Lecture 22 Ears, Nose, Mouth
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
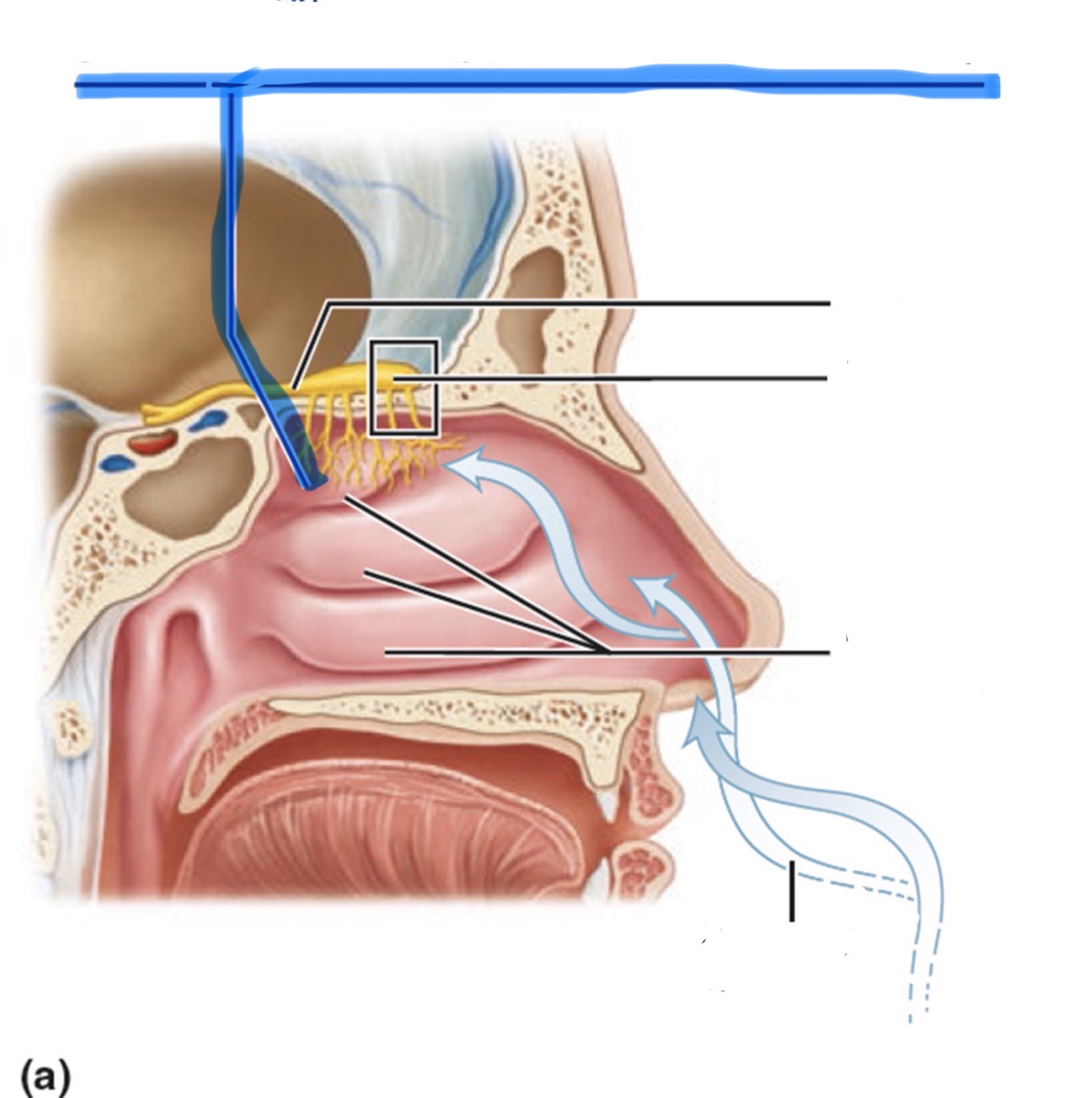
What is the highlighted part of the nose?
