Populations in Ecosystems
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Define Population
All the individuals of the same species in a habitat at the same time that can interbreed
Define community
All the populations of different species in a habitat
Define niche
The role of a species in its ecosystem and how it interacts with all the biotic and abiotic factors
Define biotic factors and give 2 examples
Living factors that can impact the size of a population
Examples:
Food
Predators
Prey
Diseases(bacteria)
Define abiotic factors and give 2 examples
Non-living factors that can affect the size of a population
Examples:
Weather
Humidity
Soil pH
Water
Light intensity
Disease (viruses)
Define carrying capacity
Th maximum population size of species an ecosystem can support
Define ecosystem
Formed from a community and the non-living components of its environment. E.g. rainforest
Define interspecific competition
Competition between different species
Define intraspecific competition
Competition between individuals of the same species
Define predation
How the population of predators and prey can affect each other
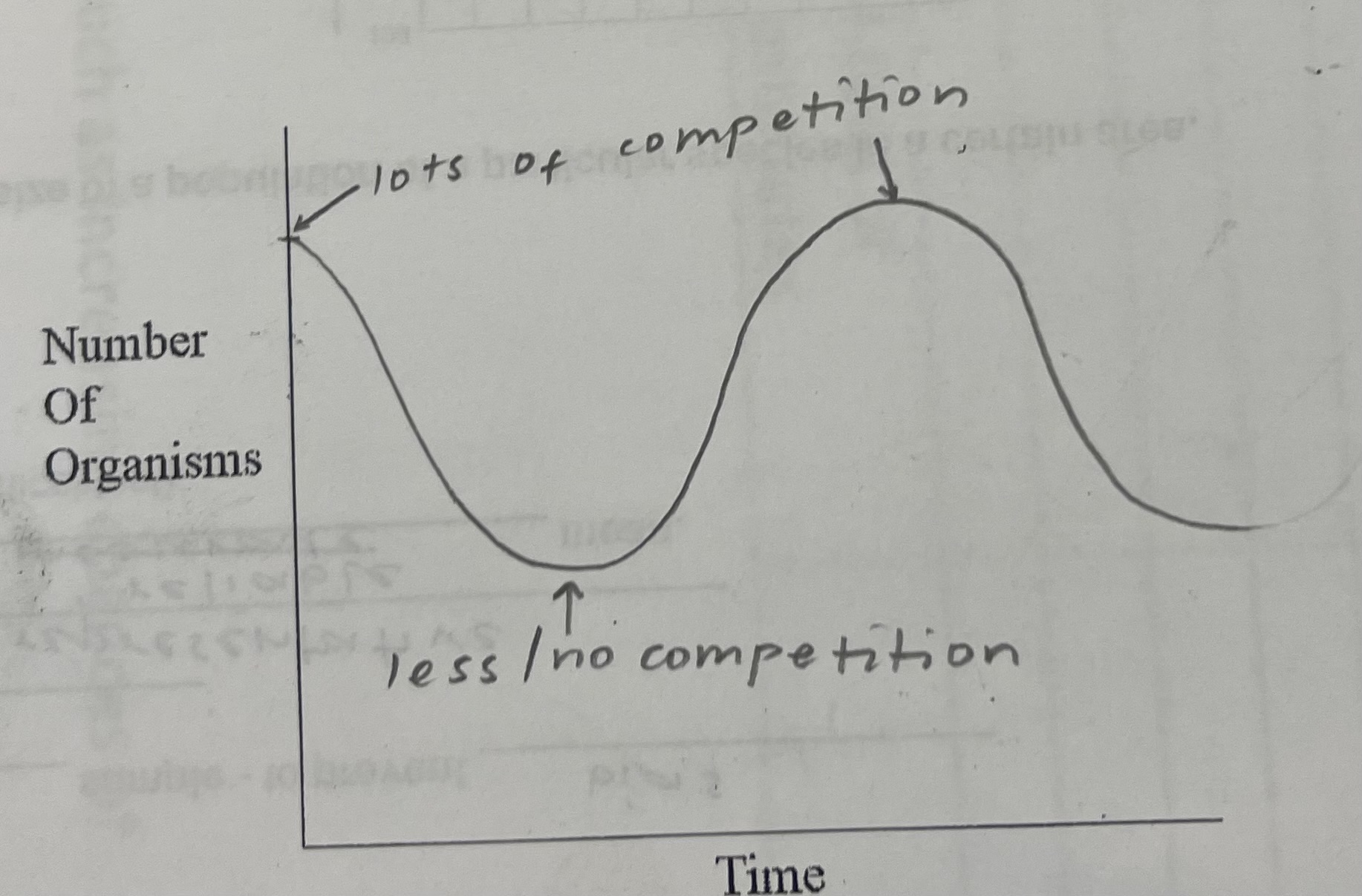
Explain how intraspecific competition affects the number of organisms. Explain the graph that shows this
Members of same species compete for the same resources eg. Food
If the population gets too big, intraspecific competition increases, so the population falls again
If the population gets too small, intraspecific competition decreases, so the population increases again
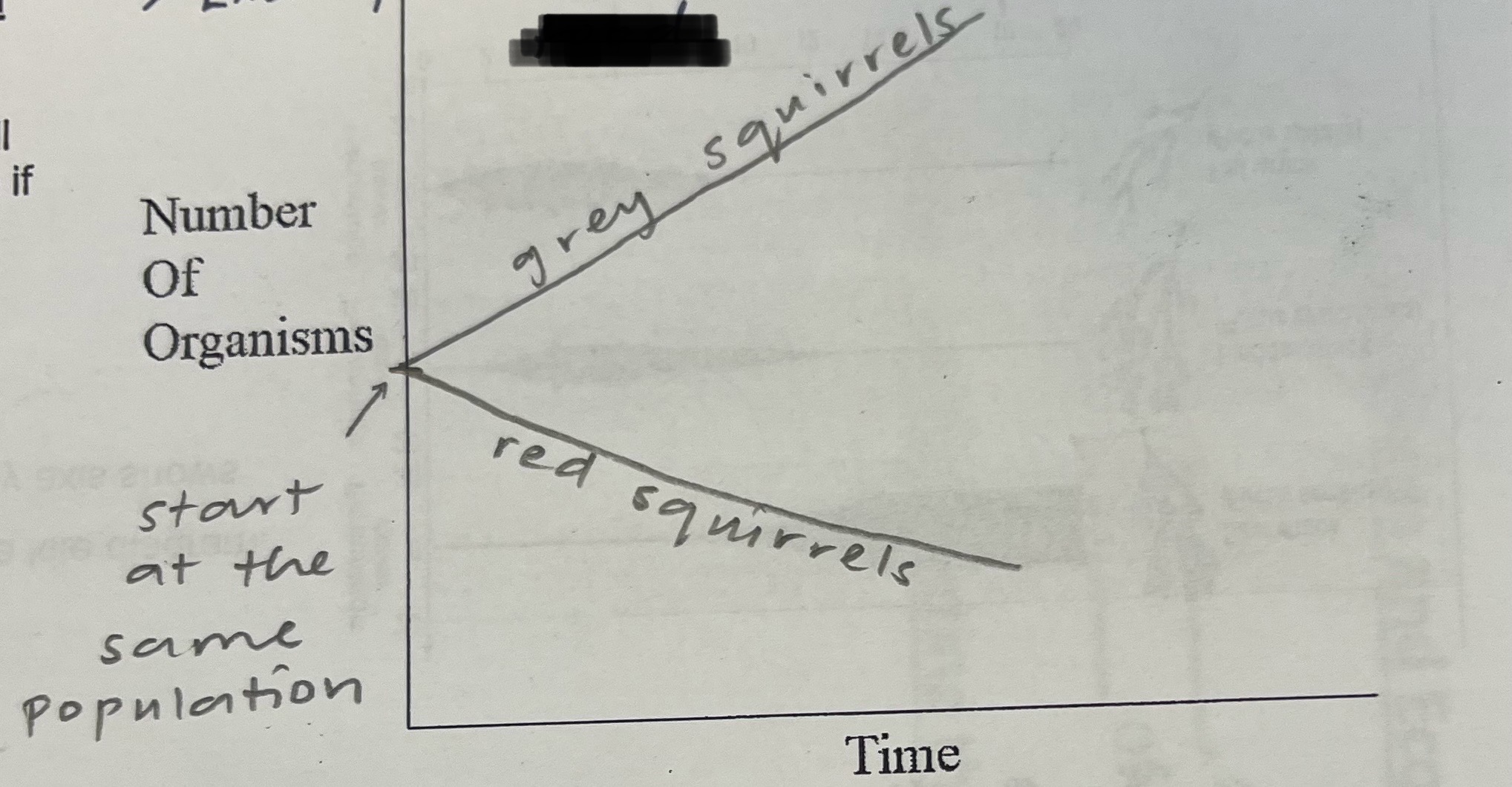
Explain how interspecific competition affects the number of organisms. Explain the graph that shows this
One species will out-compete the other one if they occupy the same niche
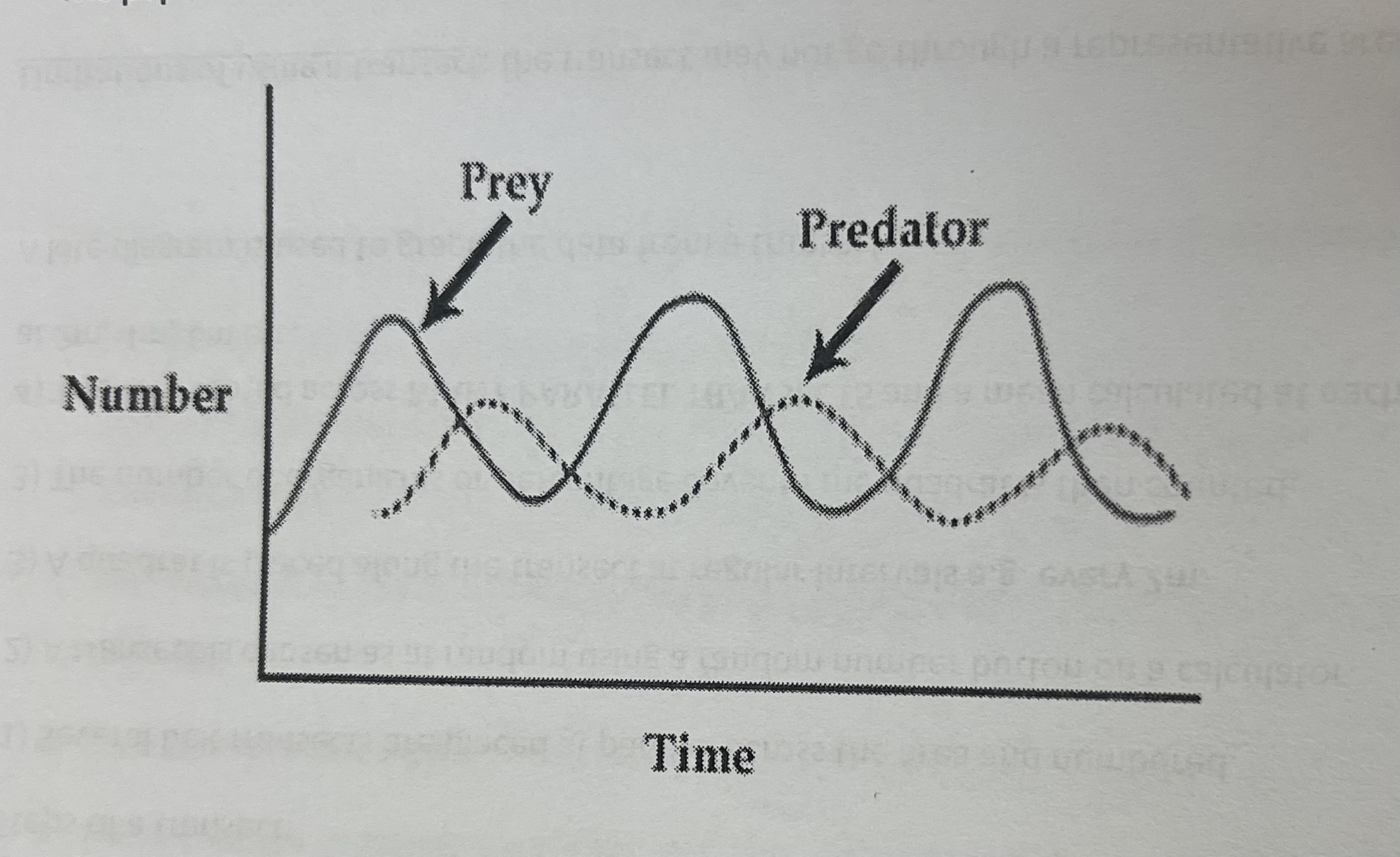
