General Classes of Organic Compounds - Q2
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes are what class of organic compounds?
Hydrocarbons.
These are composed solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms and are classified based on the type of bonds between carbon atoms.
Hydrocarbons.
This type of hydrocarbon is the simplest and only contains a single carbon-carbon bonds.
Alkanes
They are saturated (no double bonds), generally carbon-carbon bonds (C-C), non-polar (neutral charge distribution), and excellent energy stores (e.g., methane in natural gas, octane in gasoline.).
Alkanes
Octane in gasoline and methane in natural gas are examples of what type of hydrocarbons?
Alkanes
This type of hydrocarbon contains at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C).
Alkenes
These type of hydrocarbons are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of the double bond (C=C), which can be broken and reformed in reactions.
Alkenes
Why are Alkenes more reactive than Alkanes?
It is due to the presence of the double bond (C=C), which can be broken and reformed in reactions.
These type of hydrocarbons play a role in ripening fruits (ethene gas) and are starting materials for some polymers (e.g., polyethylene)
Alkenes
Ethene gas is what example of hydrocarbons?
Alkenes
This type of hydrocarbon contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond (C=C).
Alkynes
These hydrocarbons are even more reactive than Alkenes due to the presence of the triple bond.
Alkynes
Why are alkynes more reactive than Alkenes and alkanes.
It is due to the presence of the triple bond.
This type of hydrocarbons are used as fuel for welding torches (ethyne and as starting materials for various chemicals.
What type of hydrocarbons is ethyne?
Alkynes
Which hydrocarbon ripens fruits
Ethene gas
Which hydrocarbon is used as fuels for welding torches.
Ethyne gas
Which class of organic compounds contain R-OH?
Alcohols
These type of organic compounds contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to a carbon atom.
Alcohols
What does the ‘‘R’’ represent in (R-OH) which can be simple and complex in the context of alcohols?
Hydrocarbon chain.
This type/class of organic compound depends on the number of carbon atoms bonded to the carbon holding the -OH group, they are classified as primary (1o -OH), secondary (2o -OH), or tertiary (3o -OH).
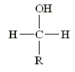
What type of alcohol is this?
Primary (1o -OH)
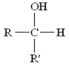
What type of alcohol is this?
Secondary (2o -OH)
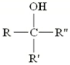
What type of alcohol is this?
Sertiary (3o -OH)
These type/class of organic compounds can form hydrogen bonds with each other and water, making them soluble in water.
Alcohols.
State why alcohols are soluble in water?
Because they form hydrogen bonds with each other.
Ethanol, methanol, and isopropanol are all examples of what class/type of organic compounds?
Alcohols
This type of alcohol is known as beverage alcohol.
Ethanol
This type of alcohol can be used as fuel.
Methanol
This type of alcohol is known as rubbing alcohol.
Isopropanol
The properties of this type/class of organic compounds is that it can act as solvents, disinfectants, antifreeze (due to its low freezing point)
Alcohols
Why can alcohols act as an antifreeze?
It is due to its low freezing points.
Which type/class of organic compounds contain (R-O-R’).
Ethers
These type/class of organic compounds contain an oxygen atom (O) bonded to two carbon atoms (R and R’).
Ethers
In this type/class of organic compounds, the two carbon groups can be the same or different.
Ethers
These type/class of organic compounds are generally less reactive than alcohols. r-o-r
Ethers
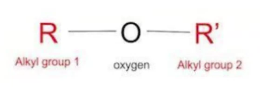
What type/class of organic compound is this?
Ethers
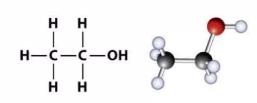
What type/class of organic compounds is this?
Alcohols
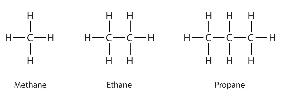
Identify which type of hydrocarbons is shown in this image.
Alkanes
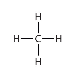
What alkane is this?
Methane
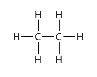
What type of alkane has this structure.
Ethane
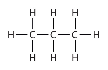
What type of alkane that has the structure as shown in the image?
Propane
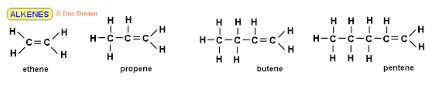
What type of hydrocarbons is this shown in the image?
Alkenes
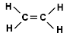
What type of alkene has this molecular structure?
Ethene
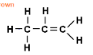
What type of alkene has this molecular structure?
