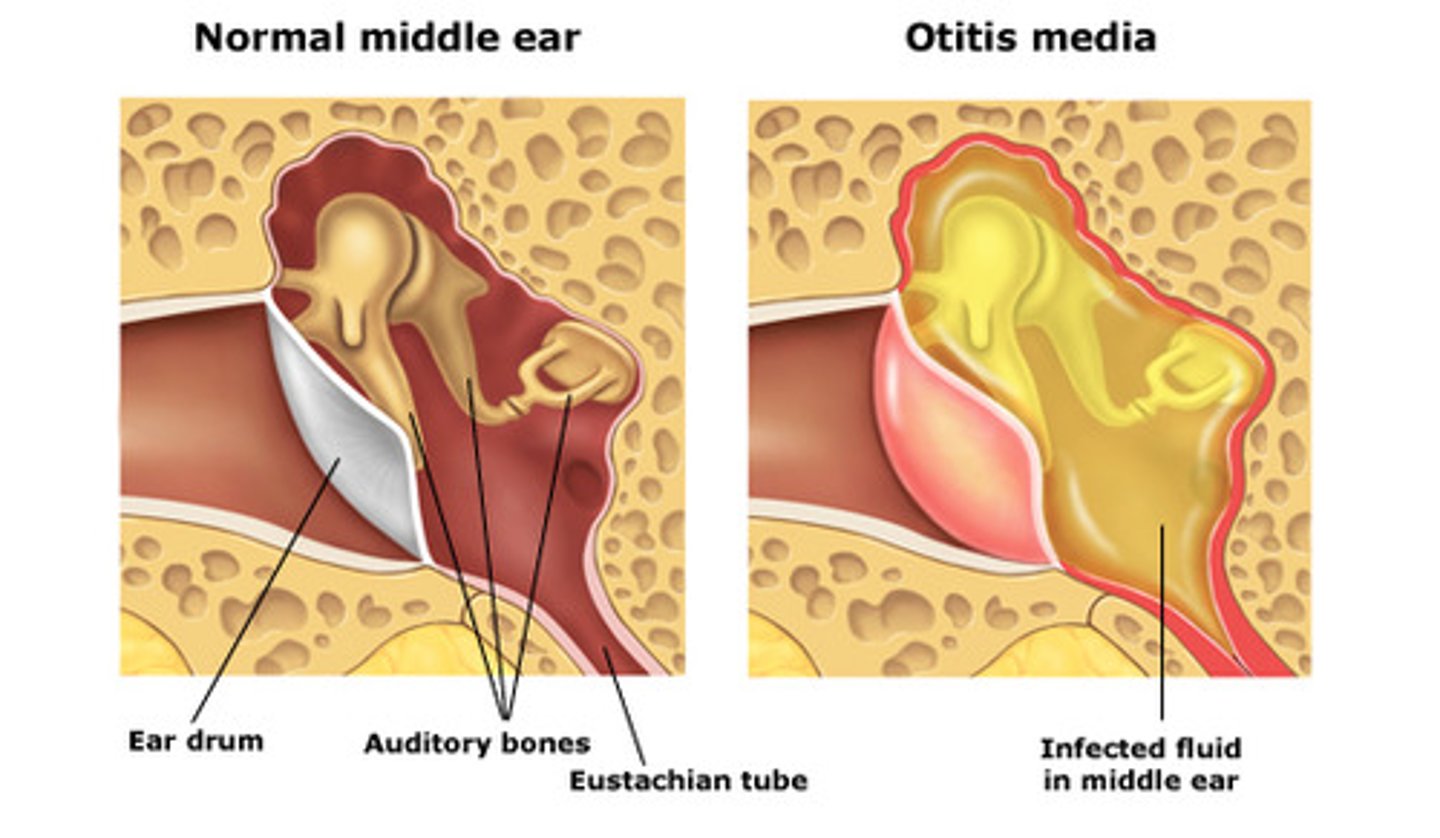
3)otitis (inflammation of ear)
4)encephalitis (inflammation of brain tissue) (seizures)
keratoconjuctivitis
inflammation of the cornea and conjunctiva
otitis
inflammation of the ear
How do you treat/prevent mumps and measels?
1)no antiviral treatment
2)live attenuated vaccine given as a combination (MMR)
There is evidence that the attenuated strains of mumps and measles can mutate to virulence (true/false)
False
What are the parainfluenza strains?
