Unit 2.6 The Kidney
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is osmoregulation
The maintenance of constant water levels in the body fluids of an organism.
Why is osmoregulation important [2]
Prevent cell bursting or shrinks when water enters or leaves by osmosis
Cellular reaction occurs in aqueous solution therefore water levels affects concentration and the rate of reaction in cells
Describe the function of the kidney
Remove toxic waste substances from the body
Maintenance the water levels of body fluids
Control the volume and concentration of urine
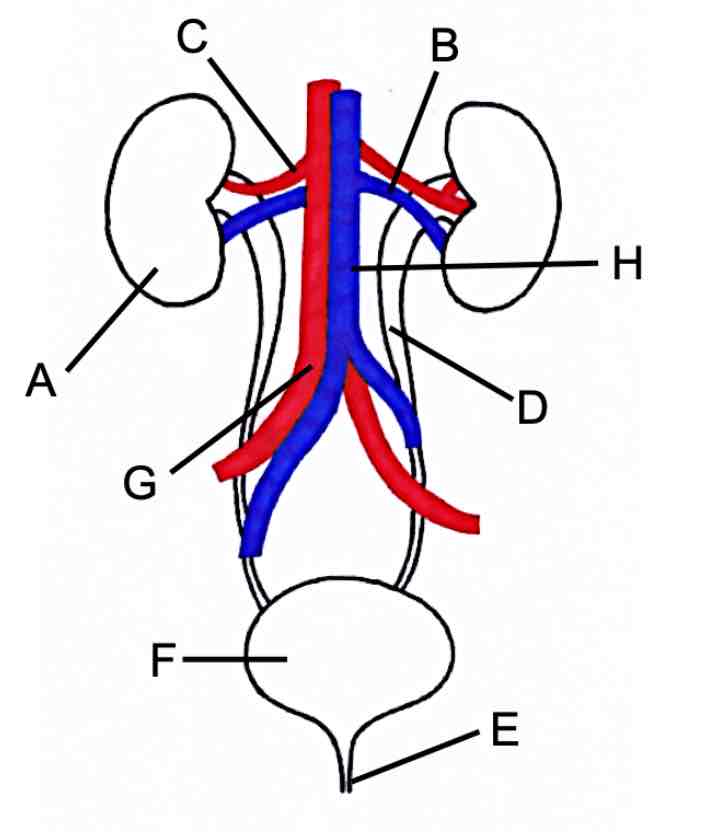
Label
What is the function of renal artery
Supplies blood to the kidney and filter the blood
What is the function of the renal vein
Drains blood from the kidney and bring oxygen for cells
What is the function of the ureter
Takes urine to the bladder from kidney
What is the function of the urethra
Release urine from the bladder, out of the body
What is a nephron
Functional unit of the kidney where filtration and selective re absorption takes place
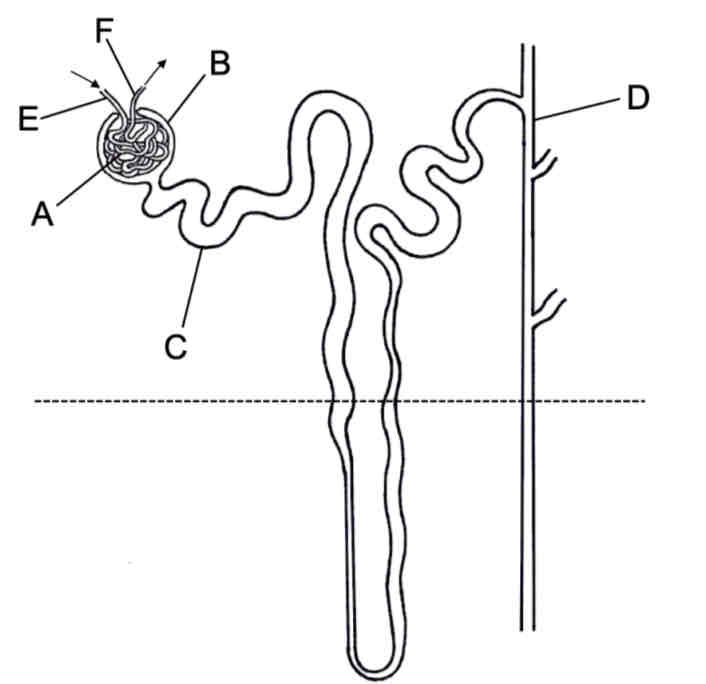
Label
What are the 3 stage involved in the formation of urine
Filtration
Selective reabsorption
Osmoregulation
Describe filtration in the kidney
Blood flows through the capillary knot under high pressure, small molecules (urea and glucose) water and salt are filtered out of the blood into the Bowman’s capsule
Why is there a build up of pressure in the capillary knot?