Explain how predation affects the number of organisms. Explain the graph that shows this
Prey population increases so more food for predator so predator population increases shortly after
More predators than prey so more prey get eaten so prey population decreases
Less prey to eat so predator population decreases because they die of starvation
Less prey eaten so prey population increases and the cycle starts again
Explain the advantage of two different species occupying different niches and give example
Reduces interspecific competition between species
Example: Animals may compete for food
Always include an example
Explain why sampling should be carried out at random
To prevent bias
Explain why a large sample should be used when sampling
So that the sample is more representative
To calculate a more reliable mean
To allow the use of statistical test
Describe how you would achieve representative data when sampling
By using a large sample size
What is the use of a quadrat
Quadrants are used to estimate the size of a population of a particular species in a certain area
Describe the steps of how you would estimate the numbers of daises in a woodland by random quadrant sampling
Split area into a grid and assign coordinates randomly using a random number table
Place quadrat at coordinate and count number of individuals or % cover
Repeat a large number of times and calculate a mean
Multiply this mean by the number of times the quadrat fits in the area
How can you find the correct number of quadrants to use to get representative data
Calculate a running mean until the mean remains constant/ shows little change
What is the use of a transect
Transects are used to show changes dawn a n environmental gradient
How would you make sure that you have a representative sample of data using transects