Olfactory epithelium
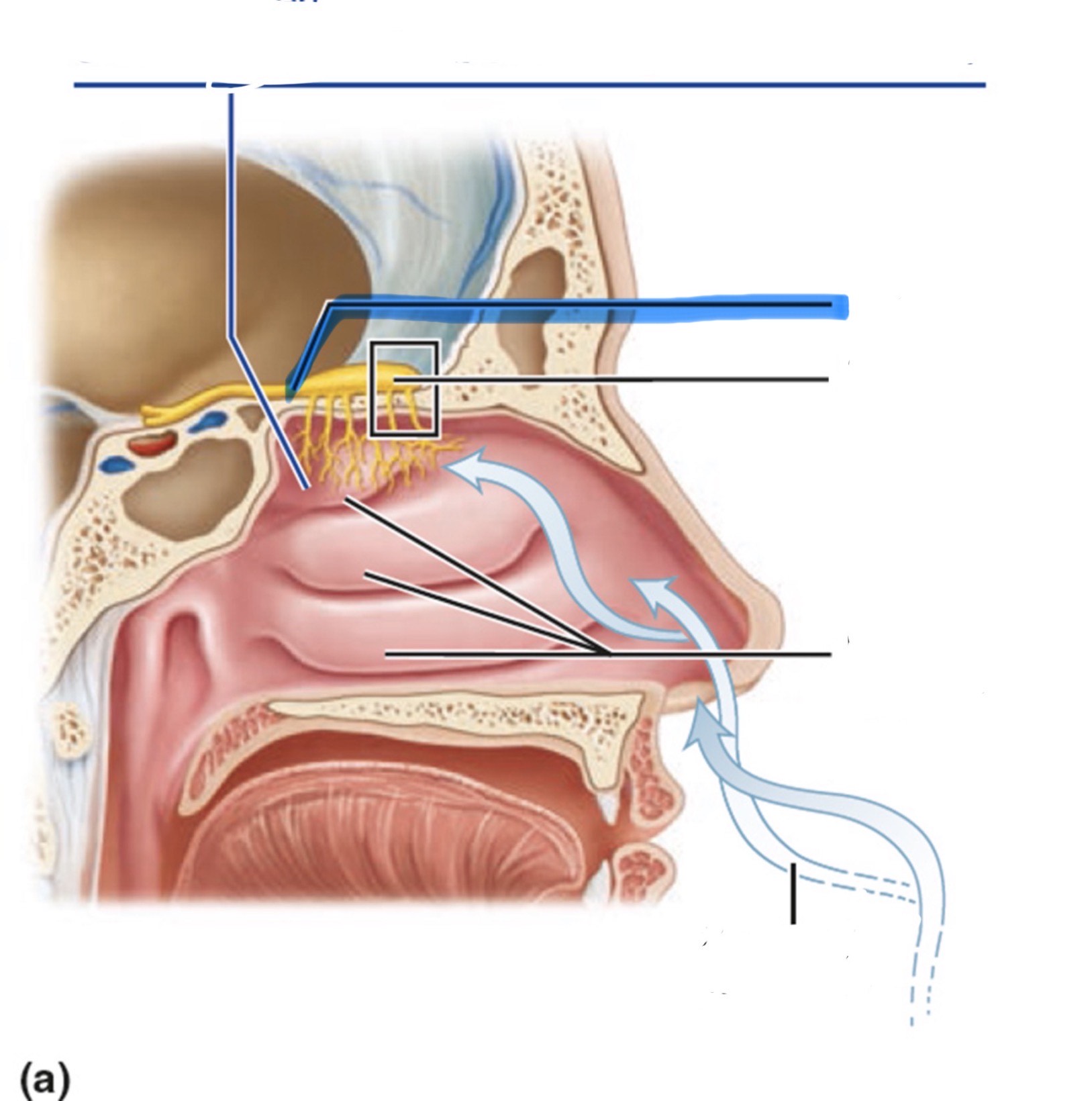
What is the highlighted part of the nose?
Olfactory tract
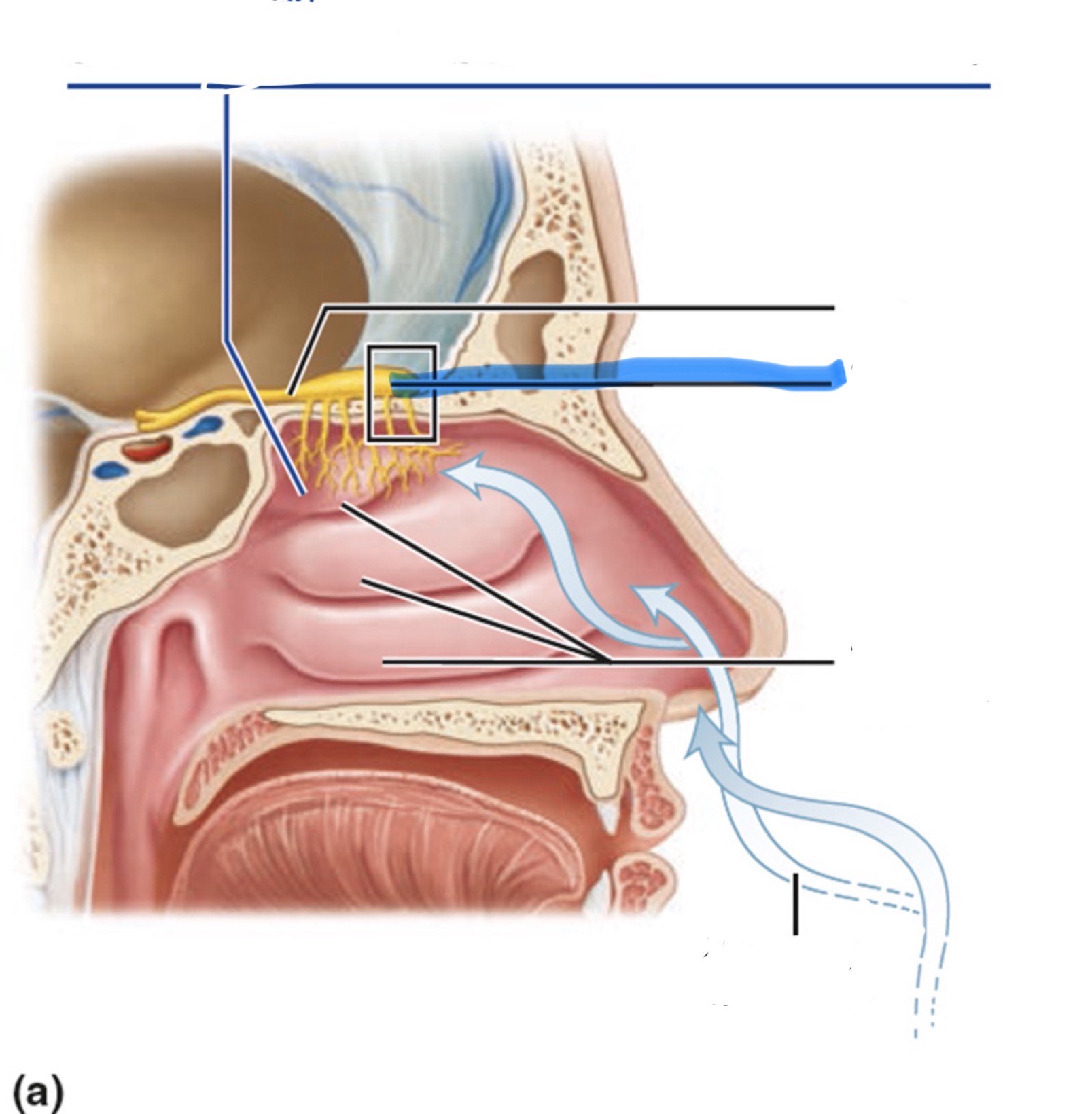
What is the highlighted part of the nose?
