Year 10 Physics: Kinematics and Forces Overview
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
245 Terms
Kinematics
Study of motion of objects.
Speed
Distance travelled per unit time.
Average Speed
Total distance divided by total time.
Velocity
Speed with direction.
Average Velocity
Displacement divided by total time.
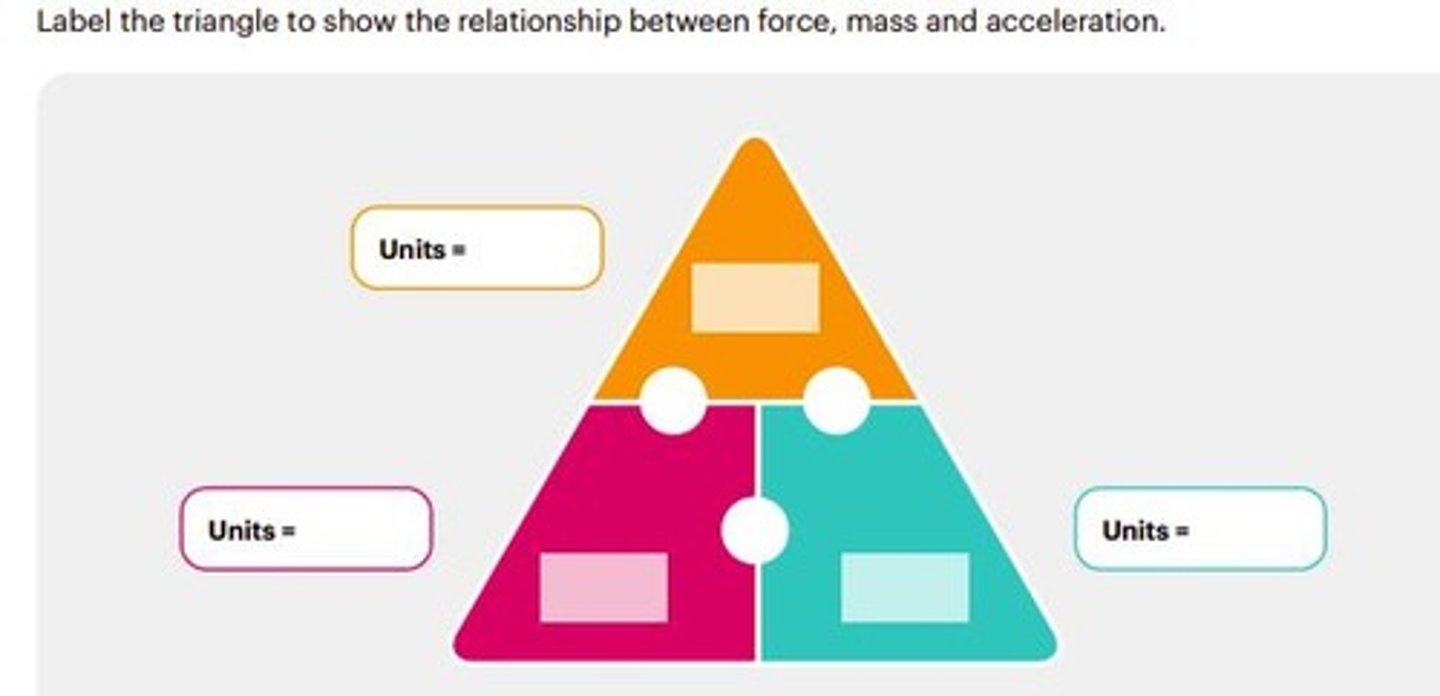
Acceleration
Change in velocity over time.
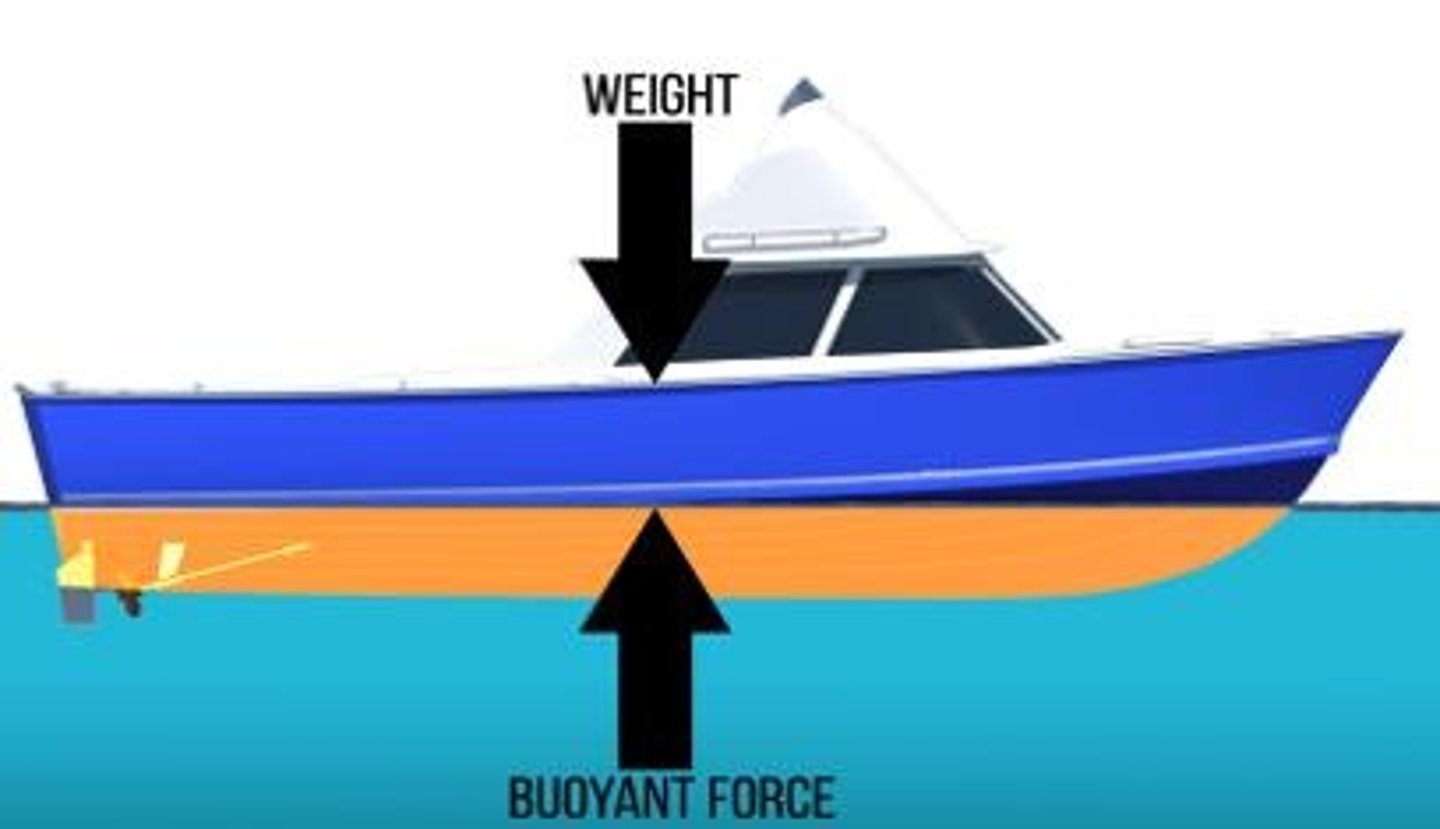
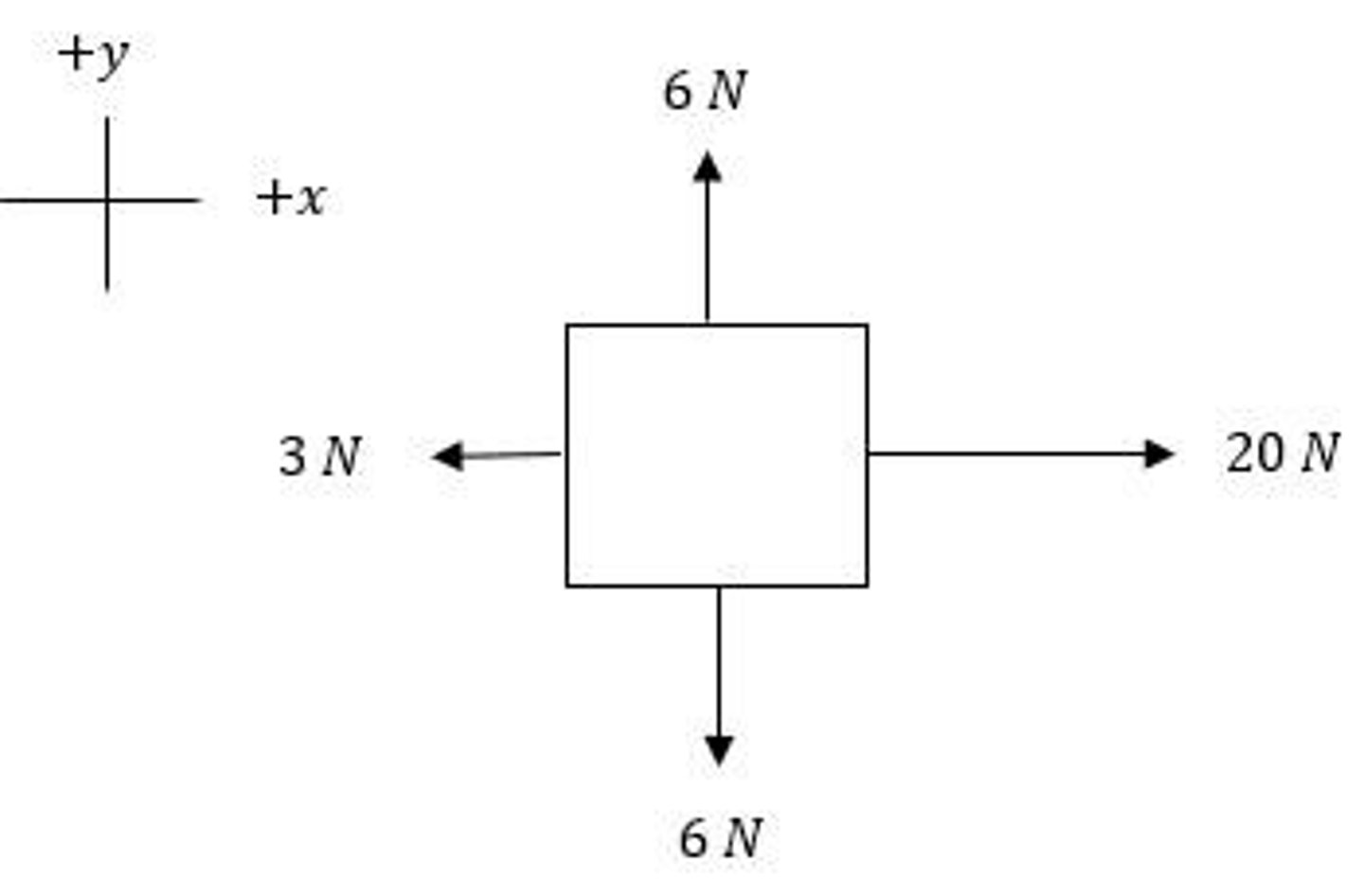
Net Force
Total force acting on an object.
Balanced Forces
Forces that cancel each other out.
Unbalanced Forces
Forces that cause motion change.
