Cell Communication & Receptors & Signal Transduction
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Signal Transduction
Molecular changes in or on a cell induced by a signaling molecules
Endogenous Ligand
Signaling molecule made by cells to activate receptors on/in cells. Usually a protein, amino acid, nucleic acid, fatty acid, or biogenic amine.
Neurotransmitter
ligand that signals between neurons via a synapses.
Hormone
ligand transported through bloodstream (endocrine signaling)
Growth Factor
ligand that stimulates cells to grow and/or divide; usually peptides.
Cytokine or interleukin
ligands that signal between immune cells; peptides.
Chemokine
cytokine that attracts migration of immune cells.
Receptor
Protein that binds and reacts to ligand by changing conformation resulting in a change in cell function, thus initiating signal transduction.
Transcription Factor
Protein that binds DNA to induce or suppress transcription/ gene expression.
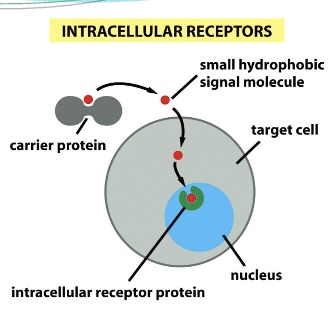
What type of receptor is Nuclear receptor (NRs)?
What are Nuclear receptor (NRs)?
Intracellular receptor: remains inside the cell
ligand binding induces gene transcription (aka ligand-activated transcription factor)
What type of receptor is Ligand-gated ion channels(LGICs)?
What are Ligand-gated ion channels(LGICs)?
Cell surface receptors: transmembrane receptor proteins with extracellular ligand-binding domains.
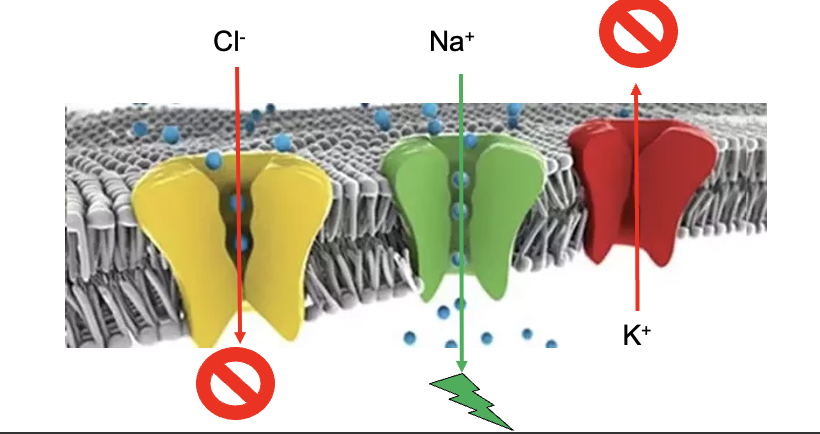
5 subunits open to allow ions to rapidly cross the membrane to hyperpolarize or depolarize the cell or increase [Ca2+]i
![<p>Cell surface receptors: transmembrane receptor proteins with extracellular ligand-binding domains.</p><p><span style="font-family: Arial">5 subunits open to allow ions to rapidly cross the membrane to hyperpolarize or depolarize the cell or increase [Ca<sup>2+</sup>]<sub>i</sub></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/66b3223a-7da4-4cfb-913c-5bb5549f1f72.png)
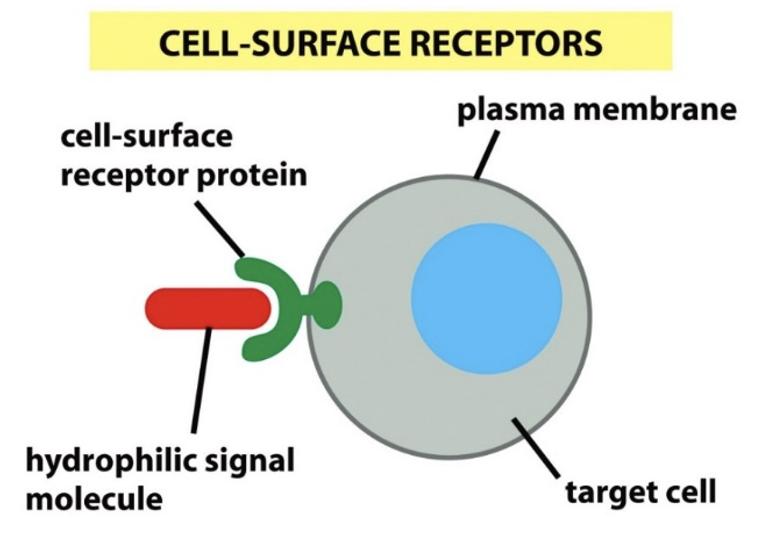
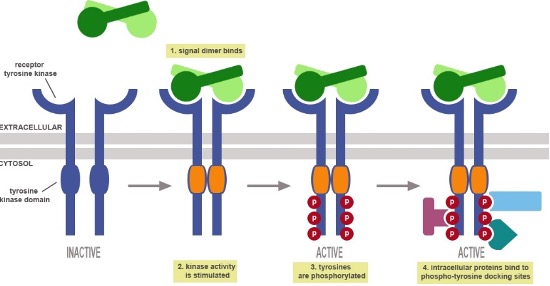
What type of receptor is Tyrosine Kinases Receptor (TKRs)?
What are Tyrosine Kinases Receptor (TKRs)?
