medsurge ECG
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
what does the P wave on an ECG represent?
upper heart, atria, beating
what does the qrs complex on an ECG represent? whats a normal duration?
lower heart, ventricles, beating - 0.06-0.12 (1.5-3 squares)
what is the PR interval and what’s normal?
start of P to start of QRS / how long it takes electrical signals to get from atria to ventricles - 0.12-0.20 seconds (3-5 squares)
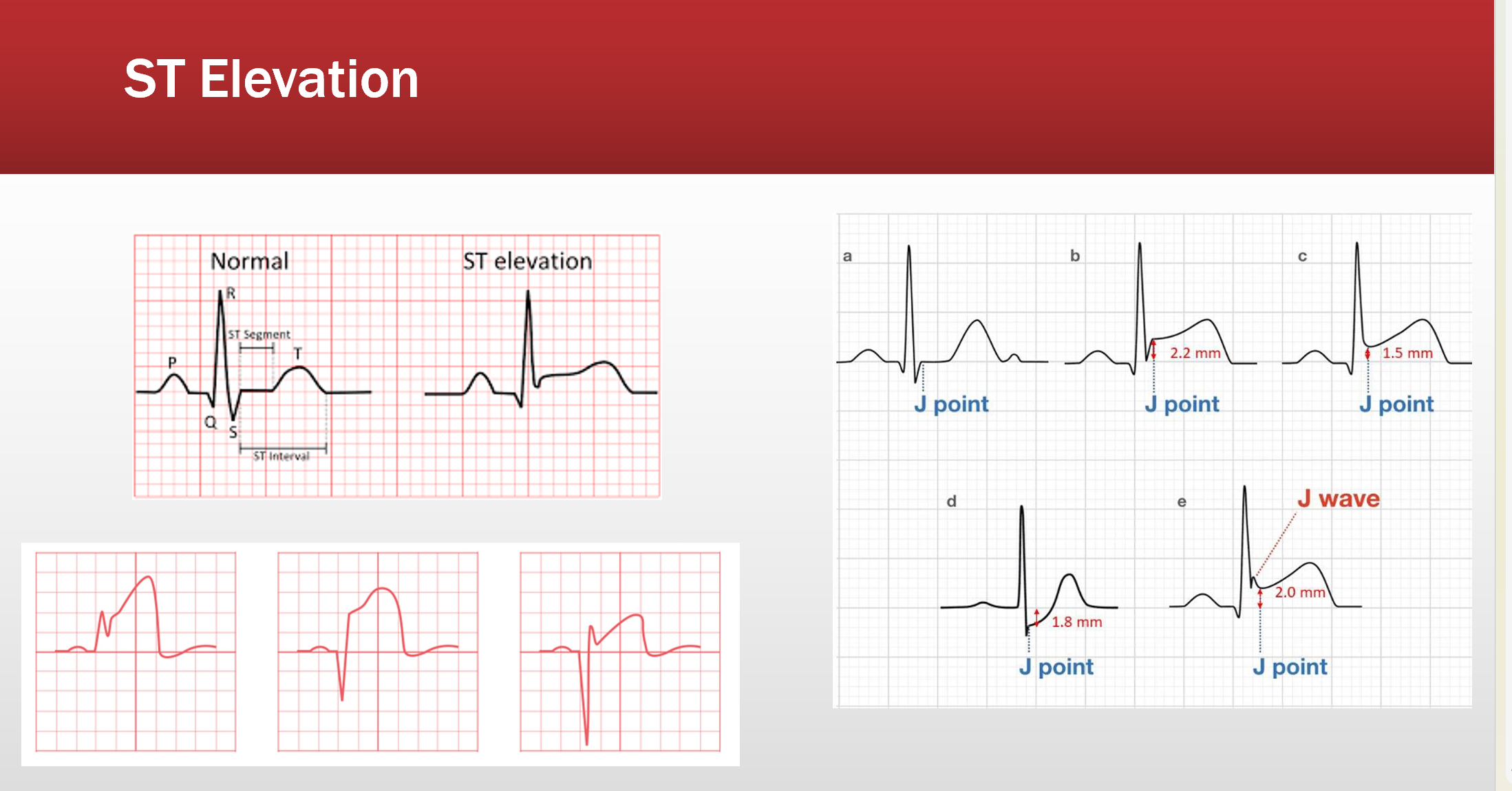
What is an st elevation/depression?
S is higher or lower than Q w/ a J point above or below it’s normal midline
What are the five steps to ECG analysis?
Rate: fast, normal, slow
Rhythm: regular or irregular
P wave for each QRS?
PR and QRS duration
Ectopy? (characteristics - PVCs, PACs, 1 degree AV block, etc)
insert image
sinus bradycardia
What are causes of bradycardia?
lower metabolic needs, vagal stimulation, meds (b-blockers, digoxin, CCBs, amio, lithium), increased intracranial pressure, CAD
What are symptoms of bradycardia?
decreased cardiac output, syncope, fatigue, lightheadedness
What are treatments for bradycardia?
treat cause if possible, medications: atropine, dopamine, epinephrine
insert image
sinus tachycardia
what are causes of sinus tachycardia?
exercise, stress, fever, sepsis, hypovolemia, low BP, PE (pulmonary embolism), MI, COPD, hypoxia, illicit drugs, etc.
what are complications of sinus tachycardia?
decreased cardiac output, coronary blood flow, and McO2 (myocardia 02 consumption)
What are treatments for sinus tachycardia?
treat the cause if possible, vagal maneuvers
Meds: B-blockers, calcium channel blockers
Electrical: syncronized cardioversion if 150+ and unstable
insert image
premature atrial complex (PAC)
What are causes of PAC’s?
caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, hypervolemia, anxiety, hypokalemia, pregnancy, atrial ischemia, MI
What are symtoms of PACs
common, Palpitations (feeling like the heart is racing, pounding, or skipping a beat) Chest tightness or discomfort Shortness of breath Dizziness or lightheadedness Fatigue AnxietyW
What are treatments of PACs?