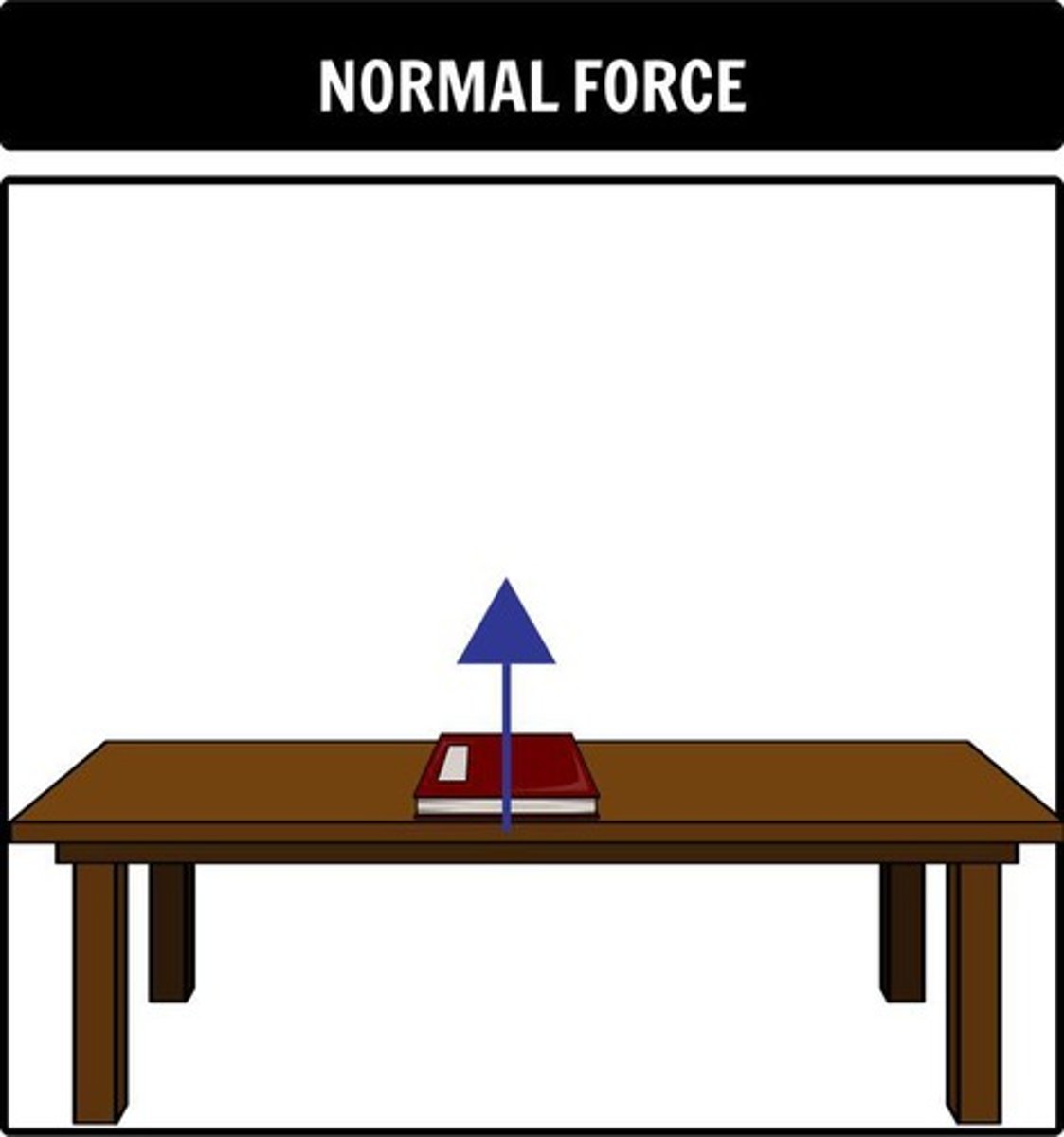
Free-Body Diagram
Illustration showing forces on an object.
Distance
Length of path between two points.
Displacement
Shortest path from initial to final position.
Vector Quantity
Has both magnitude and direction.
Scalar Quantity
Has only magnitude.
Force
Push or pull acting on an object.
Mass
Amount of matter in an object.
SI Unit of Force
Newton (N).
SI Unit of Speed
Metres per second (m s-1).
SI Unit of Acceleration
Metres per second squared (m s-2).

Position-Time Graph
Graph showing object position over time.
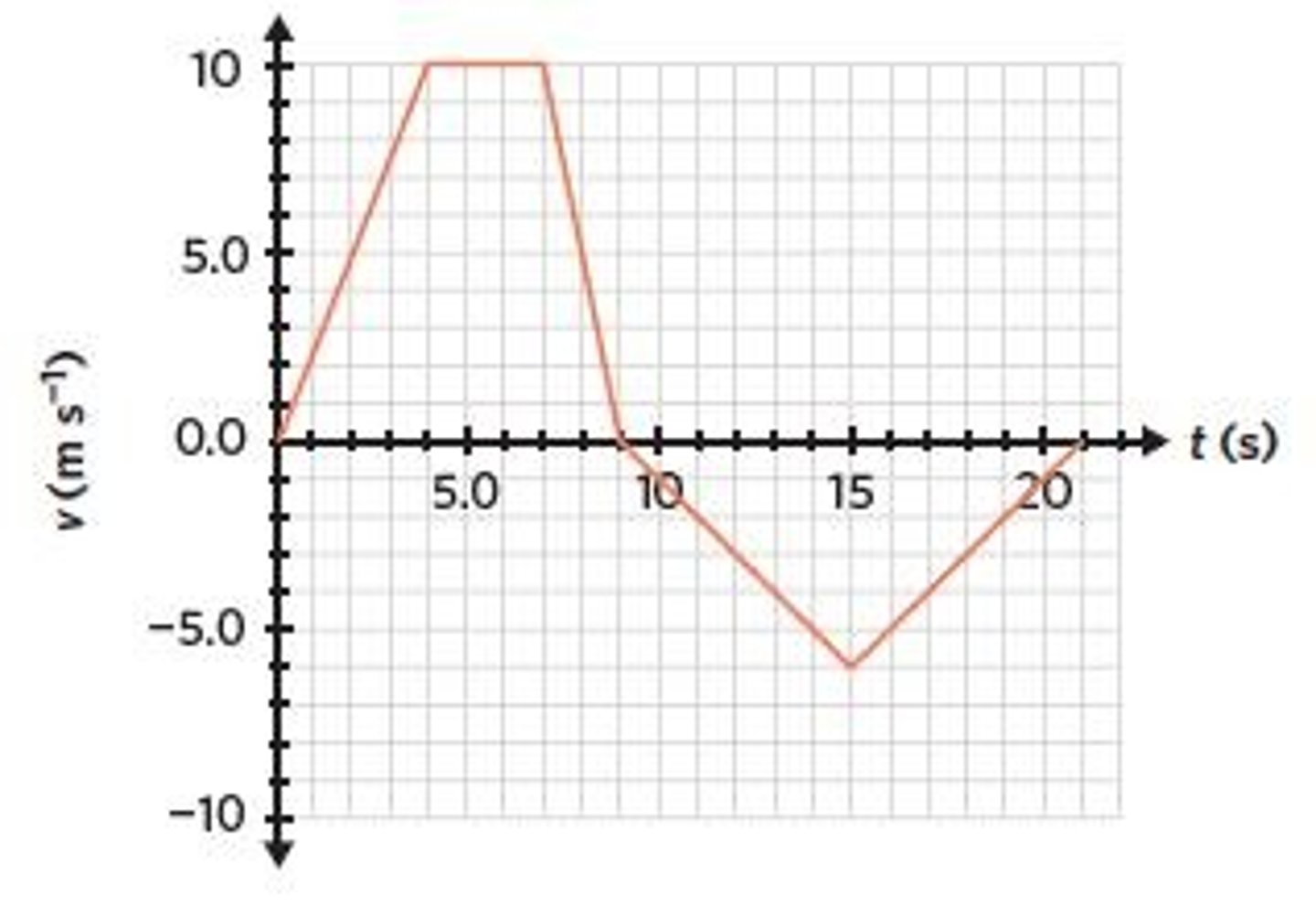
Velocity-Time Graph
Graph showing object velocity over time.