Olfactory bulb
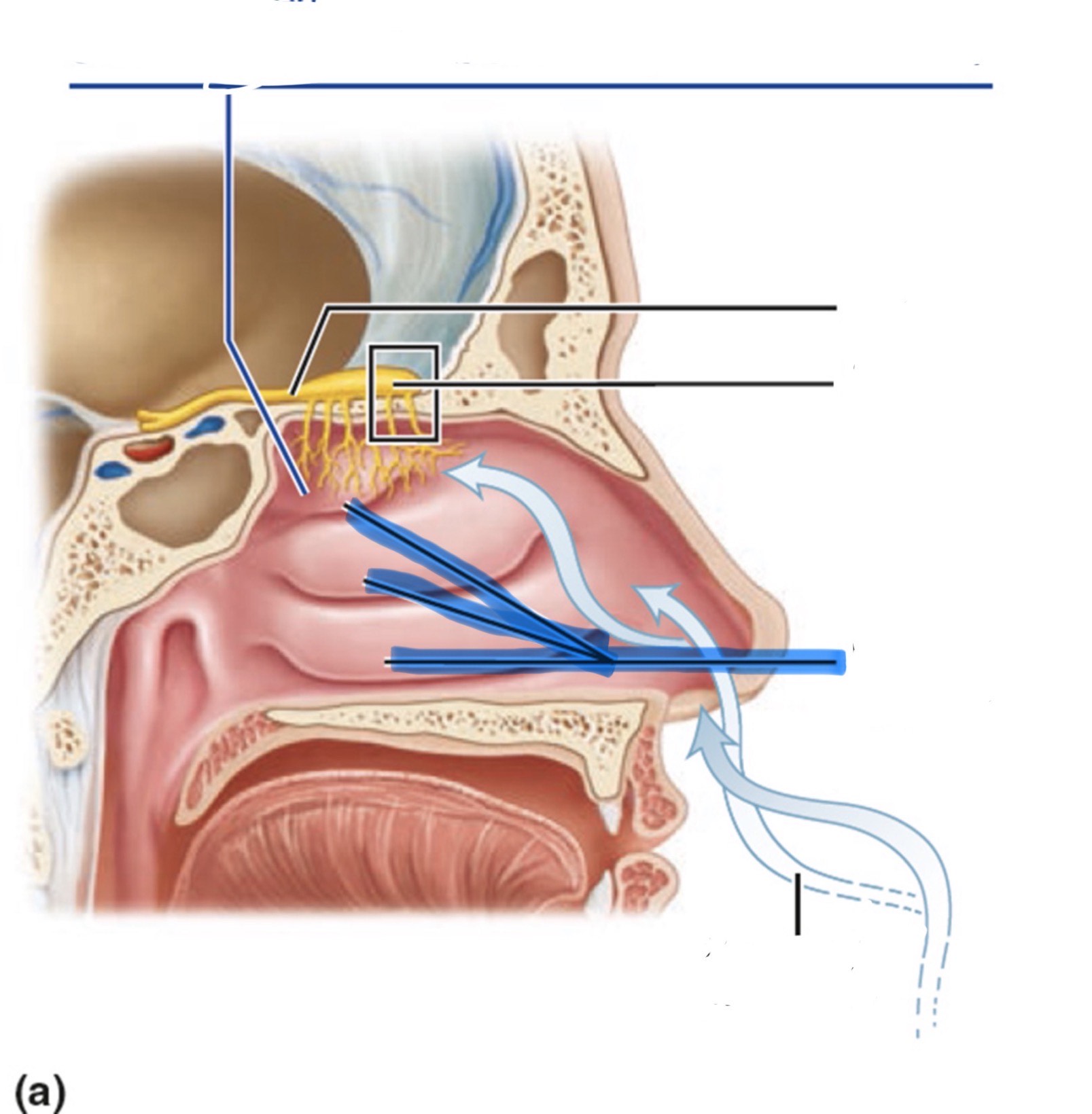
What is the highlighted part of the nose?
