L10 Corneal Ectasia
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
common hallmark of corneal ectasias is that the cornea is ______
thinning
with corneal ectasias, is the condition bilateral or unilateral
bilateral
with corneal ectasias, is the condition symmetrical or asymmetrical
asymmetrical
in corneal ectasias, is there normally inflammation? yes or no
no, its non inflammatory
what is associated with corneal ectasias normally? (4)
obesity, sleep apnea, down syndrome, atopic disease
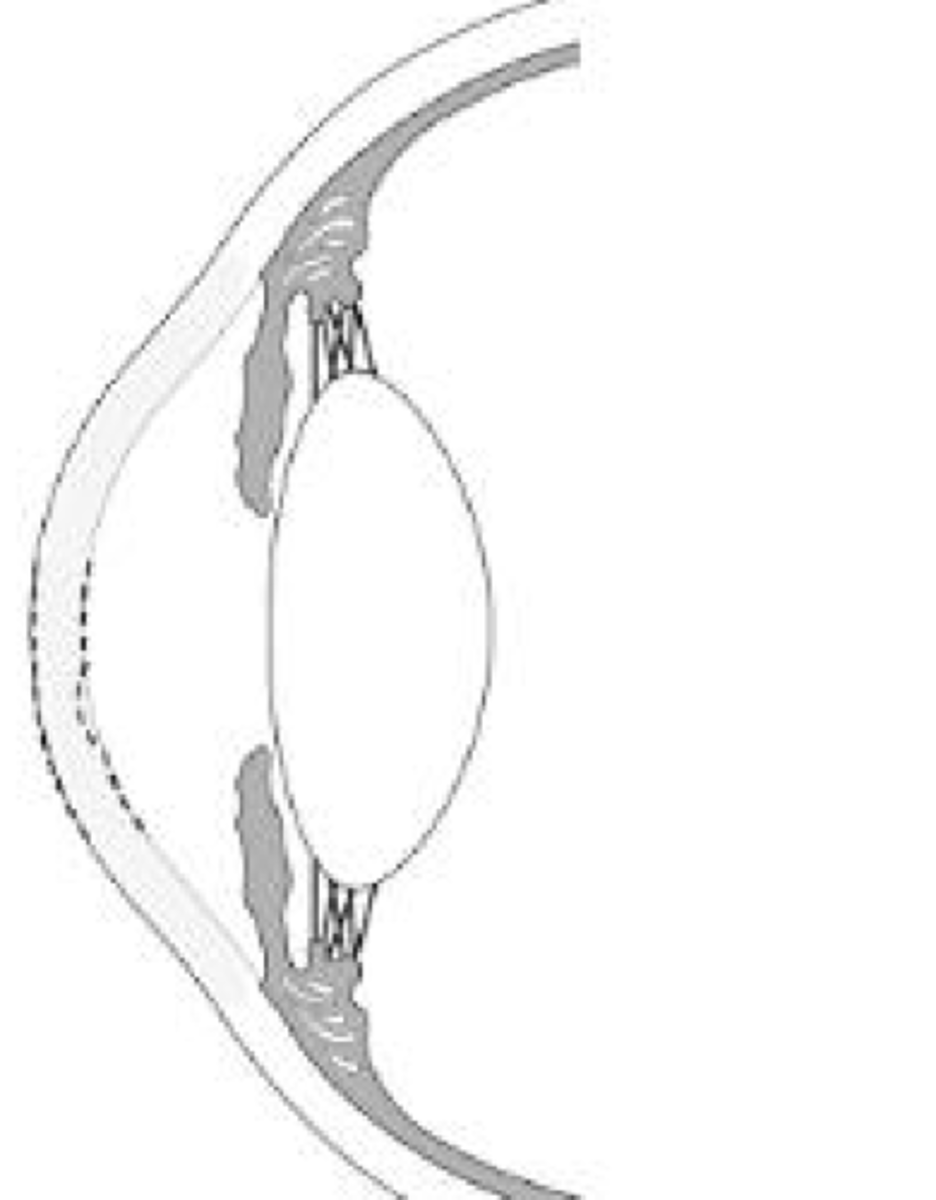
_____ is the bilateral, asymmetric, noninflammatory progressive corneal steepening and eventual corneal thinning
keratoconus
keratoconus typically effects the ___ to the ____ of the cornea
inferior, center
keratoconus usually onsets during _____ and varies its rate of progression lasting until 30s-___
puberty, 40s
does keratoconus affect one gender more than the other? yes or no
no
keratoconus has higher rates in ___/___ countries/area
asia/Middle East
keratoconus
keratoconus pathology begins with the combination of (3)
genetic, biochemical, and environment
keratoconus pathology begins with the combination of genetic, biochemical, and environment process. this gives rise to the alterations of enzyme levels causing stromal degradation leading to ____ ___. in addition to this, there is an increase levels of degradative lysosomal enzymes and decreased levels of inhibitor proteolytic enzyme
stromal thinning