SUVAT Equations
Equations for constant acceleration problems.
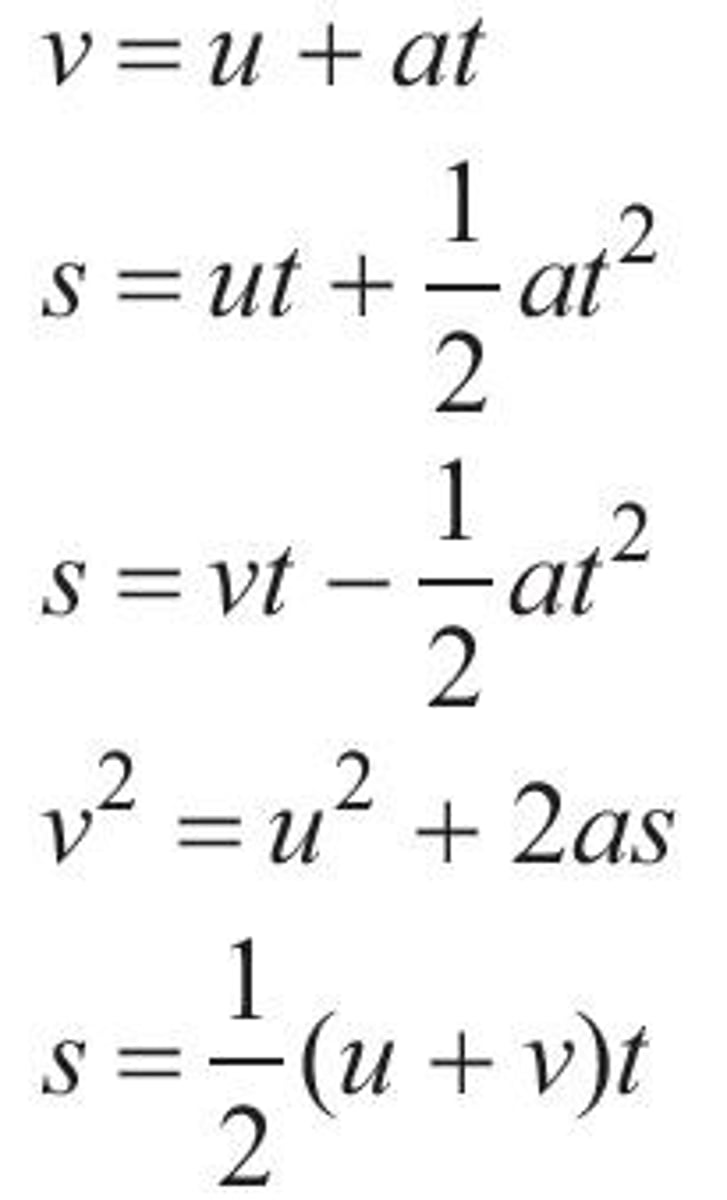
Conversion Factor
Used to convert units between systems.
Speed of Light
Distance light travels in 15 seconds: 4,500,000,000 m.
Speed Formula
Speed equals distance divided by time.
Distance Formula
Distance equals speed multiplied by time.
Time Calculation
Time equals distance divided by speed.
Formula Triangle
Visual aid for remembering speed, distance, time.
Unit of Speed
Commonly measured in m s-1 or km h-1.
Conversion Factor
To convert km h-1 to m s-1, divide by 3.6.
Conversion Factor
To convert m s-1 to km h-1, multiply by 3.6.
Example Calculation
Distance = 8 m s-1 × 50 s = 400 m.
Chase Duration
Time = 21 m ÷ 3 m s-1 = 7 s.
Distance in 10 seconds
Distance = 30 m s-1 × 10 s = 300 m.
Distance in 30 seconds
Distance = 60 m s-1 × 30 s = 1800 m.
Distance in 4.5 hours
Convert 60 km h-1 to m s-1, then calculate.
Distance in 0.4 hours
Convert 100 km h-1 to m s-1, then calculate.
Speed Calculation
Speed = 120 m ÷ 10 s = 12 m s-1.
Speed Calculation
Speed = 600 m ÷ 15 s = 40 m s-1.
Time for 1000 m
Time = 1000 m ÷ 50 m s-1 = 20 s.
Time for 10 m
Time = 10 m ÷ 25 m s-1 = 0.4 s.
Constant Speed
Same distance covered in equal time intervals.
Speed Measurement
Requires distance and time for calculation.
Units of Measurement
Speed can be measured in m s-1 or km h-1.
Distance
Total length traveled by an object.
Time
Duration taken to complete a journey.
Speed (km hr-1)
Distance traveled per hour in kilometers.
Speed (m s-1)
Distance traveled per second in meters.
Conversion Factor
1 km hr-1 equals 0.27778 m s-1.
Distance-Time Graph
Graph showing distance against time.