Nasal conchae
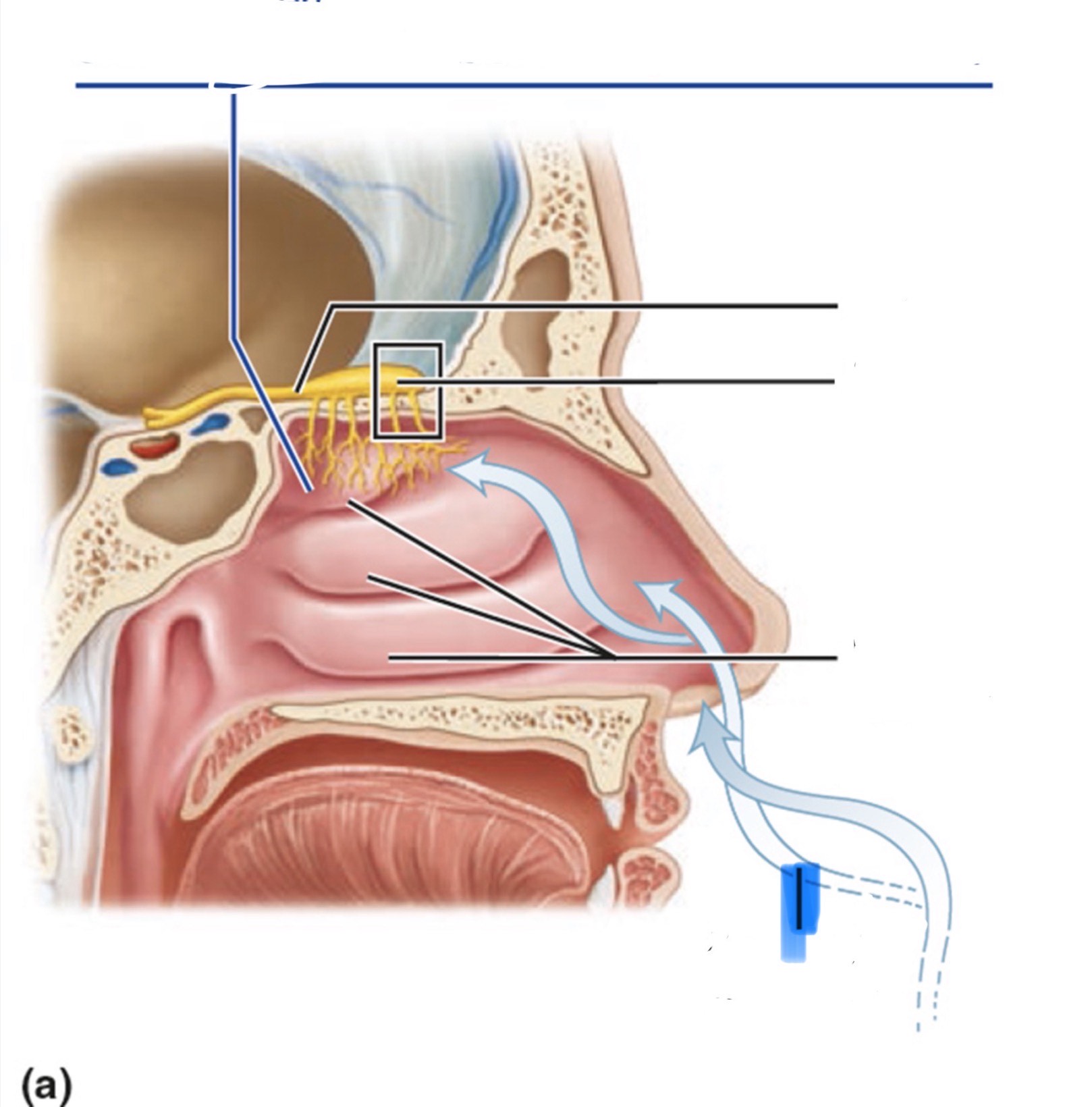
What is the highlighted part of the nose?
Route of inhaled air
What is the function of the nose?
Respiration
Filtration
Sense of smell
Speech production
Protection
Taste enhancement
How is smell received and sensed?
The axons of olfactory sensory neurons form the olfactory nerve (CN I).
They pass through the ethmoid bone and synapse in the glomeruli of the olfactory bulb.
The axons of mitral cells (the output cells of the olfactory bulb) form the olfactory tract.
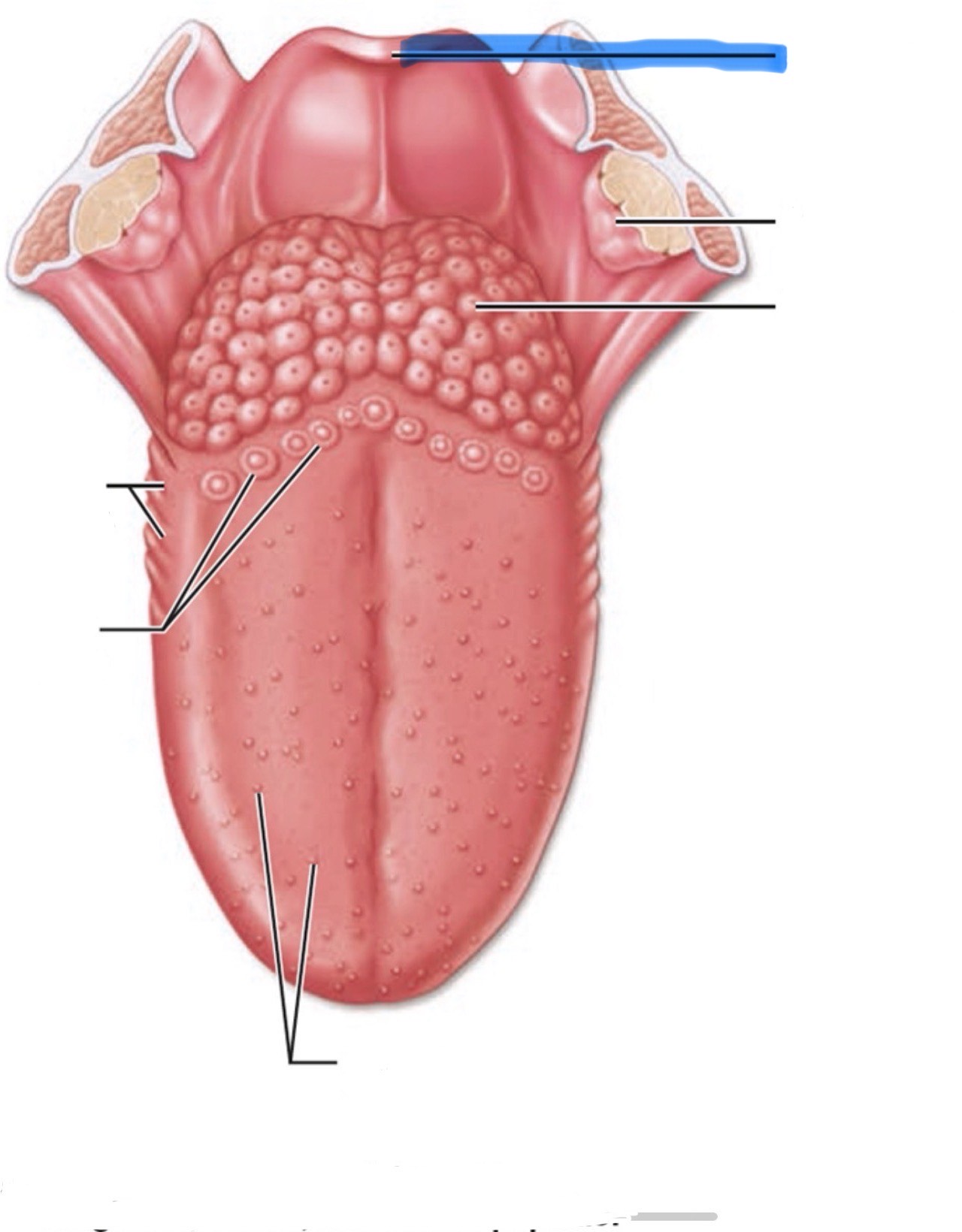
What is the highlighted part of the mouth?