none unless frequent which may lead to AFIB, treat underlying cause
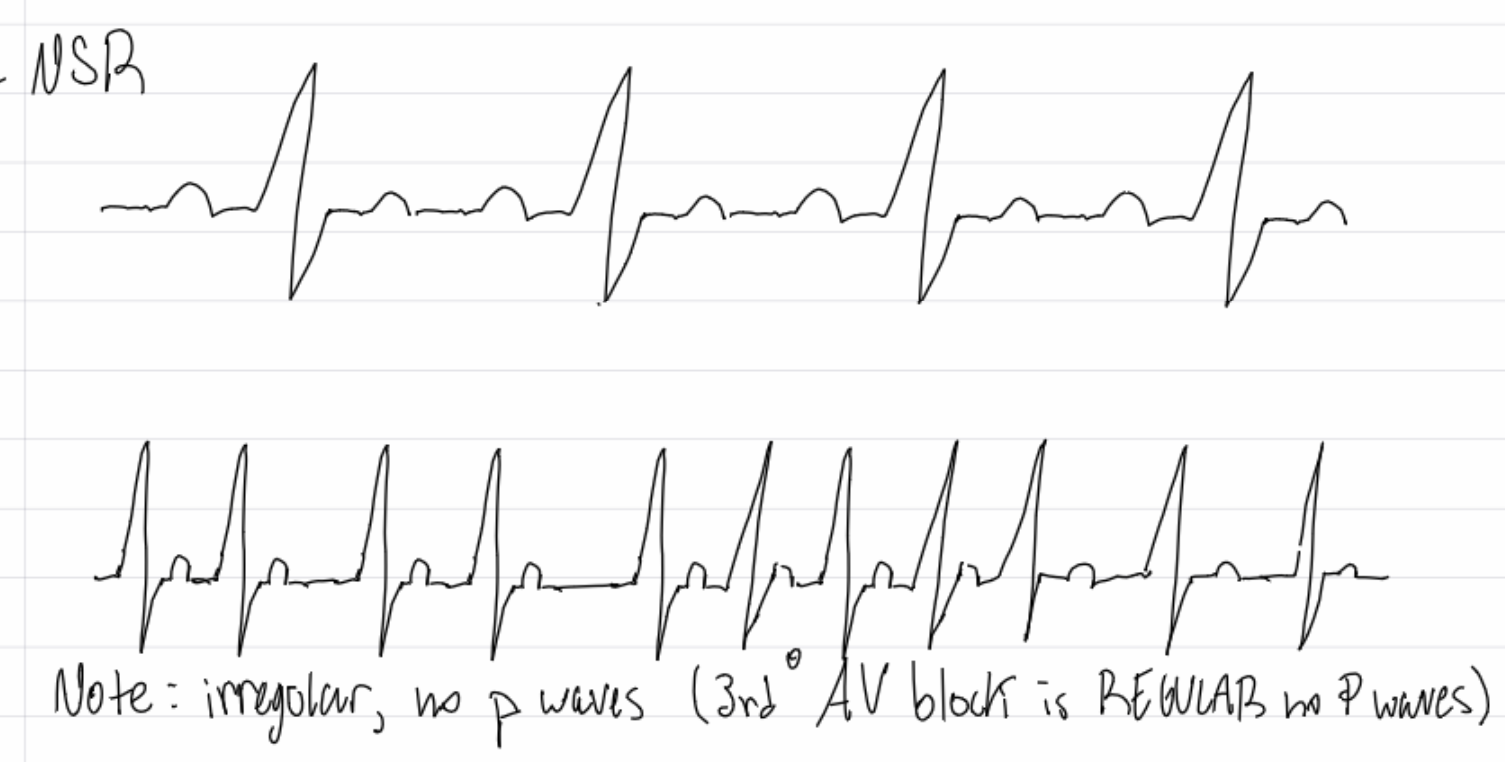
insert image
atrial fibrilation
What are causes of Afib?
CAD, MI, CABG, HF, valve disease, pericarditis, substance abuse
What are symptoms of Afib
strokes, SOB, low bp, chest pain
What are treatments for Afib?
rate/rythm control: ablation, MAZE
Meds: amiodarone, adenosine, verapamil, B-blockers, CC-blockers, digoxin
Electrical: synchronized cardioversion if rate 150+ and unstable
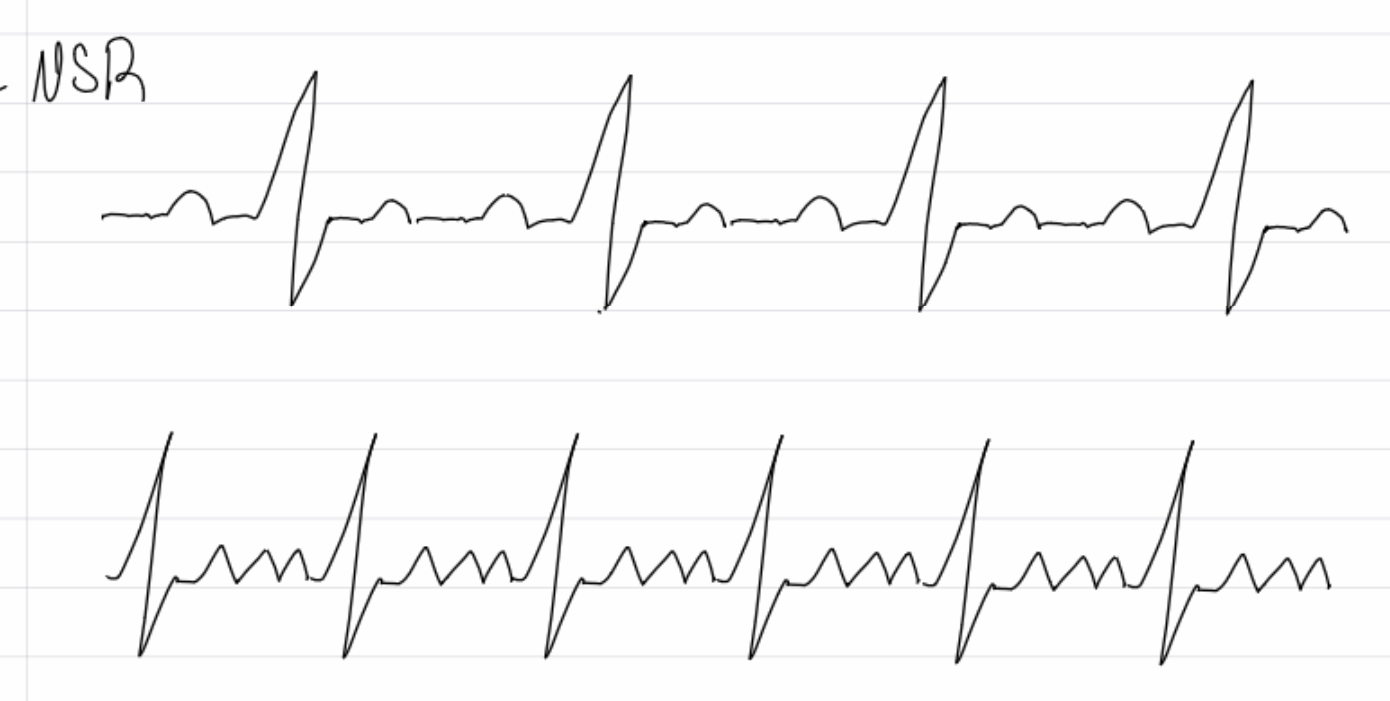
insert image
A flutter
What causes aflutter
CHF, CAD, HTN, MI, cardiomyopathy, substance abuse etc.