Arteriole leading into the capillary knot is wider than arteriole taking blood from the capillary knot
Why do large molecules such as proteins and rbc remain in the blood
They are too large to fit through the pores in capillary walls
Which substances are selective reabsorbed from the nephron tube
Glucose
Some water
Some ions
What happens to the molecules not selectively reabsorbed in nephron tube
They travel down the kidney tubules as urine and are transported to the bladder via the ureter, here they are stored and eventually excreted
If blood water level become too high, the kidney produces more __ urine
Dilute
If blood water level become too low, the kidney produces more __ urine
Concentrated
How is the concentration and volume of urine controlled
Controlled by secretion of ADH
What produce ADH?
Pituitary gland
Describe how ADH affects the kidney
ADH cause the kidney to reabsorbed more water into the blood, so more concentrated urine is produced
What does the composition of blood contain
Cells
Proteins
Water
Glucose
Salts
Urea
what does the composition of filtrate contain
water
Glucose
Salts
Urea
What does the composition of urine contain
water
Salts
Urea
What may blood or cells in the urine indicated
Kidney diseases
How can kidney failure be treated [2]
Kidney dialysis
Kidney transplant
What is kidney dialysis
A machine artificially filters a patient’s blood
What is the dialysis fluid called
Dialysate
How does kidney dialysis work
The selective permeable barrier separates the patient’s blood from dialysate
Materials exchanged across the barrier such as urea and water moves out of the blood into the dialysis fluid
Large cells and proteins remain in the blood
Describe the composition of dialysate
Fewer salts and water than patient’s own blood so excess salts and water diffuse out of the blood into the dialysate
No urea
Advantage of kidney dialysis
No surgery needed
Can undergoes kidney dialysis while waiting for a donor kidney
What does a kidney transplant involves
Taking a kidney form a living donor or someone recently pass out and implanting it into the patient
What does a kidney transplant involves
Taking a kidney form a living donor or someone recently pass out and implanting it into the patient
What is meant by kidney rejection?
The immune system detects the foreign tissue and attacks it
What is meant by kidney rejection?
The immune system detects the foreign tissue and attacks it
What precaution are taken to minimise the risk of rejection
Tissue typing ensures that the transplanted organ is compatible with the recipient
Immunosuppressant drugs helps prevent the immune system from rejecting the organ
Advantage of kidney transplant
More of a permanent solution than
Advantage of kidney transplant
More of a permanent solution than kidney dialysis
Improve patient’s quality of life
Disadvantage of kidney transplant
Difficult to find a donor
Requires surgery
Have a limited life span
Risk of organ rejection
Immunosuppressants increase the risk of their infections
Describe the stimulus that will secreted ADH
The low content of water in blood
What waste product do excess broken down of amino acid produce, how is it removed and why is it harmful for human
Excess broken down of amino acid can produce large volume of ammonia. This is harmful for human body as ammonia is toxic, so it is converted to urea in the liver and then eventually excreted out
Where are nephrons positioned at
Across the cortex and the medulla