An Introduction to Evidence-Based Investing
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Asset Class
A group of assets that have similar characteristics, attributes, and risk/return relationships.

Stocks
A type of security that signifies ownership in a corporation and represents a claim on part of the corporation's assets and earnings.

Equities (Stocks)
A share of stock represents ownership in the company. As an owner, you have certain rights and benefits.

fixed-income (debt) securities
A security such as a bond that pays a specified cash flow over a specific period.

bond
A financial security that represents a promise to repay a fixed amount of funds; issued by either a government or a business entity (corporation)

real estate
Property such as land, houses and office buildings. One of the four major "asset classes."

cash
Money in the form of bills or coins; also includes, as an asset class, checking and savings accounts; the fourth major asset class

Alternative Investments
Gold, silver, futures contracts (oil, natural gas, agricultural products), hedge funds, private equity, venture capital, and other asset classes that don't fit within the four major asset classes (stocks, fixed income, real estate, cash)

Active Investing, or active investment management
Carried out with the goal of outperforming the market; involves either picking individual stocks or bonds that the investment manager believes will outperform the "market"; or market timing (switching between asset classes, based upon expected returns)
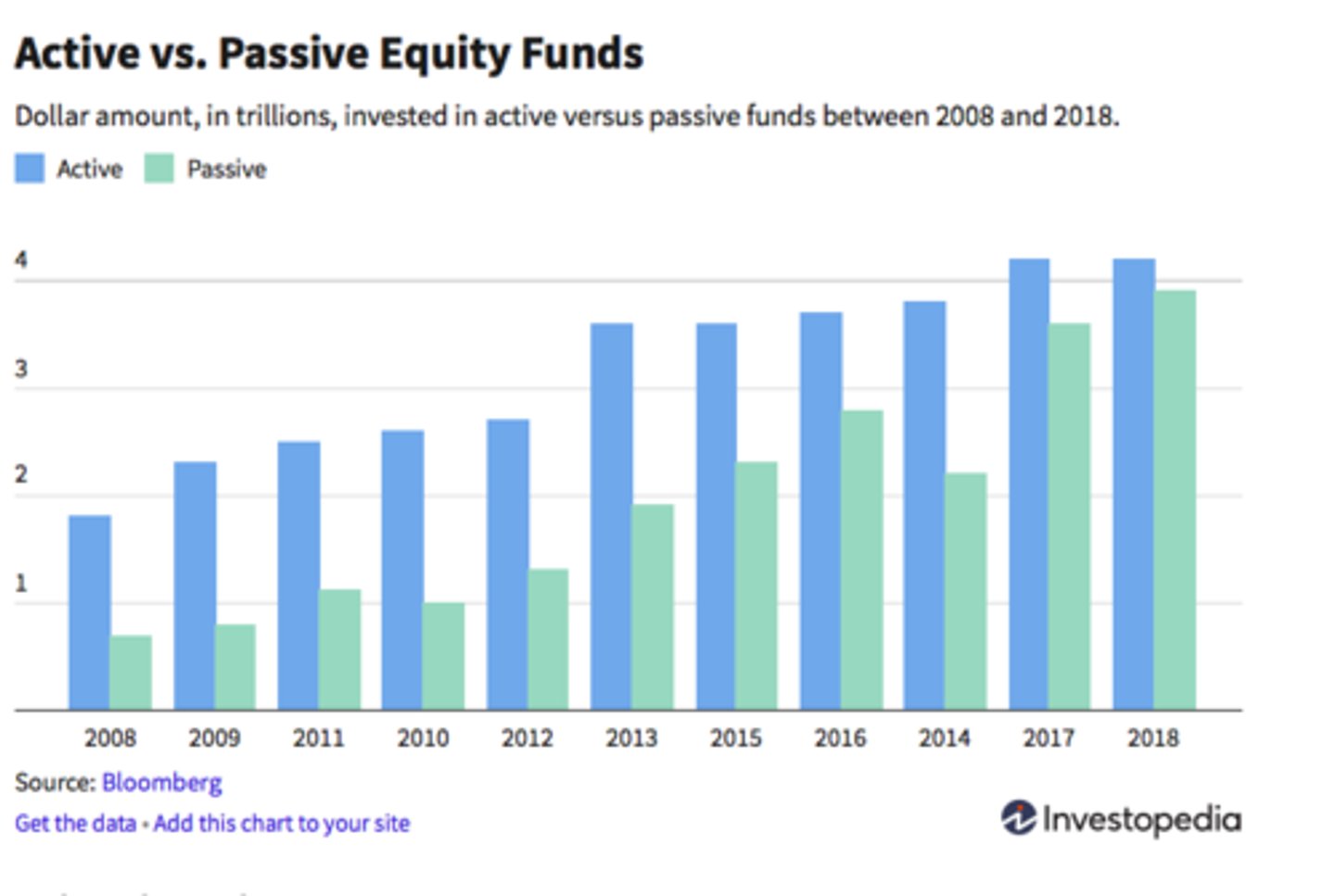
passive investment management
Investing in a well-diversified portfolio or market index without attempting to search out mispriced securities