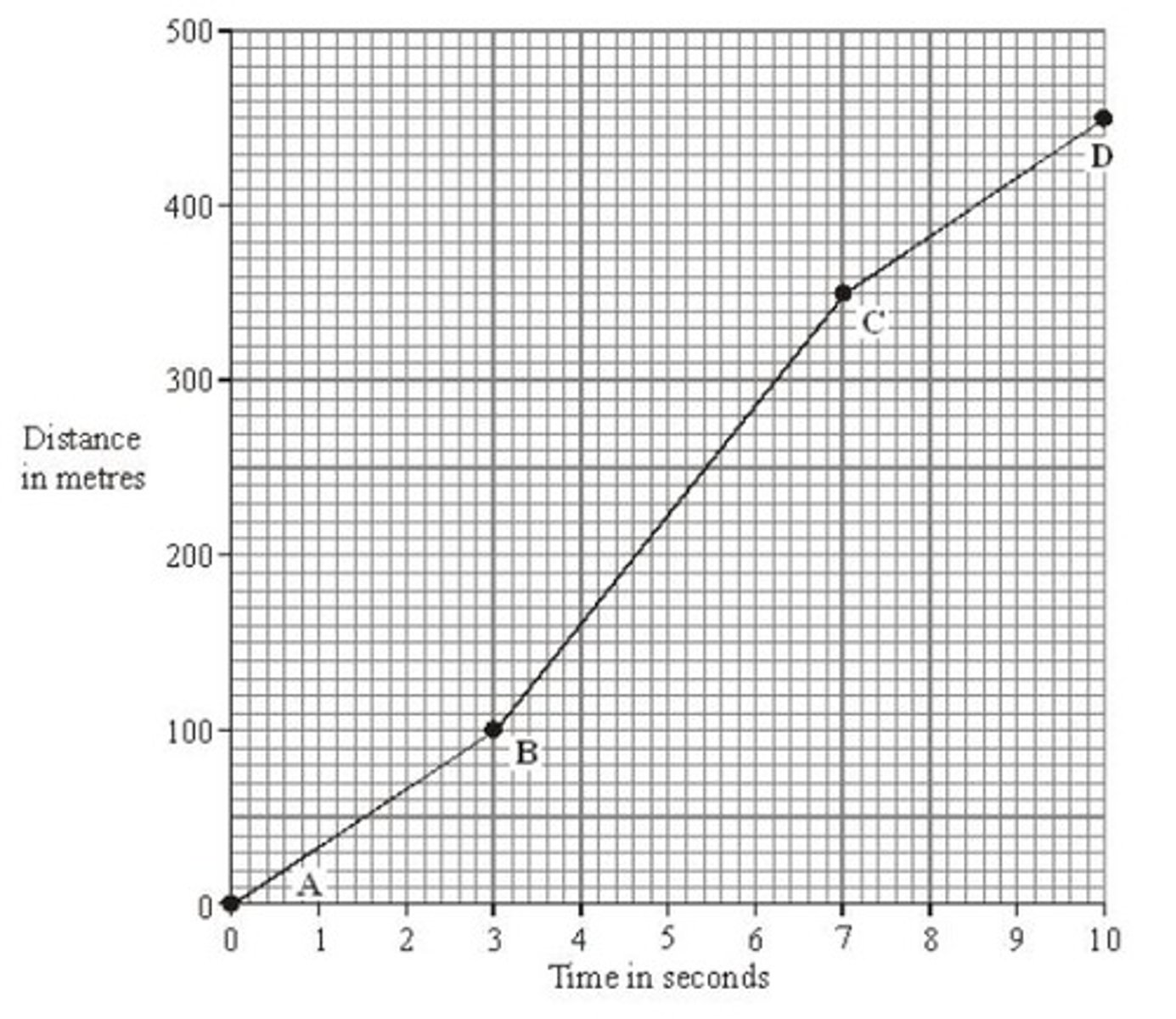
Gradient
Slope of the distance-time graph indicating speed.
Stationary Object
Object not changing position over time.
Accelerating Object
Object increasing speed over time.
Decelerating Object
Object decreasing speed over time.
Flat Line on Graph
Indicates object is stationary.
Negative Gradient
Indicates object moving back towards start.
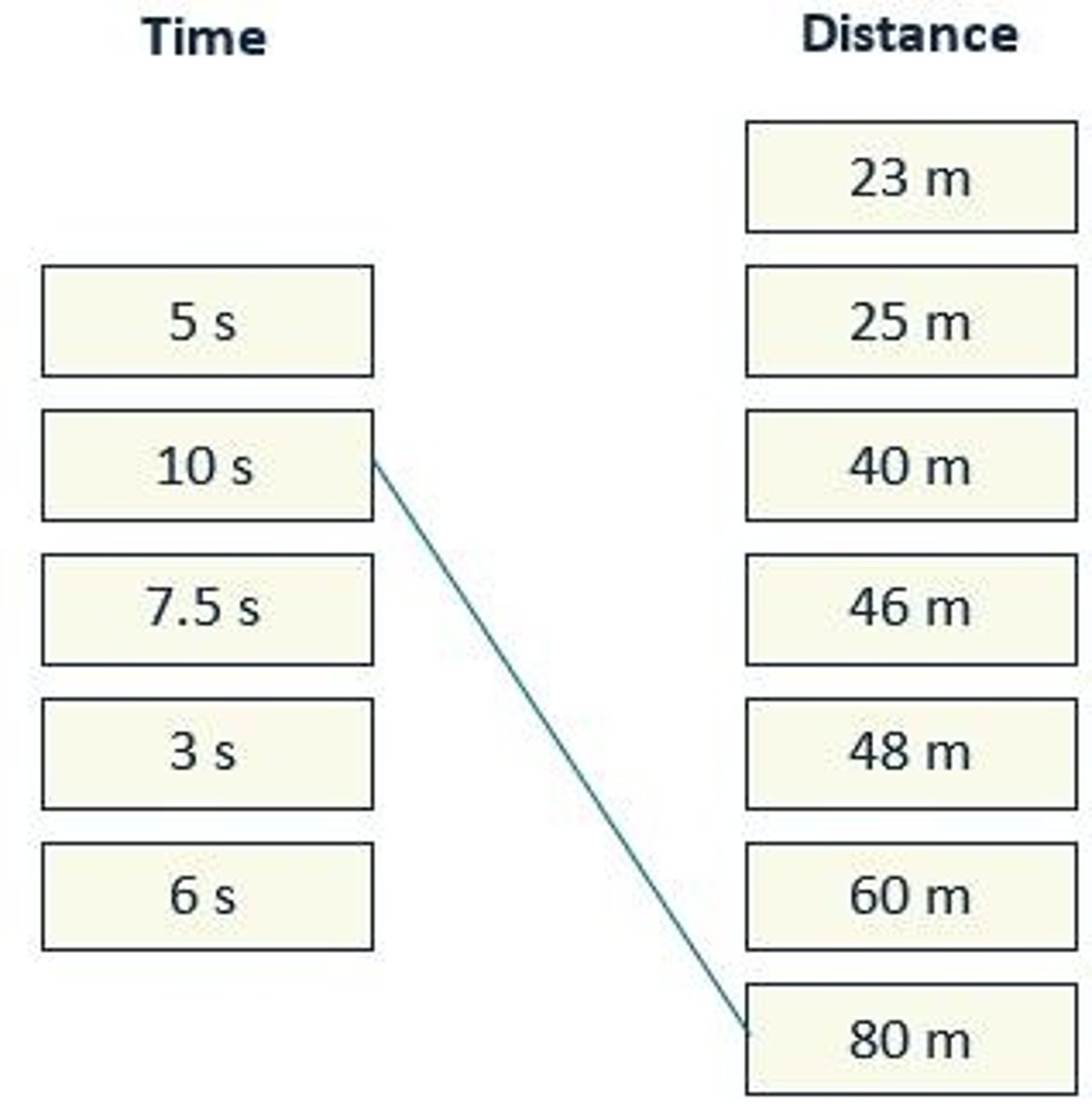
Car Speed Calculation
Distance divided by time for speed.