Cell surface receptors: transmembrane receptor proteins with extracellular ligand-binding domains
ligand binding induces activity of intracellular kinase enzymes
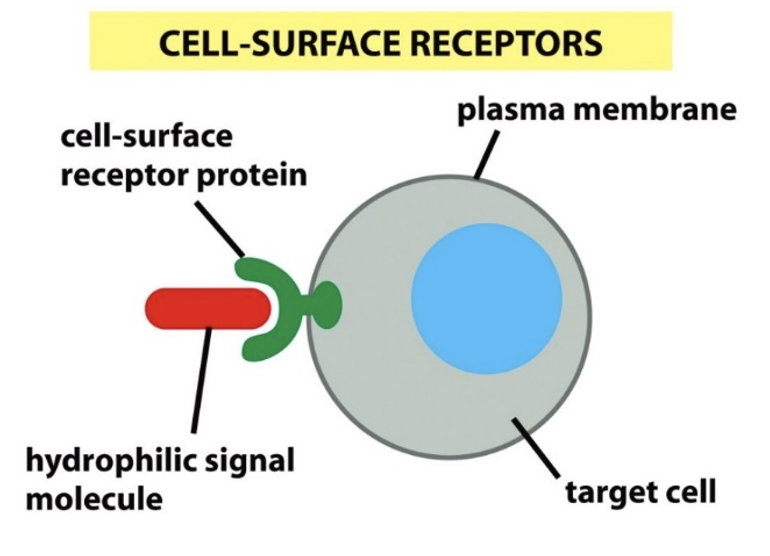
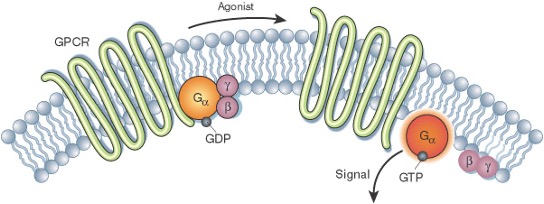
What type of receptor is G-protein-coupled/7-Transmembrane receptors (GPCRs or 7TMRs)?
What are G-protein-coupled/7-Transmembrane receptors (GPCRs or 7TMRs)?
Cell surface receptors: transmembrane receptor proteins with extracellular ligand-binding domains.
ligand binding activates intracellular G-proteins or beta-arrestins which activate or inhibit enzymes, transcription factors and/or ion channels
Cell Communication
Involves a cell producing a signaling molecules that bind and activate receptors in or on a cell to change the activity of the receiving cell.
Various categories relate to distance ligand travels to reach receptors.
Also goes from fast, short-duration to slower and longer-lasting effects.
What are the four types of cell communication that we talked about?
Surface contact
Synaptic
Paracrine & Autocrine
Endocrine
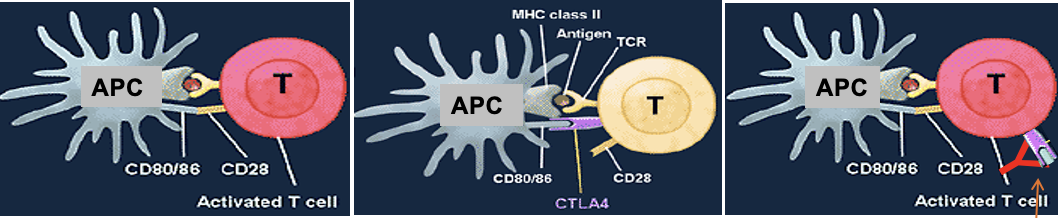
Surface Contact
Involves antigen presentation among immune cells: Tyrosine kinase receptors.
Recent cancer drugs acts at these receptors
Also, occurs in interactions between other cell types to limit their growth.
Synaptic
Occurs between one neuron and one other; very fast, short-lived.
Ligand-gated ion channel or G-protein-coupled receptors
Autocrine signaling
Cell that makes signaling molecule acted on by it.
Limited mostly to signaling between immune cells or pre-synaptic neurons.
Paracrine signaling
Signaling molecules acts on cells nearby; intermediate speed & duration.
Primarily involves local inflammatory signaling via GPCRs.
Endocrine signaling
Signaling molecule acts anywhere after traveling through blood; slow, lasting.
Involves hormones involved in development and maintenance of homeostasis
Fill in the Blank - Surface Contact
Distance: ___________
Receptor: ___________
Speed: ___________
Role(s): ___________
Distance: Direct contact
Receptor: TKR
Speed: very fast
Role(s): mostly immune modulation
Fill in the Blank - Synaptic
Distance: ___________
Receptor: ___________
Speed: ___________
Role(s): ___________
Distance: across tiny cleft
Receptor: LGIC, GPCR
Speed: very fast
Role(s): “chemical synapse”; nervous system
Fill in the Blank - Paracrine & Autocrine
Distance: ___________
Receptor: ___________
Speed: ___________
