2 - Respiratory System 2
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Alveoli
Air filled pockets within lungs where all gas exchange takes place
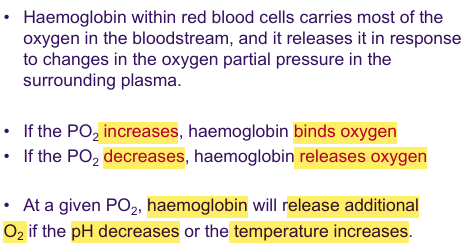
Alveolar Organisation
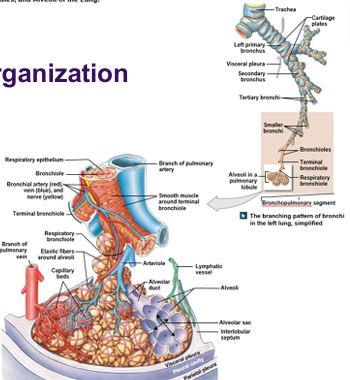
Alveolus
Extensive capillary network
Surrounded by elastic fibres
Thin
Surface area vast (35x)
Alveolar Epithelium
Simple squamous
Type 1 Cells - thin, delicate
Patrolled by alveolar macrophages
Type 2 Cells (Septal) - produce surfactant
Alveolar Macrophages (Dust Cells)
Engulf and digest foreign materials
Boyle’s Law
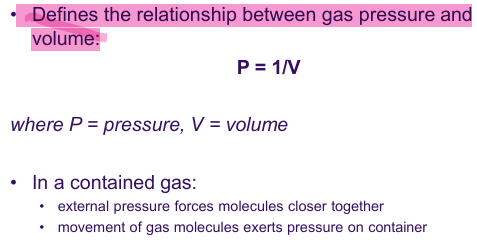
Henry’s Law
When gas under pressure comes in contact with liquid
Gas dissolves in liquid until equilibrium
Given temp - gas in solution proportional to PP of gas
The higher the pressure of a gas over a liquid, the more gas will dissolve in that liquid
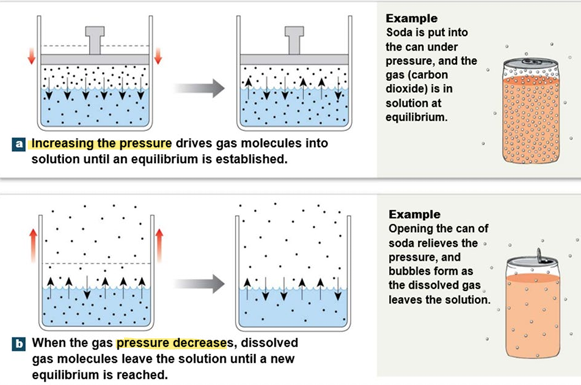
Henry’s Law and Relationship between Solubility + Pressure
5 Reasons for Efficiency of Gas Exchange
Substantial differences in PP across the respiratory membrane
Distance involved in gas exchange are short
O2 + CO2 lipid soluble
Total surface area is large
Blood flow + airflow coordinated
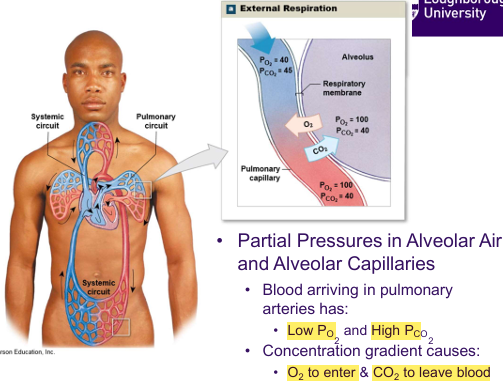
Overview of Respiratory Process + Partial Pressure (External Respiration)
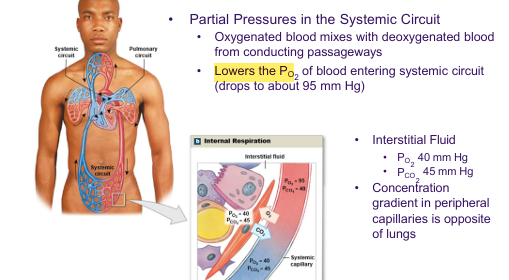
Overview of Respiratory Process + Partial Pressure (Internal Respiration)
Primary Gas Transport mechanisms
Blood plasma can’t transport enough o2/co2 to meet physiological needs
Red Blood Cells:
o2 + co2 - from peripheral
Remove o2/co2 - from plasma
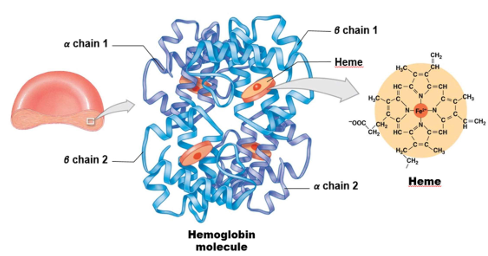
Haemoglobin