Runner's Speed
Distance covered in specific time at constant rate.
Bird's Speed Calculation
Speed equals distance divided by time.
Time Conversion
Convert minutes to seconds by multiplying by 60.
Distance Conversion
Convert kilometers to meters by multiplying by 1000.
Speed of 747 Jet
900 km hr-1 for travel calculations.
Car Average Speed
Total distance divided by total journey time.
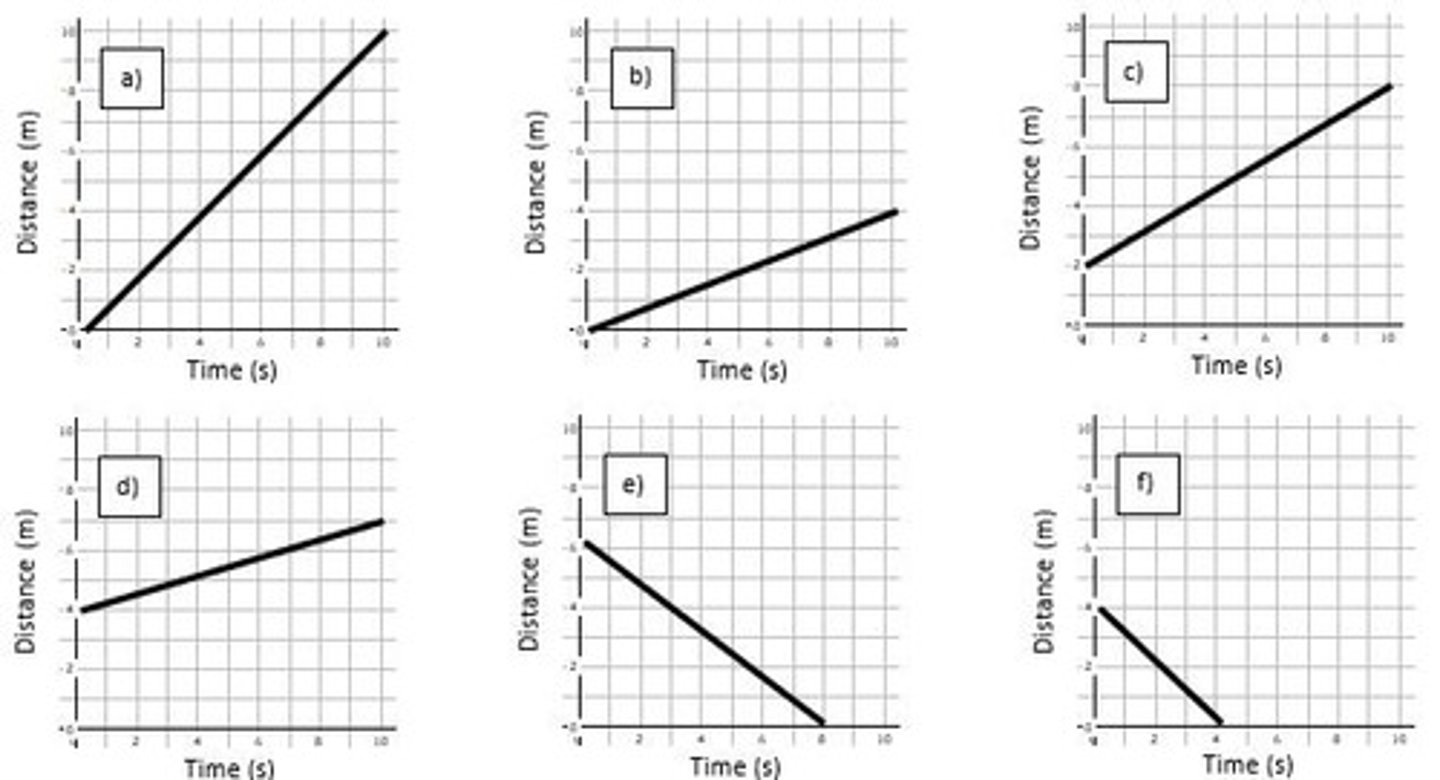
Zara's Distance Change
Graph segment indicates distance covered during run.
Jogger Speed Comparison
Determine speed by analyzing distance-time graph.
Motion Sensor
Device used to track movement and speed.