1, 2, 3, 4A, and 4B
How is parainfluenza transmitted?
aerosols where they travel to the respiratory epithelium, but do not spread systemically
How do the 1-3 strains of parainfluenza present?
severe respiratory tract infection
How do the 4 strains of parainfluenza present?
mild upper respiratory tract infection
How does the limitation of parainfluenza to only be able to infect the respiratory epithelium affect immunity?
Immunity against the virus is short-lived and can be re-infected with the same strains
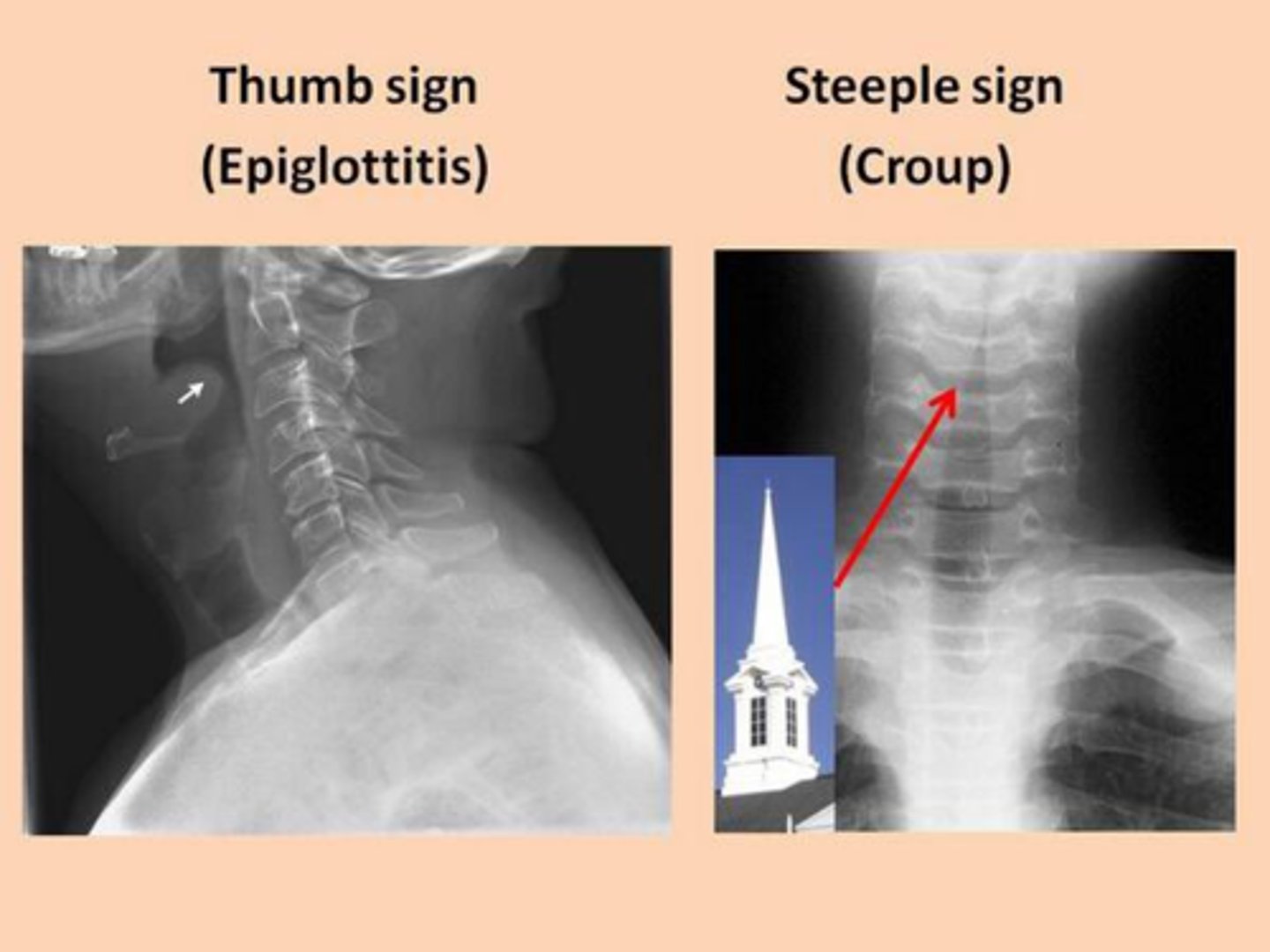
What is the leading cause of croup in infants?