Oxyhaemoglobin
Deoxyhaemoglobin
Carbaminohaeglonin
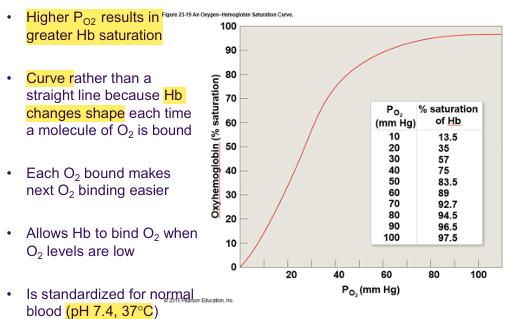
O2-Haemoglobin Saturation Curve
Temp + Hb Saturation
Increase temp = curve shifts right
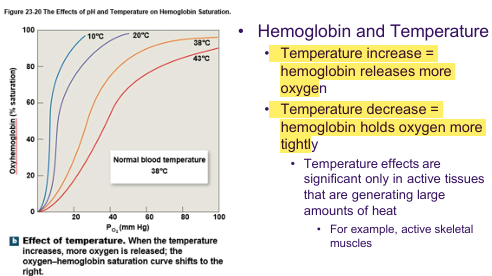
Haemoglobin + pH
Bohr effect = As the pH of the blood decreases (becomes more acidic), hemoglobin's ability to bind to oxygen decreases.
Cause HG to release o2 where its needed
Caused by co2 - diffuse into RBC
Carbonic Anhydrase - catalyse reaction H2O
Bohr effect
Result of pH on hemoglobin-saturation curve
Curve shifts right
Metabolic Activity in RBC
2,3 BPG:
RBCs generate ATP by glycolysis
Form lactic acid + BPG
More BPG - more o2 released by Hb
BPG Levels:
Rise - pH increase
Low - Hb not release o2
CO2 Transport
Generated by aerobic metabolism
3 Pathway for CO2 molecule:
Dissolve in plasma
Bind to Hb
Converted to Carbonic acid
3 Processes reversible
Key Note on Gas Transport
Control of Respiration
Normal Conditions - cellular rates of o2 absorption + co2 production = o2 absorption + co2 excretion at lungs
Normality Removed - cardiovascular + respiratory systems adjust
Local Control of Respiration (Tissues)
Increase preipheral tissue
Decrease PP o2
Increase PP co2
Changes in gas exchange
Increase blood flow
Local Control of Respiration (Alveoli)
Neural Control of Respiration
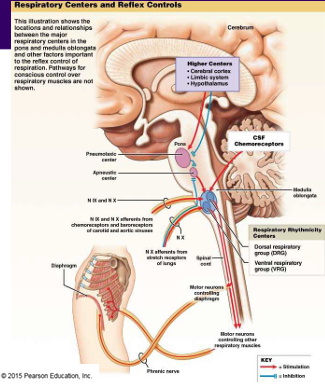
Respiratory Centres of Brain:
o2 Demand Rise - cardiac output + Respiratory rate increase
Involuntary:
Regulate respiratory muscle activity
Frequency + depth'
Respond to info from lung / respiratory tract
Voluntary:
Reflect activity in cerebral cortex
Affect respiratory centre + medulla oblongata