Epiglottis
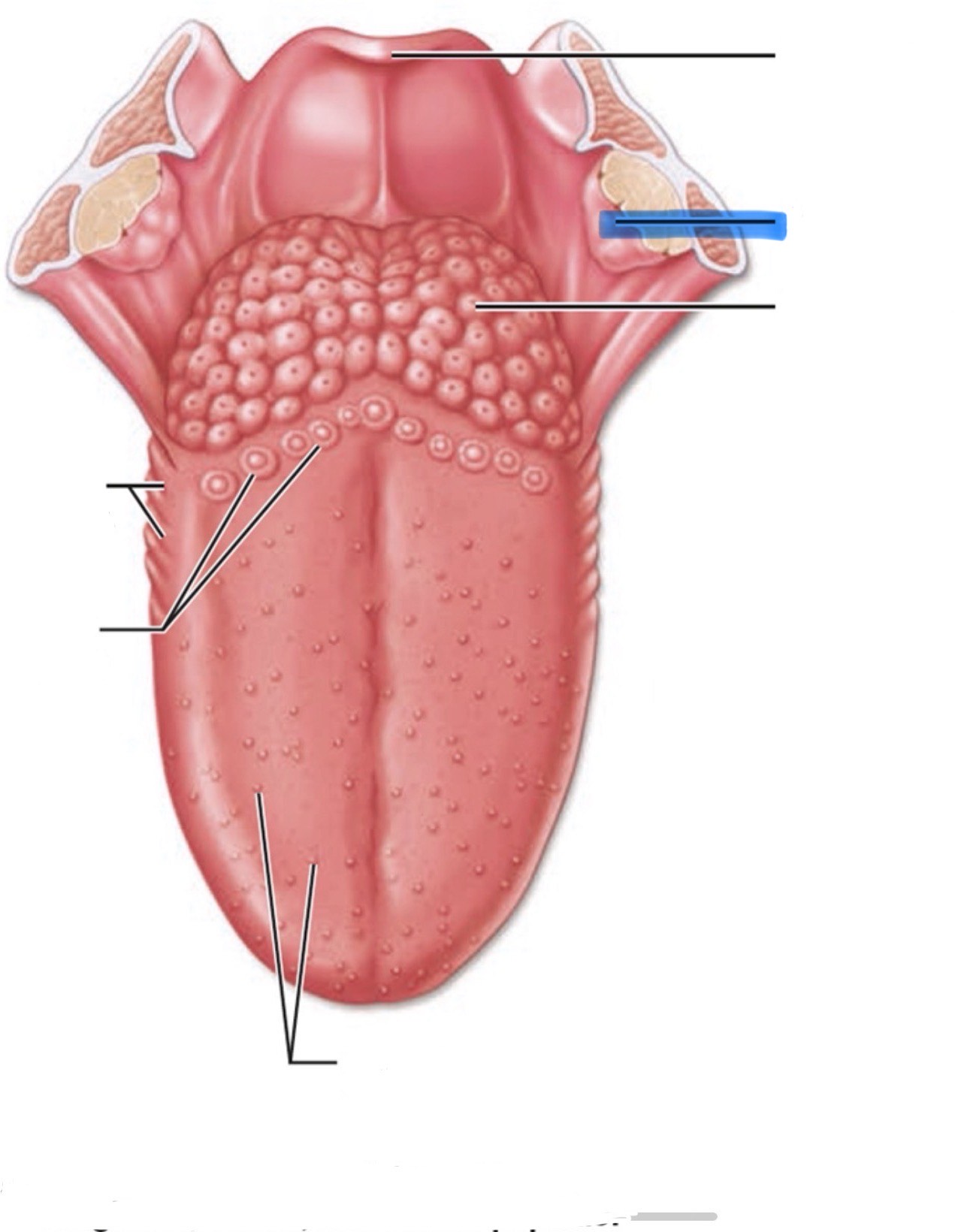
What is the highlighted part of the mouth?