Role(s): ___________
Distance: same cell or nearby cell
Receptor: TKR, GPCR
Speed: intermediate
Role(s): mostly immune modulation & inflammation
Fill in the Blank - Endocrine
Distance: ___________
Receptor: ___________
Speed: ___________
Role(s): ___________
Distance: close-very far via blood
Receptor: NR, TKR, GPCR
Speed: slow to very slow
Role(s): mostly in development or/and homeostasis
Ligand-Gates Ion Channel receptor (LGICs)
75 subunits
Fastest / shortest-lasting
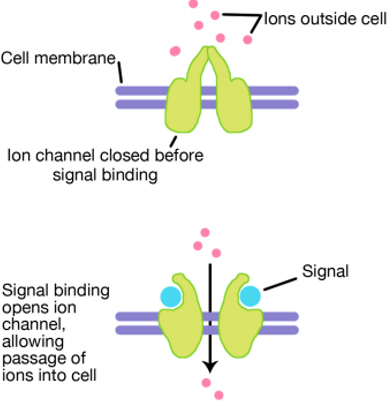
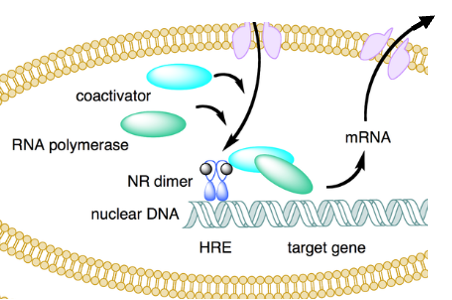
Nuclear Receptor (NRs)
48 types
Slowest / longest-lasting
Tyrosine Kinase Receptors (TKRs)
most numerous type of enzyme-linked receptor
91 types
Intermediate speed & duration
G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
800 types
Intermediate speed & duration
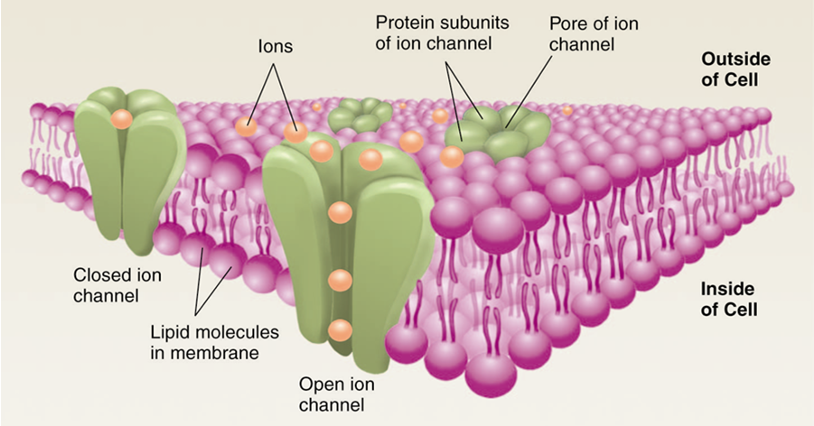
Ion Channels
Multi-subunit complexes that open in response to different stimuli.
Opening allow passage of ion types across a membrane down its gradient.
Ligand-gated ion channel
Mediate some neurotransmitter activity
many psychoactive drugs
Voltage-gated ion channel
Mediate nerve neuron action potentials and muscle contraction
drugs for hypertension or anesthesia
Mechanically-gated ion channel
Mediate sensation of touch and/or pain
No drugs
Thermally-gated ion channel
Mediate sensation of hot, cold, and/or pain
Menthol, capsaicin
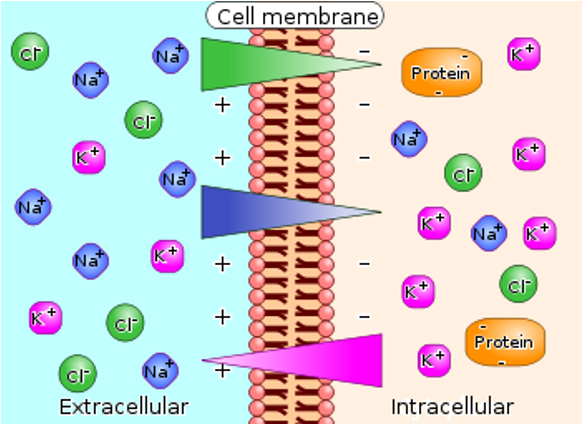
Electrochemical membrane potential
A membrane potential is established by an imbalance of charges and ion concentrations across a membrane; more net + outside and more net - inside
It is energetically-favorable for an ion to move down its concentration gradient, but unfavorable for it to increase net negative charge inside cell.
Ion | Extracellular (mM) | Intracellular (mM) | channels |
Na+ | 140 | 10 | depolarize |
Cl- | 100 | 4 | hyperpolarize |
K+ | 5 | 140 | hyperpolarize |
(macro. anions) | 0 | 65 | N/A |
When channels open, ions will move across a membrane down their concentration gradient
↓ net negative charge inside → depolarizes
↑ net negative charge inside → hyperpolarizes
Opening Na+ channels allows Na+ to flow into the cell, which depolarizes the cell (by decreasing the net - charge inside)
Opening K+ channels allows K+ to flow out of the cell, which hyperpolarizes the cell (by increasing the net - charge inside)
What does opening a Cl- channel do? Would it flow into or out of the cell?
