1 - KIDNEY AND LIVER FUNCTION TESTS
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Blood Urea Nitrogen
Kidney Function Tests
Non-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds (NPNs)
Major end product (45%) of protein and amino acid catabolism
1st to be elevated in kidney injury
10-20:1
Kidney Function Tests
Non-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds (NPNs)
Blood Urea Nitrogen
BUN: Creatinine ratio
Creatinine
Kidney Function Tests
Non-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds (NPNs)
End product of muscle metabolism derived from creatine
Generation remains fairly constant
Most specific marker in kidney injury
Blood Uric Acid
Kidney Function Tests
Non-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds (NPNs)
Major product of purine catabolism
Final breakdown of nucleic acid catabolism in humans
Monosodium Urate
Kidney Function Tests
Non-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds (NPNs)
Uric acid in crystals
Tophi
Kidney Function Tests
Non-Protein Nitrogenous Compounds (NPNs)
Uric acid in joints + inflammation
Diacetyl Monoxime Method
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Chemical Method (1)
Yellow
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Diacetyl Monoxime Method
Color of end product
Coupled Urease/ Glutamate Dehydrogenase Method – UV Enzymatic Method
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Enzymatic Method (1)
Urease Method
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Enzymatic Method (2)
Urease Method
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Enzymatic Method (2)
Most commonly used method
Derived from jack beans
Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Another methodology
Jaffe Method
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Creatinine
1st methodology
Yellow
Saturated picric acid
10% NaOH
Alkaline picrate solution
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Creatinine
Jaffe Method
Reagent: (color)
A:
B:
A + B:
Red orange complex/red tautomer
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Creatinine
Jaffe Method
APS + Serum =
Lloyd’s Reagent
Fuller’s Earth
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Creatinine
Modified Jaffe Method Reagents
_: Na Al Si
_: Al Mg Silicate
Creatinine Aminohydrolase – CK Method
Creatininase Hydrogen Peroxide Method
Creatininase-Creatine Aminohydrase
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Creatinine
Enzymatic Method (3)
Reduction-Oxidation React
Caraway Method
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Blood Uric Acid
Chemical Method (2)
Uricase Method
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Blood Uric Acid
Enzymatic Method (most common)
Isotope dilution mass spectrometry
Kidney Function Tests
Methodologies
Blood Uric Acid
Last method
Azotemia
Kidney Function Tests
Disease Correlation
Elevated level of nitrogenous substances like urea and creatinine in the blood
Pre-renal Azotemia
Hypoperfusion
Kidney Function Tests
Disease Correlation
Cause: _
Dehydration, shock, CHF
Increased: BUN
Normal: Creatinine
Renal Azotemia
Tissue damage
Kidney Function Tests
Disease Correlation
Cause: _
Decreased GFR
Striking BUN level but slowly rising creatinine value
>100 mg/dL
>20 mg/dL
>12 mg/dL
Kidney Function Tests
Disease Correlation
Renal Azotemia
BUN = _
Creatinine = _
Uric acid = _
Postrenal Azotemia
Obstruction
Kidney Function Tests
Disease Correlation
Cause: _
Decreased GFR
Nephrolithiasis, cancer or tumors of GUT
Creatinine = normal or slightly increased
Uremia
Kidney Function Tests
Disease Correlation
Clinical syndrome comprised of marked elevation in plasma urea and other nitrogenous waste products, accompanied by acidemia and electrolyte imbalance of renal failure
Osmolality
Kidney Function Tests
