meiosis
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
what are the products of meiosis?
4 genetically different haploid cells
name the 2 ways genetically different daughter cells occur in meiosis:
independent segregation
crossing over
describe the process of meiosis i:
meiosis i:
chromosomes replicate
chromosomes condense and homologous pairs join together
nuclear envelope breaks down and spindle fibres form
chromosomes are attaches to spindle fibres at the centromere and line up in pairs randomly along the equator of the cell → independent segregation
crossing over - homologous chromosomes exchange parts with each other
homologous chromosomes pulled to opposite poles of cell by spindle fibres
cytoplasm divides, forming 2 daughter cells
chromosomes decondense
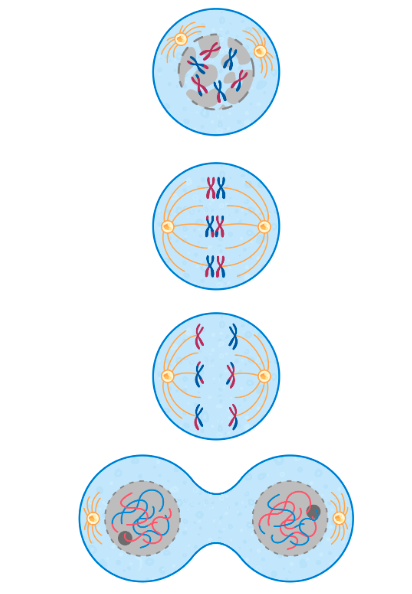
describe the process of meiosis ii:
nuclear envelope reforms and chromosomes recondense
in each cell, spindle fibres attach to centromere of chromosomes and pull sister chromatids apart to opposite poles of the cell
chromosomes recondense
cytoplasm /es and nuclear envelopes form around 4 genetically different haploid daughter cells

what is independent segregation?
random alignment of homologous pairs along the equator of the cell
what is crossing over?
non sister chromatids exchanging alleles by sections of chromatids being broken off, exchanged and rejoined
what is the formula used to calculate the number of different possible combinations of chromosomes following meiosis (w/o crossing over)?
2n