What are symptoms of aflutter?
low cardiac output, stroke, SOB, low bp, chest pain
What are treatments for aflutter?
vagal maneuvers
Meds: anticoagulants, CC-blockers, B-blockers, adenosine
Electrical: syncronized cardioversion, ablation
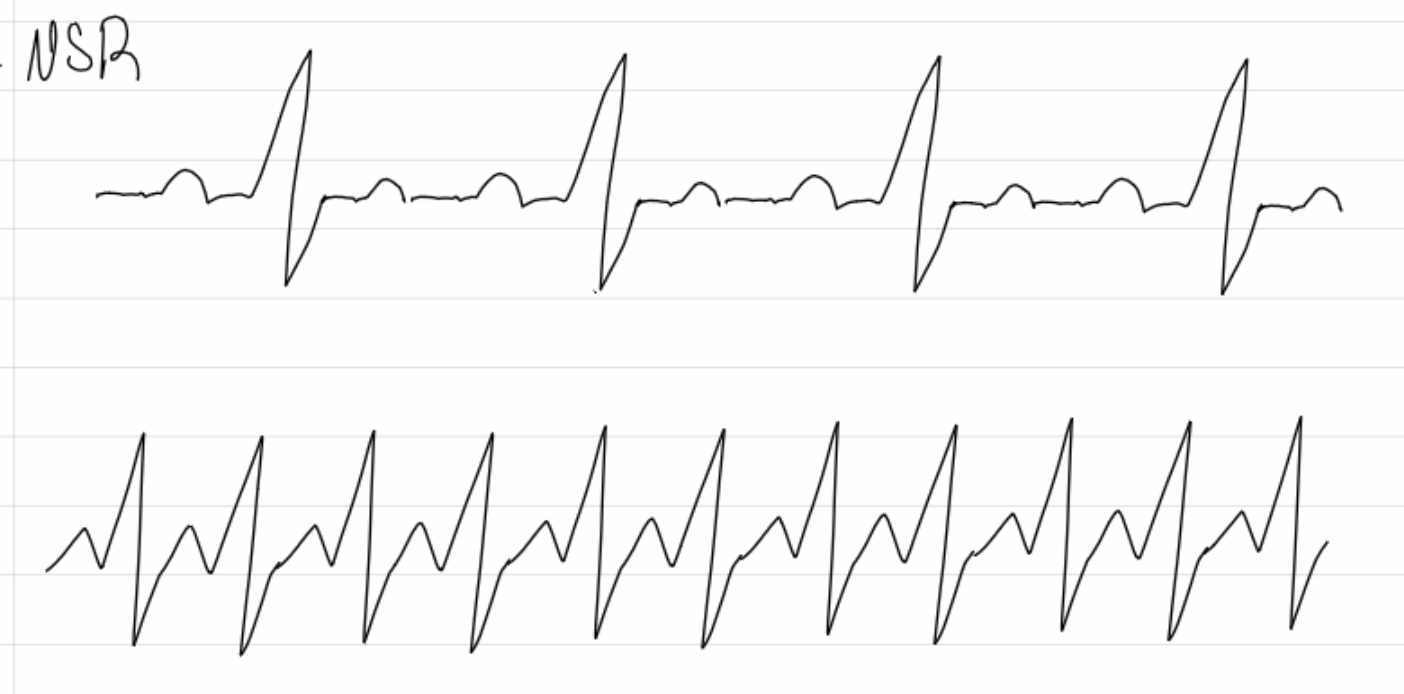
insert image
supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
what are causes of SVT
CAD, cardiomyopathy, caffeine, nicotine, hypoxemia, stress
What are symptoms of SVT’s
SOB, low cardiac output, palpitations, syncope
What are treatments for SVTs?