Select the position of the transect at random
Use a large number of parallel transects and calculate the mean at each distance
Describe the steps if how you would carry out a transects to measure the change in % cover of barnacles own a rocky seashore (using belt transects)
Several belt transects are placed at parallel across an area and numbered
A transect is chosen at random using a random number generator button on a calculator
A quadrat is placed along the straight line at regular intervals
The % cover or number of each species are counted in each quadrat
This is repeated across a large number of parallel transects and a mean at each interval is calculated
What method can be used to estimate the sizes off population of motel organisms (organisms that can move)
Mark, release and recapture
What is the equation for estimating the population
Number of organisms in the first sample X Number of organisms in the second sample
Number of marked organisms in the second sample
Describe the steps of how you could estimate the numbers of turtles on a coral reef (mark, release and recapture)
Capture a sample of a species and count individuals. Mark them all and release.
The mark should not affect the organism’s survival (should be non-toxic / not make the animal more vulnerable to predation)
After release, the organisms are left for long enough time to randomly and evenly distribute back into the population
A second sample is captured and number is counted, as well as how many are marked
State the formula for estimating the population size
Name the assumptions that are made when the mark, release and recapture method is used
Birth rate = Death rate
The marking does not influence the survival such as increasing the chances of predation and is non-toxic
There is no immigration or emigration
Large population