during the keratoconus pathologenesis and after thinning of the stroma, next is the increased ______ of stromal keratocytes. due to this there is decreased collagen and extracellular matrix production thus leading to reduced _____ ____
apoptosis, stromal mass
keratoconus has a strona assoication with ____ ____ which is the mechanical epithelial truama. this trauma leads to wound healing and then keratocyte apoptosis
eye rubbing
its theorized that keratoconus has _____-_____ pattern of inheritance aka incomplete penetrance
autosomal - inheritance
keratoconus systemic associations are (6)
sleep apnea, asthma, down syndrome, Ehlers Danlos, osteogenesis imperfecta and marfans
Keratoncus ocular associations are (7)
VKC
floppy eyelid syndrome
leber congenital amaurosis
retinitis pigmentosa
retinopathy of prematurity
Fuchs dystrophy
posterior polymorphous dystrophy
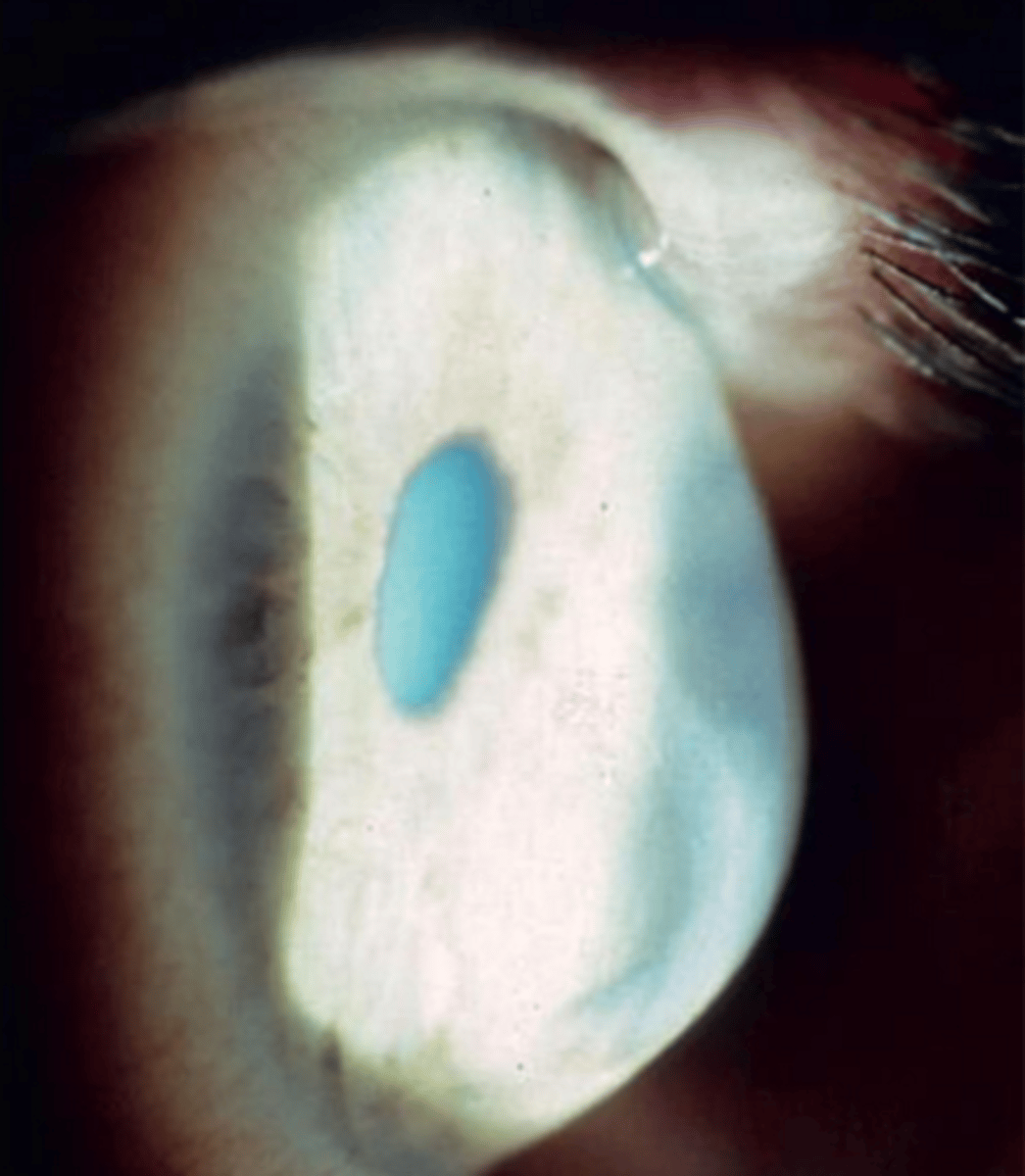
1. corneal steepening
2. thinning of corneal apex
3. scarring at level of bowmans level
4. vogt striae
5. fleishers ring
6. munsons ring
7. rizuttis sign
8. charleux sign
9. scissoring reflex
are all signs of
keratoconus
what are tow machines that can diagnose keratoconus
topography and tomography
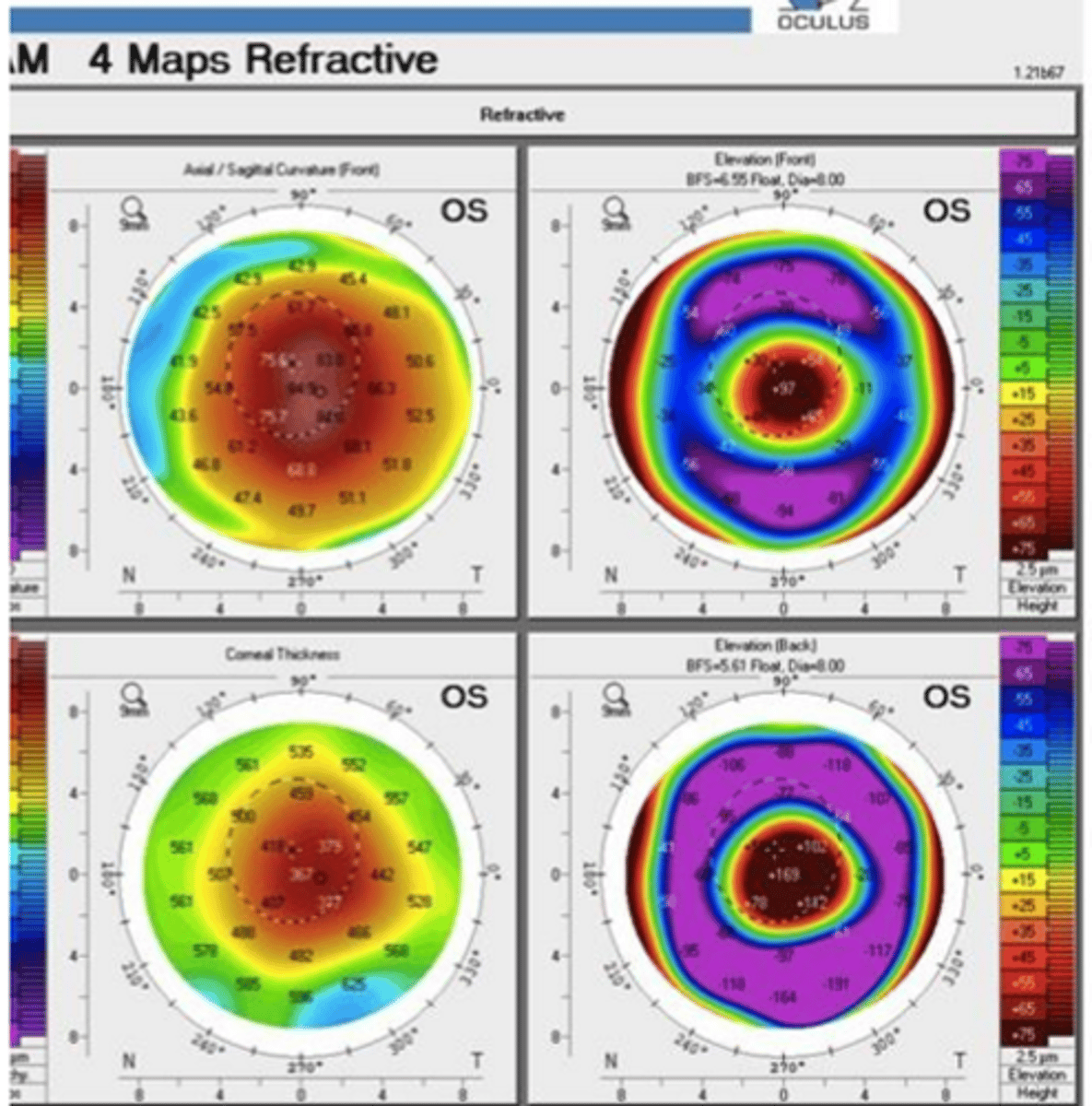
while diagnosing keratoconus, Rabinowitz criteria is used, which is ? (5)
K > +47.20D
I-S dioptric asymmetric > +1.20D
KISA% > 60%
Astigmatism >1.5D, Irregular astigmatism
pachymetry/asymmetrx index <105
what other criteria is considered while diagnosing keratoconus (3)
1. abnormal posterior elevation
2. abnormal corneal thickness distribution
3. clinical evidence of non inflammatory corneal thinning
keratoconus penatcam measures :
belin ambrosia enhanced ectasia display (BAD)
what is BAD total deviation value (BAD_D)
integrates anterior elevation, posterior elevation and pachymetry measurements relative to best fit spheres
a 22 year old patient comes in and their VA are not reaching 20/20 and you see signs of what could look like keratoconus before coming to that diagnosis, what are other differentials that it could be
pellucid marginal corneal degeneration
keratoglobus
contact lens induced corneal warpage
protrusion/thinning following ulceration
________ ____ _____ is described as one eye with bsence of clinical signs/topographic abnormalities and the other with KCN. in addition its important to consider prior to refractive sx
forme fruste kcn
____ ___ is described as one eye with topographic signs of keratoconus without slit lamp findings and the fellow eye is with KCN
subclinical KCN
1. steepening of anterior corneal surface
2. steepening of posterior corneal surface
3. thinning and/or increase in rate of corneal thickness change from periphery to thinnest point
this describes the progression of ______
keratoconus
the development of keratoconus can cause (4)
progressive myopia
irregular astigmatism
corneal scarring
corneal hydrops
there are several tx options for keratoconus such as (7)
