Psychological approaches to anxiety disorder & OCD
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are the key diagnostic features of GAD?
Chronic, uncontrollable, excessive worry for 6+ months
Associated with 3+ symptoms: restlessness, fatigue, muscle tension, irritability, difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbance
Causes significant distress or impairment
Behavioural explanation of GAD?
Learned anxiety through classical conditioning and maintained by avoidance via negative reinforcement.
Behavioural treatments for GAD?
Relaxation training and behavioural exposure (doing the behaviour despite worry)
all about changing the behaviour not the thoughts (doesn’t address the deeper pattern thinking)
Cognitive explanation of GAD?
Overestimation of threats, intolerance of uncertainty, cognitive biases → catastrophising.
How does CBT help GAD?
Identifying anxious thoughts, challenging their realism, replacing them with balanced alternatives.
addresses the root cause of the issue
Psychodynamic cause of GAD?
Unconscious conflict (ego–id struggle), early childhood experiences.
anal retentive stage leading to perfectionism and overanxious
ego becomes overwhelmed triggering anxiety
GAD – Psychodynamic Treatment
Free association + dream analysis to uncover repressed conflict.
Social perspective on GAD?
Environmental stressors (poverty, abuse, illness). Support systems, community interventions.
What defines a panic disorder diagnosis?
Repeated, unexpected panic attacks
1+ month of persistent worry about future attacks AND/OR maladaptive behaviour change
How do expected vs unexpected panic attacks differentiate PD from phobias?
Expected attacks → Phobia
Unexpected attacks → Panic disorder
Behavioural cause of panic disorder?
Panic attack initially by stress but over time, Conditioned fear of bodily sensations → avoidance maintains panic.
Behavioural treatment of PD
Interoceptive exposure (exposure to bodily sensations to break fear association).
done in a safe environment
Cognitive cause of PD?
Catastrophic misinterpretation of bodily sensations.
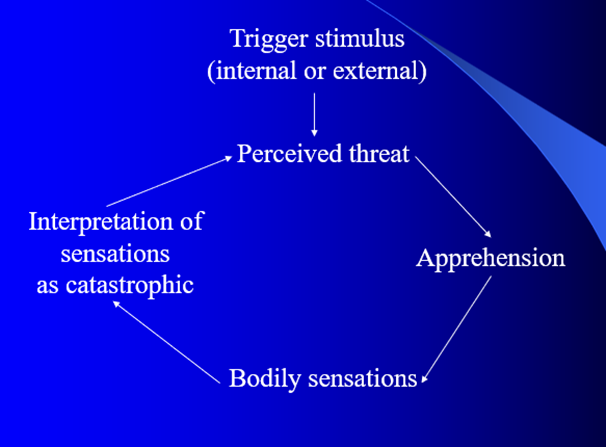
CBT for panic disorder?
Reinterpret symptoms
hyperventilation exposure
cognitive restructuring → links between behaviours and sensation
relaxation + support.
Psychodynamic cause of PD
Early oral-stage issues, inadequate caregiver support → adult panic vulnerability
lack of support as a child created a sense of panic
What is PFPP for panic disorder
Panic-Focused Psychodynamic Psychotherapy: explores repressed emotions + childhood links.
progress for this may be slower but has found to be just as effective as CBT
Social contributors & treatments to PD
Stressful environments, low support → improved using group therapy and social connection.
Diagnostic features of a specific phobia?
Fear of an object/situation for 6+ months
Out of proportion to actual threat
Consider cultural context
Causes impairment
Diagnostic features of social anxiety disorder?
Fear of social scrutiny for 6+ months
Specifier: performance only
Requirements for agoraphobia diagnosis?
Fear of public spaces for 6+ months
Fear in 2+ situations (public transport, crowds, open spaces, etc.)
Behavioural explanation of phobias?
Avoidance- conditioning formulations
Learned through classical conditioning (something scary happen and a spider was there for example)
Maintained through operant conditioning
Modelling (Bandura, 1986) -> someone else screams when they see a spider so you scream
phobias - behavioural treatment
Systematic desensitisation -> maintain relaxation while phobia is being introduced, gradual
Flooding -> instantly introduced to scary stimuli until you can maintain relaxation
Modelling -> therapist hold spider on hand -> see its not scary
Cognitive cause to phobias
Maladaptive beliefs and overestimating danger.
irrational beliefs and catastrophic thinking
Cognitive treatment to phobias
CBT with cognitive restructuring + exposure therapy combined
targets root cause of phobias = irrational thinking
Psychodynamic explanation to phobias
Displacement of unconscious conflict or avoiding anxiety
Phallic-stage conflict (Oedipus/Electra) → which is unresolved leads to displaced anxiety’s
What defines OCD?
Obsessions: intrusive thoughts/images/urges
Compulsions: behaviours to reduce anxiety (checking, counting, cleansing, avoidance)
Time‑consuming, clinically impairing
Behavioural explanation for OCD
Fear learned via classical conditioning; compulsions maintained by negative reinforcement → by performing the ritual it reduces the fear but creates a cycle
OCD – Behavioural Treatment
Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
exposing person to object of fear without allowing them to perform the ritual
OCD – Cognitive Aetiology
Misinterpretation of intrusive thoughts; catastrophic thinking; attentional bias to threat (focusing extensively on the threatening stimuli)
-use CBT and ERP to cognitive restructuring
OCD – Psychodynamic Aetiology
Anal‑stage fixation - need to be clean and intentive to keep everything in right place
defence mechanisms (reaction formation) - id‑related impulses → unconscious id wishes
Difference between fear and anxiety?
Fear = response to a specific threat or danger
Anxiety = diffuse worry without a clear stimulus