parainfluenza virus (types 1, 2, and 3 cause 75%)
croup
Laryngotracheobronchitis that causes a barking cough, stridor (vibrating noise), hoarseness, and difficulty breathing, which usually occurs at night (parainfluenza)
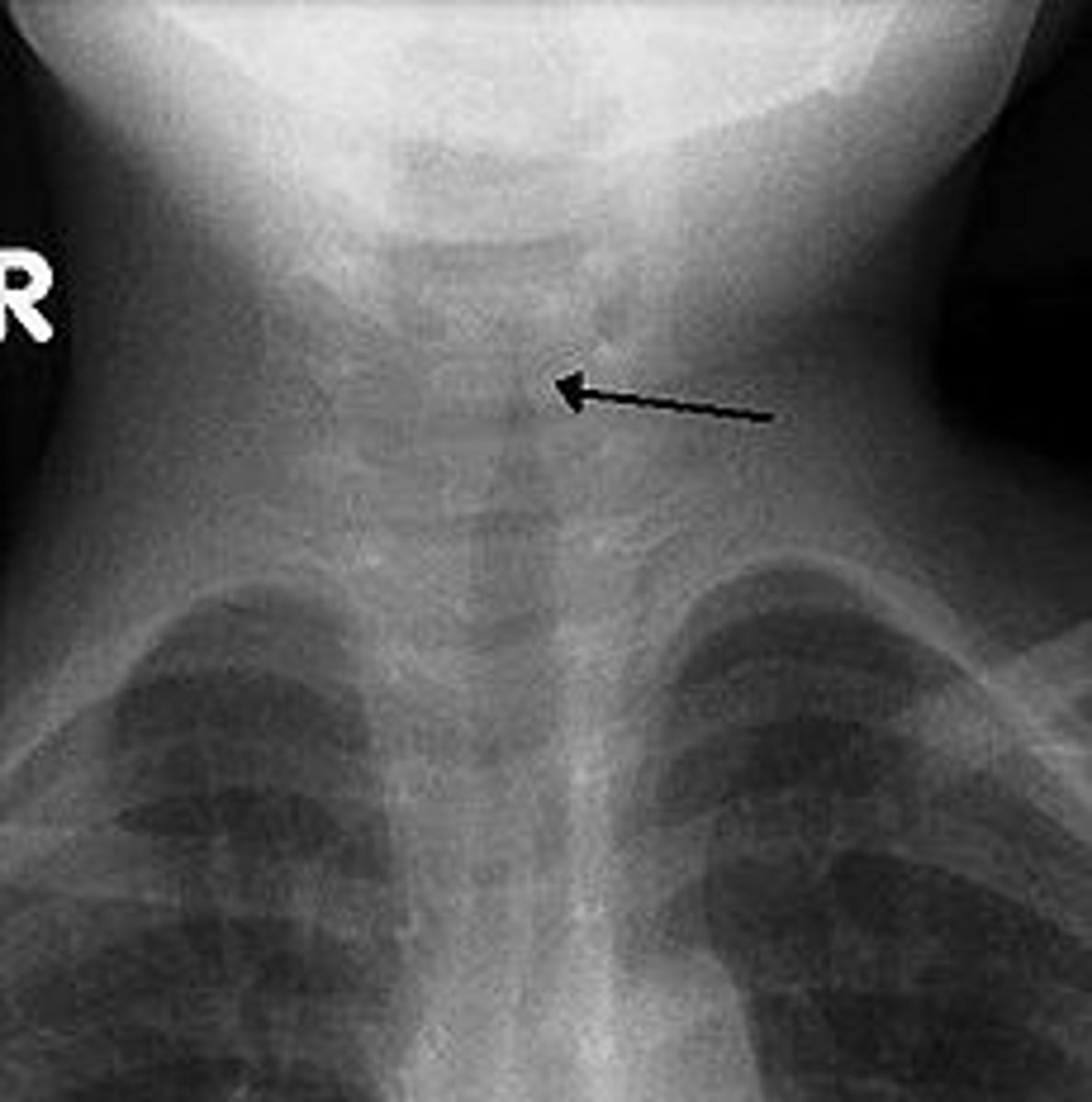
steeple sign
Subglottic stenosis or narrowing of the opening below the vocal folds is a classic sign of croup.
What treatment options are available for parainfluenza?
1)no antiviral
2)no vaccines
What is the pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)?