Stable: vagal maneuvers, adenosine
Unstable: synchronized cardioversion
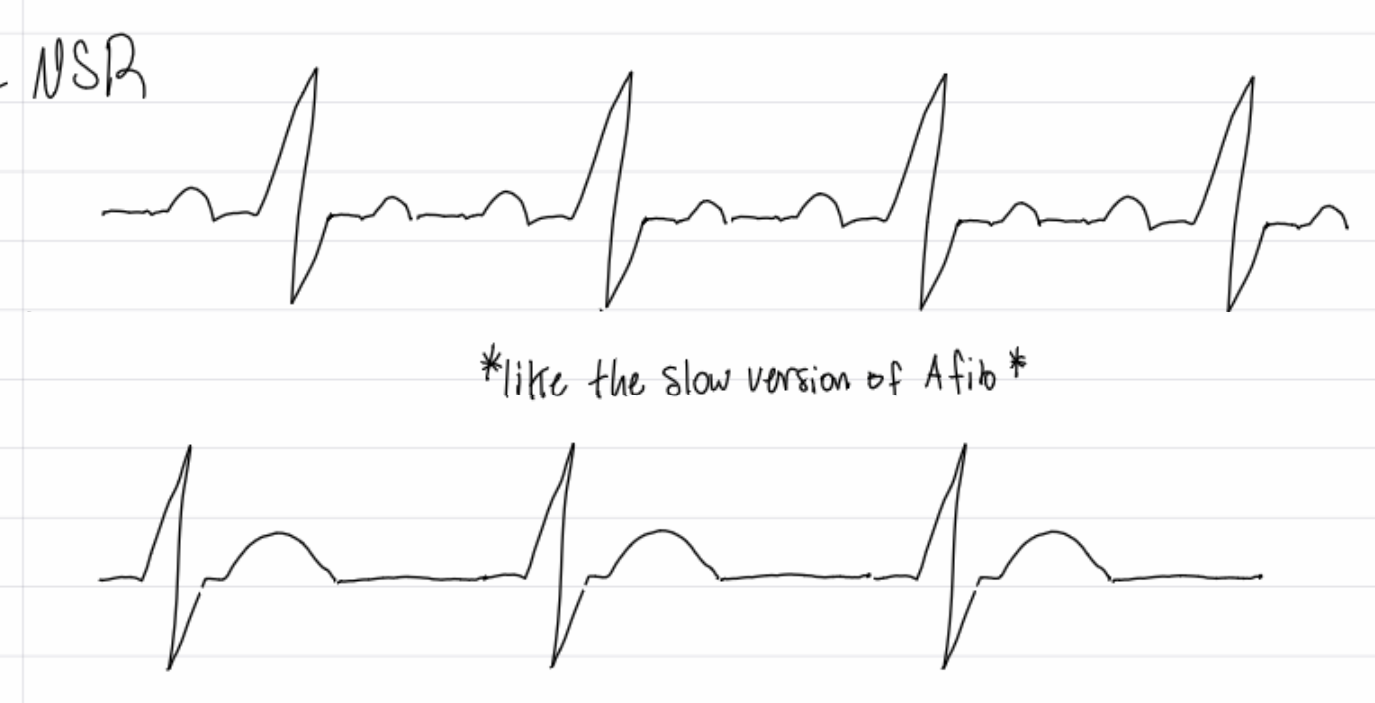
insert image
junctional rhythm
what are treatment notes for Junctional rhythms?
treat similar to sinus bradycardia, if signs of low cardiac output
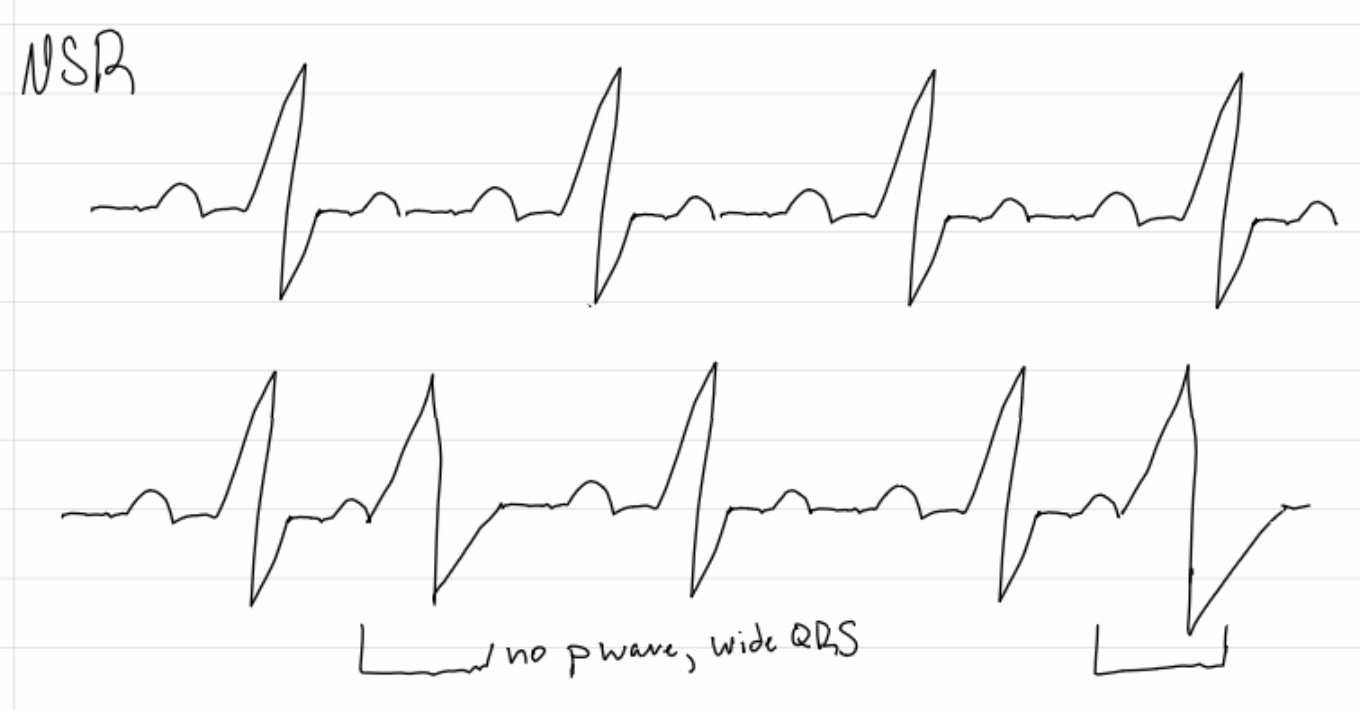
insert image
premature ventricular complex (PVCs)
What are causes and symptoms of PVCs?