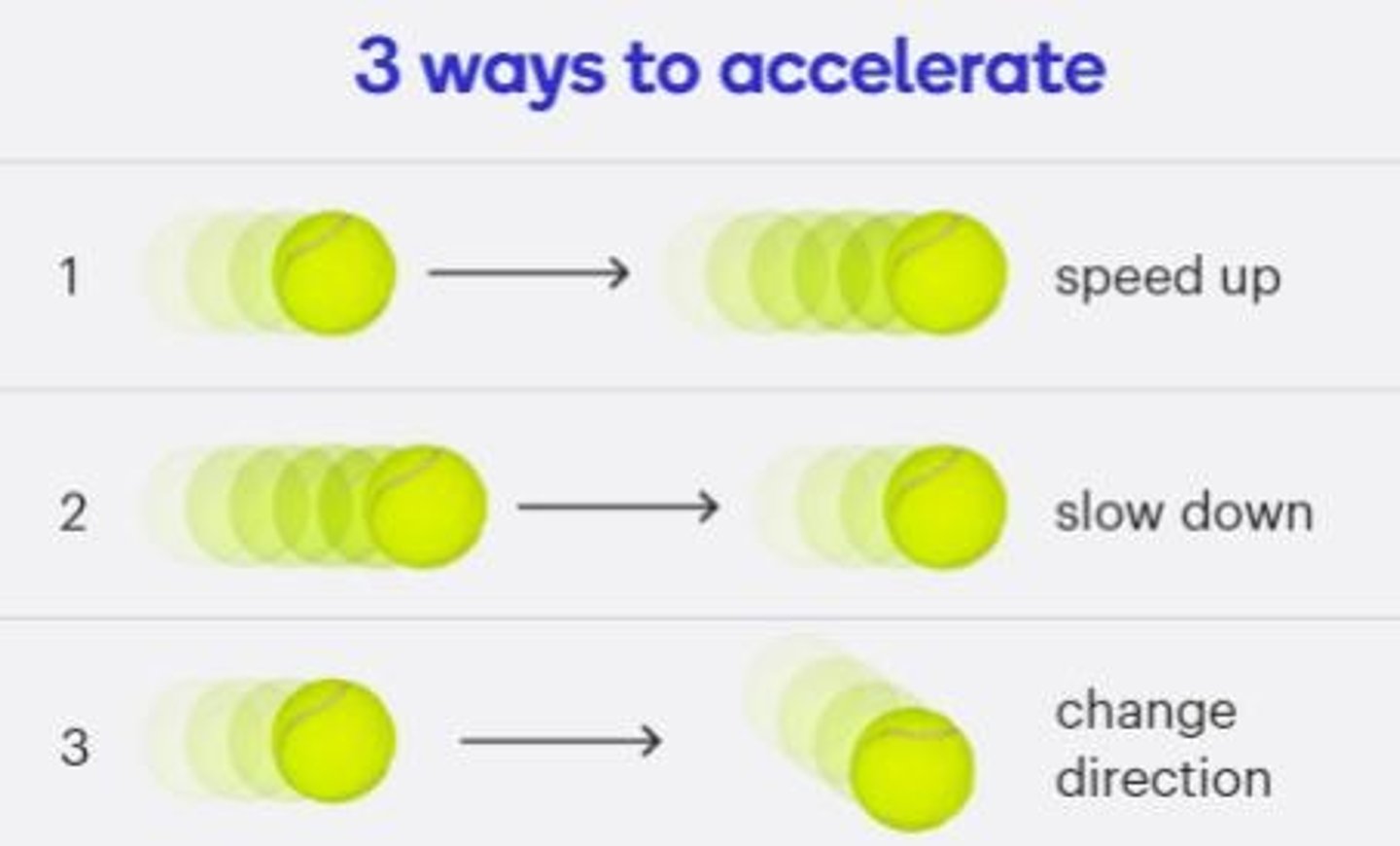
Acceleration
Rate of change of speed over time.

Deceleration
Negative acceleration; slowing down over time.
Constant Speed
Movement at a steady rate without change.
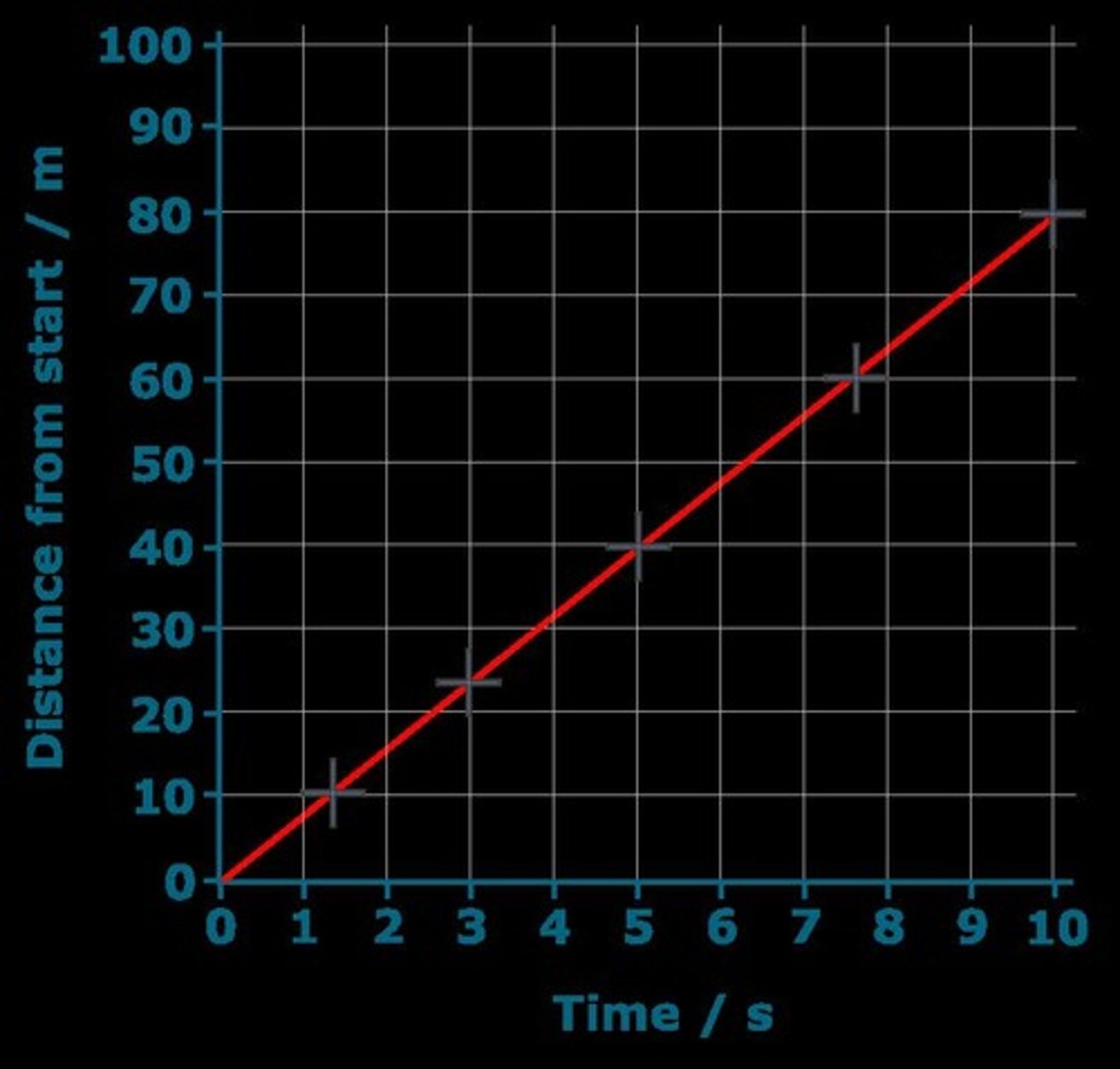
Distance-Time Graph
Visual representation of distance versus time.
