1.1-1.2: Introduction to Economics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Economics
The study of how society allocates scarce resources among unlimited wants and needs.
Microeconomics
How producers and consumers interact in individual markets.
Macroeconomics
Factors that affect the economy.
Cost-benefit analysis
Choose the option that gives the most utility by weighing up the pros and cons of each outcome.
Opportunity cost
The next best thing sacrificed as a result of a choice.
Trade-off
Anything given up as a result of a choice.
Free goods vs economic goods
Abundant
Scarce and competition for it exists
Incentive
Something that motivates an individual to act in a certain way.
Basic economic problem
What could be produced and how much?
How should thing be produced?
For whom should things be produced?
Rationing systems
Planned (command economy)
Government makes decisions
Resources owned “collectively”
DISAD: Lack of liberty and choice, and poor efficiency.
Free market economy
Resources and production are owned privately
Use of prices to ration g+s
DISAD: high income inequality, over provision of demerit goods, and poor use of resources
Mixed market economy
Some measure of government intervention
Four Factors of Production
Land: Provided by nature (property and resources found under the land)
Labor: All human resources
Capital: Anything made by humans
Entrepreneurship: Management that organizes the factors of production
Production Possibilities Curve
Graph that shows the tradeoff between the production of different items.
Maximum combinations of two types of output that can occur if all resources are being used efficiently and technology is fixed.
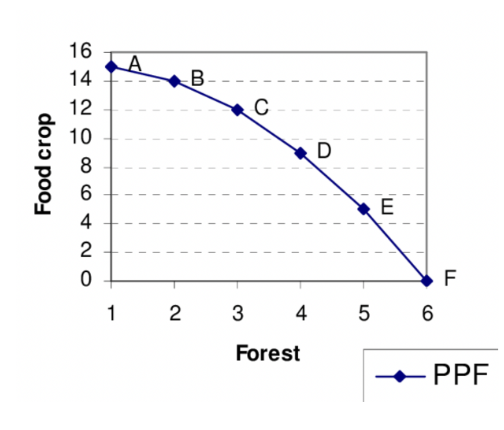