common, age caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, LV hypertrophy - feels like a skipped beat, palpitations, LV dysfunction
What are treatments for PVCs
unually none, treat underlying cause
Meds: b-blockers, amiodarone
insert image
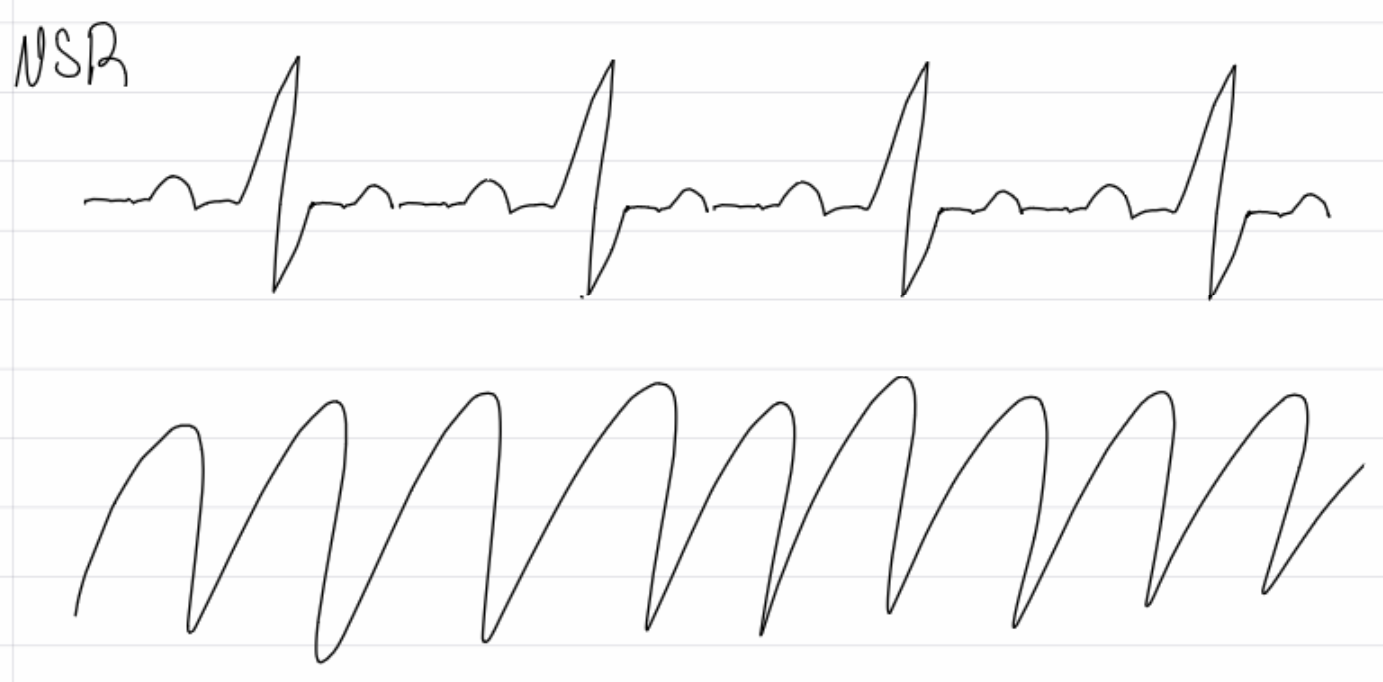
ventricular tachycardia
What are cause of v tach?
CAD, cardiomyopathy, mitral valve disease, aortic stenosis, myocarditis, MI
What are complications and treatments for v tach (3 categories)?
Sudden cardiac death
No pulse: CPR, defibrilate, Epi, Amiodarone or Lidocaine
Unstable with pulse: cardioversion
Stable with pulse: valgal maneuvers, adenosine, antiarrhythmic infusion, B-blockers, eletrolyte correction, etc. - Treat cause
insert image
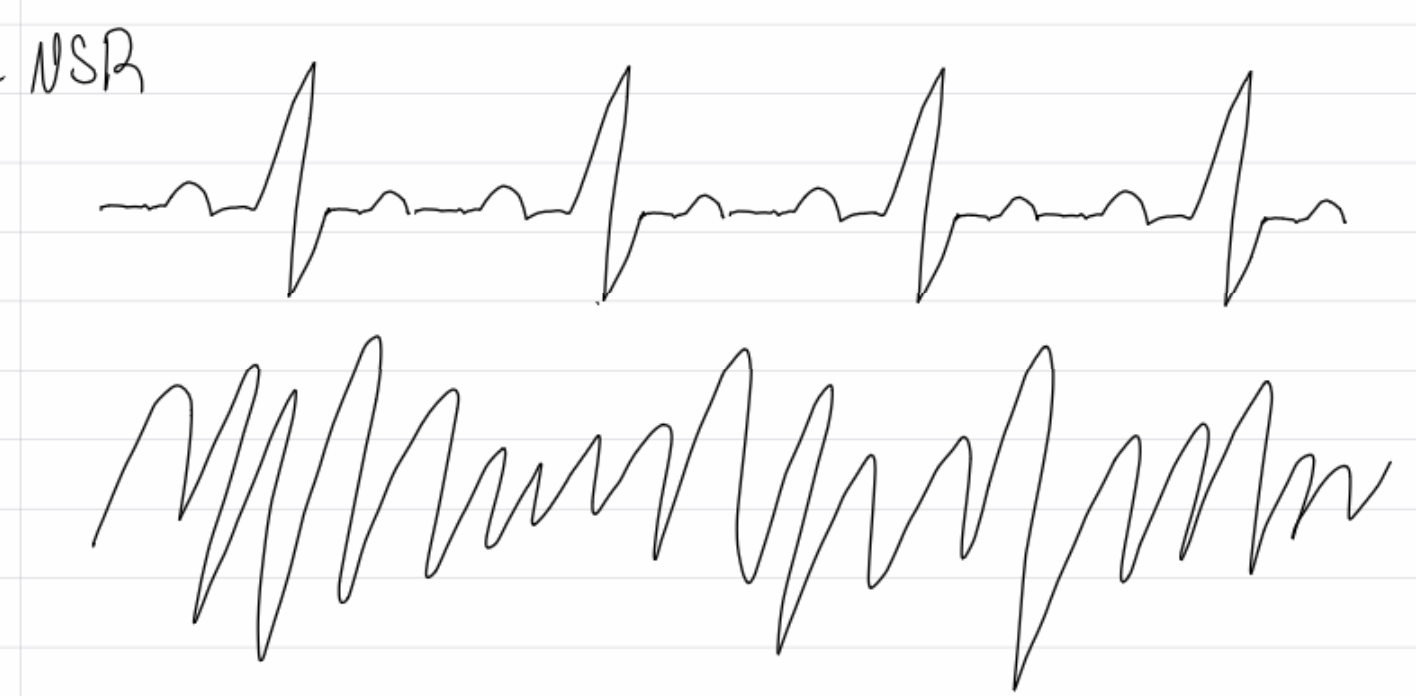
Ventricular fibrillation
What are causes and complications of v fib?