Opening the Cl- channels allows Cl- to flow out of the cell, which hyperpolarizes the cell (by increasing the net - charge inside)
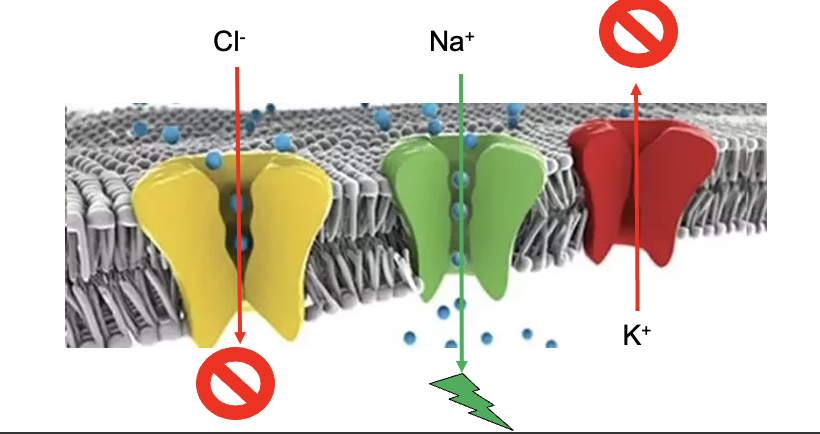
Electrochemical membrane potential summary
Decreasing – inside cell depolarizes
Opening Na+ channels
Increasing – inside cell hyperpolarizes
Opening K+ or Cl- channels
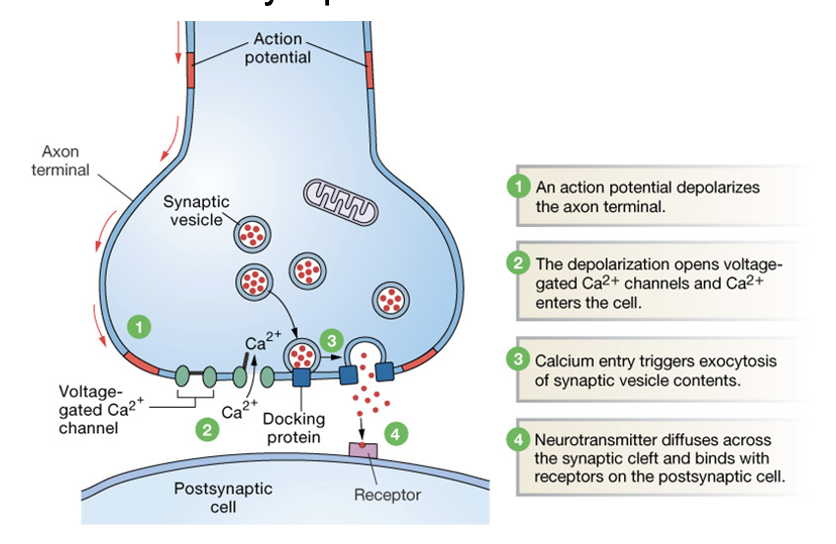
Synaptic transmission
Post-synaptic receptors may cause depolarization or hyperpolarization of the post-synaptic neuron.
Transmission is terminated by diffusion, degradation or re-uptake of neurotransmitter.
Ligand-gated Ion channel receptors
These neurotransmitters excite or inhibit depolarization of neurons.
Much synaptic/neuron signaling occurs via GPCRs
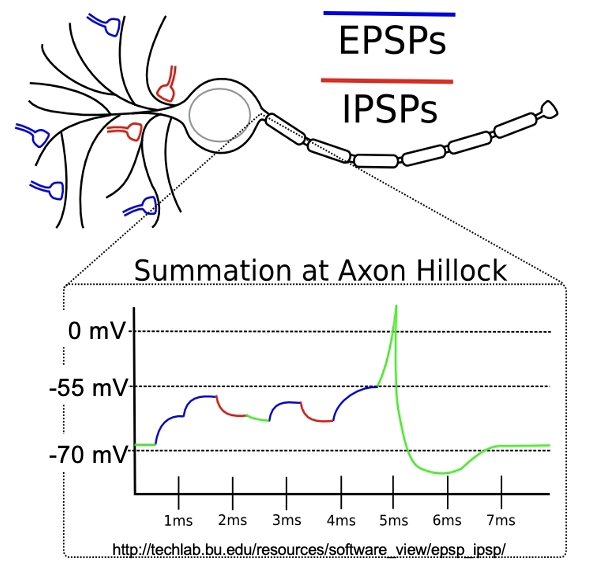
Neurons receive inputs from 1000s of other neurons
Each neuron integrate signals over times resulting in an Action Potentials or not.