Inverse relationship between two types of good (why curve is downward sloping)
The Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost:
increasing quantities of one good can only be achieved by sacrificing ever-increasing quantities of another good
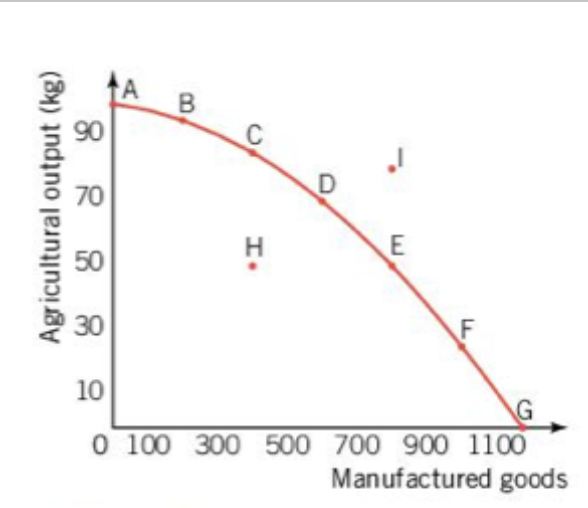
PPC Curve - Points (increasing opportunity cost)
A to G:
potential output
productive efficiency exists wherein the economy is using its resources to the maximum potential
I:
not possible, exceeds the productive capability of available resources and technology
H
resources are not fully utilized
actual economic growth is shown through a movement of H towards the PPC (utilize more resources)
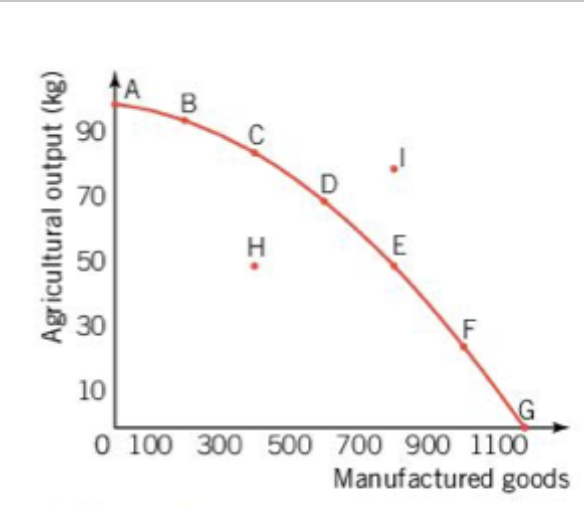
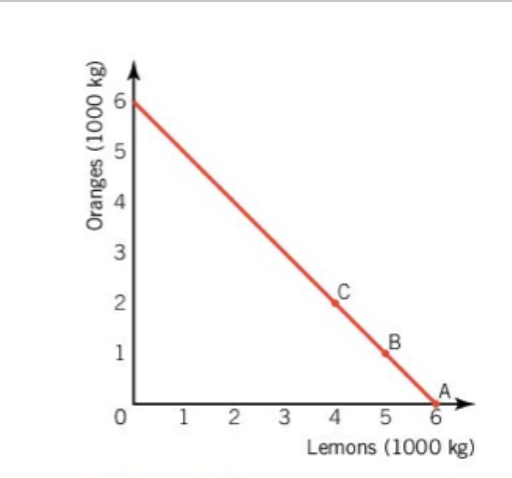
PPC Curve - constant opportunity cost
Production for producing lemons and oranges is largely the same
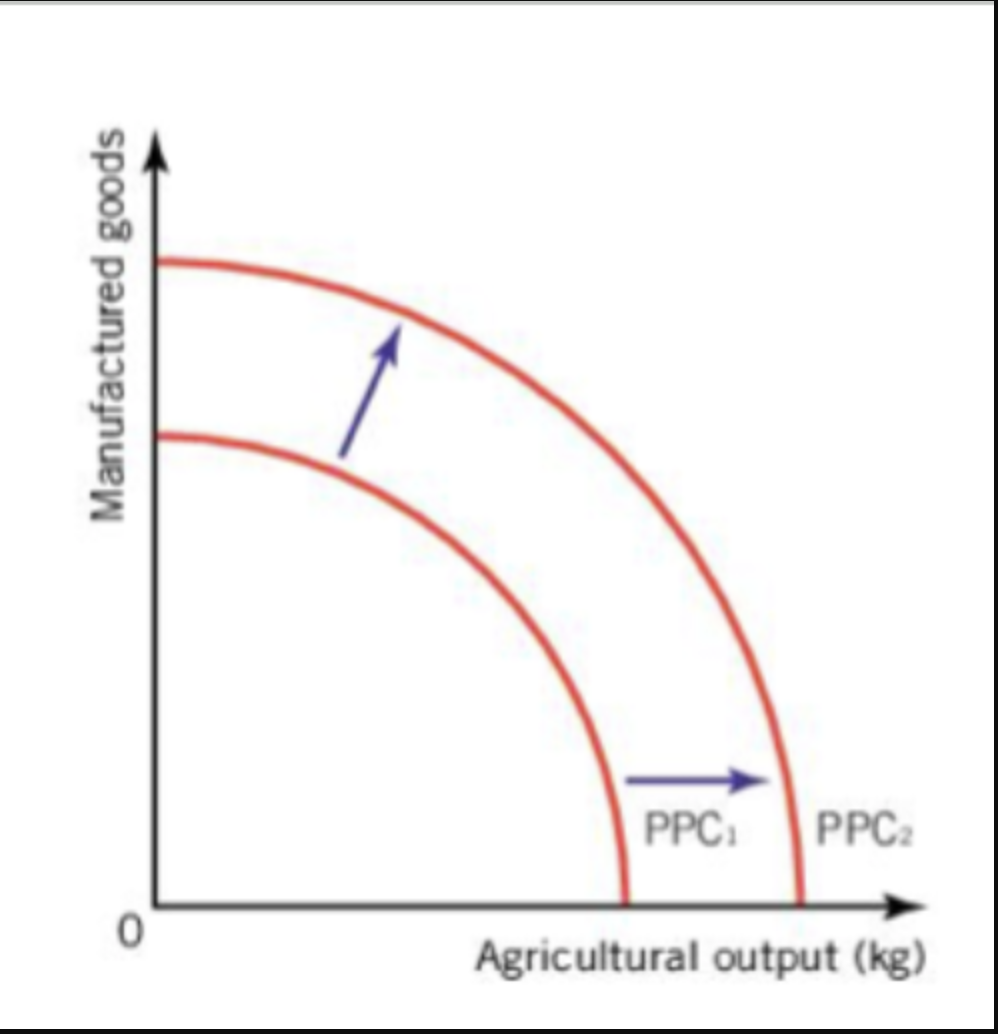
Change in production possibilities
Growth - Increase in the quality and quantity of factors of production
Improved education
Improved production technologies
New forms of energy
Reduce in quality or quantity of factors of production
Wars and natural disasters
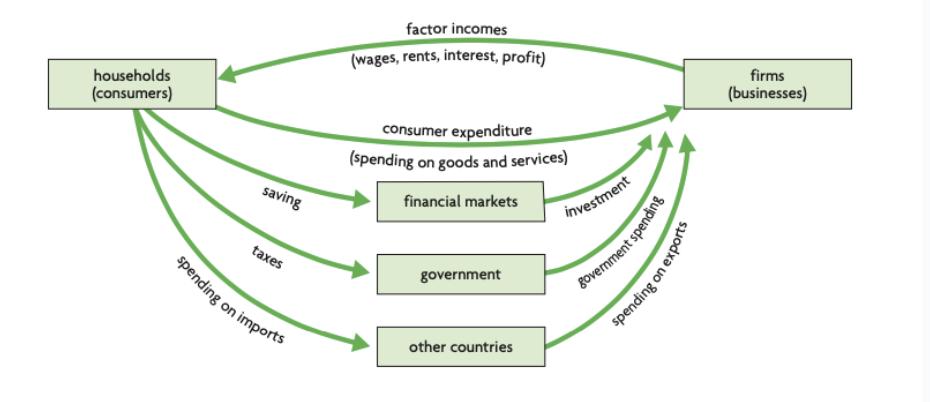
Circular flow of income
Households supply the factors of production and firms provide payments to the factor
Labour → Wages
Land → Rent
Capital → Interest
Entrepreneurship → Profit
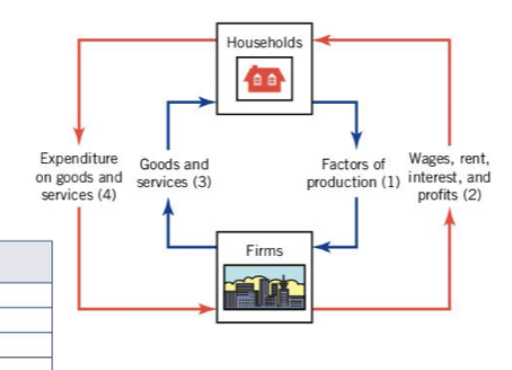
Leakages and Injections
Leakages: Some money leave the economy
Governments take money in the form of taxes
Consumers save
Households and businesses spend money on imports
Injections: money enters the economy
Governments spend on public services and infrastructure
Financial sector invests money in firms
Foreign households purchase exports