Long enough time for the marked individuals to randomly and evenly distribute into the population between release and recapture
What is succession
Succession is where communities nd abiotic factors change over time
What does succession start and end with
Succession starts with hostile conditions and develops into a climax community
What is primary succession and what does it usually start with
Occurs in an area that has not been inhabited before.
Starts with bare rock or sand.
Takes longer
What is secondary succession and what does it usually start with
Occurs in an area that has been previously inhabited but has experienced a disturbance eg. Forest fire or flooding.
Starts with soil or some vegetation
Faster than primary succession
Stages of succession (Using data)
Starts with pioneer species in hostile conditions (name the pioneer species)
Pioneer species changes the abiotic conditions (give example: for animal they provide food for others) form soil/ humus
The environment becomes less hostile and more suitable for new species to colonise (name the new species)
The new species outcompete the pioneer species, so the pioneer numbers reduce (name the species)
From stage to stage the species diversity increases (give example from the data)
Eventually a climax community is reached
Explain what the ecosystem is like in a climax community
Population is stable
Abiotic conditions remain constant
Same species present
What is conservation
The protection and management of species and habitats in a sustainable way.
It is not leaving the environment untouched but managing the existing environments
Reasons for conservation, using rainforests as an example
Conserve species
Conserve habitats
Sources of medicines / wood
Reduces climate change / takes up carbon dioxide
Reduces erosion
Tourism