Propene
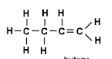
What type of alkene has this molecular structure?
Butene
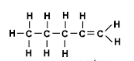
What type of alkene has this molecular structure?
Pentene
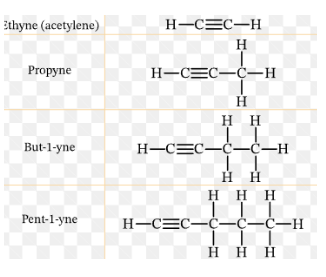
What type of hydrocarbons is shown in this picture?
Alkynes
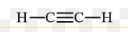
What type of alkyne has this structure as shown in this image?
Ethyne (acetylene)
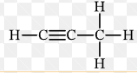
What type of alkyne has this structure as shown in this image?
Propyne
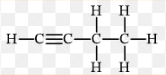
What type of alkyne has this structure as shown in this image?
But-1-yne
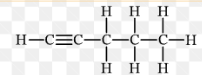
What type of alkyne has this structure as shown in this image?
Pent-1-yne
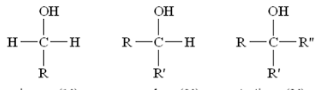
These are all examples of what type/class of organic compound?
Alcohols
Which type/class of organic compounds have a (R-COOH) structure?
Carboxylic Acids
These type/class of organic compounds feature a carboxyl group (-COOH) containing a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH).
Carboxylic Acids
What does the ‘‘R’’ represent in the (R-COOH) of Carboxylic Acids?
A hydrocarbon chain.
This type/class of organic compounds can donate a proton (H+) in solution, making them weak acids.
Carboxylic Acids
Why are Carboxylic Acids weak acids?
Because they can donate a proton (H+) in
solutions.
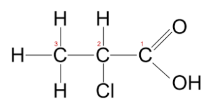
What type/class of organic compounds has this structure as shown in this image?
Carboxylic Acids
Examples of this type/class of organic compounds are; Acetic acid (vinegar), citric acid (food additive), lactic acid (muscle fatigue).
Carboxylic Acids
Which type of Carboxylic acid is found within vinegar?
Acetic acid
Which type of Carboxylic acid is known as a food additive?
Citric Acid
Which type of Carboxylic acid is the cause of muscle fatigue?
Lactic Acid
Properties of this type/class of organic compounds is that is has a sour taste, can react with bases (salts), can form hydrogen bonds.
Carboxylic Acids
This type/class of organic compounds contains the (R-CHO and
R-CO-R') structure?
Aldehydes and Ketones
Both of this type/class of organic compound contain a carbonyl group (C=O).
Aldehydes and Ketones
This type/class of organic compound have a carbonyl group bonded to a hydrogen atom (H) and another carbon atom (R).
Aldehydes
Examples of this type/class of organic compound are; Formaldehyde (used in some
building materials), and acetone
(used as a solvent).
Aldehydes and Ketones
Which of the following is an aldehyde used in some building materials?
Formaldehyde
Which of the following is a ketone used as a solvent?
acetone
Properties of this type/class of organic compound is that it can be reducing agents (donate electrons), can react with alcohols to form hemiacetals or acetals.
Aldehydes and Ketones
What type/class of organic compound has these structures (R-NH2, R2NH, R3N)?
Amines
This type/class of organic compound contain a nitrogen atom (N) bonded to one or more hydrogen atoms (H) and/or carbon atoms (R).
Amines
Depending on the number of hydrogen atoms bonded to the
nitrogen, this type/class of organic compound are classified as primary (R-NH2), secondary (R2NH), or tertiary (R3N).
Amines
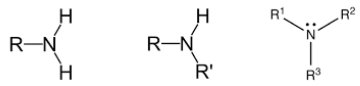
What type/class of organic compound has this structure?
Amines
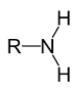
What type of amine has this structure?
Primary (R-NH2)
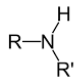
What type of amine has this structure?
Secondary (R2NH)
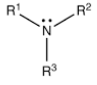
What type of amine has this structure?
Tertiary (R3N)
This type/class of organic compound can act as bases by accepting a proton (H+).
Amines
Examples of this type/class of organic compound are ammonia (NH3, a basic gas), and methylamine (used in some pharmaceuticals).
Amines
This type of amine is used in some pharmaceuticals.
Methylamine
This type of amine is a basic gas known as NH3 and its smelly.
Ammonia
Properties of this type/class of organic compound is that it can be smelly (e.g., ammonia), and can form salts with acids.
Amines