It causes upper and lower respiratory tract infections (bronchiolitis) and causes the formation of synctia
brochiolitis
inflammation of the bronchiole
synctia
fusion of multiple host cells into single large cells containing multiple nuclei
How does the limitation of RSV to only be able to infect the respiratory epithelium affect immunity?
little to no long-term immunity
What is the leading cause of brochiolitis?
RSV (30-65% of cases)
How do you treat/prevent RSV?
1)antiviral therapy (ribavarin)
2)passive immunization
3)vaccination (people over the age of 60 years)
ribavarin
analog of guanosine that inhibits RNA synthesis and viral mRNA capping
Who is the RSV vaccination given to?
people over the age of 60 and mothers (pass maternal protection to newborn)
RSV vaccines should be given to newborns (true/false)
False, they should be given to the mother so they can pass maternal protection to the child
What is the structure of rhabdoviruses?
bullet-shaped, enveloped, helical capsid with a negative-strand RNA genome
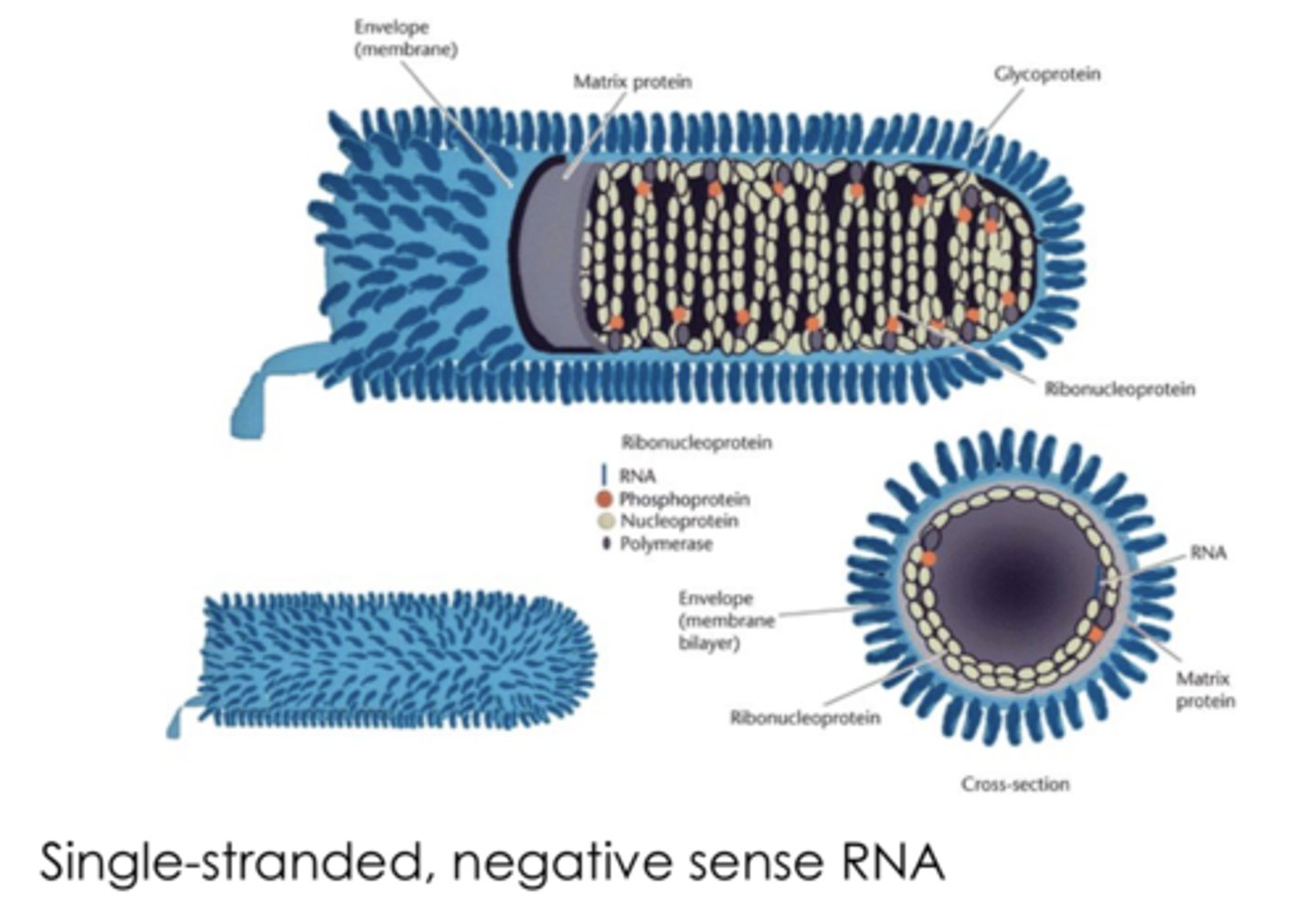
What are viruses in the rhabdovirus family?