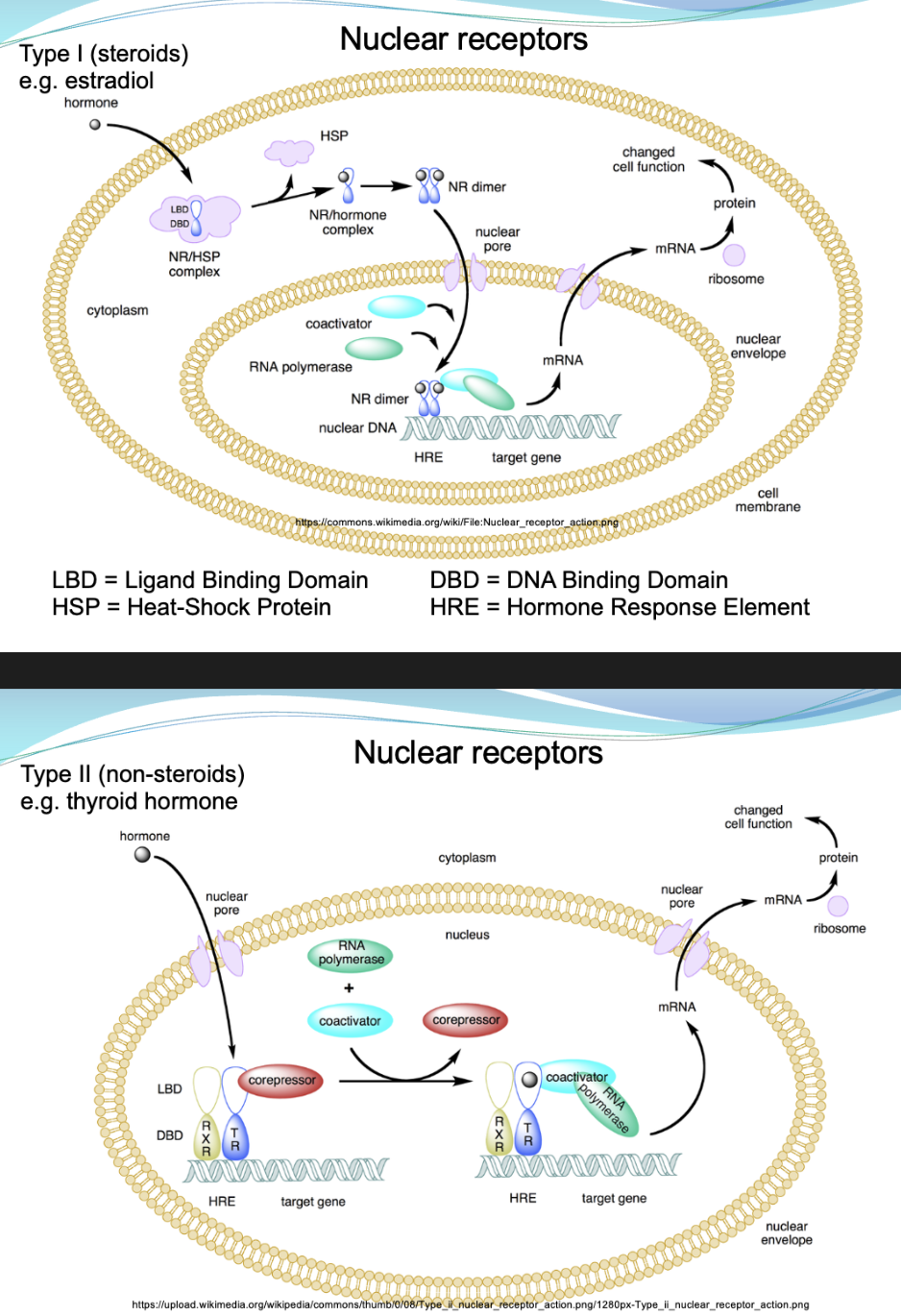
Nuclear receptors
A.K.A ligand-activated transcription factos
Only receptor type not located in cell membrane; only found in animals
Mediate long-term changes or homeostasis (endocrine systems)
What are the two types of nuclear signaling?
Type I in cytosol when inactive; activated by steroids & homodimerize
a. sexual development/function/fertility (estradiol, progesterone, & testosterone)
b. adaption to stress (cortisol)
c. electrolyte levels (aldosterone)
Type II bind DNA even when inactive, activated by non-steroids & heterodimerize.
a. metabolism (thyroid hormone, PPAR)
b. Ca2+ levels/bone remodeling (VitD)
c. some activated by xenobiotics
Enzyme-Linked Receptors
Tyrosine Kinases Receptor
91
numerous drugs
Serine/Threonine Kinase Receptors
13; 6 active + partners
few drugs; like TKRs, but attach Pi to ser or thr