spectacles
CL- spherical, custom, toric
RGP
special lens: hybrid, piggy back, slerals
surgery- PKP or DALK
INTAC corneal ring segment
_____ is full thickness transplant whereas _____ keeps the endothelium only but everything is else is from a donor.
PKP, DALK
DALK keep the patient's original endothelium this _____ chances of rejection because not foreign
decreases
___ _____ ____ halt or slows the progression of keratoconus
corneal cross linking
__ ____ ___ is the polymerization of stroma using riboflaviin and UVA
corneal cross linking
which version of corneal cross linking is FDA approved
epi off
for corneal cross linking what is the Dresden procol? (3)
removal of central epithelium
topical application of riboflavin
irradation with UVA (370nm) for 30 mins
who and when is corneal cross linking for
children at the onset of progression
corneal cross linking can result in complications such as (5)
stromal edema and haze
scarring
infectious keratitis (IK)
diffuse lamellar keratitis (DLK)
sterile infiltrates
what are contraindications of corneal cross linking (9)
corneal thickness <400um
preop K > 58D (too steep)
>35 yrs
history of herpes
concurrent infection
severe corneal scarring
history of poor wound healing
ocular surface disease
autoimmune disorder
a 40 year old patient comes to u with hx corneal scars and herpetic infection. you diagnose her with keratoconus. after a few visits she explains she wants to do corneal cross linking. you tell her she is not a good candidate. why did you say no?
she is older than 35, hx of herpes and corneal scars.
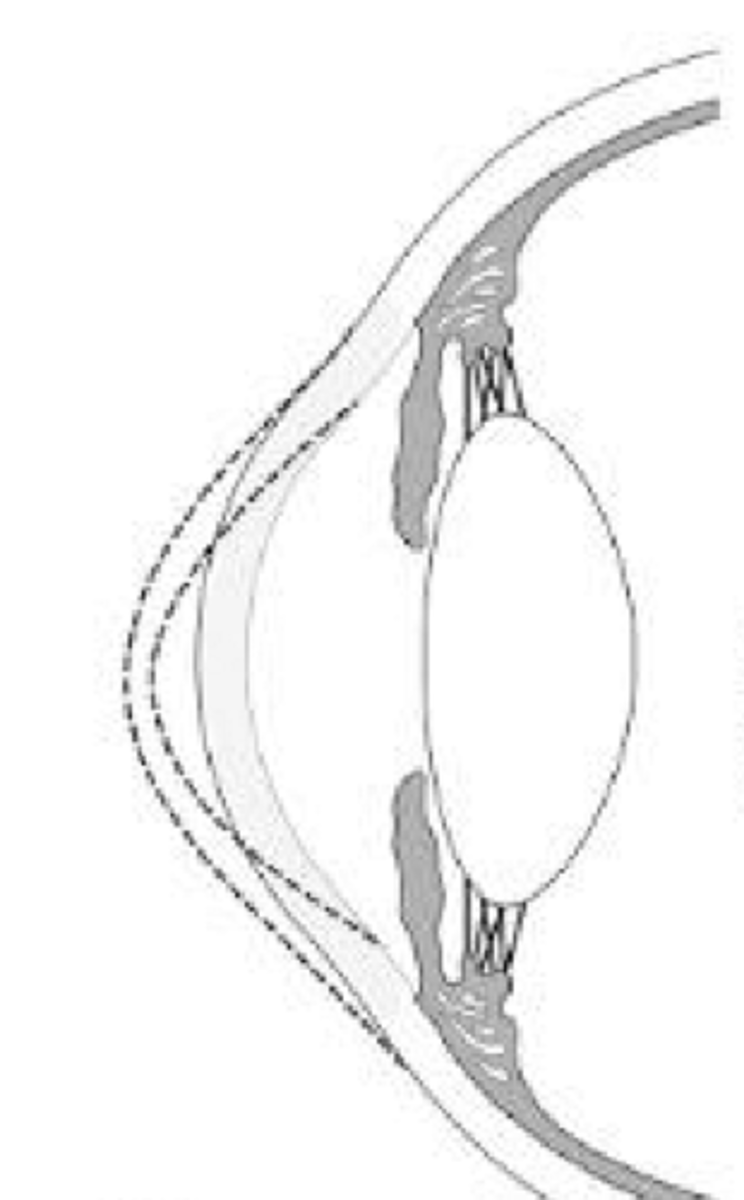
___ ____ is sporadic, usually unilateral, non progressive condition in which the posterior corneal surface protrudes into the stroma
posterior keratoconus
what are the two types of posterior keratoconus
keratoconus posticus generalis
keratoconus posticus circumscriptus

posterior associations (c/w dysgenesis) includes (7)
aniridia
ectropion uvea
glaucoma
iris atrophy
anterior lenticonus
ectopia lentis
anterior lens opacities
posterior keratoconus is associated with systemic abnormalities such as (4)