1)rabies virus
2)vesicular stomatitis virus (infects animals and sometimes humans with flu-like symptoms)
How is rabies transmitted?
It is shed in saliva and can be communicated by bites or aerosol
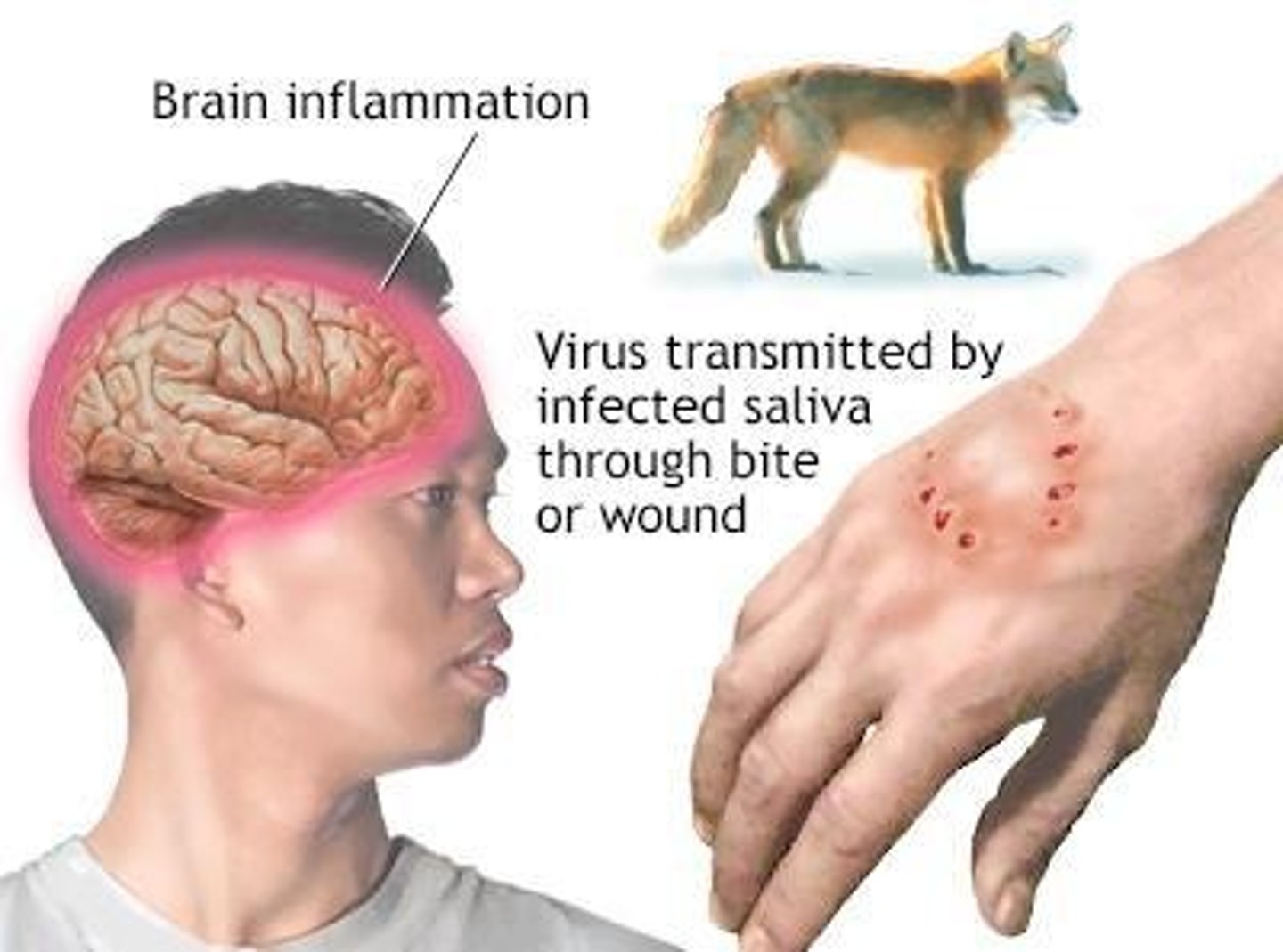
zoonosis
An infectious disease that is transmissible from animals to humans.