An expression of concentration in terms of the total number of solute particles per kilogram of solvent
Freezing point
Kidney Function Tests
Principle of osmolality
colligative property
Kidney Function Tests
Osmolality
Measured using the _ _ of sample
280-295
300-900
50-1200
Kidney Function Tests
Osmolality
Reference range:
Serum: _-_ mOsm/kg
24-hour urine: _-_ mOsm/kg
Random urine: _-_ mOsm/kg
Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1)
Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL)
Insulin-like GF binding protein 7 (IGFB7)
Tissue inhibitor metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2)
Kidney Function Tests
Biomarkers of Kidney Injury (4)
Synthetic function
Conjugation
Detoxification & drug metabolism
Excretory and secretory
Storage
Liver Function Tests
Liver Functions (5)
Primary Structure
Proteins
Protein Structures
Amino acid sequence
Secondary Structure
Proteins
Protein Structures
Winding of polypeptide chain
Specific 3-D conformations: alpha-helix, beta-pleated sheath, bend form
alpha-helix, beta-pleated sheath, bend form
Proteins
Protein Structures
Secondary Structure
Specific 3-D conformations: (3)
Tertiary Structure
Proteins
Protein Structures
Actual 3-D configuration
Ex: Myoglobin
Quaternary Structure
Proteins
Protein Structures
Association of 2 or more polypeptide chains = protein
Ex: Hemoglobin
Simple Proteins
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Hydrolysis will yield amino acids
Fibrous
Globular
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Types of simple proteins (2)
fibrinogen, troponin
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Simple Proteins
Examples of Fibrous
hemoglobin, plasma proteins
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Simple Proteins
Examples of Globular
Conjugated Proteins
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Protein (apoprotein) + nonprotein moiety (prosthetic group)
Metalloproteins
Lipoproteins
Glycoproteins
Mucoproteins
Nucleoproteins
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Types of conjugated proteins (5)
ferritin, ceruloplasmin
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Simple Proteins
Examples of Metalloproteins
CM, VLDL, LDL, HDL
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Simple Proteins
Examples of Lipoproteins
haptoglobin, AAT
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Simple Proteins
Examples of Glycoproteins
mucin
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Simple Proteins
Examples of Mucoproteins
chromatin
Proteins
Types of Proteins
Simple Proteins
Examples of Nucleoproteins
Kjeldahl (Digestion)
Proteins
Total Proteins
Reference method
Measurement of nitrogen content
6.54
15.1-16.8%
Proteins
Total Proteins
Kjeldahl (Digestion)
1 g N2 = _ grams of protein
_ = nitrogen content of CHON
Sulfuric acid
Proteins
Total Proteins
Kjeldahl (Digestion)
Reagent
Ammonia
Proteins
Total Proteins
Kjeldahl (Digestion)
End product
Biuret
Proteins
Total Proteins
Most widely used (IFCC)
Requires at least 2 peptide bonds
Alkaline CuSO4; Rochelle salt (NaK Tartrate); NaOH; KI
Proteins
Total Proteins
Biuret
Reagent (4)
Violet (545 nm)
Proteins
Total Proteins
Biuret
End product
Folin-Ciocalteu (Lowry)
Proteins
Total Proteins
Highest analytical sensitivity
Oxidation of phenolic compounds
Phenol; Biuret
Proteins
Total Proteins
Folin-Ciocalteu (Lowry)
Reagent (2)
Blue color
Proteins
Total Proteins
Folin-Cioicalteu
End product
280
210
tryptophan, tyrosine and phenylalanine
Proteins
Total Proteins
UV Absorption Method
Proteins absorb light at _ nm and _ nm
280 nm = (3)
Refractometry
Proteins
Total Proteins
Alternative test
Measurement of RI of solutes in serum
Turbidimetry
Proteins
Total Proteins
Formation of a uniform fine precipitate which blocks light
SSA or TCA
Proteins
Total Proteins