cleft lip
webbed neck
defects in extremities
genitourinary abnormalities
from posterior keratoconus it can lead stromal ____
scarring
what are the two tx options for posterior keratoconus
PKP
does not require tx
___ ___ ___ is corneal thinning and protrusion in the inferior peripheral cornea
pellucid marginal degeneration
pellucid marginal degeneration is characterized by a protrusion _____ area of maximal thinning. There is thinning _-_mm inside the inferior limbus. In addition, horizontal oval band _mm radial, 6-8mm horizontal extent
ABOVE, 1-2, 2
t/f in pellucid marginal degeneration, there is usually a clear cornea without iron line. and regular ATR astigmatism leads to irregular astigmatism
true
pellucid marginal degeneration appears as ____ ____ or ____ ____ in topography and tomography
crab claw, kissing doves
pellucid marginal degeneration usually affects people in which age group
20s-50s
pellucid marginal degeneration can lead to
hydrops
what is tx for pellucid marginal degeneration (4)
spectacles
CL
large diameter RGP
large eccentric keratoplasty
____ is defined as bilateral ectactic disorder that is nonprogressive or minimally progressive
keratoglobus
____ _____ is characterized as limbus to limbus thinning with greatest in corneal periphery/midperiphery
globular corneal protrusion
keratoglobus
what are the two types of keratoglobus
congenital/juvenile
acquired adult
what are two types of congenital/juvenile keratoglobus?
Ehlers Danlos syndrome type VI
brittle corneal syndrome
t/f keratoglobus can be associated with blue sclera
true
is keratoglobus associated with atopy or downsyndrome? yes or no
no
after the development of keratoglobus what can form next (2)
hydrops
perforations
what are the 2 tx options for keratoglobus
protection from truama
PKP but could have poor outcome
is keratoconus bilateral or unilateral and asymmetric or symmetric
bilateral,asymmetric
during which age does keratoconus typically onset?
puberty
keratoconus usually has thinning in the ____ paracentral
inferior
keratoconus has protrusion which is thinnest at the ____