security selection
the choice of which particular securities to hold within each asset class; one of the two main methods of "active investment management" ("active investing")

market timing
The investment manager anticipates the timing of when to be in or out of a specific asset class; involves switching between asset classes, usually for several months at a time; one of the two major forms of active investment management. Also called tactical asset allocation.

evidence-based investing
an approach to investing that involves the application of a substantial body of academic research, as a means of identifying asset classes in which to invest

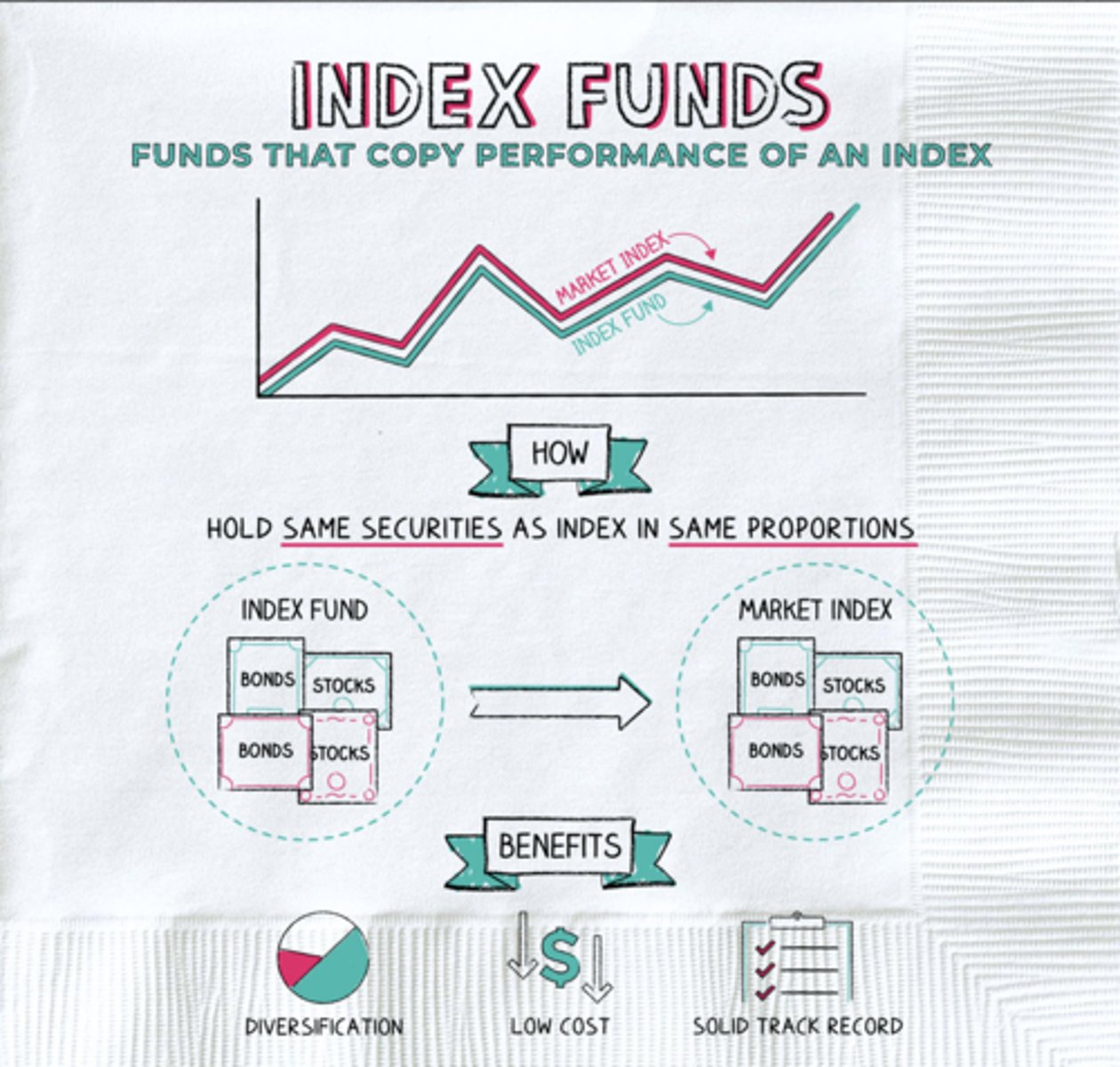