Palatine tonsil
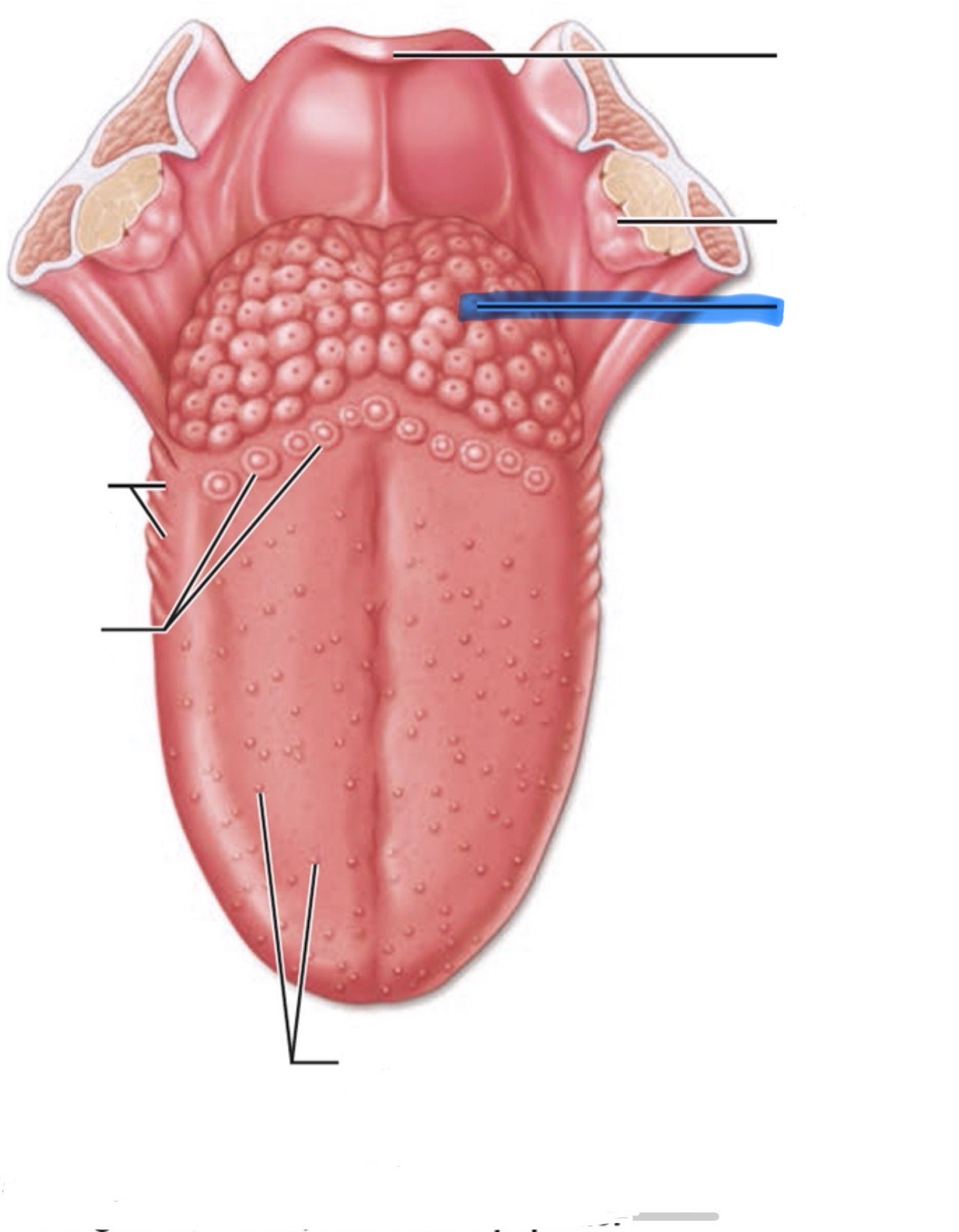
What is the highlighted part of the mouth?
Lingual tonsil
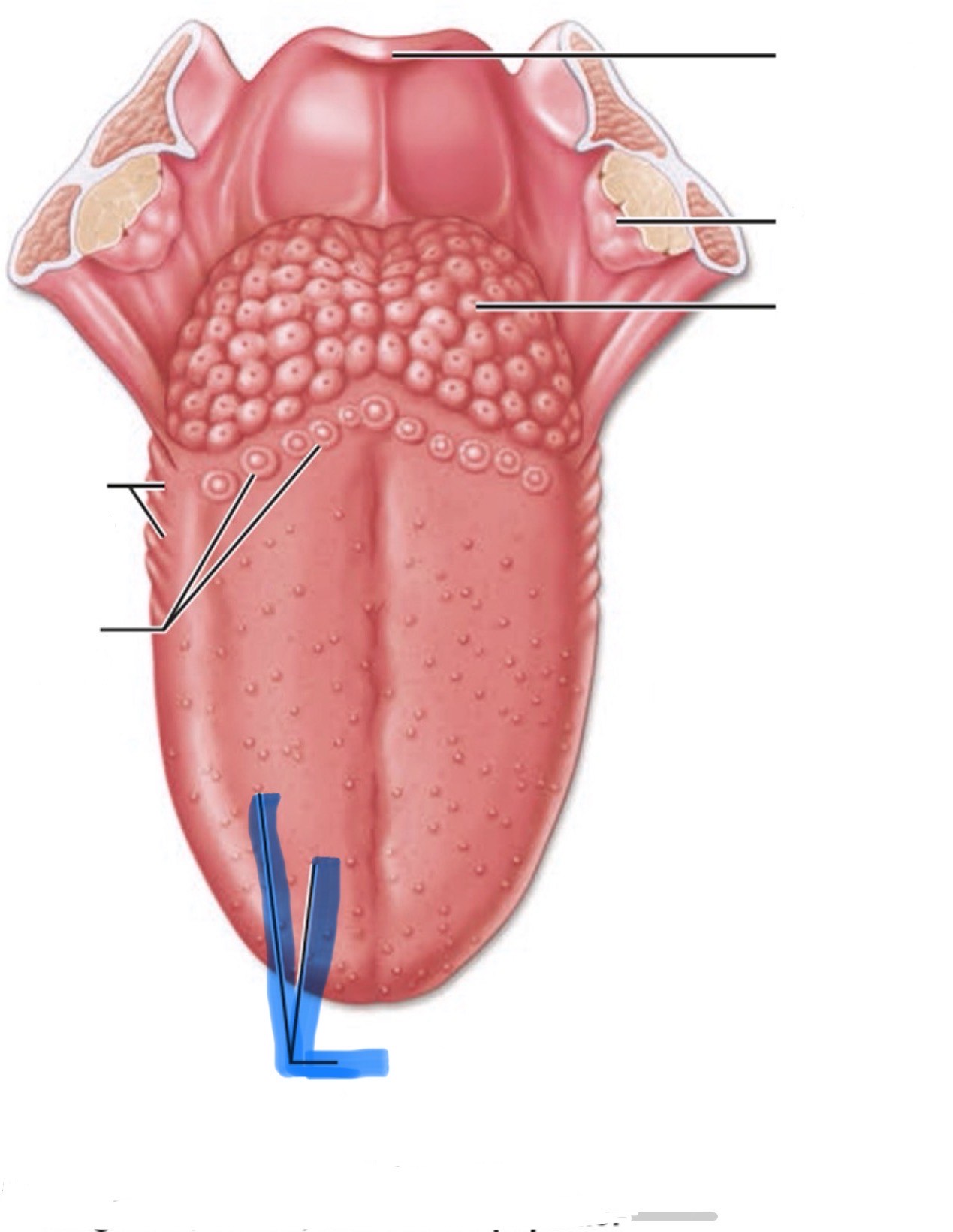