CAD and MI (most common), trauma, cardiomyopathy, congenital heart disease, drugs: cocaine/meth - sudden cardiac death
What are treatments for v fib
defibrilation, acls’s (advanced cardiac life support) - CPR, epi, amiodarone/lidocaine
ICD’s (implantable cardio device), PCI with stents, CABG
What are causes of asystole?
lack of electrical impulse, hypoxia, hypovolemia, hydrogen ion (acid base imbalance) hypo/hyperglycemia, hypo/hyperkalemia, trauma, toxins, tamponade, tension pneumothorax, thrombus
What are complications and treatments of asystole?
sudden cardiac death
CPR, EPI, fix reversible causes
What is PEA?
pulseless electrical activity - treatments and causes same as aystole
What is cardioversion?
a synchronized shock to the QRS complex that resets electrical conduction of the heart
What are indications for cardioversion?
unstable tachycardia, >150 (emergent), stable irregular fast heart rate that is not responding to medications (planned - 3 week anticoagulation for clients with afib or unknown duration)
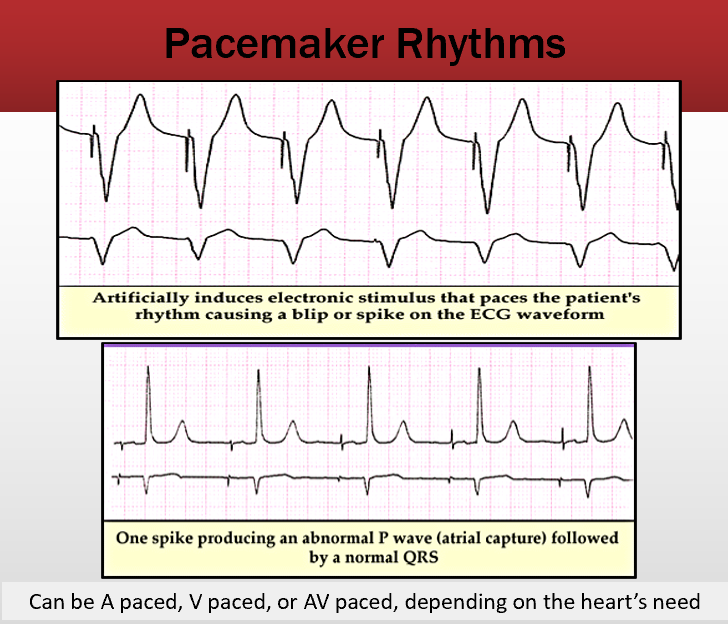
What are the three types of pace makers?
Pads, epicardial (external with direct heart attacement), and endocardial (transvenous, patient can’t shower)D
describe pacemaker modes and the related letter system w/ example
fixed, demand, tachydysrhythmia (shocks arrhythmia)
First letter - chamber paced: A, V, D (atrial, ventricular or dual)
Second letter - chamber sensed: AVorD
Third letter - pacemaker response plan: T, I, D, 0 (triggered, inhibited, dual, no sensing)
Example: DDD - atria and ventricles are paced and sensed and will inhibit or trigger pacing as needed
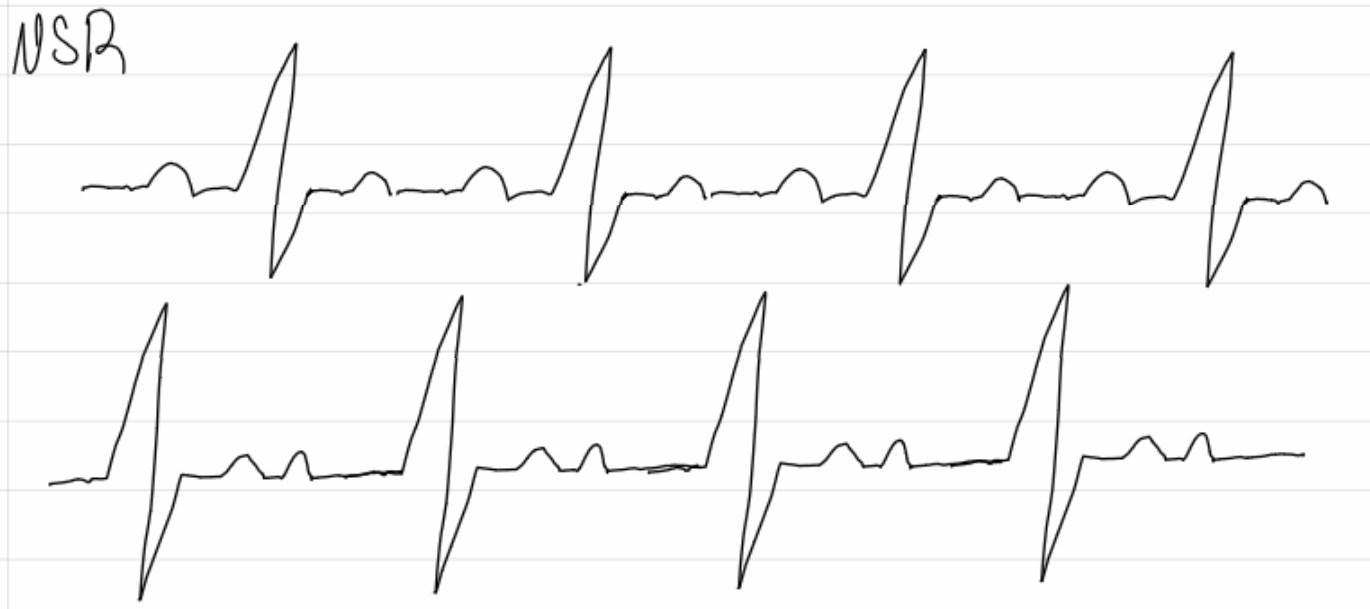
insert image
1st degree av block (long PR interval) - an ectopy: must have a rhythm associated with it
What are causes of 1st degree AV blocks?