apex
pellucid marginal degeneration is bilateral or unilateral
bilateral
pellucid marginal degeneration onsets durings which years of life
20-40s
pellucid marginal degeneration has thinning at the ____ band 1-2 mm from limbuus
inferior
pellucid marginal degeneration has protrusion _____ to _____
superiorly, thinning
keratoglobus is bilateral or unilateral
bilateral
what is the age of onset for keratoglobus
birth
keratoglobus has thinning ____ but mostly peripherally
global
keratoglobus protrusion is _____
generalized
Posterior KCN is bilaterally or unilateral
unilateral
age of onset for posterior KCN ?
birth
posterior KCN has thinning? (2)
paracentral posterior or
global
posterior KCN has protrusion? yes or no
usually non
keratoconus
pellucid marginal degeneration
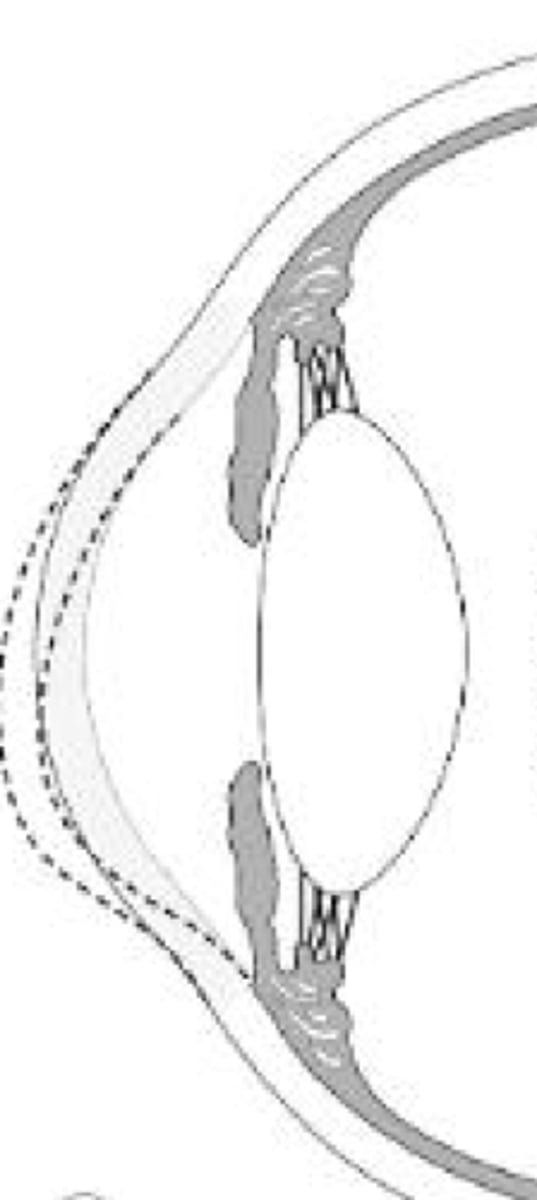
keratoglobus
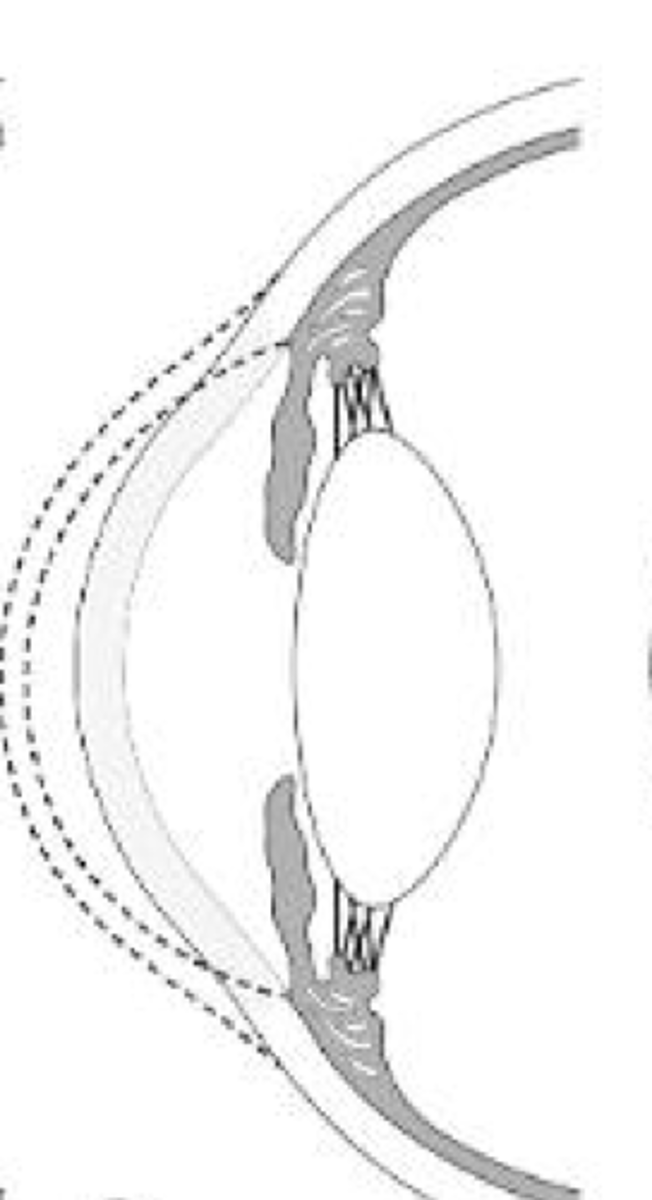
posterior keratoconus
___ ____ ____ ____ ____ is thought to be due to distruption of biomechanical integrity of the cornea even years after
post-refractive surgery corneal ectasia
for refractive sx, FDA requires at least ____um of untouched tissue
250
someone wants to undergo refractive surgery but there are some risks factors that need to be considered such as (5)
abnormal preoperative corneal topography
>40% of tissue altered
low operative corneal thickness
high myopia
younger age
if someone undergoes post refractive surgery and they have corneal ectasia, what are the tx options ?
glasses and CL
possibly CXL (corneal crosslinking
& ICRS(intracorneal ring segment)
___ ____ ___ occurs when there is a break in decemets membrane with inward curling of the membrane
acute corneal hydrops
in acute corneal hydrops, there is stromal ____ due to aqueous entering the breaks as well as intrasomal clefts
edema
acute corneal hydrops commonly seen in patients with
down syndrome
a established patient with keratoconus enters complaining of redness, discomfort, and photophobia. in the slit lamp you notice there is edema and it is not transparent. you also note the patient has down syndrome. what is causing these symptoms?