What is the highlighted part of the mouth?
Fungiform papillae
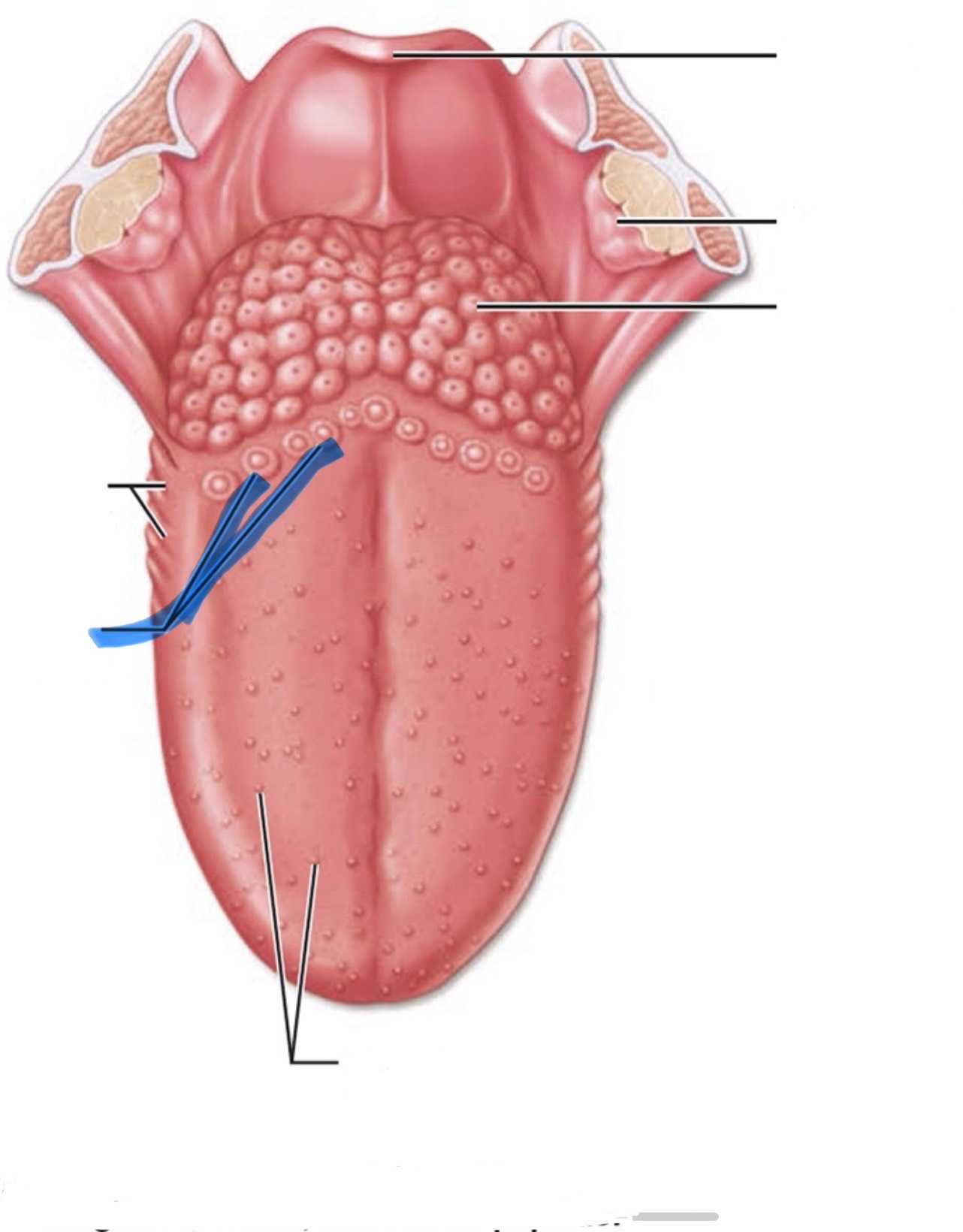
What is the highlighted part of the mouth?
