immune system
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
what does SCID stand for?
severe combined immunodeficiency
what is SCID?
a genetic disease of the immune system
what is the first line of defense?
skin, mucus membranes, antimicrobial substances
what is the second line of defense?
inflammation, fever, phagocytes
what is the third line of defense?
humoral and cellular immunity (B and T cells)
what is immunity?
ability to ward off disease
what is susceptibility?
lack of resistance to a disease
what is skin?
a mechanical barrier that has acid (which inhibits bacterial growth) and sebum (which has antibacterial/antifungal properties)
what part of tears and saliva attack bacteria?
lysozomes
what do mucus membranes do?
trap microorganisms and debris
what does the stomach do?
HCL within it destroys most microorganisms
what were isla-mae’s symptoms?
red spots
what did isla’s blood sample show
that she has leukemia
what was isla-mae diagnosed with?
leukemia
which type of cancer is leukemia
blood
lymphoblastic
leukemia’s effect on cells
what is acute cancer
cancer that progresses quickly
what are some ways leukemia disrupts body systems
weight loss, fever, frequent infections, fatigue, loss of appetite, easy shortness of breath, swelling, muscle weakness, pain and tenderness
compare the size of WBCs to RBCs
WBCs are larger and have a longer nucleus than RBCs
why is the % of each type of WBC important to doctors
because irregular percentages can indicate a disease
what are the 2 groups of WBCs
agranulocytes and granulocytes
what is the diff between agranulocyte and granulocyte
granulocytes have granular cytoplasm while agranulocytes lack it
what are 2 examples of agranulocytes
monocytes and lymphocytes
3 examples of granulocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
neutrophils have _____ phagocytes
active
neutrophils are _____% of WBCs
60
neutrophils are present in the _____
pus
eosinophils mostly attack _____
parasites
eosinophils are _____% of WBCs
2
basophils produce _____ (blood _____)
heparin
thinner
basophils produce _____ (important in _____ reaction)
histamines
inflammatory
what do histamines cause
swelling and itching
what suppresses the swelling and itching that histamines cause
antihistamines
basophils are _____% of WBCs
1
monocytes are _____ (size) cells
large
monocytes have a _____-shaped nucleus
horseshoe
monocytes can become _____ or _____
macrophages
dendritic cells
dendritic cells consume _____ and present _____ on their surface to signal immune system
pathogens
antigens
the nucleus of lympocytes are _____ and take up almost the whole _____
dark
cell
lymphocytes are the _____ defense (B and T cells)
main
what do B cells produce
antibodies
where do lymphocytes live
in lymph nodes
lymphocytes are _____% of WBCs
30
what is Epstein Barr Virus commonly known as
mononucleosis / mono
how do you contract mono
through shared saliva or close contact w an infected person, dormant virus alr in body turns active
diff between aids and hiv
hiv weakens immune system by infecting specific immune cells
aids is acquired immune deficiency syndrome
hiv does not always = _____, but can develop into the syndrome
aids
when do u get opportunistic infections in aids
when # of CD4 cells falls below 200 cc’s
what are the 3 phases of leukemia treatment?
remission induction
consolidation
maintenance
remission inductions kills as many _____ cells as possible thru _____
cancer
chemo
consolidation eliminates any remaining _____ cells that are not _____
cancer
detectable
maintenance keeps cancer from _____ through low doses of _____
returning
drugs
what r 5 therapies used in cancer treatment
chemotherapy
radiation therapy
stem cell transplant
bone marrow transplant
immunotherapy
chemo targets _____ cells but can also attack _____ cells
cancer
healthy
what is the 5-year survival rate for leukemia
84%
what makes up the lymphatic system
lymph, lymphatic vessels, lymphoid organs, and lymphocytes
lymph is a _____ fluid that bathes _____ and drains through _____ _____ into _____
colorless
tissues
lymphatic vessels
heart
lymphatic system is closely associated w
cardiovascular system
what is elephantiasis
enlargement of lymphatic vessels due to obstruction caused by parasite
where does the parasite that causes the obstruction in elephantiasis usually come from
mosquito bite
what is a physical symptom of elephantiasis
enlarged legs
3 functions of lymphatic sys
maintains normal blood volume
fights infection
eliminates variations in composition of interstitial fluid
relationship between lymphatic system and cancer
lymphatic sys helps spread cancer cells
innate immunity defends against _____ pathogen (_____), is present at _____, and produced by _____, physical _____, fever, _____
any
non-specific
birth
macrophages
barrier
inflammation
adaptive immunity defends against _____ pathogen, _____ to respond than innate, has _____, produced by _____
specific
slower
memory
lymphocytes
3 roles of fever in immunity
speeds up body rxns to resolve infections
inhibits growth of certain microbes
stimulates the liver to hoard substances that bacteria require to grow
antigen
any foreign substance that enters the body (bacteria, virus, toxin, pollen grain, etc.)
antibody
protein produced by body to attack antigen and protect body (specific antibody for each antigen)i
2 types of adaptive immunity
humoral and cellular
humoral immunity: _____ cells _____ to specific antigens, develop in red _____ _____, responsible for producing specific _____, attack _____ and their toxins
B
respond
bone marrow
antibodies
bacteria
cellular: _____ cells _____ to specific antigens, produced in _____ _____ and then migrate to _____ to mature, responsible for attacking _____ cells (especially viruses and _____)
T
bond
bone marrow
thymus
foreign
fungi
2 main types of T cells
CD4
CD8
CD4 is a
helper
CD8 is
cytotoxic
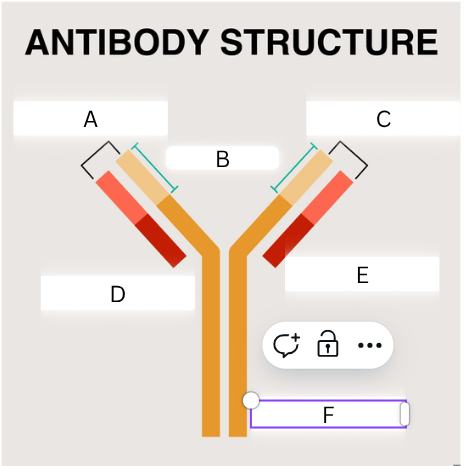
label
A) antigen binding site
B) variable region
C) antigen binding site
D) constant region
E) light chain
F) heavy chain