Enzyme Kinetics
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
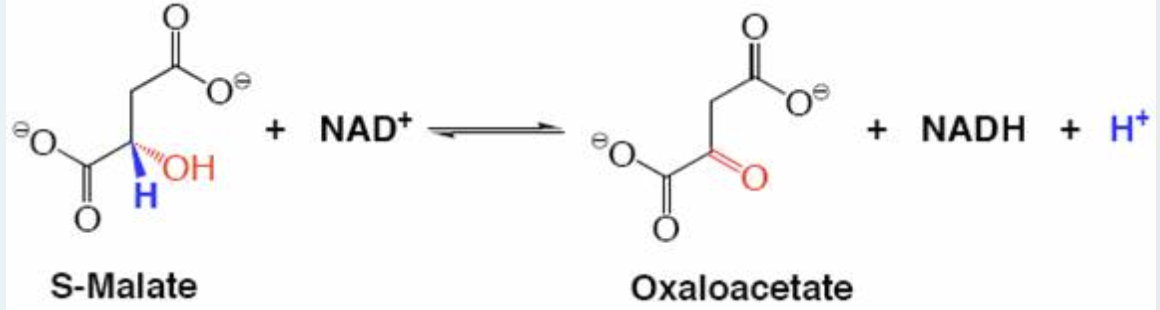
Chemical reaction calalysed by malate dehydrogenase
NAD+/NADH
cofactor
helps enzyme enlarge thier fucntionality beyond that of the natural amino acid side chain residues
It is the redoc currecny
In which biological molecules do you find phosphate groups?
DNA
RNA
Where is Micotinamide found
functional group of NAD+
Role of NAD+/NADH
NAD+ is used for the oxidation of a substrate.
NADH is used for the reduction of a substrate.
What wavelgnth is used for NADH
One that is the greatest difference to NAD+
so that we can distinguish the change
Continuous assay
assay gives an uninterupted reading of substrate or procuct
Discontinuous assay
samples are taken, the reaction stoppped and then the concentration of substrates/products determined
What could be the potential reasons why the absorbance increase over time is not entirely linear?
The reaction product produced in the reaction is structurally similar to the starting material and thus a fraction of the product does not leave the active sites. The product residing in the active site then blocks the entry of a new substrate molecule.
Product inhibition→ systematic deviation
The enzyme activity decreases after a number of turnovers because the enzyme gets less active.
Denaturation, partial unfolding
HOw make a michalis menem plot
V0 against suubstrate concentration
The Km is the substrate concentration when vmax/2
Other way→ Lineweaver burk plot
LInerlised form
1/v0 against 1/substrate concentration
Where is the Km read?
-1/Km is the x intercept
What is Kcat
Vamx/[E]
Which enzyme (MDH1 or MDH2) shifts the equilibrium constant, Keq, more in the direction of product?
The correct answer is: The equilibrium constant is the same for both enzymes
The equilibrium constant is dependent on the thermodynamics of the reaction; enzymes change the kinetics by lowering the transition state energy, but cannot change the equilibrium thermodynamics.
MDH is an important enzyme, with several roles in metabolism - it is found in a number of different locations (in chloroplasts and in mitochondria as well as in the cytoplasm). Using the following data, calculate the number of molecules of malate and of malate dehydrogenase in the cytoplasm plus organelles of a single leaf cell.
1g leaf tissue has 2 x 106 cells and 2 mg protein
1 leaf cell has a volume of 6 x 10-5 μl of which 10% is cytoplasm plus organelles
The concentration of malate in the cytoplasm plus organelles is 1mM
Malate dehydrogenase has a Mr of 70,000 and is 0.1% of the total protein in the cell.
Avogadros number is 6 x 1023.
I can do this woo