Ex/wild animals or unvaccinated domestic animals
What is the disease process of rabies?
1)incubation (20 days to 1 year)
2)prodrome (2-10 days)
3)acute neurologic phase (2-7 days)
4)coma
5)death
How was the rabies vaccine developed?
Louis Pasteur (1885) infected rabbits with the virus and harvested nerve tissue, which was then dried for 5-10 days. He then administered many shots over weeks in the abdomen. Now, the virus is grown in a human cell line and inactivated with beta-propiolactone to be given intramuscularly multiple times.
How do you treat rabies?
1)no antiviral treatment
2)post-exposure prophylaxis
a)local wound care
b)passive immunization (human rabies immunoglobulin)
c)active immunization (inactivated rabies vaccine)
When must the rabies vaccine be given for it to be effective?
early after bite/exposure
What is the structure of rubella virus?
Enveloped, icosahedral, non-segmented, positive-stranded virus
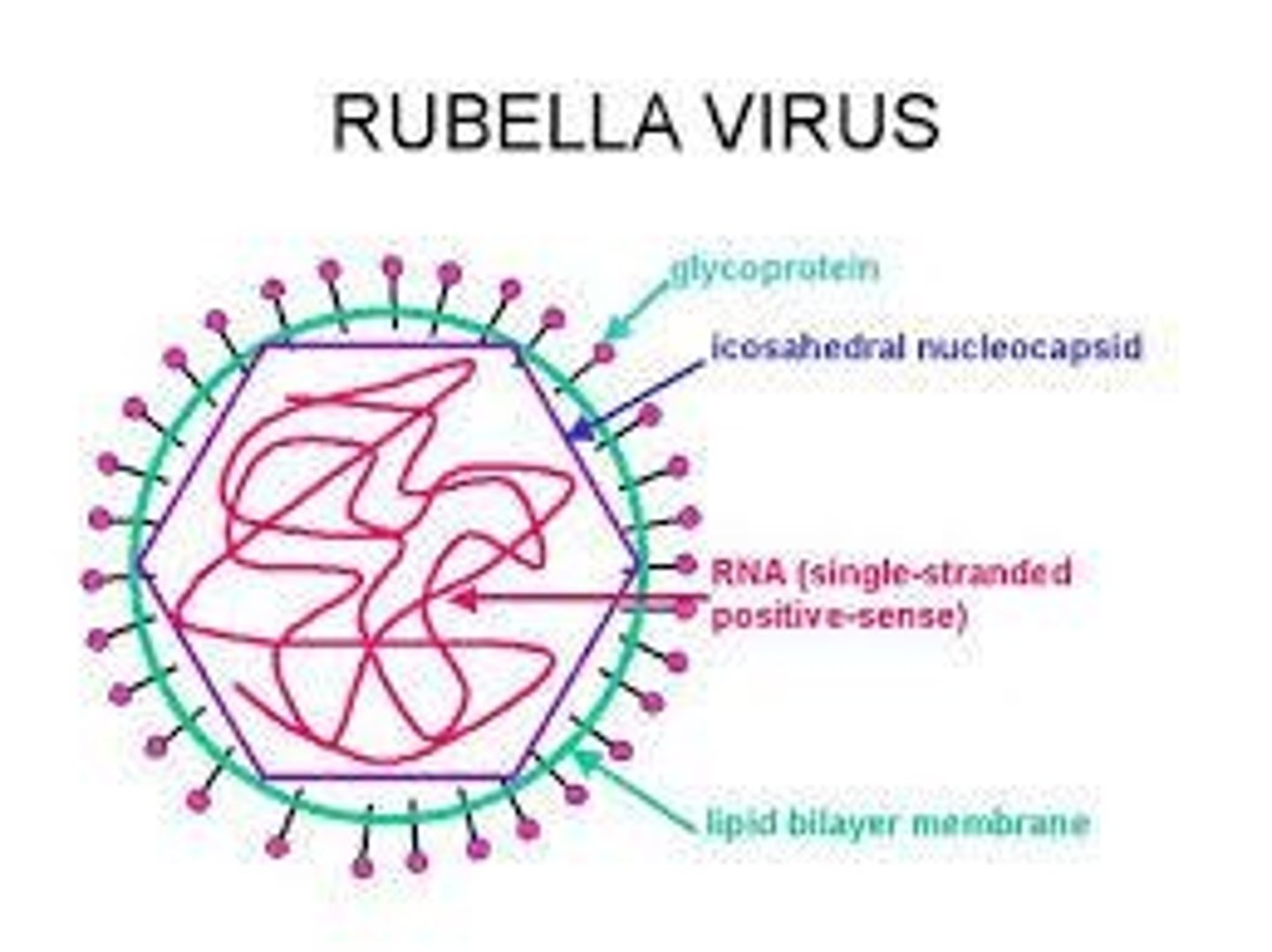
What are the types of togaviruses?