Turbidimetry
Reagent
Nephelometric Methods
Proteins
Total Proteins
Formation of a uniform fine precipitate which scatters light
SSA or TCA
Proteins
Total Proteins
Nephelometric Methods
Reagent
Salt fractionation
Proteins
Total Proteins
Globulins are separated from albumin by salting-out procedures using sodium salts
Sodium sulfate salt
Proteins
Total Proteins
Salt fractionation
Reagent
Prothrombin Time (Vitamin K Response Test)
Proteins
Differentiates intrahepatic from extrahepatic liver disease
II, VII, IX, X, Protein C, Protein S
Proteins
Vitamin K dependent factors
Hydroquinone
Proteins
other name for Vitamin K
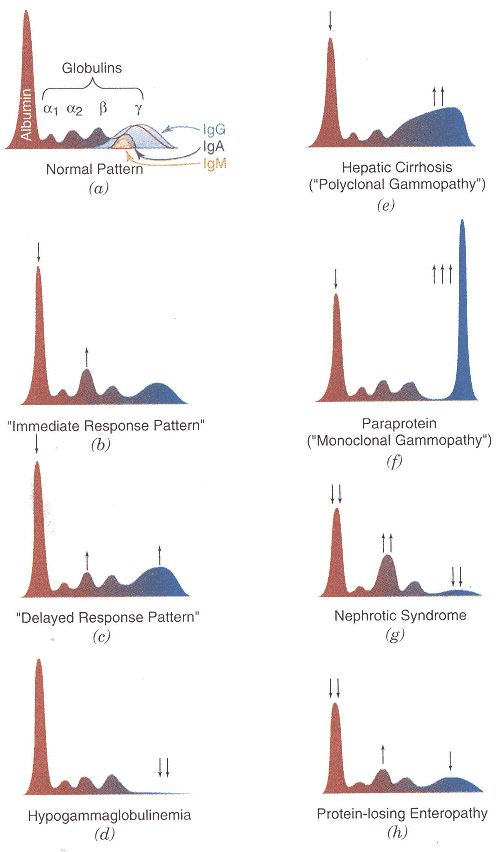
SPE
SPE
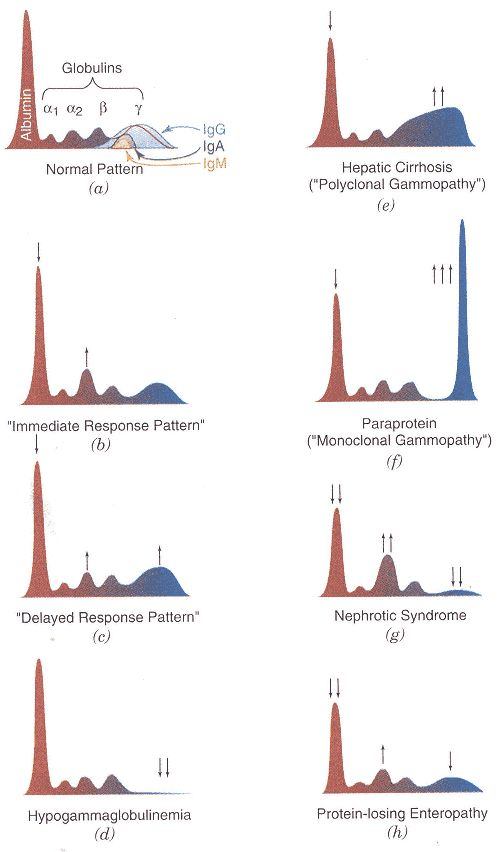
Cellulose acetate
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Medium used
Prealbumin
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Also called as transthyretin which carries thyroxine and retinol
Abundant in CSF
All have “a1” in the name
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
α1
Ceruloplasmin, haptoglobin, a2 macroglobulin
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
α2
Hemoglobin, transferrin
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
ꞵ
Immunoglobulins
IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Ɣ:
Hypoalbuminemia
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
↓ albumin
Hyperalbuminemia
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
↑ albumin
Emphysema
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
↓ α1
Nephrotic syndrome
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
↑ α2
Liver cirrhosis
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Ꞵ + Ɣ bridging
Endosmosis
Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Proteins that migrate in the same charge
Severe dehydration
Prolonged tourniquet application
Proteins
Albumin
Hyperalbuminemia (2)
Decreased synthesis
Proteins
Albumin
Hypoalbuminemia
CLD
Malabsorption syndrome
Malnutrition and muscle wasting
Increased loss
Proteins
Albumin
Hypoalbuminemia
Nephrotic syndrome
Massive burns
Protein-losing enteropathy
Orthostatic proteinuria
Increased catabolism
Proteins
Albumin
Hypoalbuminemia
Massive burns
Widespread malignancy
Thyrotoxicosis
Analbuminemia
Proteins
Albumin
Absence or inability to synthesize albumin
Bisalbuminemia
Proteins
Albumin
Presence of two albumin bands
Bromocresol Green – most common
Bromocresol Purple – most specific
Methyl Orange
HABA (2-(4'-hydroxyazobenzene)-benzoic acid)
Proteins
Albumin
Dyes used for Albumin measurement (4)
total protein
Proteins
Albumin
Albumin/Globulin Ratio
Ratio of albumin and globulin in relation to the _ _
1.3-3:1
Proteins
Albumin
Albumin/Globulin Ratio
NV
Cirrhosis, multiple myeloma, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
Proteins
Albumin
Albumin/Globulin Ratio
Inverted ratio (3)
Bilirubin
Test Measuring Conjugation and Excretion Function
End product of hemoglobin metabolism and the principal pigment in bile
myoglobin
catalase
cytochrome oxidase
Test Measuring Conjugation and Excretion Function
Bilirubin
Also formed from _, _ and _ _
Unconjugated
Water-insoluble
Non-polar
Indirect acting
Hemobilirubin
Test Measuring Conjugation and Excretion Function
Bilirubin 1 (5)
Conjugated
Water-soluble
Polar
Direct acting
Cholebilirubin
Test Measuring Conjugation and Excretion Function
Bilirubin 2 (5)
B1
B1 + B2
B2
Types of Jaundice | Pre-hepatic | Hepatic | Post Hepatic |
Bilirubin increased | _ | _ | _ |
Increased
±
Absent
Types of Jaundice | Pre-hepatic | Hepatic | Post Hepatic |
Urine urobilinogen | _ | _ | _ |
Normal
Dark Yellow
Dark Yellow
Types of Jaundice | Pre-hepatic | Hepatic | Post Hepatic |
Urine color | _ | _ | _ |
Dark brown
Normal
Clay colored
Types of Jaundice | Pre-hepatic | Hepatic | Post Hepatic |
Stool color | _ | _ | _ |