Tyrosine Phosphatase Receptors (RTPs)
20
no drugs
Guanylyl cyclase-coupled Receptors
6
Natriuretic factor receptors
1 drug
Kinases
Very important regulators of cell function/protein activity.
Phosphorylation may active or inactive substrate
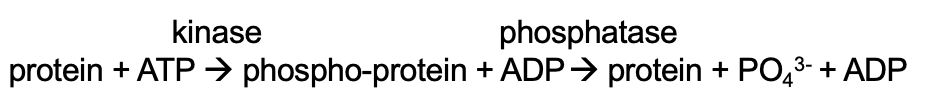
What are Tyrosine Kinase Receptors(TKRs)?
Protein ligands, may stimulate growth
Most cancers derived from mutations in growth factor signaling
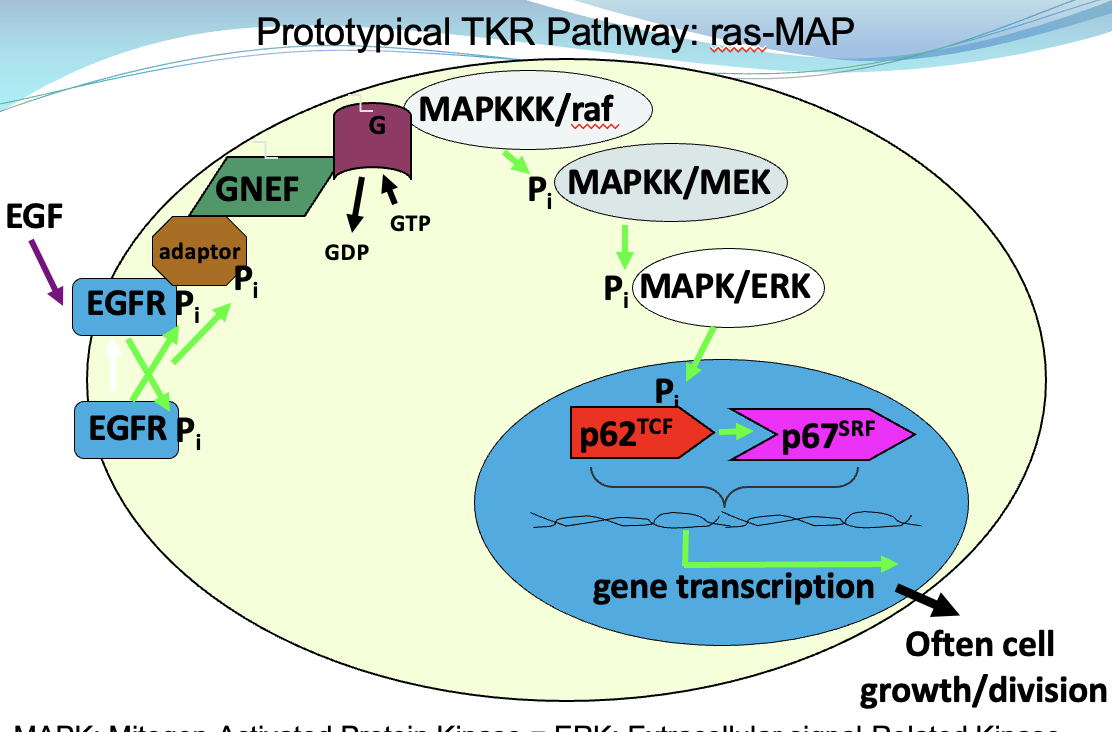
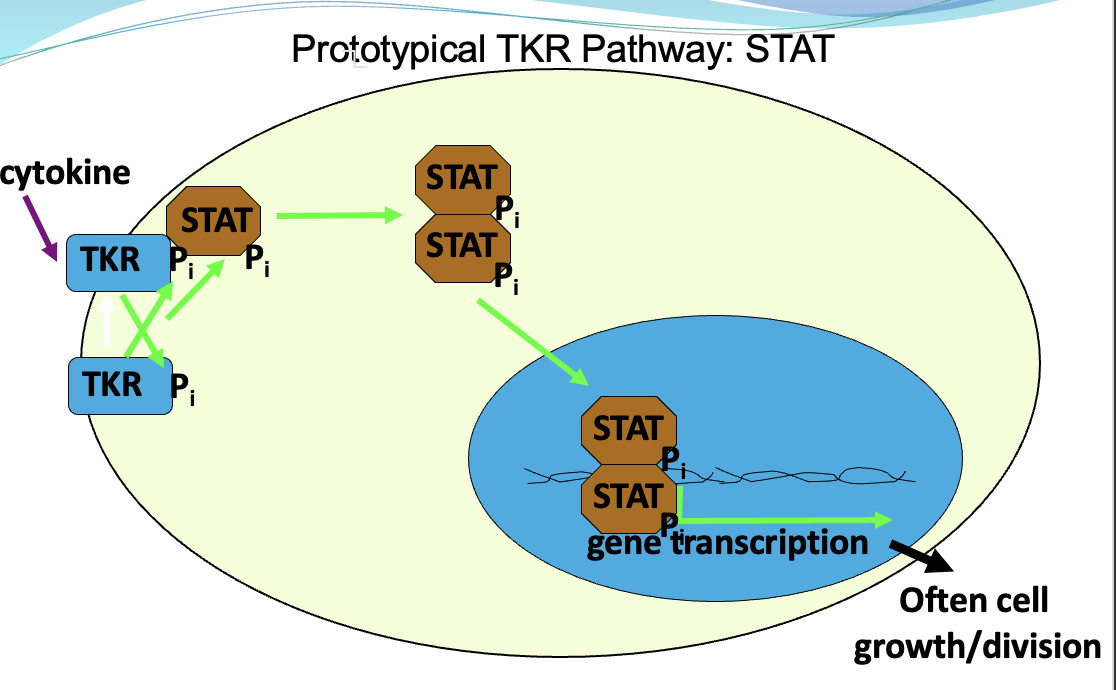
Where are TKRs located? What are the 4 canonical pathways?
In cell membrane with extracellular ligand-binding domain, and intracellular kinase domain.
Drug replace/supplement hormones or block growth (mostly treat cancer)
Canonical Pathways:
Ras-MAPK
Protein Kinase B (PKB)/Akt
Phospholipase C (PLC)
STAT
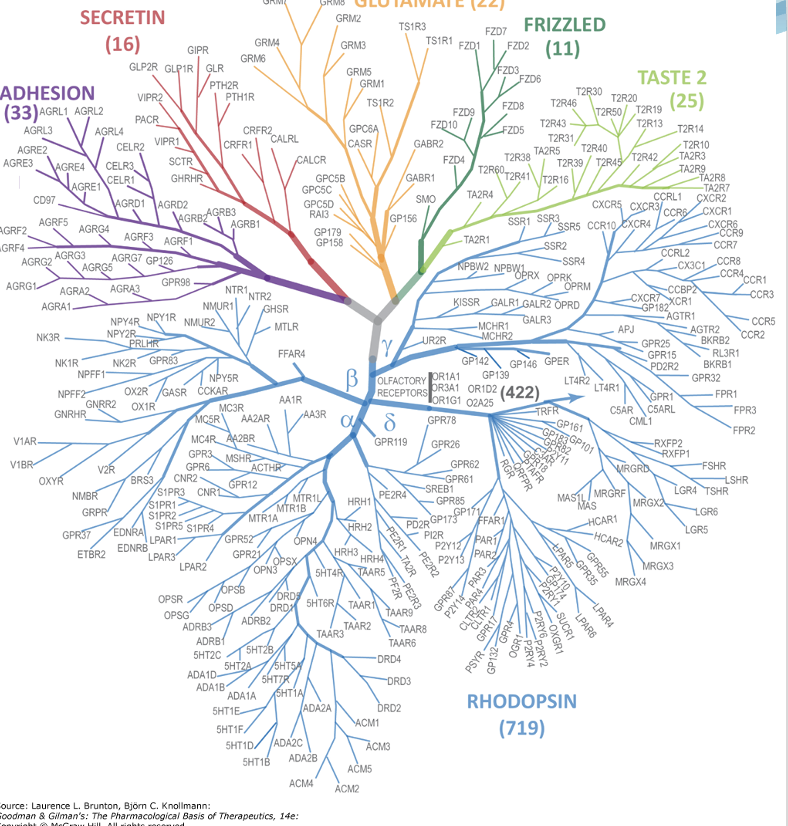
What are some examples of ligands for GPCRs?