Respiratory Centre
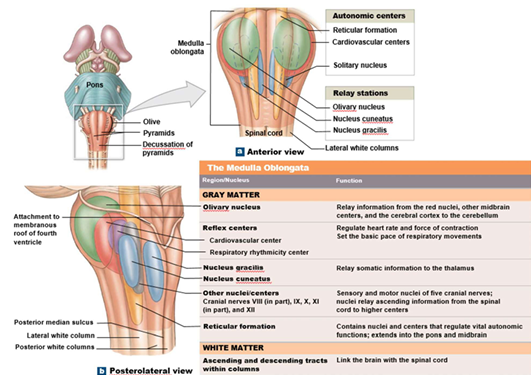
Control of Respiratory in the Pons
Paired nuclei that adjust output of respiratory rhythmicity centres
Apneustic - DRG (inspiration + depth)
Pneumotaxic - inhibit inspiration + control rate
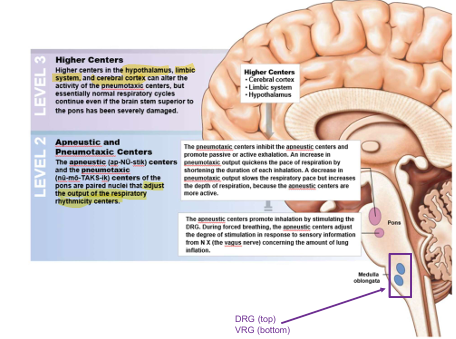
Respiratory Centre of Medulla Oblongata
Establish basic pace and depth of respiration
Dorsal Respiratory group (DRG):
Inspiratory center
Function - Quiet/Forced breathing
Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG):
Inspiratory/Expiratory center
Function - Forced breathing
Respiratory Centres + Reflex Controls
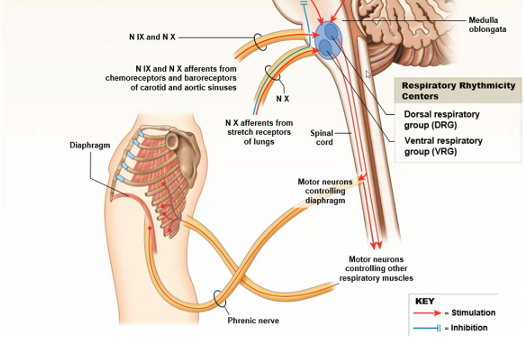
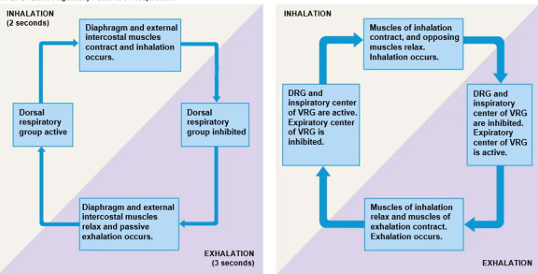
Basic Regulatory Patterns of Respiration
Respiratory Reflexes
Chemo - Pco2, Po2, Blood pH, CSF
Baro - changes in blood pressure
Stretch - changes in lung volume
Mechanoreceptors
Baroreceptors in aortic/carotid sinuses:
Changes in blood pressure
Stretch Receptors:
Changes in lung volume
Herong-Beur Reflexes
2 mechanoreceptor reflexes involved in forced breathing
Inflation Reflex - prevent overexpansion of lungs
As lung vol increases, DRG inhibited - VRG stimulated
Deflation Reflex - inhibit expiratory centres
Stimulates inspiratory centre during lung deflation
Chemoreceptor Reflexes
Cranial nerve IX - Carotid bodies
Cranial nerve X - Aortic bodies
Monitor CSF
Chemoreceptor Stimulation

Chemoreceptor Responses to Increase pCO2
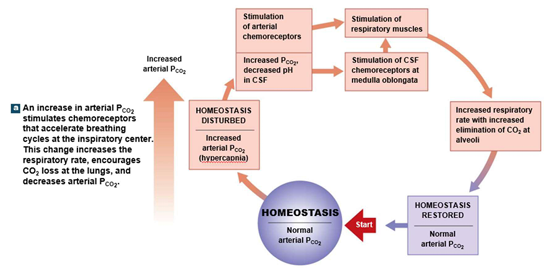
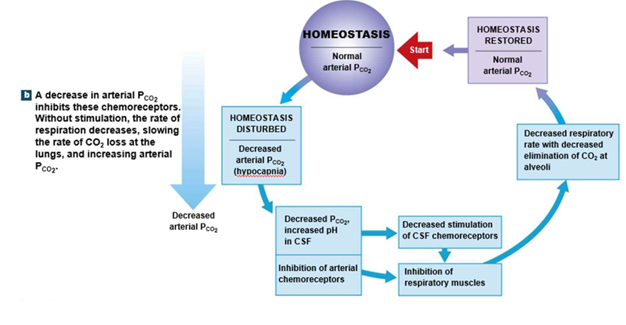
Chemoreceptor Responses to Decrease pCO2
Control by Higher Centres
Control of Respiration

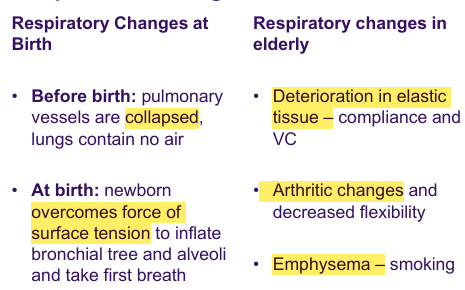
Respiration and Age