1)alphaviruses
2)rubiviruses
How is rubella trasmitted?
respiratory and intrauterine (mother to fetus)
What are the two types of rubella?
1)German measles
2)congenital rubella
What are the symptoms of German measels?
1)50% asymptomatic
2)rash starts on the face and spreads to the body (similar appearance to measels)
3)low fever (<101 degrees Fahrenheit)
4)lymphadenopathy (inflamed lymph node)
5)arthralgia (joint pain)
Forscheimer spots
Petechiae (small red spots that do not blanch with pressure) on the soft palate in 20% of patients with rubella.
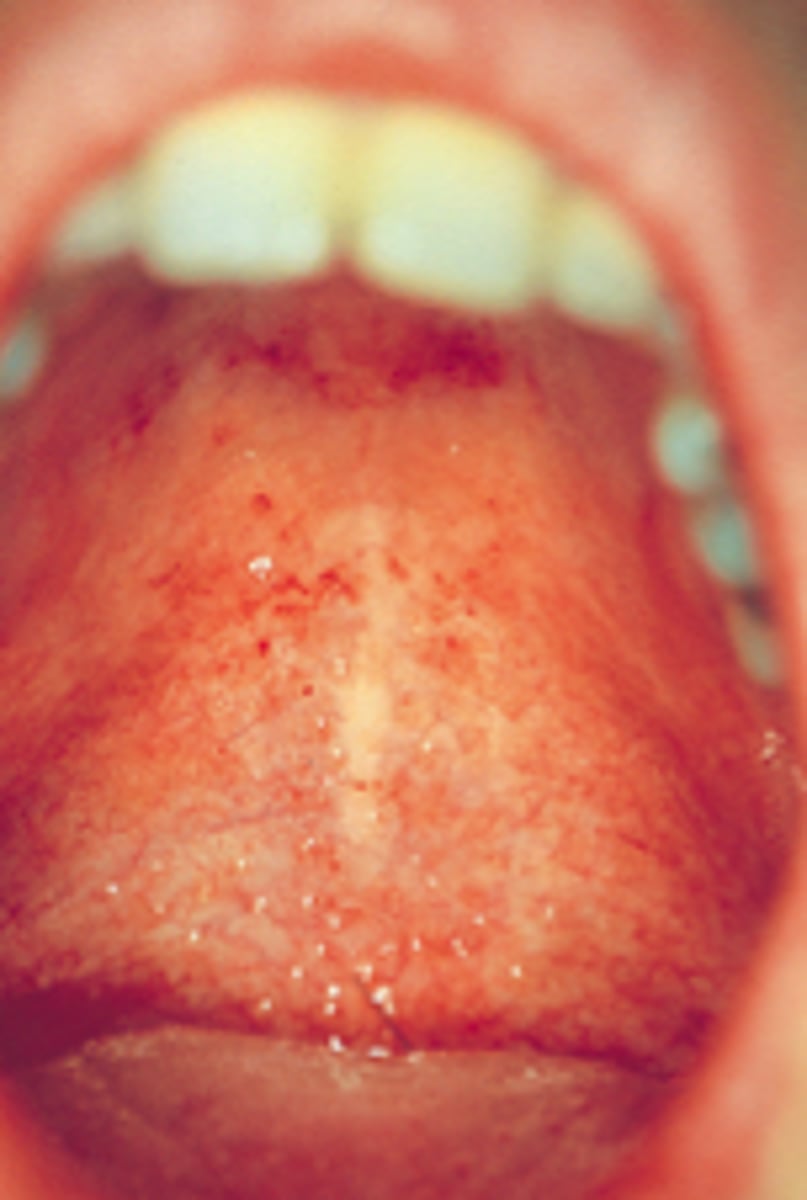
Forschheimer spots are diagnostic of rubella (true/false)
False, it can still be seen in measles and scarlet fever
What are the symptoms of congenital rubella?