photons
neuropeptides
monoamines
scent molecules
a protease
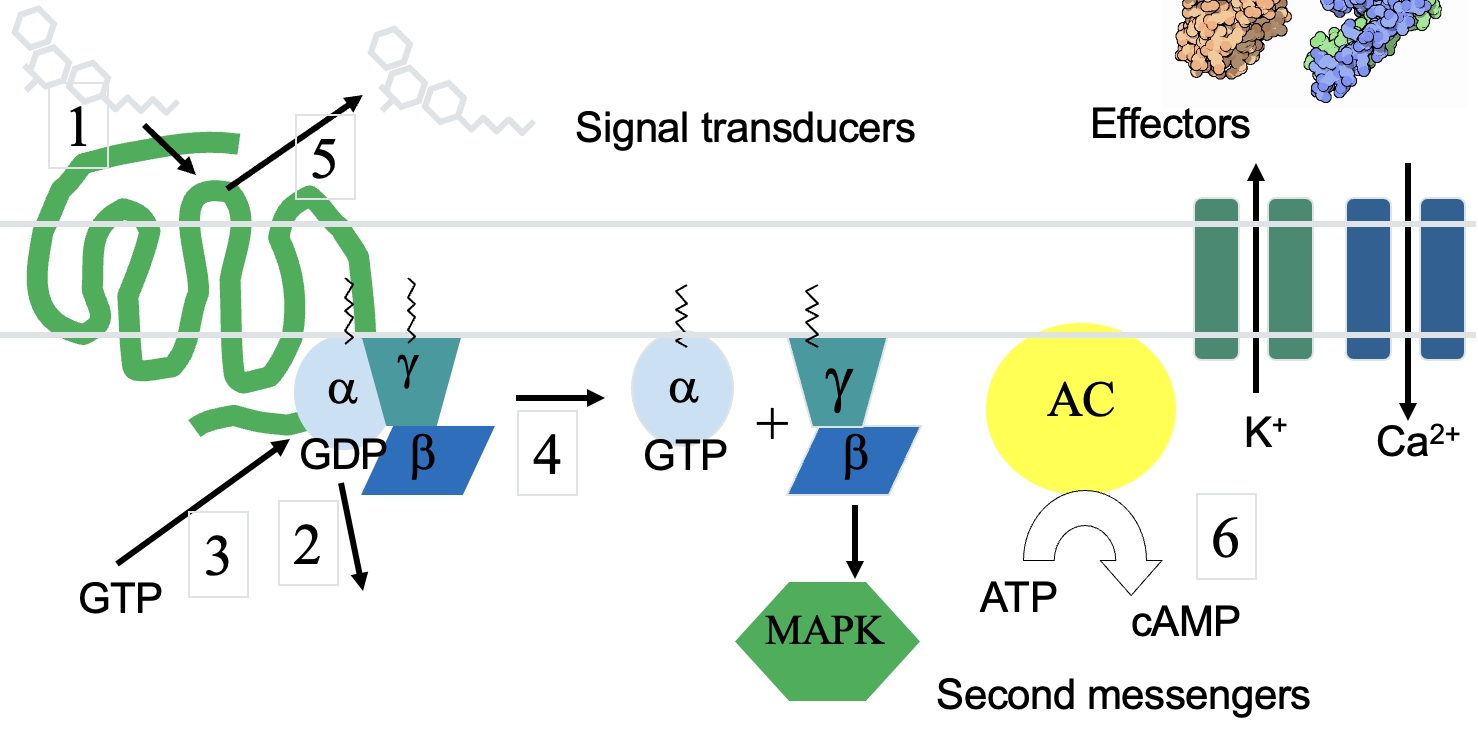
The G-protein cycle steps
Inactive form of G-protein has GDP bound to Ga.
G-protein activated by GPCR (usually via agonist binding) to release GDP and bind GTP.
Ga -GTP uncouples from GPCR and Gbg, and each complex acts on effector(s).
Intrinsic GTPase of Ga cleaves GTP to GDP + PO43- (inactivates Ga)
then Gbg can couple to Ga (inactivates Gbg)
Heterotrimerthen can couple GPCR again.
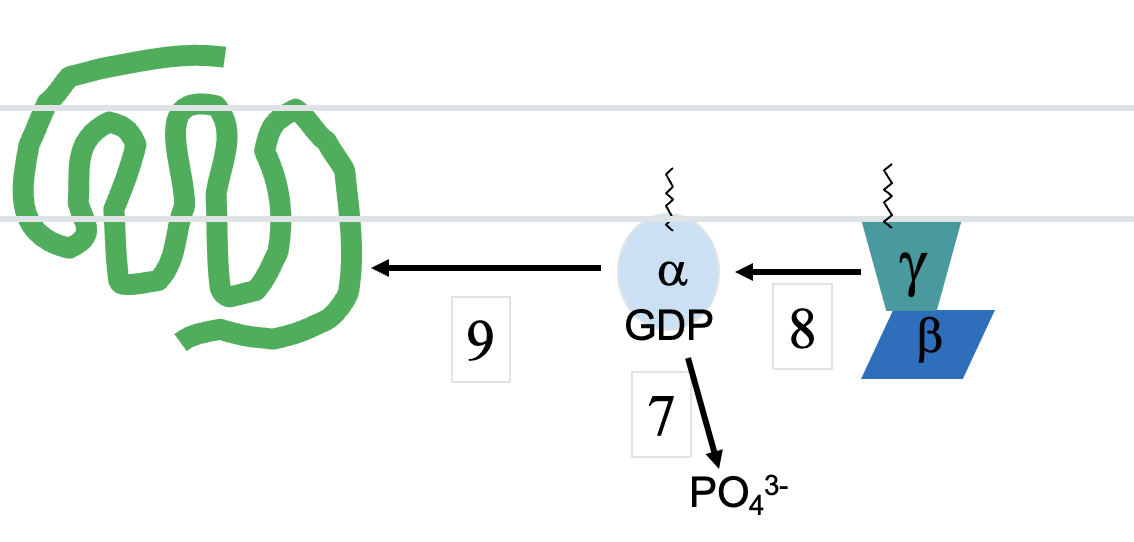
Ga protein effectors
Ga (~20 types) Effector :
as stimulates AC (Adenylyl Cyclase) ATP à cAMP à PKA
ai/o inhibit AC
aq stimulates phospholipase C (PLC) à ↑ [Ca2+]I
a12/13 stimulate RhoGEF à RhoA (small G-proteins) à ROCK & kinases
Gbg protein effectors
Gb (6 types) form tight heterodimers with Gg (12 types) AC
PLC, TKRs, too
↑ GIRK (G-protein-gated Inwardly-Rectifying K+ channel = Kir) activity
↓ voltage-gated Ca2+ channel (CaV2) activity
PI3-kinase (à PKB/Akt), TKRs, too
Src (à MAPK/ERK), TKRs, too
Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK)