Speeding Up
Increasing speed over a period of time.
Slowing Down
Decreasing speed over a period of time.
Stationary
Object not moving; speed equals zero.
Overtaking
When one object passes another in motion.
Displacement
Distance moved in a specific direction.
Bus Stop
Designated point where a bus halts.
Cyclist's Journey
Path taken by a cyclist over time.
Distance Calculation
Finding distance using speed and time.
Graph Interpretation
Analyzing graphs to understand motion characteristics.
High Speed
Movement at a fast rate over time.
Low Speed
Movement at a slow rate over time.
Motion Description
Explanation of an object's movement pattern.
Distance Measurement
Quantifying how far an object travels.
Time Measurement
Quantifying duration of an event.
Constant Velocity
Unchanging speed in a straight line.
Graphical Representation
Visual depiction of data or motion.
Speed Calculation
Determining speed using distance and time.
Speed
Rate of motion, measured in m s-1.
Steady Speed
Constant speed without acceleration changes.
Higher Speed
Increased speed compared to another object.
Same Speed
Maintaining constant speed while cycling uphill.
Freewheel
Move without pedaling, relying on momentum.
Losing Speed
Decrease in speed over time or distance.
Brakes
Device used to slow down or stop a vehicle.
Positive Acceleration
Object speeds up, acceleration value is positive.
Negative Acceleration
Object slows down, acceleration value is negative.
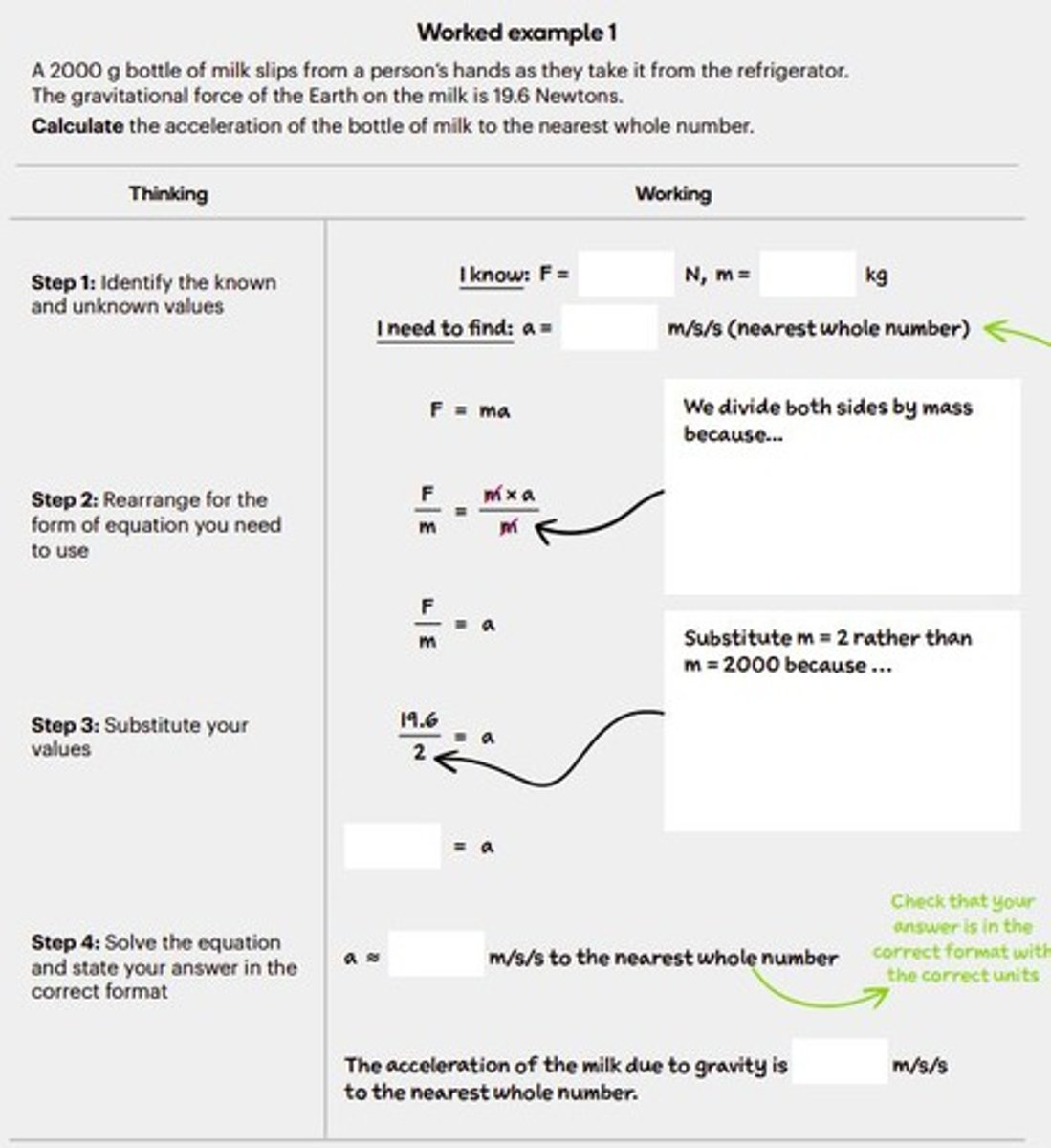
Acceleration Equation
a = (Vf - Vi) / t.
Initial Velocity (Vi)
Starting speed before acceleration occurs.
Final Velocity (Vf)
Speed after acceleration has taken place.
Time (t)
Duration over which acceleration occurs.