1)deafness
2)cataracts (blindness)
3)heart defects
4)microcephaly (mental retardation)
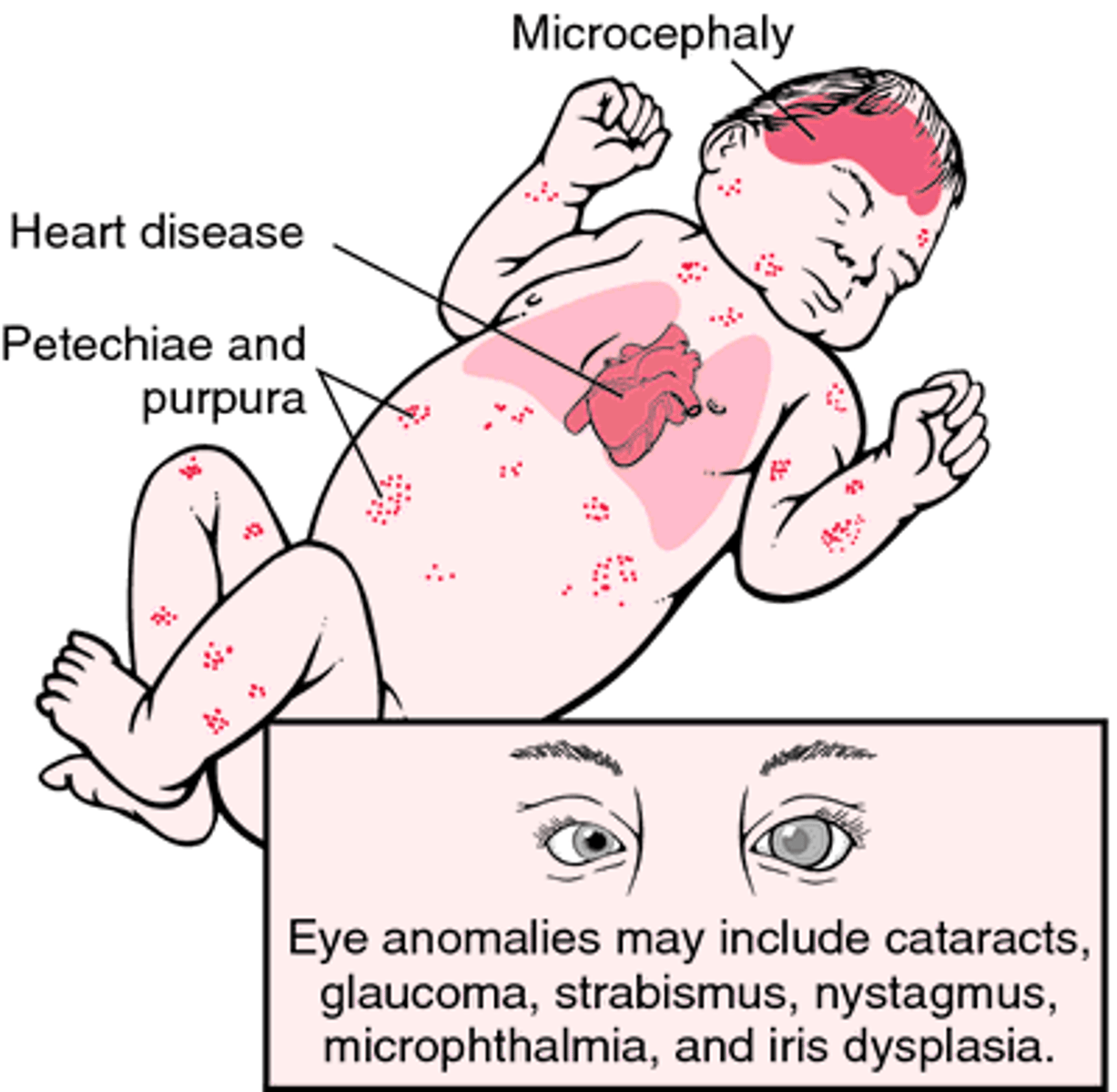
What stage of pregnancy is at the greatest risk for congenital rubella?
<12 weeks (85%)
How is rubella treated/prevented?
1)no antivirals
2)live attenuated vaccine in the MMR vaccine
What is the MMR vaccine?
Vaccine for measles, mumps, and rubella.