GRK (G-protein coupled Receptor Kinase)
Phosducin (Phd) [binds/sequesters Gbgs]
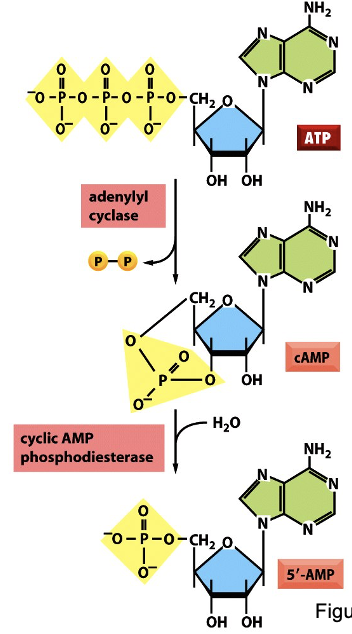
cAMP Signaling
Gas & some Gbg stimulate AC
Gai & some Gbg inhibits AC
Gat & Gagust stimulate PDE: cAMP à AMP
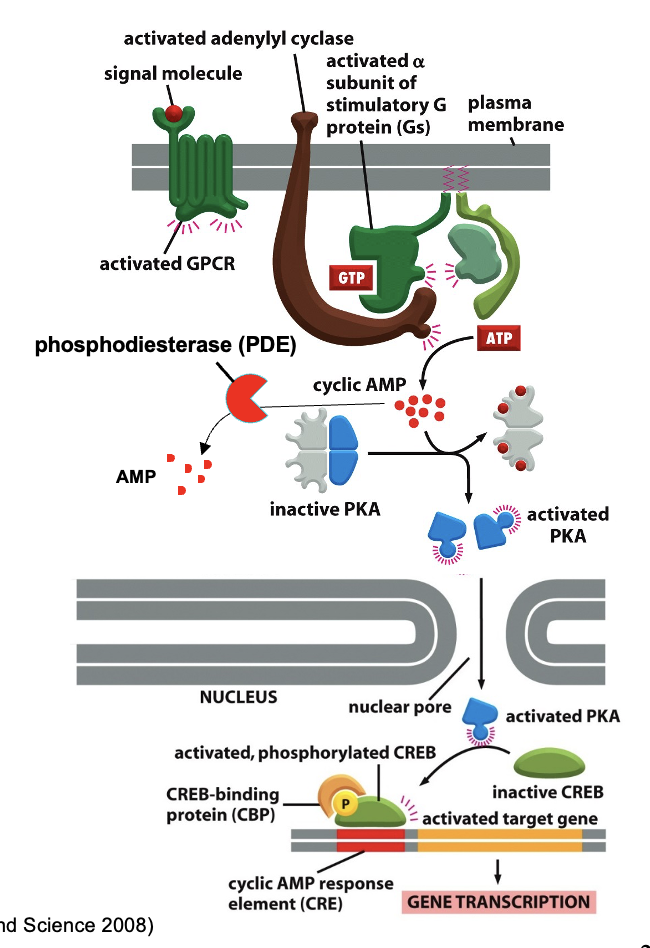
Ca2+ channel signaling
Activation of Gao and some Gbg combinations decreases the opening of Ca2+ channels
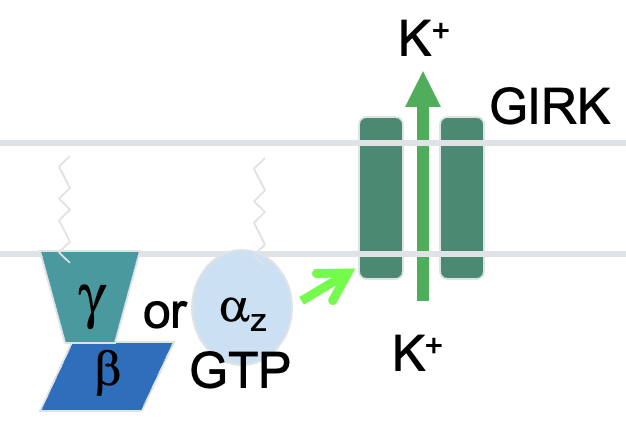
K+ channel signaling
Activation of Gaz or other Gbg combinations increases the opening of GIRK (G-protein-gated inwardly-rectifying potassium) channels.
Phospholipase C (PLC) signaling
Activation of Gaq or some Gbg combinations stimulate phospholipase C, which cleaves PIP2 to IP3 and DAG, increasing [Ca2+] in the cytosol and PKC activity (and other Ca2+-dependent processes)
GRKs and arrestins
beta-arrestin1 and beta-arrestin2 might interact with all GPCRs
GRKs phosphorylate GPCRs to create beta-arrestin binding site
3 possible effects: 1) block G-protein signaling, 2) couple GPCRs to clathrin (internalization/desensitization of GPCR), and/or 3) activate signaling pathways