Burns AP Biology 8.1-8.7
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
stimulus
A change in an organism's surroundings that causes the organism to react

endotherms
Animals (such as birds or mammals) that can regulate their body temperature.
Ex:Muscular contractions require energy

ectotherms
An animals that warms itself mainly by absorbing heat from its surroundings
Ex:Snakes require less energy

metabolic rate
the rate at which the body uses energy
-gain results in energy storage OR growth
-loss results in loss of mass and death
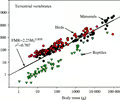
trophic levels
levels of nourishment in a food chain
-based on what they eat AND relationship to other organisms

food chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
-10% rule
autotrophs
Organisms that make their own food by capturing energy from physical or chemical sources
-photosynthetic or chemosynthetic
Ex:Consuming hydrogen (w/without 02)

heterotrophs
An organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms or their by-products.
-metabolizes major MACROMOLECULES
Ex: Chemical energy such as coffee

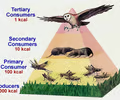
10% law
only 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next
-reason for various reproductive strategies
population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area

density dependent
limiting factor that DEPENDS on population SIZE (abiotic/biotic)
Ex: competition, territoriality, disease, predation

density independent
limiting factor that affects ALL populations in similar ways, REGARDLESS of population SIZE (abiotic/biotic)
Ex: natural disasters, floods, forest fires, volcanic eruptions, and pollution

logistic growth model
a growth model that describes a population whose growth is initially exponential, but slows as the population approaches the carrying capacity of the environment
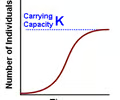
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
-both limiting factors can cause a pop to reach this

community
assemblage of different populations that live together in a defined area

species diversity
The number AND relative abundance of species in a biological community.
Ex: 15 sharks and 62 sea turtles

species composition
refers to the IDENTITY of EACH species in the community
Ex: An ocean community having 2 species of angelfish

mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit

commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected

predator prey
When one organism feeds on another organism (negative)

parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed (negative)

trophic cascade
The negative effect the removal of or decrease in a key species has on other trophic levels
niche partitioning
natural division of resources based on competitive advantages

keystone species
A species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem
-usually smaller because overpop depletes resources

invasive species
plants and animals that have migrated to places where they are not native

interspecific competition
competition between members of different species

intraspecific competition
competition between members of the same species