Vallate papillae
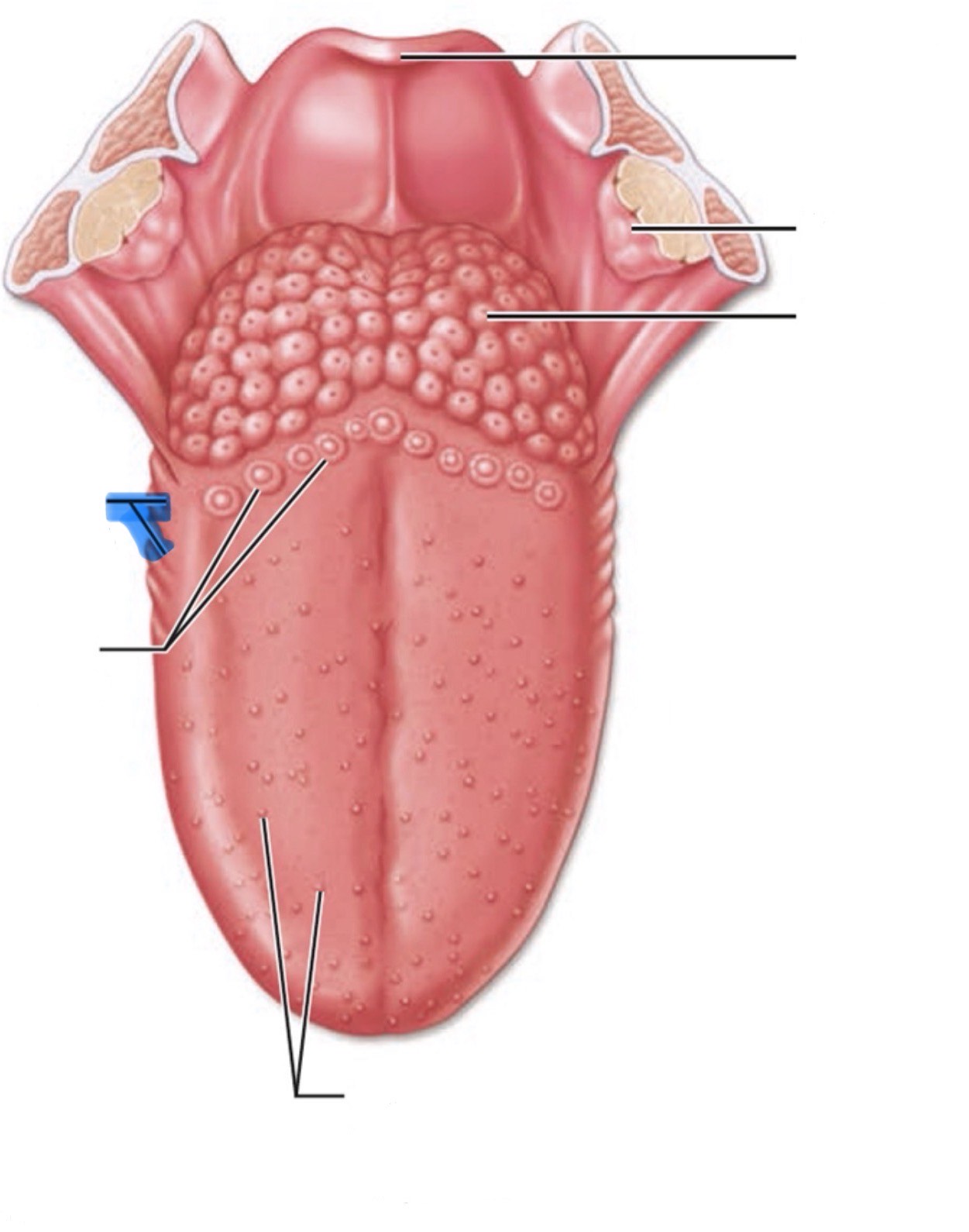
What is the highlighted part of the mouth?
Foliate papillae
What is the function of the mouth?
Digestion
Respiration
Speech
Sensory perception
Protection
How is taste received and sensed?
Binding of Taste stimuli- different taste modalities are detected when taste stimuli interacts with specific taste receptors on the taste receptor cell
Activation of G-protein complex receptors- when activated they trigger intracellular signaling pathways
Release of Neurotransmitters- The activation of taste receptors leads to the releases of neurotransmitter which stimulate nearby sensory nerve fibers
What are the three major areas of the ears?
External ear
Middle ear
Internal ear
What are the different parts of the external ear?
Auricle (pinna)
External acoustic meatus
Tympanic membrane (ear drum)
Meatus
What are the different parts of the middle ear?
Malleus
Incus
Stapes
What are the different parts of the internal ear?
Cochlea
Cochlear nerve
Vestibular nerve
Explain how the parts of the ear function to transmit sound (15.9)
External Ear
Eardrum- Vibrates in response to sound which. Send the sounds into the inner ear
Middle ear
Ossicles- amplify the vibrations and help transmit them to the cochlea
Eustachian Tube- equalizes air pressure on either side of the eardrum during swallowing or yawning. It prevents pressure related pain during rapid changes in pressure
Inner Ear
Cochlea- Converts sound vibration into electrical signals for the brain to interpret as sound. This allows us to hear the world around us