acute corneal hydrops
acute corneal hydrops usually self resolved within _-_ monhs
2-4
after corneal hydrops corneal ____ could form
scarring
what is the management for acute corneal hydrops (1)
follow up every 1-4 weeks until resolved
what are the tx options for acute corneal hydrops (7)
bandage CL
topical cycloplegia
NaCI 5%
topical steroids
aquous suppressant
injection of gas
pkp
for acute corneal hydrops why is NaCI 5% an option
pulls water out
acute corneal hydrops
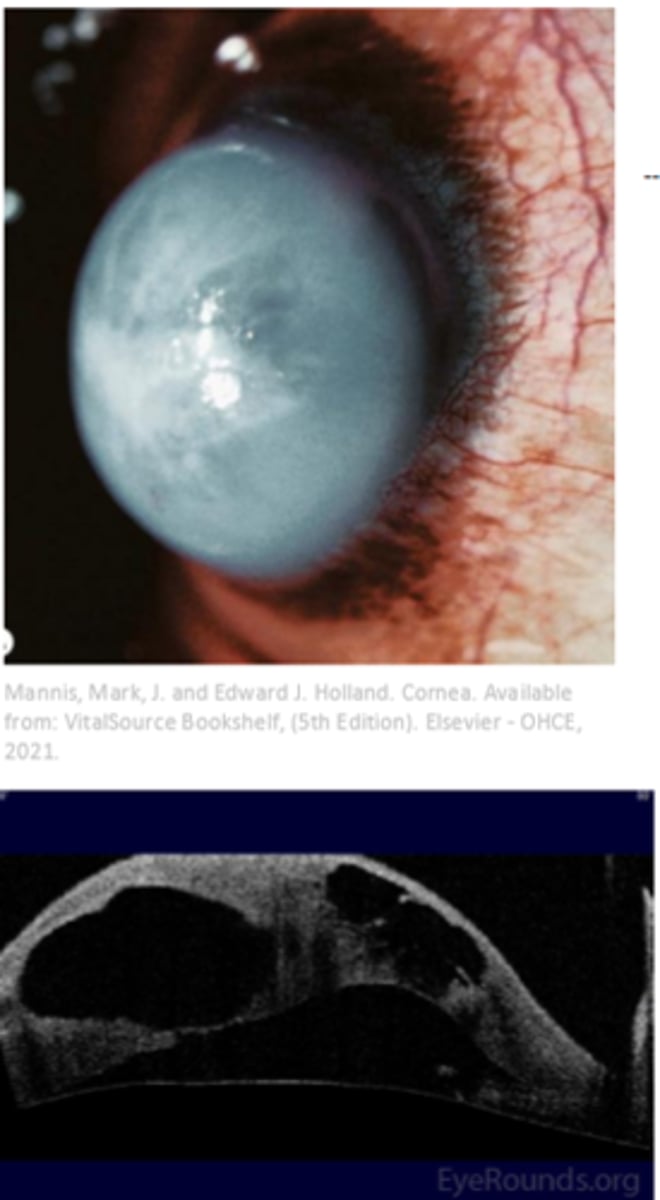
keratoglobus
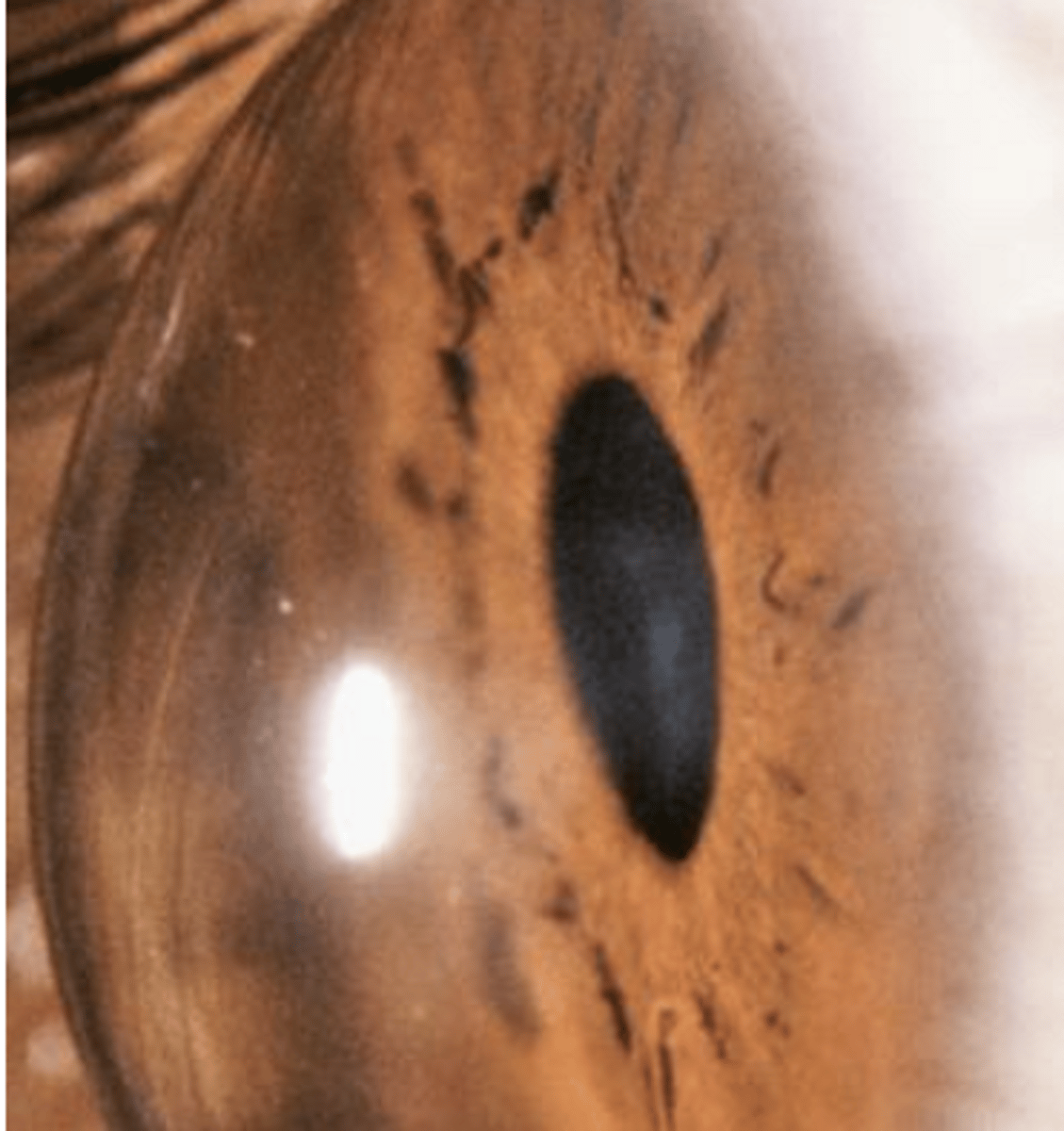
pellucid marginal degeneration
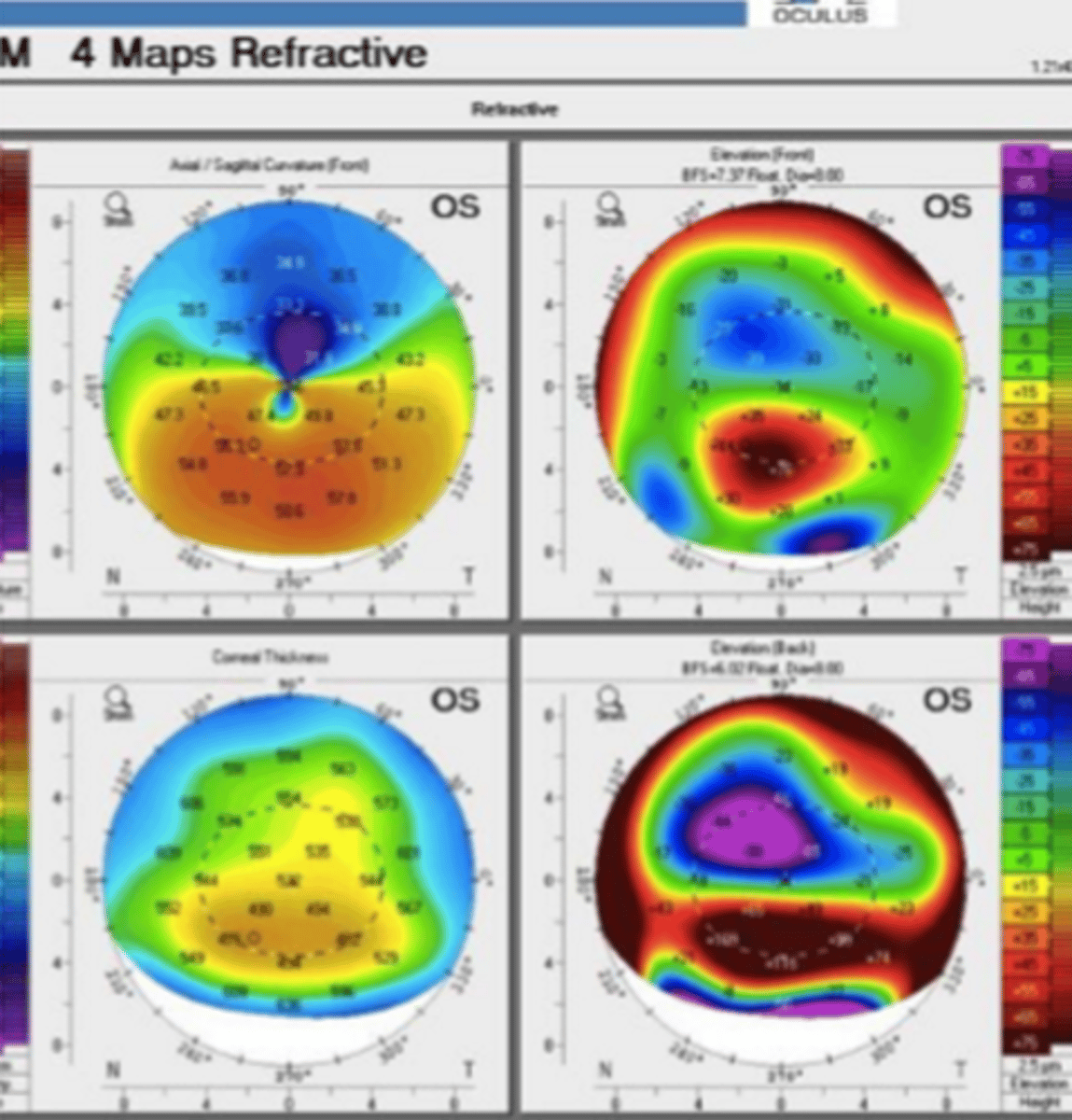
keratoconus