increased vagal tone (vagus nerve activity), CCBs (calcium channel blockers), B-blockers, digoxin, hyperkalemia
What are complications of 1st degree av blocks?
rarely causes complications, decreased cardiac output
What are treatments for 1st degree AV blocks?
treat reversible causes, discontinue rate lowering meds
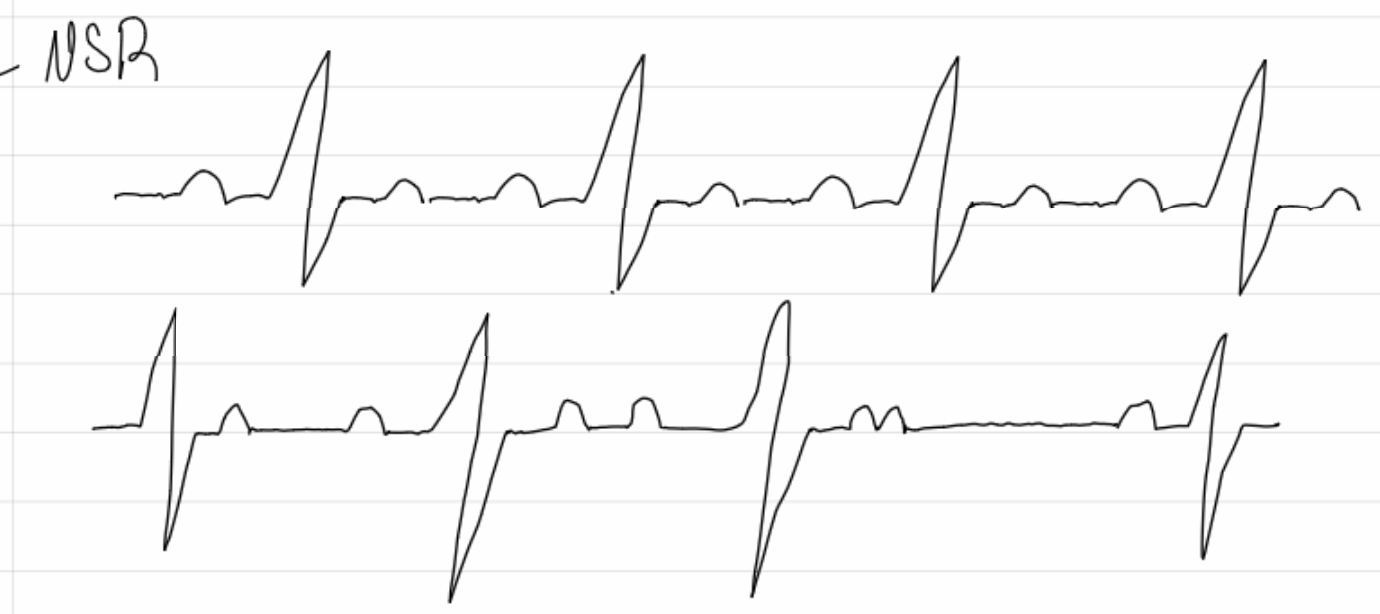
insert image
2nd degree AV block type 1 - irregular PR interval w/ dropped QRS
What are causes for 2nd degree av block type 1
high vagal tone (athletes), acute MI, AV nodal disease, myocarditis
What are complications and treatments for 2nd degree av block type 1
heart failure, decreased cardiac output
atropine, pace, reverse cause (MI, meds)
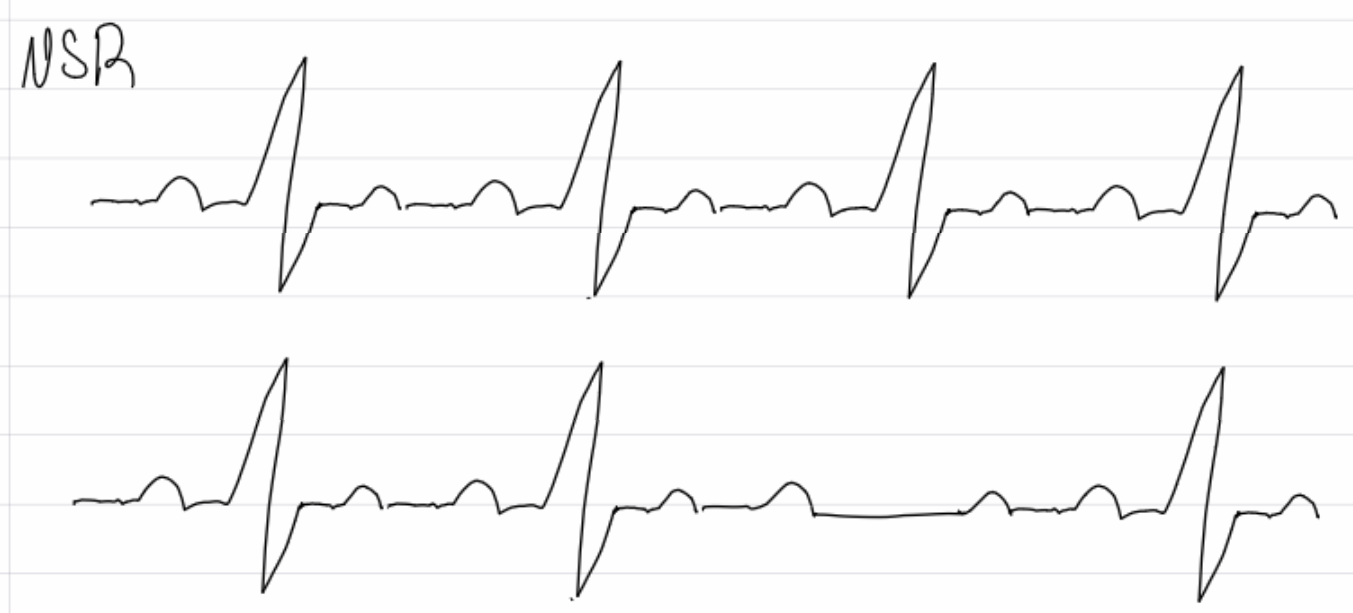
insert image
2nd degree av block type 2 - regular PR interval w/ dropped QRS
What are causes and complications of 2nd degree av block type 2?