Index Fund
A mutual fund that tries to match the performance of a particular index by investing in the companies included in that index.
asset allocation
the process of spreading your assets among several different types of investments to lessen risk
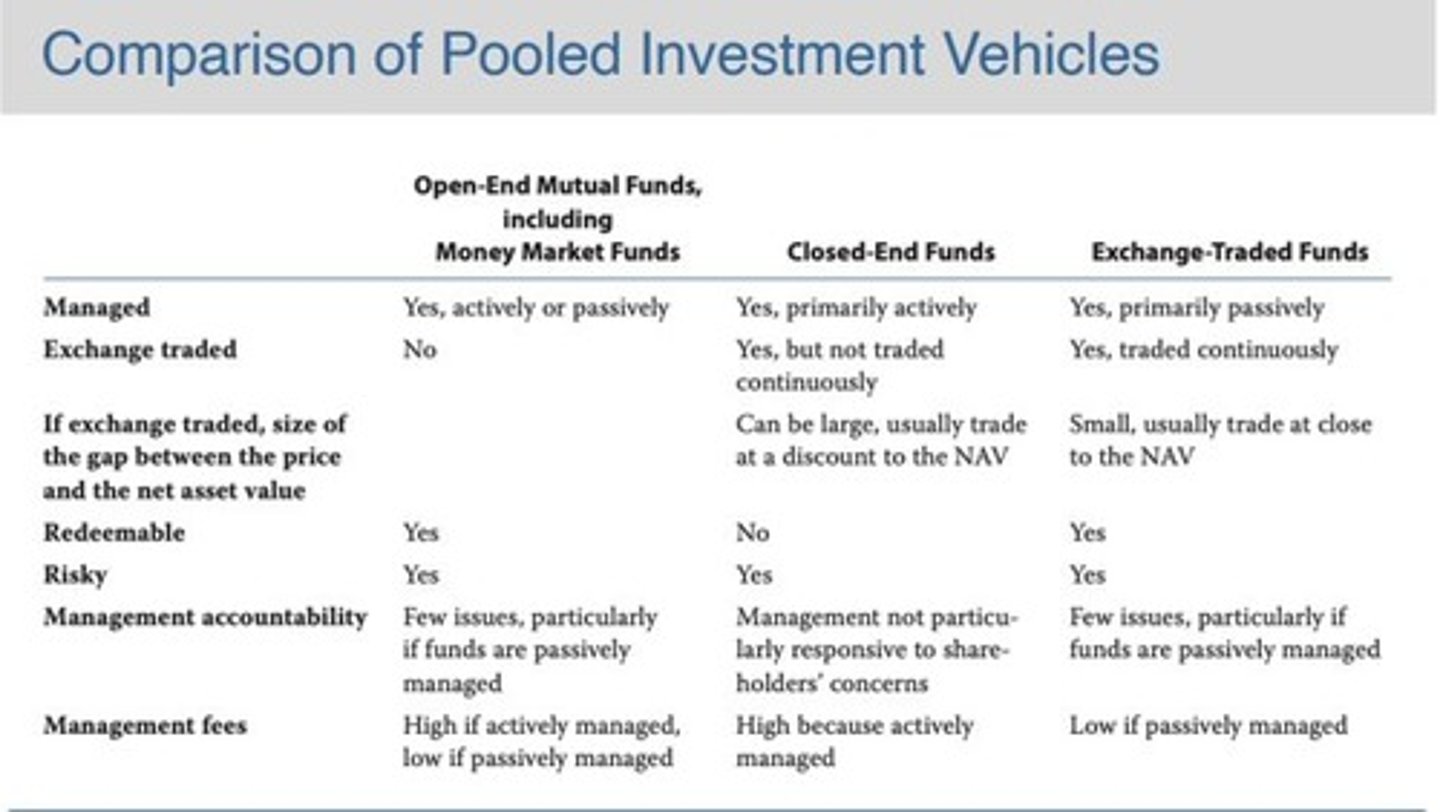
Pooled Investment Vehicles
Investment companies that pool funds from many investors for common management. Includes (open-end) mutual funds, closed-end mutual funds, hedge funds, unit investment trusts, limited partnerships, exchange-traded funds, pension funds, and other collective investment vehicles.
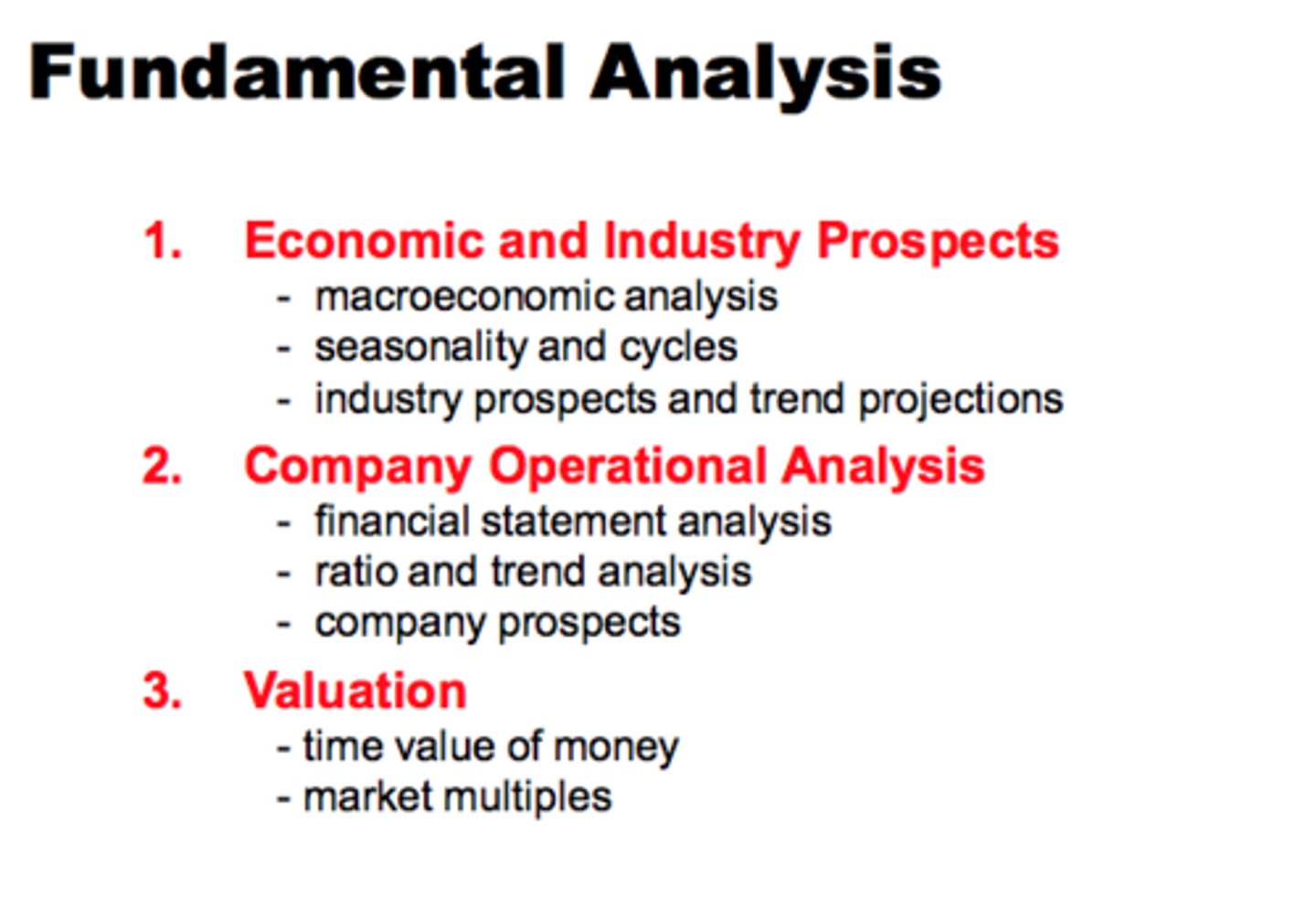
Fundamental Analysis
Research undertaken by a stock analyst to determine the intrinsic value of a stock, such as examining its earnings and dividend prospects, the expectations for future interest rates (or other macro-economic trends), and risk of the firm. Fundamental analysis is one of the two major forms of active investment management utilized today.
financial freedom
While definitions vary, a common definition is the ability to provide for your needs and reasonable wants without the need to generate income from work. This may be done by security streams of income (such as Social Security retirement benefits, pension checks) and/or by saving and investing (thereby being able to withdraw from an investment portfolio, for the rest of your life).