MI, AV node blocking meds (digoxin, CCBs, BBs)
Progression to heart block, decreased cardiac output
What are treatments for 2nd degree AV block type 2?
correct reversible causes, (MI, increased vagal tone, meds), avoid meds that impair AV node conduction, pacemaker
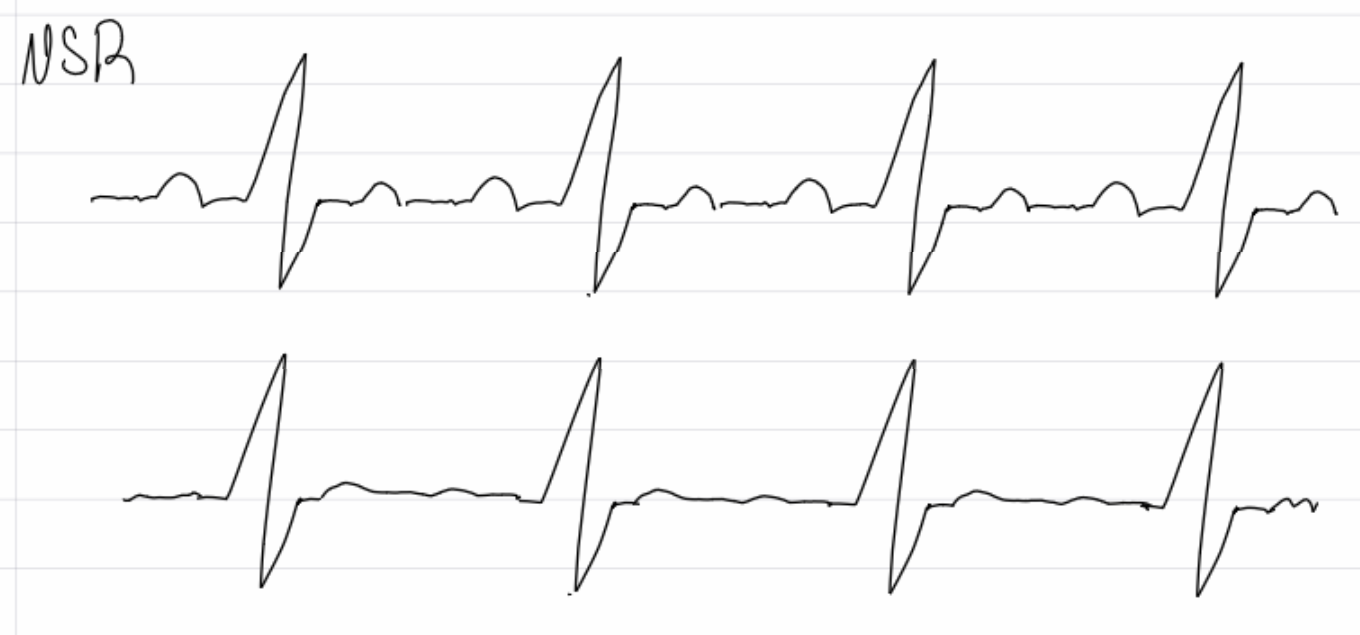
insert image
3rd degree AV block (complete heart block, no p waves)
What are causes and complications of 3rd degree AV blocks?
acute MI
VT, VF, worsening symptoms of HF
What are treatments of 3rd degree av block
pacing, correct reversible causes (MI, increased vagal tone, meds that depress conduction), avoid meds that impair AV conduction
bundle branches
qrs is longer than .12
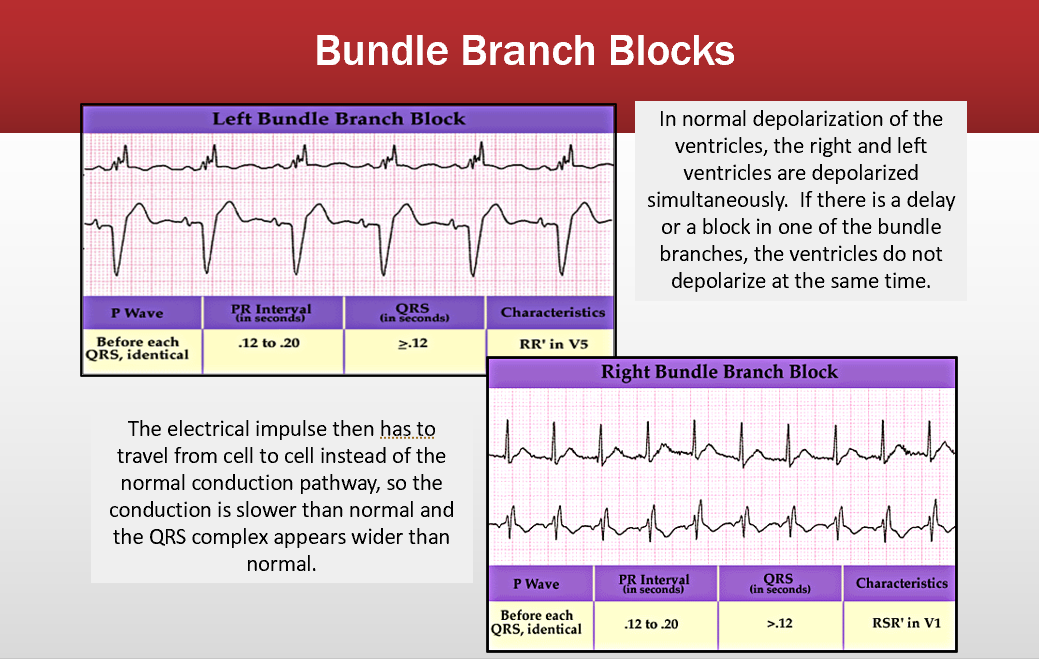
pace makers
, A is before the p wave V paced is after P wave

what is this rythm and what med will you give during the code?
torades - a type of v tach: give magnesium