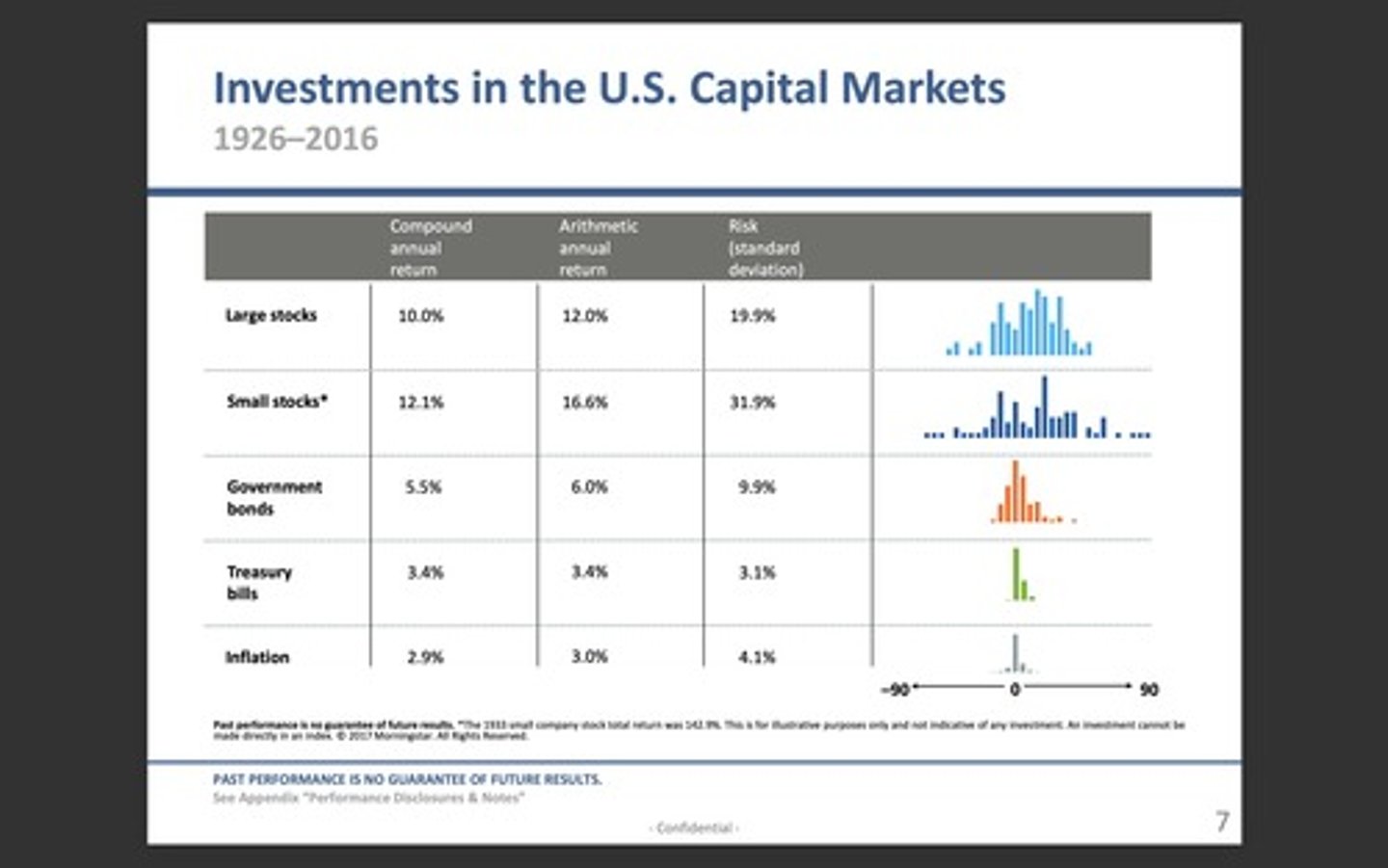
capital markets
Markets that trade debt (bonds) and equity (stock) instruments